中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (18): 4771-4781.doi: 10.12307/2026.721
• 组织工程相关大数据分析 Big data analysis in tissue engineering • 上一篇 下一篇
运动干预多发性硬化症的研究热点与主题演变
杨姜茜1,李黄岩1,张业廷1,余佐银2
- 1中国民用航空飞行学院航空体育学院,四川省广汉市 618307;2西华师范大学体育学院,四川省南充市 637000
-
收稿日期:2025-07-04接受日期:2025-08-30出版日期:2026-06-28发布日期:2025-12-12 -
通讯作者:张业廷,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,中国民用航空飞行学院,四川省广汉市 618307 -
作者简介:杨姜茜,女,2001年生,四川省内江市人,汉族,中国民用航空飞行学院在读硕士,主要从事体育与健康的研究。 -
基金资助:中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(PHD2023-003),项目负责人:张业廷
Research hotspots and thematic evolution in the field of exercise interventions for multiple sclerosis
Yang Jiangxi1, Li Huangyan1, Zhang Yeting1, Yu Zuoyin2
- 1Aerospace Sport College, Civil Aviation Flight University of China, Guanghan 618307, Sichuan Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, China West Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2025-07-04Accepted:2025-08-30Online:2026-06-28Published:2025-12-12 -
Contact:Zhang Yeting, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Aerospace Sport College, Civil Aviation Flight University of China, Guanghan 618307, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Yang Jiangqian, MS candidate, Aerospace Sport College, Civil Aviation Flight University of China, Guanghan 618307, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. PHD2023-003 (to ZYT)
摘要:
文题释义:
多发性硬化症(Multiple Sclerosis,MS):是一种中枢神经系统慢性炎症性脱髓鞘疾病,患者中枢神经系统内多部位出现髓鞘破坏、脱落,导致神经冲动传导受阻。多发性硬化症的病因尚不明确,可能与病毒感染、自身免疫反应、遗传因素及环境因素等有关,患者常出现视力下降、肢体无力、感觉异常、共济失调等症状。
运动干预(Exercise Intervention,EI):指的是以科学化、系统化的身体活动方案为核心,用于改善个体身体功能、心理状态或疾病症状的治疗手段。在多发性硬化症患者中,常见干预形式包括有氧运动、抗阻运动与多元训练等,目的是提升神经可塑性、缓解疲劳、增强功能独立性等多方面健康指标。
背景:研究表明,多模式运动训练能够有效地改善中重度行动障碍多发性硬化症患者的耐力性步行能力以及认知加工速度,这种效应似乎同心肺功能的优化存在相关性,但是缺少对这一领域的文献梳理。
目的:通过文献计量学方法探究运动干预多发性硬化症领域的研究热点与主题演变。
方法:对Web of Science核心合集数据库进行检索,检索式为TS=(“multiple sclerosis”) AND TS=(“physical activity” OR exercise OR sport),检索语言为英文,利用CiteSpace软件对运动干预多发性硬化症领域3 761篇文献进行可视化分析。
结果与结论:①运动与多发性硬化研究领域关键词关注点的变化反映出该领域研究从单个学科深入到多个学科交织,从传统疗法朝着数字康复革新转型的趋向;研究热点逐渐从基础免疫学及病程监测转向康复干预和生活质量改善。②主题分类包括干预方式、研究设计方法以及干预指标,并随着现代信息康复手段的发展,虚拟现实、VR游戏以及机器人辅助训练等手段也应用到对多发性硬化症患者的干预研究中,运动干预多发性硬化症正在由经验性操作朝理论引导下的精确化方向转变。③早期研究关注于多发性硬化症的临床表现、常见合并症(如抑郁、疲劳)以及初期的运动干预考察情况;中后期研究着重于运动康复效果的规范化验证,其中随机对照试验和元分析的数量不断增加,同时研究范围扩展到认知障碍、行为调整等方面;最新阶段研究在前期成果基础上,结合虚拟现实等新技术,并采用以患者体验为核心的方法,从而形成全面且有循证依据的治疗策略。其研究主题的发展历程可被划分成4个时期,依次为“宏观效益验证”“理论建模与机制初探”“行为动机建构与参与促进”以及“精准化与技术融合”。该研究为临床上针对多发性硬化症制定运动干预计划提供了理论依据。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-8449-2331(杨姜茜)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨姜茜, 李黄岩, 张业廷, 余佐银. 运动干预多发性硬化症的研究热点与主题演变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4771-4781.
Yang Jiangxi, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting, Yu Zuoyin . Research hotspots and thematic evolution in the field of exercise interventions for multiple sclerosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4771-4781.
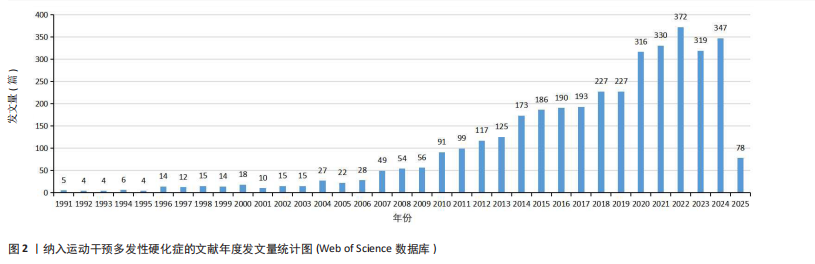
全年发文量达372篇之多。伴随时代发展与科技不断提升,以及多发性硬化症患病人数逐渐增多,其康复医治慢慢不再局限于传统药物干涉形式,不少研究及临床应用显示,运动对于多发性硬化症的医疗有着重大价值,正在成为综合康复手段里的重要形成单元[19]。总体来看,关于运动干预多发性硬化症的研究文献数量呈持续上升趋势。至2025年,运动干预仍然是多发性硬化症研究领域的热点话题之一。
2.2 运动与多发硬化症领域研究热点分析 关键词是论文核心思想的高度提炼,是研究主题的集中表现。通过分析文献关键词,能把握领域热点及发展趋势[20]。此项研究采用Pathfinder算法,以3年为时间切片,筛选每片前50个关键词,绘制共词网络图,沿时间轴展示研究热点的动态演变。
2.2.1 运动与多发性硬化研究领域的关键词关注点的变化 依据图3中时段划分及各时段关键词数量分布,将运动干预多发性硬化症领域关键词关注点划分为4个时期。1991-2005年期间,研究大多聚集在多发性硬化症的疾病原理、康复手段的初步探寻以及诸如抑郁之类的心理健康问题上。从共词网络来看,“多发性硬化(multiple sclerosis)”处于核心位置,其邻近高频词包括“抑郁(depression)”
“疲劳(fatigue)”“生活质量(quality of life)”等、这表明早期研究关注多发性硬化症患者的精神心理状态与生

活质量,同时“运动(exercise)”等词项的出现表明研究者开始大量研究运动干预多发性硬化症。总的来说,第一阶段的研究主题主要围绕多发性硬化症相关功能障碍和症状管理,采用描述性研究和初步的随机对照试验等方法,为后续干预研究奠定基础。随着研究的深入,2006–2014年间,多发性硬化症领域研究进入以实证干预和功能评估为主的阶段。共词图中“身体活动(physical activity)”“随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial)”“有氧运动(aerobic exercise)”“平衡(balance)”“步态(gait)”“肌肉力量(muscle strength)”“老年患者(older adults)”等关键词出现,体现了对运动干预效果的重视。此时大量随机对照试验开始聚焦有氧、抗阻等运动对多发性硬化症患者平衡能力、行走功能和体能状况的影响,并使用量化指标检验疗效。这一阶段研究注意到了不同年龄层(如老年多发性硬化症患者)和多维度功能指标(如步态与平衡)的差异。此外,“试验方法的可靠性(reliability)”“元分析(meta analysis)”等词项共现表明研究方法趋于规范化和循证化。总体而言,第二阶段的关键词反映出多发性硬化症研究重心由早期的疾病特征描述转向大规模的康复运动干预研究,强调科学验证和多中心研究的结果可靠性。2015–2020年间,多发性硬化症研究主题逐步拓展到认知功能和整体干预策略的整合。网络中出现了“认知损伤(cognitive impairment)”“指南(guidelines)”“虚拟现实(virtual reality)”“行为改变(behavior change)”“实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,EAE)”等新词。认知功能损害在多发性硬化症患者中极为常见(40%–65%患者出现不同程度的认知障碍),因此研究者开始关注认知康复、计算化认知测试等方面[21]。同时,“指南”关键词的出现表明已有学者着手总结前期循证成果,制定临床实践指南;“行为改变”反映出对生活方式和依从性等因素的重视。虚拟现实技术等新兴工具也被引入康复研究,为平衡、步行和认知训练提供了创新方法。另外,共现的“EAE”词条表明基础研究模型与临床研究相互渗透,用于探索多发性硬化症发病机制和治疗策略。该阶段呈现出多学科交叉的趋势,研究主题由单一运动功能向认知-行为及免疫学等维度扩展,追求综合性干预。2021–2025年,多发性硬化症研究进一步迈向以技术驱动和患者中心的综合管理。共词图顶端出现“虚拟现实(virtual reality)”“抗阻训练(resistance training)”“定性研究(qualitative research)”等词汇,这体现出研究焦点出现新的特征。新技术的应用不断深入,有研究显示,采用虚拟现实等技术对多发性硬化症患者实施平衡及运动功能训练,能明显优化平衡能力,削减跌倒危险,进而改善生活品质,减轻疲劳[22];而且经颅磁刺激(Transcranial magnetic stimulation,TMS)、机器人辅助训练、经颅直流电刺激(Transcranial direct current stimulation,tDCS)等多种前沿干预手段也相继融入到多发性硬化症康复研究中[23]。“定性研究”这一关键词的出现,表现出研究者越发重视患者主观感受以及循证实践的融合,注重以患者为中心的管理方法。“抗阻训练”这类词语显示对改良运动处方的不断关注。综合来看,第四个时期的关键字着眼于现代康复技术以及整体化治疗框架,这显示出多发性硬化症研究正朝着多元且规范的方向迈进。
总体来说,从1991年到2025年,多发性硬化症研究领域的关键词关注点有明显的变化,最初主要集中在多发性硬化症的临床症状及常见的并发症,且开始尝试用运动来干预;之后的重点放在怎样规范地验证运动康复的成效(随机对照试验和元分析越来越多),慢慢拓展到认识阻碍、行为改变等方面;最近的研究在前期成果的基础上,结合虚拟现实等新科技以及重视患者感受的方式,产生了更为综合且根据证据的治疗手段。整个过程反映出多发性硬化症领域研究从单个学科深入到多个学科交织,从传统疗法朝着数字康复革新转型的趋向,表现出学界一直以来对改进多发性硬化症患者全方位功能与生活品质的重视。
2.2.2 运动与多发性硬化研究领域关键词研究热点的爆发 图4展示的是1991–2025年期间出现的27个高强度突现关键词。根据图示数据,“多发性硬化(multiple sclerosis)”关键词在1994–2008年间出现了强烈的研究热点爆发(强度36.02)。早期研究重点在于阐明多发性硬化症的发病机制和临床特征,并探索药物和理疗手段控制症状。随着认识加深,研究热点逐渐从基础免疫学及病程监测转向康复干预和生活质量改善。总体来看,多发性硬化症本身作为核心疾病概念的高强度爆发,奠定了该领域的研究基础,为后续交叉学科研究提供了方向。
“运动(exercise)”在1995–2008年间发生研究热点爆发(强度18.31),反映出该阶段对运动干预的关注度提升。运动在多发性硬化症及神经康复领域具有重要作用,低到中等强度的有氧训练可显著提高患者的心肺耐力、减轻疲劳,并改善情绪和生活质量[24-25]。此外,运动研究经历了从小样本临床试验到大规模随机对照试验发展的过程。随着技术进步,近年来也出现了基于可穿戴设备和远程监测的运动干预研究,推动了从传统康复向远程医疗和个性化治疗的应用转型[26]。关键词“运动”突出了从基础研究到临床应用的演变过程,这对多发性硬化症康复医学、健康管理等交叉领域的研究发展起到了推动作用。
关键词“双盲 (Double-Blind)”在1997–2011年间爆发(强度12.48),表明该时期对临床试验设计质量的高度关注。双盲随机对照试验被视为干预研究的“黄金标准”[27],可以最大限度地减少偏倚,提供可信的因果推断。在多发性硬化症和神经康复等领域,早期研究大多重视通过双盲设计
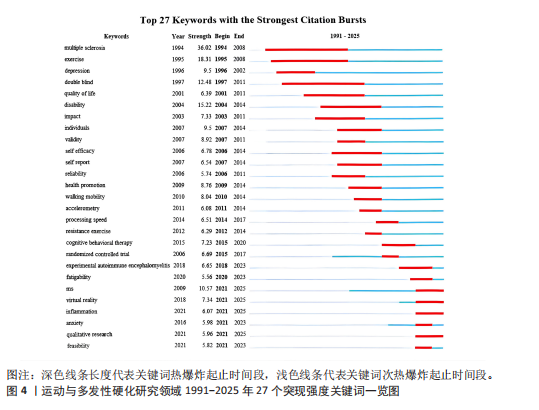
来评定药物治疗、训练干预或者康复方案是否有效,双盲设计关键词的研究热点变化体现出学科对于高质量循证研究方法的探求,这对提升研究可靠性以及推进规范化临床研究有着重要意义。
“残疾 (Disability)”在2004–2014年爆发(强度15.22),表明对功能障碍及康复效果关注的转变点。多发性硬化症常造成不同程度身体与认知残疾(运动障碍、平衡失调、疲劳、情绪障碍等),所以残疾评估成为研究重点之一[28]。患者无论残疾程度如何,持续康复训练均能改善生活能力,康复可提升多发性硬化症患者日常活动自理水平,增加社会参与度。残疾作为关键词推进康复医学、物理治疗、公共卫生政策等领域交叉发展,为个性化治疗和社会支持体系创建提供研究基础。
“定性研究 (Qualitative Research)”在2021–2025年出现研究爆发(强度5.82),显示出近年定性方法在多发性硬化症研究中的崛起。传统上,多发性硬化症领域多采用量化研究(如随机对照试验和队列研究)评估治疗效果,但对患者主观体验和决策过程的关注不足。随着“以患者为中心”理念的普及,研究者采用访谈、焦点小组等定性研究方法,探究多发性硬化症患者及其照护者的实际感受和需求,PExMS(Patient Experiences of MS Therapies)运用标准化定性访谈方法系统收集分析多发性硬化症患者对于不同治疗方式(康复,生活方式调整等)的个人体验和决策过程,这些方法揭示出不能用临床指标衡量的心理社会因素,给改善医患交流、完善康复服务带来新视角[29]。定性研究的兴起标志着研究热点从传统生物医学范式向人文社科方法的转变。
“焦虑 (Anxiety)”关键词在2021– 2025年间爆发(强度5.96),反映出精神心理健康议题在多发性硬化症及相关研究中的新关注。焦虑在多发性硬化症患者中很常见,约有1/3的多发性硬化症患者存在临床显著的焦虑症状,这一比例远高于一般人群[30]。焦虑会加剧患者的症状负担,并且和功能障碍及残疾程度有关。研究热点涉及焦虑在多发性硬化症中的流行病学、引发机制,以及如何借助运动、认知行为疗法和正念冥想等干预措施来改善焦虑状况。尽管针对多发性硬化症患者的焦虑干预研究仍处于摸索阶段,不过已有研究显示运动训练、虚拟现实放松训练等方法也许能对焦虑产生积极作用。焦虑这个词的突然出现表明研究重点从单纯的神经机制慢慢拓展到了心理和社会层面,促使神经科学和心理学、精神病学等学科之间展开交叉研究,有益于创建起完整的多发性硬化症治疗计划。
“炎症 (Inflammation) ”在2021– 2025年爆发(强度6.70),体现出针对免疫与生物标志物研究关注度的上升,多发性硬化症的关键病理进程在于中枢神经系统的炎症与脱髓鞘反应,相关研究涉及促炎和抗炎细胞因子在多发性硬化症发生和发展中所起的作用,还包含运动和药物干预给炎症反应带来的影响[24]。近年来,有研究发现多发性硬化症患者接受运动训练后,炎症标志物水平并未恶化,反而出现?肿瘤坏死因子α下降的趋势[25]。这表明运动可形成抗炎效果,有益于病情活动的掌控,就热点走向而言,由先前着重于炎症递质的基本病理学过渡到把它当作衡量干预成效的分子指标,从而推动神经科学、免疫学和运动医学等诸多学科共同向前迈进。炎症关键词的研究进展增强了对多发性硬化症病因的认识,精准医学和个体化治疗策略有了新的生物学目标。
“虚拟现实 (Virtual Reality)”关键词在2018–2025年(2021–2025部分爆发强度7.34)迅速崛起,突出技术在康复应用中的地位。虚拟现实技术可作为一种沉浸式交互方式,给残疾人群体营造出极具吸引力的运动练习场景[31]。在多发性硬化症康复领域,研究显示虚拟现实训练有益于优化患者的平衡能力,步态功能以及精细运动控制,而且能够减小其对摔倒的恐惧心理[32]。针对普遍存在的多发性硬化症相关疲劳和心理问题,虚拟现实中的游戏化运动也被探究作为辅助疗法,这个关键词的出现显示了研究热点转向高科技应用领域,这体现了康复工程学、计算机科学与临床神经康复的融合趋向。虚拟现实研究带动了远程康复及智能健康的产业发展,这对于改善残疾人群的运动参与率以及生活品质十分关键。
2.2.3 运动与多发性硬化研究领域关键词主题分类 表1对重要关键词按照不同主题进行了分类,包括干预方式、研究设计方法以及干预指标。运动干预方式包括有氧运动、抗阻运动、水疗法等多种方式。系统评价显示,将有氧运动作为干预方式,能显著缓解多发性硬化症患者的疲劳并提升其生活质量,其已成为康复的重要组成部分。另有研究显示,结合有氧运动在内的运动干预显著改善了平衡能力、步行能力及整体生活质量[33]。此外,若干临床指南亦将有氧运动列为康复核心推荐,强调其在提升功能性活动与日常生活适应中的关键作用?。一项针对抗阻训练干预18–45岁复发缓解型多发性硬化症女性的12周随机对照试验(每周3次,强度为60%–80%1RM)发现,抗阻训练组患者的下肢和上肢(卧推)力量得到了显著提升,此外患者疲劳度显著下降,生活质量得到显著提升[34]。
值得注意的是,水疗法在缓解疲劳、改善平衡与步行能力方面效果优异,并具备良好接受度与安全性,适合功能受限或热敏反应明显的患者[35]。随着现代信息康复手段的发展,虚拟现实、VR游戏以及机器人辅助训练等手段也应用到对多发性硬化症患者的干预研究中。一项系统综述指出,VR相较于传统治疗,有望能够改善患者的平衡与姿势控制[36]。最高效的VR干预方案为每次40–45 min,每周至少2–5次,总共 8–19周,累计至少40场训练[37]。这些研究成果为临床实践提供了有力的科学依据,也为未来的研究方向指明了道路,推动了运动干预多发性硬化症领域的持续发展。
2.3 运动与多发硬化症领域主题演变分析 根据图5中主题的时间演变和主题相似度,将主题演变过程划分为4个阶段。第一阶段为“宏观效益验证”,包括#0体力活动(Physical Activity)一个聚类;第二阶段为“理论建模与机制初探”,包括#2概念模型(Conceptual Model)、#3身体活动变化(Physical Activity Change)和# 4脑脊液(Cerebrospinal Fluid)3个聚类;第三阶段为“行为动机建构与参与促进”,包括#5锻炼参与(Exercise Participation)、#6社会认知理论变体(Social Cognitive Theory Variation)和#8文献综述(Literature Review)3个聚类;第四阶段为“精准化与技术融合”,包括#1预防性锻炼(Preventive Exercise)和#7个性化训练(Individualized Training)两个聚类。早期研究奠定了运动对有氧能力、肌肉力量与生活质量的直接效益基础,已有研究说明应在疾病早期,将运动作为“处方”纳入临床管理,构建系统化的医患互动框架来促进运动。通过社会认知理论等行为科学方法,设计并评估了多种远程与团体干预方式,以提升并维持多发性硬化症患者的日常活动行为。最新阶段则结合了生物标志物检测、可穿戴设备和人工智能,实现了闭环优化的个性化运动处方[38-39]。
在1991-2005年期间的宏观效益验证阶段,有关多发性硬化症与体力活动的研究发生了从“防止运动”向“积极干预”的改变。1991-1995年间,对于多发性硬化症患者来说,一般会被提议防止运动,以防加剧神经损害或者引发复发,不过这个看法大多源于专家意见和少数病例报告,并没有系统的数据支撑[40]。PETAJAN等[41]开展了一项包含54例多发性硬化症患者的随机对照实验,把受试者分成运动组和非运动组,结果显示运动组在经过15周的有氧训练之后,VO2max平均提升大约10%,而且在疲劳严重程度、心境以及日常功能都有明显改善。在轻中度残疾的多发性硬化症患者中,系统评价表明运动训练能够显著提高有氧

能力和肌肉力量,并改善疲劳和健康相关生活质量[28]。通过路径模型研究发现,总体症状与身体活动之间受到疲劳和抑郁的间接影响,为复发缓解型多发性硬化症的运动干预提供理论依据[42]。在量化评估方面,Godin闲暇时间锻炼问卷(Godin Leisure Time Exercise Questionnaire,GLTEQ)和国际身体活动问卷(International Physical Activity Questionnaire,IPAQIPAQ)分数与加速度计数据高度相关,多发性硬化症步行量表12(The MS Walking Scale 12,MSWS-12)和患者确定的疾病步骤(Patient-Determined Disease Steps,PDDS)评分也显著相关,证明自我报告与客观测量的一致性[43]。横断面研究表明,自我效能感通过目标、自我评估结果预期和复发缓解型多发性硬化症患者的障碍与身体活动间接相关[44]。MOTL等[39]“Exercise as Medicine”视角,初步研究确定运动是一种有效的对症治疗(即三级预防),但最近的研究评估了运动的疾病缓解作用(即二级预防)和对多发性硬化症风险的影响(即一级预防),提倡将运动处方与药物一样对待。运动干预多发性硬化症研究的早期阶段,学术界主要聚焦于探究体力活动对多发性硬化症患者的基本影响情况,着重考察体力活动给患者带来的有氧能力、肌肉力量以及生活品质的直接影响效果,为后来更为深入的研究工作打下了基础,第一阶段的研究借助宏观效益验证,展现了运动在多发性硬化症管理当中的潜在价值,突出了运动这种非药物干预手段的意义。
在2006–2015年的理论建模与机制初探阶段。早期研究发现运动对多发性硬化症患者在有氧耐力、肌肉力量、疲劳、生活等方面都有积极的影响后,研究者们开始思考运动干预对疾病早期的益处。根据最新的研究,提倡在多发性硬化症早期就开“运动处方”,把中等阻力和有氧运动训练作为与药物一样同等的补充疗法[38]。随机对照试验也表明,早期将运动纳入常规管理,以减缓功能退化[45]。MOTL等[46]开发了一个患者与提供者互动的概念模型,该模型分为3个层次:医疗保健提供者培训/支持、患者与提供者之间的互动以及参与者锻炼参与,作为多发性硬化症中促进运动的方法。多项定性研究建立了并评估了多发性硬化症患者运动促进的概念框架。RICHARDSON等[47]针对28位多发性硬化症医疗提供者做了半结构化访谈,证明了“医患互动运动促进模型”结构合理,也提出需要细化模型各个部分来指导临床。基于行为学理论的干预研究出现增多情况,最近针对新诊断多发性硬化症患者的干预研究使用了能力、机会、动机-行为(COM-B)模型,找出了影响体育活动参与的内在和外在因素,提醒个性化干预要涵盖知识教育、动机提升和环境支持三大方面[48-49]。此外,随机对照试验表明,依托社交认知理论的远程辅导干预能够在12周之内突出改善中高强度体育活动量,并且在追踪期间保留住一部分行为改变[47]。脑脊液生物标志物研究显示了多发性硬化症病理过程中的关键分子。早期研究显示,95%多发性硬化症患者会出现寡克隆带,成为诊断辅助金标准[50]。一项研究表明,首次诊断时检测脑脊液神经丝轻链蛋白能预测未来2年内的临床和影像学复发风险,为个体化干预提供参考[51]。最新的队列研究报告称,脑脊液中神经丝轻链蛋白、髓系细胞上表达的可溶性髓样细胞触发受体2等水平与多发性硬化症严重程度显著相关,可以预测多发性硬化症的进展和功能预后[52]。系统综述指出,脑脊液相比血液更能准确反映中枢炎症状态,未来或用于监测干预效果及个体化治疗决策[53]。锻炼对多发性硬化症患者来说,是一种有益的康复策略,它可以帮助控制症状,恢复功能,改善生活质量,促进健康,促进日常生活的参与[54]。随着研究的深入,第二阶段的研究开始关注如何建立并验证促进多发性硬化症患者运动参与的概念模型,研究者们采用行为干预策略来探讨如何促进患者长期坚持运动,如何通过概念模型改善医患互动以提升运动干预效果,并开始关注运动对多发性硬化症患者生理及分子机制的影响,包括脑脊液中生物标志物的变化,为精准化治疗提供了新的科学依据。
在2016–2020年的行为动机建构与参与促进阶段,于概念模型研究的基础上,强调了行为干预的需求,特别是促进多发性硬化症患者长期坚持运动。PILUTTI等[55]设计的互联网行为干预提高了多发性硬化症患者的生活方式身体活动,证明了远程干预的可行性和有效性。基于社会认知理论,自我效能被认为是预测多发性硬化症患者运动行为最重要的变量,它独自解释了体育活动的方差,并且与目标设定、计划等因素一起影响行为改变[56]。对于疲劳多发性硬化症亚组的研究发现,自我效能、结果期望和社会支持更为重要,它们是专门针对疲劳的干预措施的重点目标[57]。多发性硬化症群体干预案例是一个基于社会认知理论每周进行一次的团体锻炼计划,有同伴指导、行为改变教育、多种锻炼形式和坐姿指导来支持长期锻炼参与,研究发现团体运动对于长期依从性的支持[58]。明确意图、行动掌控、行动自身效能、行动方案、成果预期、目标指定以及复原自身效能感和疲惫都是新确诊多发性硬化症患者身体活动的主要关联性因素[48]。JONGEN等[59](2016年)研究发现,在支持伙伴参加的情况下开展为期3 d的加强型社会认知疗法(Can Do疗法)6个月之后,复发缓解型多发性硬化症患者的自身效能以及健康相关生活质量均得到了一定程度的提升。对于多发性硬化症患者来说,以团体为单位的运动干预看上去既可以被接纳又具备可行性,定性研究成果支撑了前面提到过的有关定量研究的结论,也就是Step it Up干预(一种系统性的运动干预计划)能够切实推动身体活动并优化心理成果[60]。有研究针对过去10年运动训练的安全性进行了更新回顾,发现干预组的复发率明显小于对照组,并且没有出现严重不良事件,从而进一步验证了运动干预的安全根基[55]。多篇回顾研究一致指出,运动对于多发性硬化症患者的抑郁与焦虑存在小到中度的改善效果,特别是那些融合了社交支持的干预方案更为明显[61]。第三阶段的研究加深了人们对社会心理层面的认识,并且开始关注如何促使多发性硬化症患者更多地参与运动,研究者利用社会认知理论之类的架构来规划各种不同的干预手段,试图帮助患者克服长期运动所遭遇的难题,而文献综述则为后续的研究走向给予指引,重视理论的发展以及知识的累积对于该领域向前推进有着不可或缺的意义。
在2021–2025年的精准化与技术融合阶段,于社会认知理论等框架设计多种干预措施的基础上,研究者开始探索个性化和数字化治疗,以推动精准化治疗的发展。基于可穿戴设备和AI算法的“闭环式”训练监控平台可以实时采集生理和行为数据,并根据训练状态动态调整运动强度,实现个性化处方[62]。从分子层面来看,运动诱发的脑源性神经生长因子和白细胞介素 6水平改变同步行速度以及疲劳程度联系紧密,这表现出运动具有神经营养和抗炎作用[63]。高强度阻力训练研究显示,此方案在安全耐受范围内可以调控免疫标志物和脑脊液炎症因子,改善主观疲劳及生活质量[63]。远程数字监测工具融合大数据和AI技术之后,可以随时跟进多发性硬化症症状,还能识别行为模式,从而给闭环改良给予决策支撑[62]。一项最近发表的综合评述以388项随机对照试验为依据,提出多发性硬化症患者每周两三次中等强度有氧+阻力训练作为个性化最小推荐剂量,并且要按照患者功能水平和喜好加以调整[64]。凭借脑源性神经生长因子、白细胞介素6等生物标记物去揭露运动对于神经营养和炎症的修复机制,借助可穿戴装置和AI闭环监测平台来达成个性化且动态调节的训练处方,从而把“运动为何有效”深入到“怎样根据不同病型、不同生理状况做到精准干涉”。新阶段的研究主要集中在预防措施以及个性化的训练上,研究人员开始重视运动干预在多发性硬化症早期阶段的积极作用,强调在疾病早期阶段就开出个体化的“运动处方”,借助生物标志物和数字技术(比如可穿戴设备、人工智能等)融合起来,使运动处方在多发性硬化症全程管理中的地位越发突出,彰显出精准医疗和个性化治疗策略的走向。
运动干预多发性硬化症研究有着从宏观效应观察到精准化管理的系统发展过程,早期研究依靠回顾性和横断面分析证实了运动对于多发性硬化症患者疲劳、肌肉无力、平衡障碍等症状具有改善效果[65]。在此基础上,学者们提出“运动处方”概念并搭建起系统化的干预架构,主张尽早把运动融入多发性硬化症的常规管理当中,随后研究重点转到行为干预策略上,运用社会认知理论等框架设计多种干预手段,解决患者长期坚持运动的难题。“如何让患者持续运动”这个问题有了成效之后,研究就深入到运动的生理和分子层面,探究个性化处方的可能性,依靠生物标志物和数字技术,像可穿戴设备和人工智能,做到了多发性硬化症运动管理的精细和闭环改善[66]。第四阶段发展表明运动干预多发性硬化症正在由经验性操作朝着理论引导下的精确化方向转变,日后应当继续把技术革新同个人化需求相融合,促使运动处方变成多发性硬化症全程管理的关键支柱。

| [1] MOTYER A, JACKSON S, YANG B, et al. Neuronal somatic mutations are increased in multiple sclerosis lesions. Nat Neurosci. 2025;28(4):757-765. [2] ABASıYANıK Z, ERTEKIN Ö, KAHRAMAN T, et al. The effects of clinical pilates training on walking, balance, fall risk, respiratory, and cognitive functions in persons with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. Explore. 2020;16(1):12-20. [3] WALTON C, KING R, RECHTMAN L, et al. Rising prevalence of multiple sclerosis worldwide: Insights from the atlas of MS, third edition. Mult Scler. 2020;26(14):1816-1821. [4] SETAYESHGAR S, KINGWELL E, ZHU F, et al. Use of the new oral disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis in british columbia, canada: The first five-years. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2018;25:57-60. [5] ROBERTSON D, MOREO N. Disease-modifying therapies in multiple sclerosis: Overview and treatment considerations. Fed Pract. 2016;33(6):28-34. [6] MCKENNA A, LIN GA, WHITTINGTON MD, et al. Oral and monoclonal antibody treatments for relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis: Effectiveness and value. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023;29(7):857-861. [7] DONZE C, MASSOT C, HAUTECOEUR P, et al. The practice of sport in multiple sclerosis: Update. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2017;16(4):274-279. [8] GHEITASI M, BAYATTORK M, ANDERSEN LL, et al.Effect of twelve weeks pilates training on functional balance of male patients with multiple sclerosis: Randomized controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021;25:41-45. [9] CRITCHLEY DJ, PIERSON Z, BATTERSBY G. Effect of pilates mat exercises and conventional exercise programmes on transversus abdominis and obliquus internus abdominis activity: Pilot randomised trial. Man Ther. 2011;16(2):183-189. [10] ELDEMIR K, ELDEMIR S, OZKUL C, et al. The effects of online pilates training on cognitive functions and dual task performance in people with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled study. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2025;97:106393. [11] ADIGUZEL TAT H, KIRMACI ZIK, EREL S, et al. The effects of neurodynamic mobilization exercises on upper extremity pain, muscle strength, and functions in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomised controlled, single blinded study. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2025;93:106240. [12] SANDROFF BM, BOLLAERT RE, PILUTTI LA, et al. Multimodal exercise training in multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial in persons with substantial mobility disability. Contemp Clin Trials. 2017;61:39-47. [13] PAN Y, HUANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. The effects of baduanjin and yoga exercise programs on physical and mental health in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther Med. 2022;70: 102862. [14] ZAREI H, NORASTEH AA.The effect of 8 weeks proprioception training without visual input on single-limb standing balance time in deaf students: A randomized controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2020;24(2):63-68. [15] 李慧军, 李黄岩, 张业廷. 身体活动与老年人认知领域研究热点与主题演变[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(5):1073-1080. [16] CHEN C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2006;57(3):359-377. [17] HAN Q, KIM SM. Research progress and trends in exercise interventions for mild cognitive impairment: A bibliometric visualization analysis using CiteSpace. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025;18:505-529. [18] ZHANG R, GE Y, XIA L, et al. Bibliometric analysis of development trends and research hotspots in the study of data mining in nursing based on CiteSpace. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024;17:1561-1575. [19] COWAN RE. Exercise is medicine initiative: Physical activity as a vital sign and prescription in adult rehabilitation practice. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(9): S232-S237. [20] 邓嘉禧, 邓雅文, 隗金水. 基于CiteSpace的我国近10年体能训练研究可视化分析[J].体育科技文献通报,2024,32(8):66-69. [21] KORAKAS N, TSOLAKI M. Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: A review of neuropsychological assessments. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2016;29(2):55-67. [22] BASALIC EB, ROMAN N, TUCHEL VI, et al. Virtual reality applications for balance rehabilitation and efficacy in addressing other symptoms in multiple sclerosis-a review. Appl Sci. 2024;14(10):4244. [23] DUAN H, JING Y, LI Y, et al. Rehabilitation treatment of multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1168821. [24] HALABCHI F, ALIZADEH Z, SAHRAIAN MA, et al. Exercise prescription for patients with multiple sclerosis; potential benefits and practical recommendations. BMC Neurol. 2017;17:185. [25] BROWN TR, KRAFT GH. Exercise and rehabilitation for individuals with multiple sclerosis.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2005;16(2):513-555. [26] ALEXANDER S, PERYER G, GRAY E, et al. Wearable technologies to measure clinical outcomes in multiple sclerosis: A scoping review. Mult Scler. 2021;27(11):1643-1656. [27] MISRA S. Randomized double blind placebo control studies, the “gold standard” in intervention based studies. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2012;33(2):131-134. [28] LATIMER-CHEUNG AE, PILUTTI LA, HICKS AL, et al. Effects of exercise training on fitness, mobility, fatigue, and health-related quality of life among adults with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review to inform guideline development. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013; 94(9):1800-1828.e3. [29] GHAIDAR D, SIPPEL A, RIEMANN-LORENZ K, et al. Experiences of persons with multiple sclerosis with rehabilitation—a qualitative interview study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022; 22(1):770. [30] GASCOYNE C, KARAHALIOS A, DEMANEUF T, et al. Effect of exercise interventions on anxiety in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J MS Care. 2020;22(3):103-109. [31] MINTZ M, RIMMER J, WILROY J, et al. Current trends in virtual exercise interventions among people with disabilities: A scoping review. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2024;6(4):100373. [32] MASSETTI T, TREVIZAN IL, ARAB C, et al. Virtual reality in multiple sclerosis-a systematic review. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2016;8:107-112. [33] DU L, XI H, ZHANG S, et al. Effects of exercise in people with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1387658. [34] NEZHAD NN, PARNOW A, KHAMOUSHIAN K, et al. Resistance training improves functional capacities in women with multiple sclerosis: A randomized control trial. BMC Neurol. 2024;24(1):457. [35] KARGARFARD M, SHARIAT A, INGLE L, et al. Randomized controlled trial to examine the impact of aquatic exercise training on functional capacity, balance, and perceptions of fatigue in female patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(2):234-241. [36] DE KEERSMAECKER E, GUIDA S, DENISSEN S, et al. Virtual reality for multiple sclerosis rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025;1(1):CD013834. [37] CORTES-PEREZ I, OSUNA-PEREZ MC, Montoro-Cardenas D, et al. Virtual reality-based therapy improves balance and reduces fear of falling in patients with multiple sclerosis. a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2023; 20(1):42. [38] DALGAS U, LANGESKOV-CHRISTENSEN M, STENAGER E, et al.Exercise as medicine in multiple sclerosis-time for a paradigm shift: Preventive, symptomatic, and disease-modifying aspects and perspectives. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(11):88. [39] MOTL RW, SANDROFF BM, KWAKKEL G, et al. Exercise in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(10):848-856. [40] WHITE LJ, Dressendorfer RH. Exercise and multiple sclerosis. Sports Med. 2004;34(15): 1077-1100. [41] PETAJAN JH, GAPPMAIER E, WHITE AT, et al. Impact of aerobic training on fitness and quality of life in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1996;39(4):432-441. [42] MOTL RW, MCAULEY E, WYNN D, et al. Symptoms and physical activity among adults with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2010;198(3): 213-219. [43] WEIKERT M, MOTL RW, SUH Y, et al.Accelerometry in persons with multiple sclerosis: Measurement of physical activity or walking mobility?. J Neurol Sci. 2010;290(1-2):6-11. [44] SUH Y, WEIKERT M, DLUGONSKI D, et al. Social cognitive correlates of physical activity: Findings from a cross-sectional study of adults with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Phys Act Health. 2011; 8(5):626-635. [45] RIEMENSCHNEIDER M, HVID LG, RINGGAARD S, et al. Study protocol: Randomised controlled trial evaluating exercise therapy as a supplemental treatment strategy in early multiple sclerosis: the early multiple sclerosis exercise study (EMSES). BMJ Open. 2021; 11(1):e043699. [46] MOTL RW, BARSTOW EA, BLAYLOCK S, et al. Promotion of exercise in multiple sclerosis through health care providers. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2018;46(2):105. [47] RICHARDSON EV, BARSTOW E, FIFOLT M, et al. Evaluation of a conceptual model regarding exercise promotion through the patient-provider interaction in multiple sclerosis: Health care provider perspectives.Qual Health Res. 2020;30(8):1262-1274. [48] HUYNH TLT, SILVEIRA SL, MOTL RW. Physical activity behavior in persons newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis: Applying the capability-opportunity-motivation-behavior (COM-B) model. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023;69:104432. [49] HUYNH TLT, NEAL WN, BARSTOW EA, et al. Physical activity in individuals newly diagnosed with multiple sclerosis through the lens of the COM-B model. Int J MS Care. 2024;26(2):49-56. [50] DEISENHAMMER F, ZETTERBERG H, FITZNER B, et al. The cerebrospinal fluid in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:726. [51] GAETANI L, EUSEBI P, MANCINI A, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain predicts disease activity after the first demyelinating event suggestive of multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;35: 228-232. [52] TOLENTINO M, PACE F, PERANTIE DC, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers as predictors of multiple sclerosis severity. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2025;94:106268. [53] SCHILKE ED, REMOLI G, FUNELLI, E., et al. Current use of fluid biomarkers as outcome measures in multiple sclerosis (MS): A review of ongoing pharmacological clinical trials. Neurol Sci. 2024;45(5):1931-1944. [54] MOTL RW, SANDROFF BM, KWAKKEL G, et al. Exercise in patients with multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(10):848-856. [55] PILUTTI LA, DLUGONSKI D, SANDROFF BM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of a behavioral intervention targeting symptoms and physical activity in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2014;20(5):594-601. [56] USZYNSKI MK, CASEY B, HAYES S, et al. Social cognitive theory correlates of physical activity in inactive adults with multiple sclerosis. Int J MS Care. 2018;20(3):129-135. [57] JENG B, CEDERBERG KLJ, HUYNH TL, et al. Social cognitive theory variables as correlates of physical activity in fatigued persons with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022;57:103312. [58] ADAMSON B, WYATT N, KEY L, et al. Results of the MOVE MS program: A feasibility study on group exercise for individuals with multiple sclerosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(16):6567. [59] JONGEN PJ, HEERINGS M, RUIMSCHOTEL R, et al. Intensive social cognitive treatment (can do treatment) with participation of support partners in persons with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: Observation of improved self-efficacy, quality of life, anxiety and depression 1 year later. BMC Res Note. 2016;9:375. [60] RUSSELL N, GALLAGHER S, MSETFI RM, et al. Experiences of people with multiple sclerosis participating in a social cognitive behavior change physical activity intervention. Physiother Theory Pract. 2023; 39(5):954-962. [61] CHAN CT, GARIKIPATI KK. Factors associated with physical activity and exercise participation in people with multiple sclerosis: a qualitative systematic review.Eur J Physiother. 2024;26(3):148-159. [62] DINI M, COMI G, Leocani L.Digital remote monitoring of people with multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2025;16:1514813. [63] DEVASAHAYAM AJ, KELLY LP, WILLIAMS JB, et al. Fitness shifts the balance of BDNF and IL-6 from inflammation to repair among people with progressive multiple sclerosis.Biomolecules. 2021;11(4):504. [64] MOTL RW, PILUTTI LA. Advancements and challenges in exercise training for multiple sclerosis: Comprehensive review and future directions for randomized controlled trials. Neurol Ther. 2024;13(6):1559-1569. [65] LOCATELLI G, STANGEL M, ROOKS D, et al. The therapeutic potential of exercise for improving mobility in multiple sclerosis.Front Physiol. 2024;15:1477431. [66] 锁冬梅, 刘海杰, 张大启, 等. 多发性硬化患者的运动康复现状[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,40(10):795-797. |
| [1] | 徐灿丽, 何文星, 王玉萍, 巴寅颖, 迟 莉, 王文娟, 王佳佳. 核因子κB激活激酶在自身免疫、信号通路、基因表达、肿瘤防治等领域的研究脉络与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | 钟彩红, 肖晓歌, 李 明, 林剑虹, 洪 靖. 运动相关髌腱炎发病的生物力学机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1417-1423. |
| [3] | 孙尧天, 徐 凯, 王沛云. 运动影响铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病调控的潜在机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
| [4] | 黄 杰, 曾 浩, 王文驰, 吕柱成, 崔 伟. 脂代谢影响骨质疏松症的文献可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [5] | 张海文, 张 贤, 许太川, 李 超. 衰老在骨质疏松领域研究现状及趋势的文献可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [6] | 文 凡, 向 阳, 朱 欢, 庹艳芳, 李 锋. 运动干预改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [7] | 杨泽雨, 支 亮, 王 佳, 张婧欹, 张清芳, 王玉龙, 龙建军. 高频重复经颅磁刺激研究热点宏观角度的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [8] | 彭 皓, 陈奇刚, 申 震. H型血管在不同骨骼疾病中研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [9] | 章安琪, 化昊天, 蔡恬媛, 王子成, 孟 卓, 占效谦, 陈国茜. 全膝关节置换后疼痛:研究现状及趋势分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [10] | 张树立, 侯超文, 袁珊珊, 马玉华. 运动调控自噬在不同生理系统中的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4737-4748. |
| [11] | 陈园月, 沈俊帆, 于 翠, 陆建霞, 胡文萱, 朱 军, 郭 川. 表面肌电图在肌肉骨骼疼痛康复领域应用的知识结构与演化趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4791-4801. |
| [12] | 李瑞颖, 夏 翃. 铜死亡研究进展可视化分析:全球视野下的热点与前沿[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4529-4541. |
| [13] | 魏婧怡, 王潇婧, 刘西花. 眼动追踪技术在康复领域的应用:基于CiteSpace和VOSviewer的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4265-4277. |
| [14] | 彭 皓, 蒋 阳, 宋艳萍, 姚 娜, 申 震, 宋粤渝, 陈奇刚. 运动训练与专项运动者身体姿势异常及脊柱曲度紊乱的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3127-3133. |
| [15] | 肖美娜, 姜传银. 全身振动训练的国内外应用研究进展、热点及展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(11): 2896-2908. |
近年来,运动干预对于优化多发性硬化症患者神经功能、运动能力、心理健康以及生活质量的作用日益受到重视[7]。当前的证据显示,普拉提训练可明显改善多发性硬化症患者的功能性平衡能力,改良姿势稳定性与运动控制状况,而且在某种程度上减小了本体感觉障碍、步态不稳和核心肌群无力等摔倒相关风险要素[8-10]。有研究表明,把神经肌肉训练内容纳入针对多发性硬化症患者的上肢加强训练计划当中,将有益于大幅减轻肌肉疼痛,改进肩关节的伸肌、肘关节的屈肌和伸肌的力量,也可有效提升手部的灵敏性及细致运动能力[11]。多模式运动训练能够有效地改善中重度行动障碍多发性硬化症患者的耐力性步行能力以及认知加工速度,这种效应似乎同心肺功能的优化存在相关性[12]。另外,一些研究也显示,八段锦、瑜伽等身心整合运动,可以明显提升多发性硬化症患者的运动功能和姿势控制水平,而且对于减轻疲劳感和抑郁情绪也有益处。身心整合运动干预在促进多发性硬化症患者身心健康、改善生活质量方面展现出良好的效果与临床应用前景[13]。同样的,普拉提训练作为一种集核心稳定性、身体控制与协调性于一体的低强度运动形式,也逐渐显现出它在功能康复中的独特价值[14]。
大量研究表明,运动干预已成为多发性硬化症患者重要的康复手段。近年来关于运动干预多发性硬化症领域的相关文献大量涌现出来,然而目前仍缺乏对该领域文献的全面梳理。因此,为了深入了解该领域的研究热点和主题演变,此项研究利用CiteSpace软件来剖析Web of Science数据库中的相关文献,并生成可视化科学知识图谱加以分析,主要涉及文献共被引分析、关键词及突现词分析等,从而明确该领域的研究热点及其主题演变过程,为该领域研究者提供借鉴和参照[15]。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 设计 利用CiteSpace软件对Web of Science数据库中关于“运动干预多发性硬化症”领域相关文献进行文献计量学分析,以探明该领域的研究热点与主题演变。
1.2 时间及地点 该研究于2025年4-5月在中国民用航空飞行学院完成。
1.3 资料
1.3.1 数据的来源与检索策略 对Web of Science(www.webofscience.com) 核心合集数据库进行检索,文献类型为Article或Review,检索时间跨度为“建库日起至2025年4月8日”;检索库包括:SCI-EXPANDED,SSCI,AHCI,CPCI-S,CPCI-SSH,BKCI-S,ESCI,CCR-EXPANDED,IC等。检索语言为英文,检索式为:TS=(“multiple sclerosis”) AND TS=(“physical activity” OR exercise OR sport)。在对初步检索结果进行多次审阅与人工筛选后,最终明确了此次研究的文献检索方案,共检索到4 502篇文献,所有文献均为运动干预多发硬化症领域相关文献。剔除重复发表的论文、题录不完整的论文、与主题不相关的论文、社会材料、新闻、信函、会议的摘要等,最终纳入3 761篇文献。
文献检索筛选流程图见图1。
1.3.2 纳入与排除标准
(1)纳入标准:①在Web of Science核心合集数据库检索出的文献;②研究设计包括动物实验、随机对照试验、系统综述、系统评价、荟萃分析和普通文献综述;③内容聚焦于运动干预与多发性硬化症相关领域的研究。
(2)排除标准:①剔除重复发表的论文;②题录不完整的论文;③与主题不相关的论文;④社会材料、新
闻、信函、会议的摘要等;⑤发布缺少关键信息或已被撤回的。
1.4 研究方法 研究借助CiteSpace软件对运动干预多发性硬化症领域的相关文献进行文献计量可视化分析。CiteSpace是由美国德雷塞尔大学Chaomei Chen教授所研发的一种依靠网络科学和信息可视化技术的分析工具,其普遍应用于知识图谱绘制以及科学文献的结构化分析[16]。通过CiteSpace对所选文献数据展开共现分析、聚类分析以及突现词探测,以此来找出该研究领域的高频关键词、关键研究话题、发展趋向及其研究前沿。在分析进程之中,通过指定时间切片、节点种类以及算法参数,塑造起文献共被引网络和关键词共现网络,进而把该领域的研究脉络和知识架构以可视化形式体现出来。这种方法有益于提升文献分析的系统性与客观性,缩减主观判断造成的误差,为后续研究赋予数据支撑和理论参照[17]。分析时将关键词(Keyword)、参考文献(CitedReference)当作节点类型(NodeTypes),利用Pathfinder网络剪枝算法(Pruning:Pathfinder)来削减多余的边,保存网络结构的大致框架,布局算法用聚类视图(ClusterView-Static),清楚显示主题聚类情况。在生成的知识图谱中,节点的直径代表出现频率,直径越大就显示这个节点在研究里出现得越频繁。节点间的连线体现了共现频率,线越粗就表示节点间的联系越密切;节点颜色体现所属时间区间,从冷色过渡到暖色表现出时间上的演进,从而看出研究的走向,紫色外环表示这个节点有较高的中介中心性,这显示它在结合不同子领域时起着关键的桥梁作用,可以当作潜在的研究前沿或者交叉点[18]。
3.2 研究的不足之处 此项研究借助信息可视化工具CiteSpace针对Web of Science核心合集中有关运动干预多发性硬化症方面的文献做了可视化处理,但实际上,运动干预多发性硬化症的相关研究并非仅仅局限于此数据库当中,其同样散布在Web of Science非核心合集,Scopus,CNKI,CSSCI等诸多数据库里面,所以采用单一的数据源可能会造成研究偏倚。为了使研究更加全面、准确,后续研究应该扩大数据来源,使用多个数据库,进行文献对比分析,减少研究偏倚在做关键词分析的时候,部分高频词项存在表层语义与深层学术意涵的映射断裂现象。这一现象并不表征相关文献的学术价值缺失,而是直观揭示了基于词频统计的可视化方法在语义深度解析方面的方法学局限。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
多发性硬化症是一种复杂的慢性神经系统疾病,对患者的生活质量产生了深远的影响。近年来,运动干预作为一种有效的康复手段,受到了越来越多的关注。运动干预方式主要涉及有氧运动、抗阻训练,以及平衡训练和认知运动疗法等多种类型。研究发现,有氧运动可提高患者的心肺功能,减轻疲劳;抗阻训练则有助于增强肌肉力量,改善运动能力。另外,结合虚拟现实技术的运动干预,为患者提供了沉浸式的康复体验,使康复训练更有趣、高效。通过文献计量学研究发现,该领域早期研究集中在运动对患者基本功能的影响上。如今,研究者开始关注运动干预对患者认知功能、心理健康以及生活质量的综合影响。一些研究表明,运动干预可显著改善患者的认知障碍,减轻抑郁和焦虑情绪,提高生活质量。另外,研究者还探索了运动干预的长期效果以及如何将其融入到患者日常生活中。未来,运动干预将更注重个性化和精准化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||