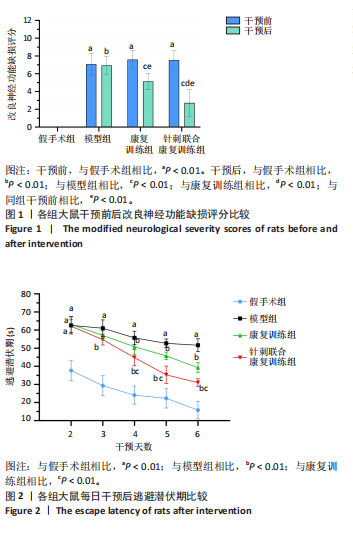
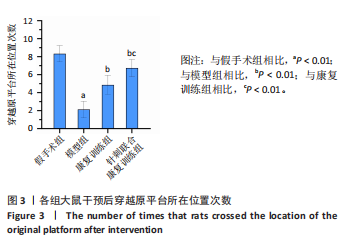
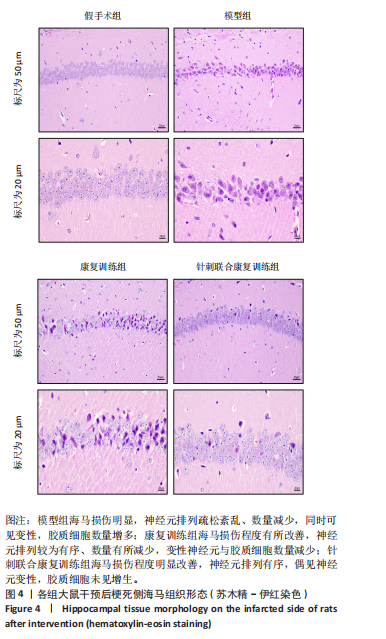
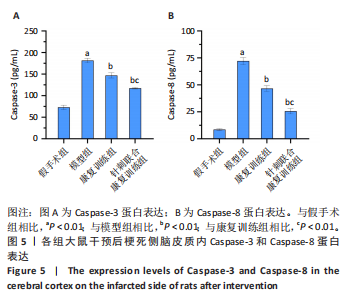
[1] 朱冉冉,王津翔,潘蓓,等.脑卒中中西医结合康复临床循证实践指南[J].上海中医药杂志,2024,58(6):1-11.
[2] 倪小佳,林浩,罗旭飞,等.脑卒中中西医结合防治指南(2023版)[J].中国全科医学,2025,28(5):521-533.
[3] FEIGIN VL, STARK BA, JOHNSON CO, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820.
[4] FESKE SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021;134(12):1457-1464.
[5] 《中国脑卒中防治报告2021》编写组,王陇德.《中国脑卒中防治报告2021》概要[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(11):783-793.
[6] 李曼玲,董苗苗,黄春江,等.电针对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶-3表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2022, 47(5):422-427.
[7] 唐红,郑慧娥,汪红娟,等.针刺对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠海马细胞凋亡的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2023,39(3):326-332.
[8] 苏凯奇,吕转,吴明莉,等.电针对缺血再灌注后学习记忆障碍大鼠BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/Akt通路的影响及对海马神经元保护作用研究[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(33):4187-4193.
[9] WEI L, ZENG K, GAI J, et al. Effect of acupuncture on neurovascular units after cerebral infarction in rats through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2020;75(4):387-397.
[10] 汤博,王霞,吴福建,等.头针疗法对缺血性中风大鼠脑神经元的保护作用及对PI3K/AKt通路的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(2):213-219.
[11] LAI HC, CHANG QY, HSIEH CL. Signal Transduction Pathways of Acupuncture for Treating Some Nervous System Diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:2909632.
[12] ZHANG XQ, WANG YH, SUN L, et al. Electroacupuncture Promotes Motor Function Recovery in MCAO/R Rats by Activating Astrocyte-Related PI3K/AKT Pathway. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022;15(5):322-332.
[13] ZHANG Y, YIN YL, JIN ZY, et al. Electroacupuncture Activates Neuroplasticity in the Motor Cortex and Corticospinal Tract via the mTOR Pathway in a Rat P-MCAO Model. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:3470685.
[14] 肖亮,殷小成,曹强强.PI3K/AKT通路在二烯丙基二硫诱导K562细胞凋亡中的作用机制研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2016,18(10): 1050-1054.
[15] 王博,张晓明,吴松,等.标本配穴电针预处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马神经元p53与caspase-3表达的影响[J].中国针灸, 2019,39(9):957-962.
[16] QI G, SUN D, TIAN Y, et al. Fast Activation and Tracing of Caspase-3 Involved Cell Apoptosis by Combined Electrostimulation and Smart Signal-Amplified SERS Nanoprobes. Anal Chem. 2020;92(11):7861-7868.
[17] TUMMERS B, GREEN DR. Caspase‐8: regulating life and death. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):76-89.
[18] YIN F, ZHOU H, FANG Y, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of key factors in death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;248:112319.
[19] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989; 20(1):84-91.
[20] CHEN JL, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005-1011.
[21] 中国针灸学会.实验动物常用穴位名称与定位第2部分:大鼠[J].针刺研究,2021,46(4):351-352.
[22] 姚璐,赵睿婷,周菊,等.灯盏乙素对缺氧缺血性新生大鼠脑缺氧诱导因子-1α和水通道蛋白9表达水平的影响[J].中国医院药学杂志,2018,38(4):364-368.
[23] 高长玉,吴成翰,赵建国,等.中国脑梗死中西医结合诊治指南(2017)[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(2):136-144.
[24] 孟文婷,李东翔,佟玲.缺血性脑卒中的治疗研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2016,25(10):1114-1120.
[25] WANG L, SU XT, CAO Y, et al. Potential mechanisms of acupuncture in enhancing cerebral perfusion of ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2022;13:1030747.
[26] WANG Z, WANG M, ZHAO H. Acupuncture and its role in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024; 103(40):e39820.
[27] 章薇,娄必丹,李金香,等.中医康复临床实践指南·缺血性脑卒中(脑梗死)[J].康复学报,2021,31(6):437-447.
[28] CHEN J, ZHANG J, XIANG J, et al. Impact of intelligent convolutional neural network -based algorithms on head computed tomography evaluation and comprehensive rehabilitation acupuncture therapy for patients with cerebral infarction. J Neurosci Methods. 2024;409: 110185.
[29] JIANG H, ZHANG C, LIN M, et al. Deciphering the mechanistic impact of acupuncture on the neurovascular unit in acute ischemic stroke: Insights from basic research in a narrative review. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;101:102536.
[30] ZHANG W, HAN L, WEN Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2912.
[31] CAO BQ, TAN F, ZHAN J, et al. Mechanism underlying treatment of ischemic stroke using acupuncture: transmission and regulation. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(5):944-954.
[32] 黄志霖,朱涛,黄淦,等.针刺调控炎症反应治疗缺血性脑卒中机制研究进展[J].山东中医杂志,2023,42(9):1009-1014.
[33] SIU FK, LO SC, LEUNG MC. Electroacupuncture reduces the extent of lipid peroxidation by increasing superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in ischemic-reperfused rat brains. Neurosci Lett. 2004;354(2):158-162.
[34] KIM YL, KIM SS, SIN RS, et al. Study on the Cerebral Blood Flow Regulatory Features of Acupuncture at Acupoints of the Goveror Vessel. Med Acupunct. 2018;30(4):192-197.
[35] 黄菊芳,罗婷,罗伟生.针刺治疗缺血性脑卒中的机制研究进展[J].针刺研究,2022,47(1):78-82.
[36] 唐丽娟,张慧,冯卫星.针刺治疗缺血性脑卒中的作用机制研究进展[J].江苏中医药,2023,55(2):77-81.
[37] CHANG QY, LIN YW, HSIEH CL. Acupuncture and neuroregeneration in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):573-583.
[38] QIN S, ZHANG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. The impact of acupuncture on neuroplasticity after ischemic stroke: a literature review and perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:817732.
[39] LIN D, DE LA PENA I, LIN L, et al. The neuroprotective role of acupuncture and activation of the BDNF signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):3234-3252.
[40] WU P, ZHOU YM, LIAO CX, et al. Structural Changes Induced by Acupuncture in the Recovering Brain after Ischemic Stroke. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:5179689.
[41] CHUANG CM, HSIEH CL, LI TC, et al. Acupuncture stimulation at Baihui acupoint reduced cerebral infarct and increased dopamine levels in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemia-reperfusion injured sprague-dawley rats. Am J Chin Med. 2007;35(5):779-791.
[42] WANG HL, LIU FL, LI RQ, et al. Electroacupuncture improves learning and memory functions in a rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(6):1011-1016.
[43] 全爱君,魏巍,张师伟,等.基于PI3K/AKT通路探讨电针预处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用机制[J].针灸临床杂志,2021, 37(6):79-83.
[44] 陈明明,潘小霞,郑法文,等.朱琏针刺兴奋法对缺血缺氧性脑损伤幼鼠神经细胞凋亡和PI3K、AKt、Caspase-3蛋白表达的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2016,35(5):592-595.
[45] 郑海清,胡昔权,潘三强,等.康复训练对脑梗死大鼠功能恢复及皮质梗死边缘区神经细胞超微结构的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2008,23(7):605-608.
[46] 张丽颖,胡昔权,郑海清,等.运动训练对脑梗死大鼠梗死边缘区神经细胞自噬及凋亡的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(8): 863-868.
[47] MIZUTANI K, SONODA S, KARASAWA N, et al. Effects of exercise after focal cerebral cortex infarction on basal ganglion. Neurol Sci. 2013; 34(6):861-867.
[48] LANGHORNE P, COUPAR F, POLLOCK A. Motor recovery after stroke: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(8):741-754.
[49] LEVIN MF, DEMERS M. Motor learning in neurological rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil. 2021;43(24):3445-3453.
[50] 高希言,马巧琳.督脉与脑的关系浅探[J].世界中医药,2007,2(3): 134-135,137.
[51] 汪子栋,姜婧,史术峰,等.“通督启神”针法治疗神志病的理论探析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2020,22(8):2641-2646.
[52] 武峻艳,王杰,张俊龙.从督脉的循行和作用谈“脑为元神之府”[J].中医杂志,2015,56(8):636-639.
[53] 徐勤红,彭拥军.“通督调神针法”治疗急性脑梗死临床疗效观察及其对自噬的影响[J].中国针灸,2018,38(5):457-461.
[54] 李璟,刘艳艳,赵海音,等.秦亮甫“督脉为要”之临证经验[J].江苏中医药,2014,46(7):14-16.
[55] 卢长龙.浅析脑为经脉循行的核心[J].江苏中医药,2014,46(6):10-11.
[56] 黄金,李瑞青,吴明莉,等.电针神庭、百会穴对脑缺血再灌注大鼠学习记忆能力及自噬相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2019,37(4):838-841,1041.
[57] 詹杰,潘锐焕,郭友华,等.针刺百会、神庭联合基础治疗和常规康复训练治疗脑卒中后认知障碍:随机对照研究[J].中国针灸, 2016,36(8):803-806.
[58] SONG MK, JO HS, KIM EJ, et al. Gene Expression of Neurogenesis Related to Exercise Intensity in a Cerebral Infarction Rat Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(16):8997.
[59] DEHQANIZADEH B, MOHAMMADI ZF, KALANI AHT, et al. Effect of early exercise on inflammatory parameters and apoptosis in CA1 area of the hippocampus following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Research Bulletin. 2022;182:102-110.
[60] 郭金赫,夏青,范文,等.康复训练促进大鼠脑缺血半暗带区星形胶质细胞向神经元转化的作用研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019, 34(12):1403-1410,1455.
[61] HERS I, VINCENT EE, TAVARÉ JM. Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal. 2011;23(10):1515-1527.
[62] FRANKE TF, HORNIK CP, SEGEV L, et al. PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene. 2003;22(56):8983-8998.
[63] LAPLANTE M, SABATINI DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149(2):274-293.
[64] FISCHER U, JÄNICKE RU, SCHULZE-OSTHOFF K. Many cuts to ruin: a comprehensive update of caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10(1):76-100.
[65] KURANAGA E, MIURA M. Nonapoptotic functions of caspases: caspases as regulatory molecules for immunity and cell-fate determination. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(3):135-144.
[66]PORTT L, NORMAN G, CLAPP C, et al. Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(1):238-259.
|