1 对象和方法 Subjects and methods
1.1 设计 基于Transformer-CNN架构的单惯性测量单元康复动作识别方法。
1.2 时间及地点 2025年2-4月收集志愿者数据,在中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所内基于机器学习算法进行模型训练与数据验证实验。
1.3 对象 招募了6名健康成年男性志愿者,年龄(26.0±4.0)岁,体质量指数(22.3±5.0) kg/m²,这些志愿者没有神经、精神或身体功能障碍的病史。在试验开始前,所有被试者都详细了解了试验的细节,并签署了知情同意书。该研究方案的实施符合苏州高新区人民医院的相关伦理要求,经苏州高新区人民医院医学伦理委员会批准通过(医院伦理批件号2023-141,审批时间:2023-12-12)。
1.4 材料 实验设备采用BWT901BLECL5.0六轴惯性测量单元[采样频率98 Hz,加速度量程±2 g,角速度量程±500 (°)/s]构建无线运动捕捉系统。传感器通过医用级弹性绑带固定于被试者胸骨柄处(解剖学定位点:T3椎体水平线),见图1所示,该位置可有效捕捉躯干前屈、侧弯等动作的矢状面与冠状面动力学特征[14]。

1.5 方法
1.5.1 试验方案设计 在试验开始前,被试者被要求接受阅读试验说明,工作人员演示在试验中受试者需要模仿执行的5个腰部康复动作。在通过绑带与医用胶带固定佩戴在受试者的胸口处之前,惯性传感模块都会进行重置与矫正,并通过上位机程序并观察运动数据波形以确保数据采集正常。在正式开始前每个被试者在人工指导下进行动作纠正,保证能够准确地执行5个康复动作后开始试验,被试者跟随指引程序语音提示与倒计时按顺序完成运动数据的采集。腰部康复动作选取康复训练中的5个常见项目,每个动作采集40段周期性完整序列。依据腰部康复动作效果对比研究[15-16],选取5类康复训练效果良好的康复训练动作,见表1。每个动作执行周期包含:准备阶段(3 s),自然站立/卧位姿势;执行阶段(2 s),标准动作完成;保持阶段(5 s);恢复阶段(2 s):返回初始姿势。

为尽量还原康复训练的自然执行过程,试验过程中未刻意限制受试者的呼吸、语言表达或手部自然摆动,也未对服装穿着及皮肤贴附进行特殊约束。在数据采集中动作执行阶段不可避免地伴随若干日常环境干扰因素,包括胸部自然呼吸起伏引起的周期性轻微振动、上肢在非指令阶段的小幅度附加移动、正常交谈过程中的胸部微小振动、传感器因弹力带固定方式限制出现的轻微滑动或偏移等等。这些干扰信号均未从原始数据中剔除,保留在最终训练样本之中,以增强模型在接近真实使用场景下的适应性与鲁棒性。
1.5.2 数据预处理与特征提取 原始数据采集自佩戴于受试者胸部的六轴惯性测量单元,以98 Hz采样频率记录三轴加速度与三轴角速度时序序列。针对运动伪影干扰,采用改进型滑动窗口对加速度异常值修正,同时保留已在微控制器层面进行过卡尔曼滤波的角速度原始波动特性。通过列向量空间映射检测确保数据文件的特征维度一致性。通过基于加速度协方差矩阵的时变特性构建动作事件检测模型,采用双约束二分搜索算法确定最优检测阈值,计算动作保持阶段中心点,以相位中心C为基准,镜像截取长度为1 100个数据点的区间信号段,当C靠近信号边界时,采用边缘延拓实现样本长度标准化。
传统模型所需要的样本需要由标准化长度样本进行多域特征融合得到,即对中心化样本Sm∈R1 100×6进行时频域特征提取。时域特征包括计算均值、标准差、均方根、峰度系数等11个统计量,同时通过Welch周期图法估计功率谱密度(PSD),提取主频分量f及对应幅值作为频域特征。
由上述特征提取流程获取到的72维特征向量F执行Z-score标准化以消除量纲差异,依据文件命名规则映射所执行动作标签0-5,利用分组标识符G实现留一法交叉验证分组。
该处理流程通过严格的信号质量控制与特征空间优化,构建了包含1 100×6原始时序数据和72维统计特征的双模态数据集,为后续深度学习与经典机器学习模型提供标准化输入,整个流程见图2。
1.5.3 模型实现
(1)模型架构设计:针对单一惯性传感器信号在复杂康复训练动作中存在时序依赖建模能力不足、局部关键特征捕捉能力弱以及序列表示压缩方式简单的问题[17-20],此次研究提出一种基于一维卷

积与Transformer编码器融合的深度识别模型,采用注意力池化机制完成序列降维与特征聚合,在提升模型分类性能的同时保持网络结构的紧凑性与部署的可行性。该方法的整体结构如图2所示,主要包括局部特征提取模块、全局时序建模模块与注意力特征聚合模块,见图3。试验环境采用基于 Python 的Pytorch 深度学习框架,具体为 Python 3.9和 Pytorch 2.6.0,GPU 为 NVIDIA GeForce RTX3060,CUDA 12.2。
局部特征提取模块(卷积神经网络):输入数据为尺寸为 [B,1 100,6] 的三维张量,表示批量为[B] 的原始时间序列,每段长度为1 100,特征维度为六轴惯性测量单元输出(加速度与角速度各3个通道)。为捕捉不同康复动作在短时范围内的显著动态变化模式,引入两层一维卷积网络进行局部感受域建模。具体过程如下:
F1=ReLU(BN(Conv1Dk=5,Cin=6,Cout=64(X))) (1)
F2=ReLU(BN(Conv1Dk=5,Cin=6,Cout=64(F1))) (2)
其中,Conv1D 表示一维卷积运算,BN表示BatchNorm归一化,ReLU为非线性激活函数,核大小为5,通道数保持一致。Dropout操作被嵌入在各卷积层后用于防止过拟合。经过该模块,原始信号的六维通道被映射至64维特征空间,输出特征张量

维度为 [1 100,64]。该结构能够提取如动作起始突变、短时加速度冲击、身体部位角速度峰值等关键信息。
全局时序建模模块(Transformer 编码器):卷积神经网络模块输出的局部特征无法捕捉跨时间点的长期依赖关系,难以有效建模如“转换-保持-复位”全过程中的上下文联动模式。为此,引入Transformer编码器结构对局部特征进行全局建模:
H0=F2+P (3)
其中P为可学习的位置编码向量,能够保留时序信息。该向量与卷积神经网络输出相加后,输入至两层堆叠的Transformer编码器中:

其中,MultiHeadAttn表示4头自注意力机制,每头维度k=16,总维度model=64;FFN为前馈神经网络,维度扩展至256后再压缩回64。Transformer模块通过自注意力机制显著增强了模型对动作整体模式与长期演化结构的感知能力,适用于检测如“伸展-维持-恢复”中的缓变状态。
注意力池化与分类器模块:传统序列模型通常采用平均池化或最大池化对时序特征进行压缩,易忽略关键时刻特征的重要性分布。此次研究设计了基于注意力机制的池化方式,通过加权聚合提取时序维度上的重要特征:

其中,W1和W2为可训练权重矩阵,αt为注意力权重。注意力机制自动聚焦于时序中判别能力较强的片段,如姿态变化的转折点或角速度峰值点。最终输出经LayerNorm与Dropout后输入至两层全连接网络:

最终输出为5类康复动作的分类概率,分别对应于“站立腰部伸展”“普拉提锯式”“单腿风车”
“斯芬克斯式”“俯卧撑式上撑”。
(2)训练参数设置分析:输入序列长度设定为1 100,基于98 Hz采样率约对应11.2 s,可完整覆盖一次标准康复动作的“转换-保持-复位”全流程,避免动作裁剪导致的特征丢失。输入维度为6,对应胸部惯性测量单元的三轴加速度与三轴角速度数据。
卷积神经网络部分采用两层一维卷积结构,每层使用kernel_size=5,即在时域上提取约0.05 s时间窗内的局部动态特征。该设定用于捕捉短时间突变(如动作启动、反向发力等)特征,同时也避免过小核导致的模型过拟合。卷积输出通道数d_model=64,兼顾特征表达能力与参数规模控制,为Transformer模块提供统一维度的输入,同时与后续注意力模块结构保持一致。全局Dropout设置为0.2,作为轻度正则化手段,避免模型训练初期对时序特征的过度破坏。
此次模型中Transformer编码器结构为2层,每层包含头数为4的多头自注意力机制。Transformer深度设置为2,是小样本任务中防止深层结构过拟合的常见设置,可保证基本的全局依赖建模能力;而注意力头数为4(nhead=4)在保持子空间解耦能力的同时,避免头数过多引发的训练不稳定问题,适用于通道数较低的惯性传感器信号输入。内部前馈网络宽度设为d_model×4=256,保持标准Transformer设计比例以提升非线性建模能力。
在时序聚合阶段,引入两层感知机注意力池化模块,通过tanh激活与softmax权重机制,对各时间步进行加权融合。该结构相比平均池化与最大池化更具表达灵活性,可自适应赋予关键动作片段(如转换点、保持中段等)更高注意力分数。中间隐藏层设为d_model数的一半,即32,在保持判别能力的同时控制参数量。该机制对不规则动作具有较强鲁棒性,实际可视化结果亦证实其聚焦能力。
最终分类器由两层全连接网络组成,中间维度设为64,与d_model保持一致,配合ReLU激活函数与Dropout构建基本非线性判别器,避免过度压缩特征空间,同时确保参数量小、收敛快,为适配嵌入式部署环境提供有利条件。
为提高模型的泛化能力,训练过程中使用AdamW优化器,设置初始学习率1×10-4,配合ReduceLROnPlateau调度器动态调整。正则化方面使用Dropout函数(丢弃率设置为为0.3)与L2正则化(参数λ=1×10-4);训练过程每批次设置为64个样本,自动监控验证集loss值,若连续10个epoch无改善,则触发早停机制停止训练。
此次所提出的CNN-Transformer融合架构在结构层级、超参数配置与正则化策略上均进行了系统性设计与多轮预实验验证。模型采用留一交叉验证方法,确保测试组中受试者与训练组完全独立,有效评估跨个体泛化能力,所有训练样本统一来自预处理后的标准化数据集,每段样本包含1 100帧、6个通道,标签前述数据预处理操作时已标注。
(3)评估策略
数据集划分:采用留一(Leave-One-Group-Out)交叉验证,确保受试者独立性,每组包含1名受试者的全部数据作为测试集,其余作为训练集,即将6位受试者的样本划分为6个组,每轮选取其中一位受试者的全部样本作为测试集,其余5位受试者的数据作为训练集。在训练集中再随机划分20%样本作为验证集,用于监控模型的loss值大小以实现早停机制。在每一轮划分中,训练集、验证集、测试集的比例为4∶1∶1。此策略确保模型测试数据与训练过程完全隔离,有效评估模型对新受试者的泛化能力,避免因个体运动习惯差异导致的过拟合问题[21-23]。

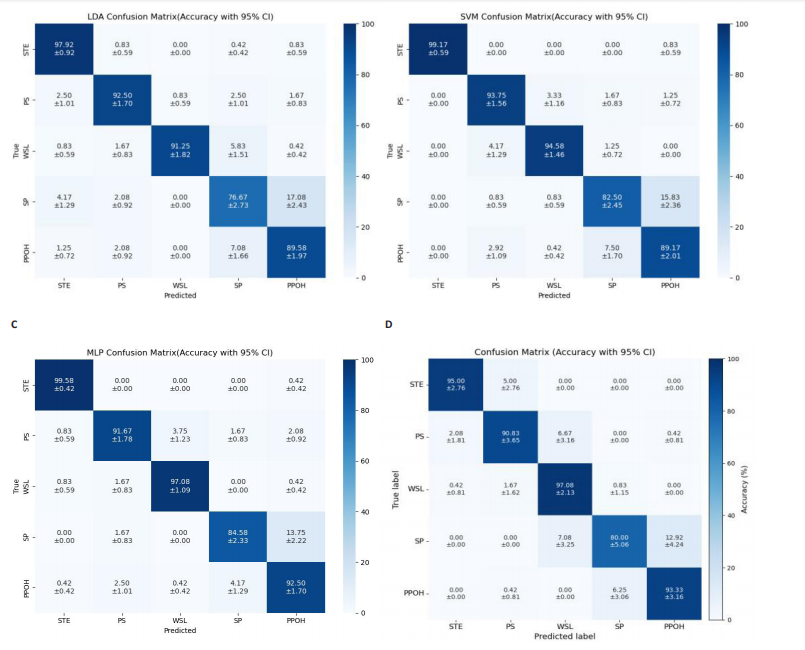
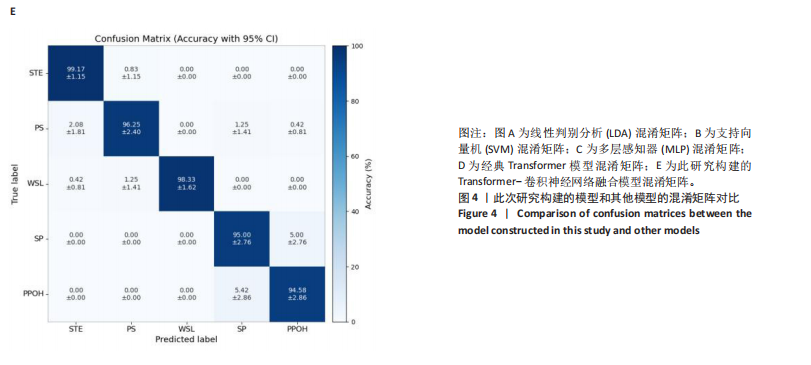
试验评估指标:姿态识别本质上是分类问题,分类器混淆矩阵见表2。其中TP全称为True Positive,指某个样本经模型判定为正样本,事实上也是正样本;FP全称为False Positive,指某个样本经模型判定为正样本,但事实上是负样本。以此类推TN是模型正确预测的负类,FN是模型误判的负类。
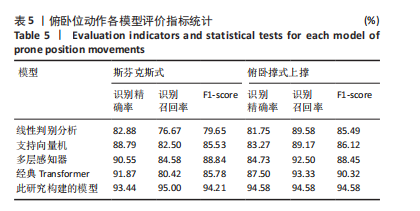
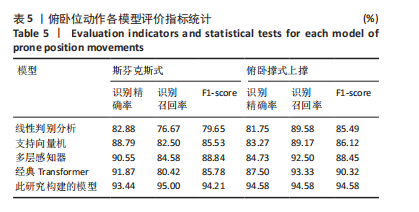
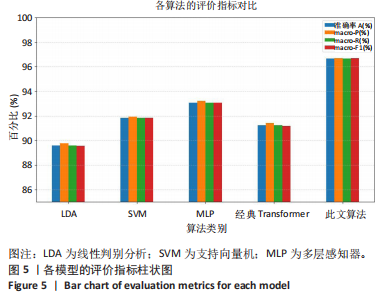
使用准确率 A(Accuracy)、精确率(P)、宏精确率(macro-P)、宏召回率(macro-R)、宏 F1 值 (macro-F1)来评估算法的性能。
准确率(ACC)展示分类模型正确判断样本类型的能力,表示为分类模型正确进行分类识别的能力其计算公式如下:

精确率(P)也称查准率,表示正确判别为正的样本在所有判别为正的样本中的占比。macro-P 为多分类宏精确率,i为每个康复动作的编号,Pi为动作i的精确率,用于衡量所有动作的整体查准效果,其值越接近1,说明算法整体查准效果越好,计算公式如下:

召回率(R)也称查全率,表示正确判定为正的样本在所有正的样本中的占比。macro-R为多分类宏召回率,i为每个康复动作的编号,Ri为动作i的召回率,用于衡量所有动作的整体查全效果,其值越接近1,说明算法整体查全效果越好,计算公式如下:

F1-score 是中用来衡量二分类模型精确度的一种指标,它同时兼顾了分类模型的精确率和召回率。macro F1是所有动作的F1-score均值,用于衡量整个模型的性能,其值越接近1,则算法性能越好,计算公式如下:

1.6 主要观察指标 通过腰部康复动作数据集对Transformer-CNN融合模型进行训练,构建动作分类模型。通过留一交叉验证评估模型准确性,并与线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)、支持向量机(Support Vector Machine,SVM)、多层感知器(multilayer perceptron,MLP)、经典Transformer等模型进行性能对比。