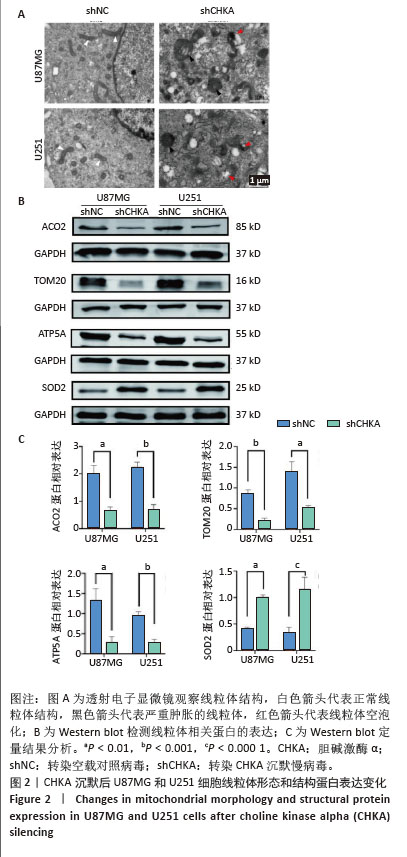
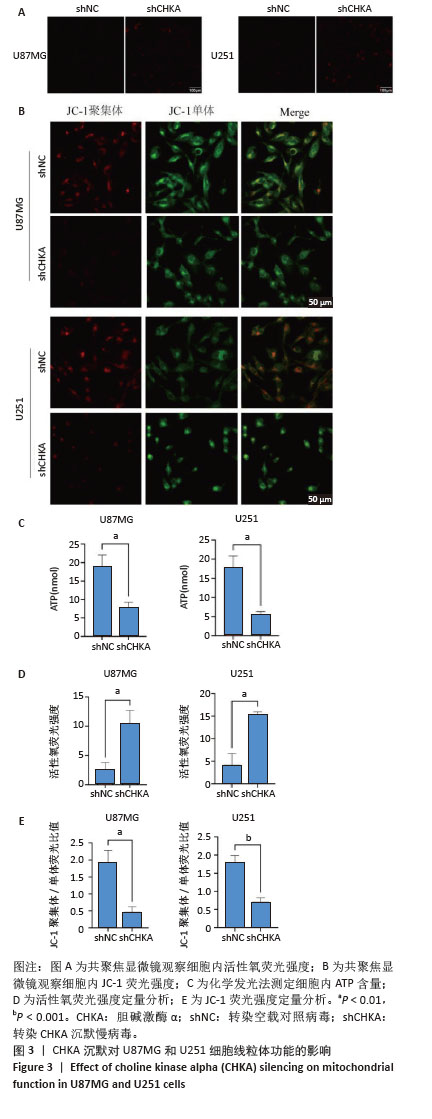
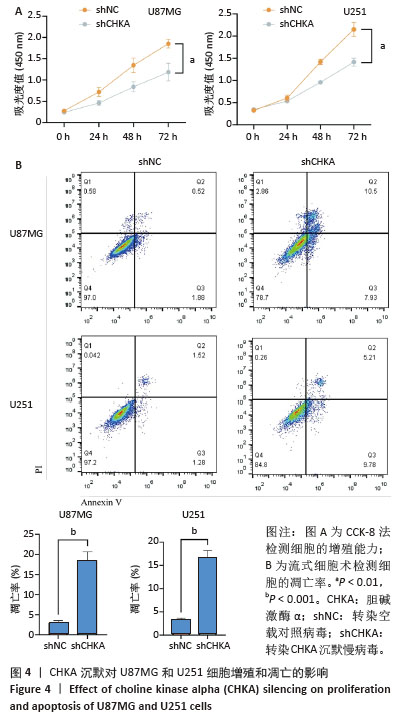
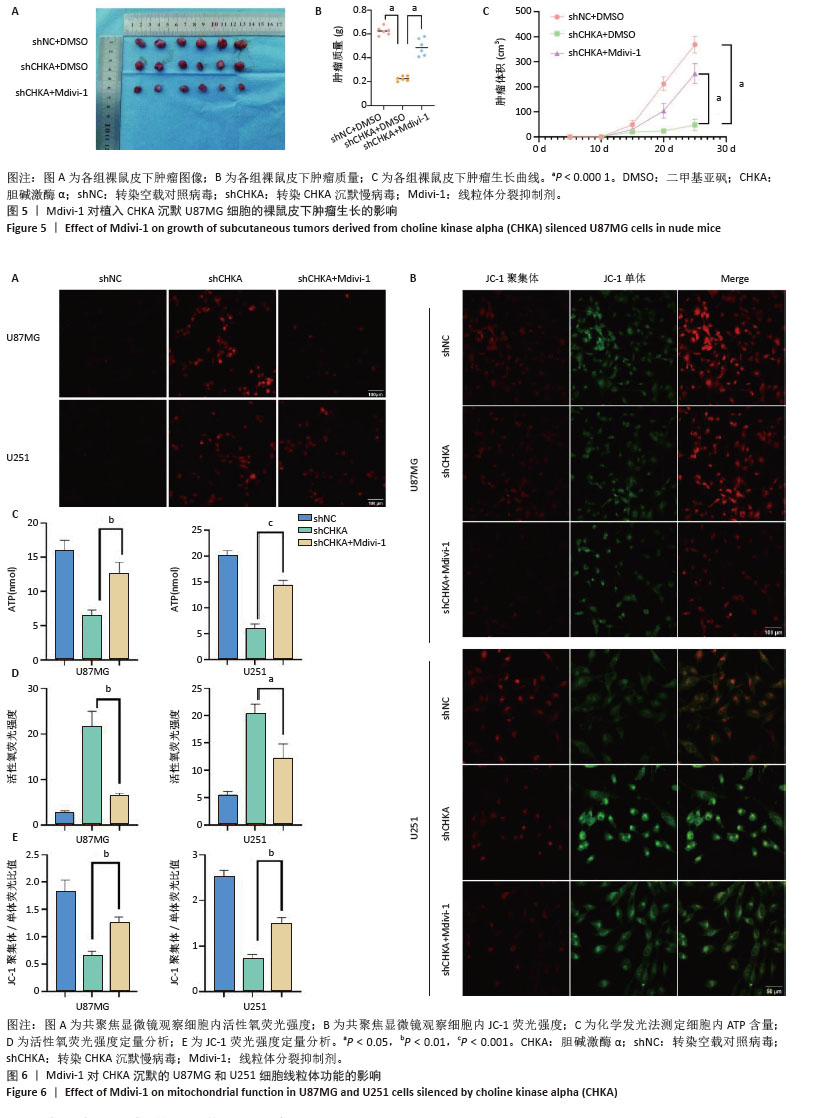
[1] TAN AC, ASHLEY DM, LÓPEZ GY, et al. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(4): 299-312.
[2] THOMAS AA, BRENNAN CW, DEANGELIS LM, et al. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71(11):1437-1444.
[3] LAN Z, LI X, ZHANG X. Glioblastoma: An Update in Pathology, Molecular Mechanisms and Biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(5):3040.
[4] MA Q, JIANG H, MA L, et al. The moonlighting function of glycolytic enzyme enolase-1 promotes choline phospholipid metabolism and tumor cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(15): e2209435120.
[5] GOKHALE S, XIE P. ChoK-Full of Potential: Choline Kinase in B Cell and T Cell Malignancies. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(6):911.
[6] GLUNDE K, BHUJWALLA ZM. Choline kinase alpha in cancer prognosis and treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(10):855-857.
[7] ZONG Y, LI H, LIAO P, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):124.
[8] GRANATH-PANELO M, KAJIMURA S. Mitochondrial heterogeneity and adaptations to cellular needs. Nat Cell Biol. 2024;26(5):674-686.
[9] DECKER ST, FUNAI K. Mitochondrial membrane lipids in the regulation of bioenergetic flux. Cell Metab. 2024;36(9):1963-1978.
[10] ZOU Y, HUANG L, SUN S, et al. Choline Kinase Alpha Promoted Glioma Development by Activating PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2021.0294.
[11] HORVATH SE, DAUM G. Lipids of mitochondria. Prog Lipid Res. 2013; 52(4):590-614.
[12] BEREITER-HAHN J, JENDRACH M. Mitochondrial dynamics. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;284:1-65.
[13] LEÃO BARROS MB, PINHEIRO DDR, BORGES BDN. Mitochondrial DNA Alterations in Glioblastoma (GBM). Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5855.
[14] PENG Y, ZHAO T, RONG S, et al. Young small extracellular vesicles rejuvenate replicative senescence by remodeling Drp1 translocation-mediated mitochondrial dynamics. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024; 22(1):543.
[15] PARK SW, KIM KY, LINDSEY JD, et al. A selective inhibitor of drp1, mdivi-1, increases retinal ganglion cell survival in acute ischemic mouse retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(5):2837-2843.
[16] ZHANG WK, YAN JM, CHU M, et al. Bunyavirus SFTSV nucleoprotein exploits TUFM-mediated mitophagy to impair antiviral innate immunity. Autophagy. 2025;21(1):102-119.
[17] YANG Z, YANG Z, HU Z, et al. UAP1L1 plays an oncogene-like role in glioma through promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(7):542.
[18] 李艳花,张晓娟,张思羽,等.Mdivi-1通过抑制少突胶质细胞凋亡信号通路发挥髓鞘保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2024,40(3): 527-534.
[19] STRIBBLING SM, RYAN AJ. The cell-line-derived subcutaneous tumor model in preclinical cancer research. Nat Protoc. 2022;17(9):2108-2128.
[20] PADALKO V, POSNIK F, ADAMCZYK M. Mitochondrial Aconitase and Its Contribution to the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(18):9950.
[21] PANDA PK, NAIK PP, MEHER BR, et al. PUMA dependent mitophagy by Abrus agglutinin contributes to apoptosis through ceramide generation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(3):480-495.
[22] TANG D, KROEMER G, KANG R. Targeting cuproplasia and cuproptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2024;21(5):370-388.
[23] DING D, LI N, GE Y, et al. Current status of superoxide dismutase 2 on oral disease progression by supervision of ROS. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175:116605.
[24] JENKINS BC, NEIKIRK K, KATTI P, et al. Mitochondria in disease: changes in shapes and dynamics. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024;49(4):346-360.
[25] KENNY TC, BIRSOY K. Mitochondria and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2024;14(12):a041534.
[26] SUOMALAINEN A, NUNNARI J. Mitochondria at the crossroads of health and disease. Cell. 2024;187(11):2601-2627.
[27] LI Y, ZHANG H, YU C, et al. New Insights into Mitochondria in Health and Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(18):9975.
[28] ZHANG Y, YAN H, WEI Y, et al. Decoding mitochondria’s role in immunity and cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024; 1879(4):189107.
[29] LIU BH, XU CZ, LIU Y, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in human health and disease. Mil Med Res. 2024;11(1):32.
[30] ARLAUCKAS SP, POPOV AV, DELIKATNY EJ. Choline kinase alpha-Putting the ChoK-hold on tumor metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 2016;63:28-40.
[31] MIYAKE T, PARSONS SJ. Functional interactions between Choline kinase α, epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Src in breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1431-1441.
[32] 黄灵,邹有瑞,马悦,等.胆碱激酶 α 在不同级别胶质瘤中的表达差异及临床意义[J].中国癌症杂志,2021,31(10):892-898.
[33] 岳芳倩,邹有瑞,孙胜玉,等.敲低胆碱激酶α(CHKA)抑制U87MG人胶质瘤细胞增殖和侵袭及迁移[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2020,36(8):724-728.
[34] 岳芳倩,邹有瑞,孙胜玉,等.胆碱激酶α抑制剂MN58b对U87胶质瘤干细胞增殖及凋亡的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021, 37(12):1468-1471.
[35] LI J, ZHAO Y, WU X, et al. Choline kinase alpha regulates autophagy-associated exosome release to promote glioma cell progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025;746:151269.
[36] RUBIO-RUIZ B, SERRÁN-AGUILERA L, HURTADO-GUERRERO R, et al. Recent advances in the design of choline kinase α inhibitors and the molecular basis of their inhibition. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(2):902-927.
[37] CHEN X, QIU H, WANG C, et al. Molecular structure and differential function of choline kinases CHKα and CHKβ in musculoskeletal system and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;33:65-72.
[38] CASSIDY-STONE A, CHIPUK JE, INGERMAN E, et al. Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell. 2008;14(2):193-204.
[39] SONG N, MEI S, WANG X, et al. Focusing on mitochondria in the brain: from biology to therapeutics. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1):23.
[40] RODRIGUES T, FERRAZ LS. Therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondrial dynamics in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;182: 114282. |