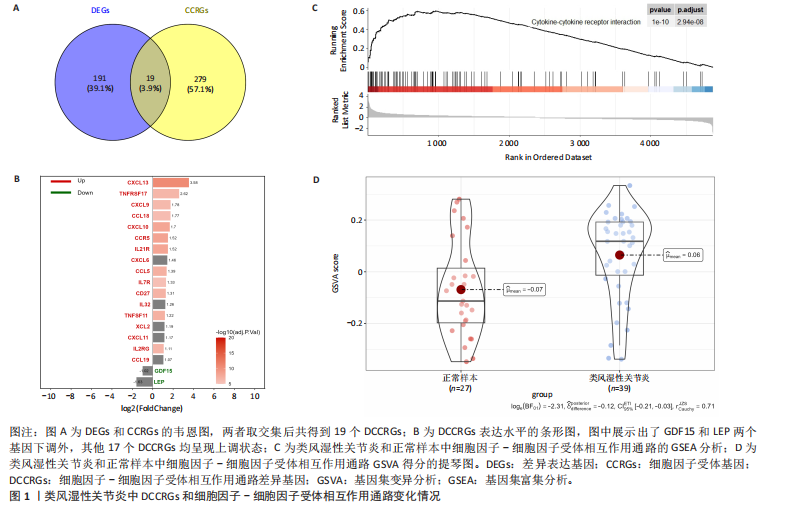
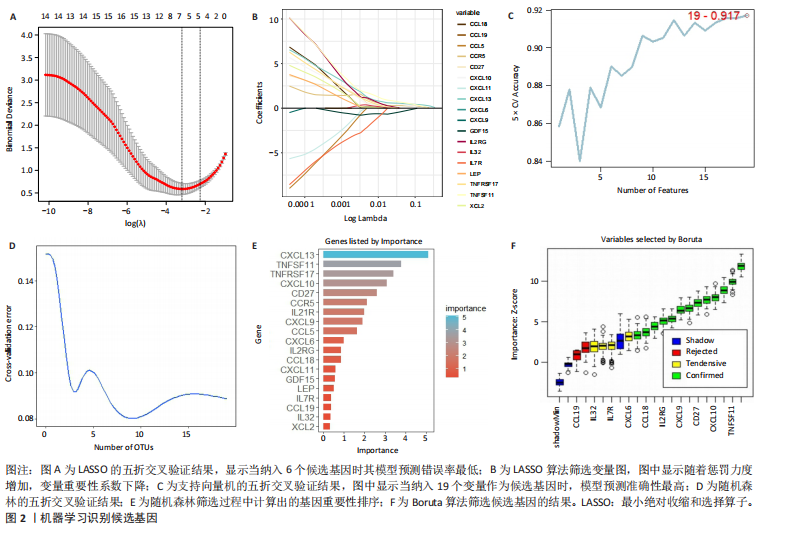
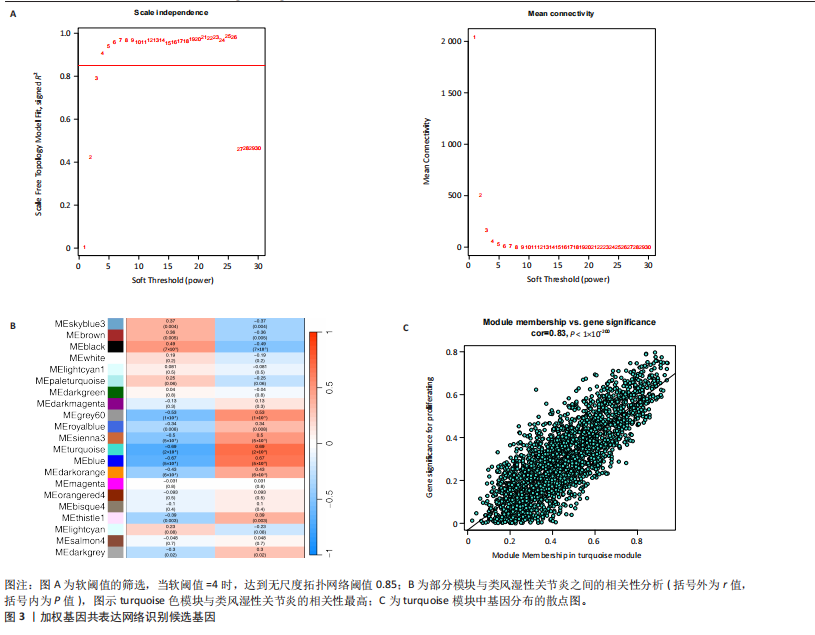
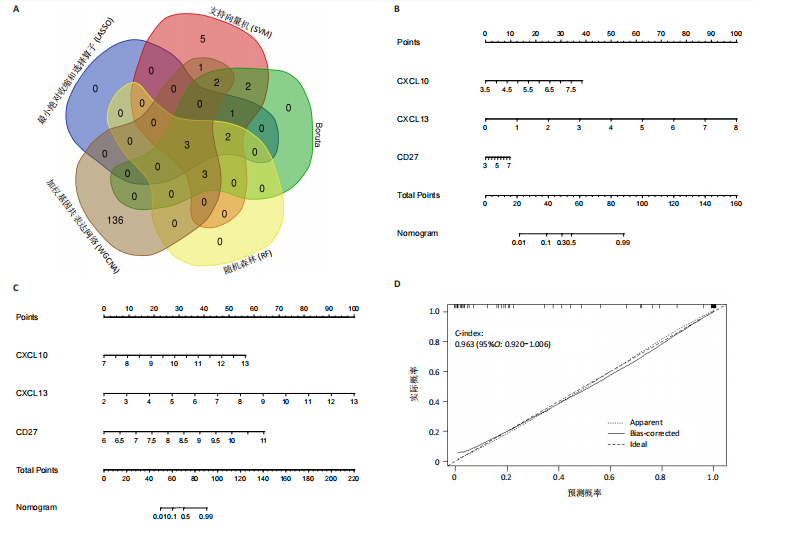
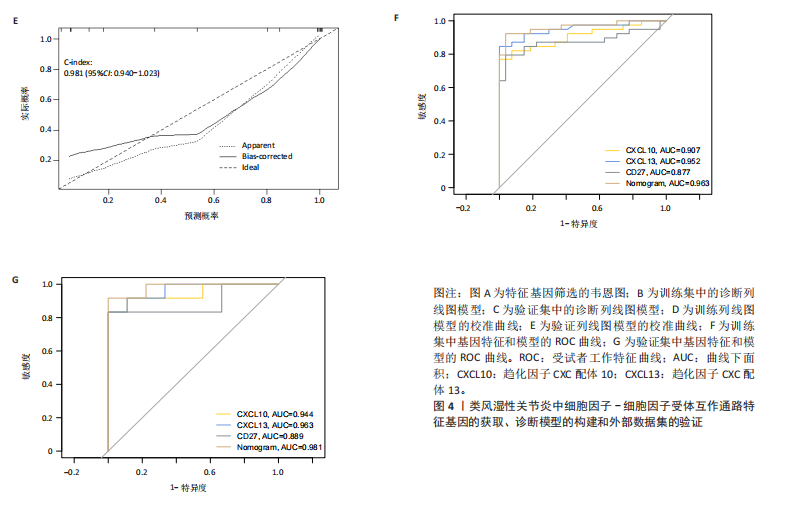
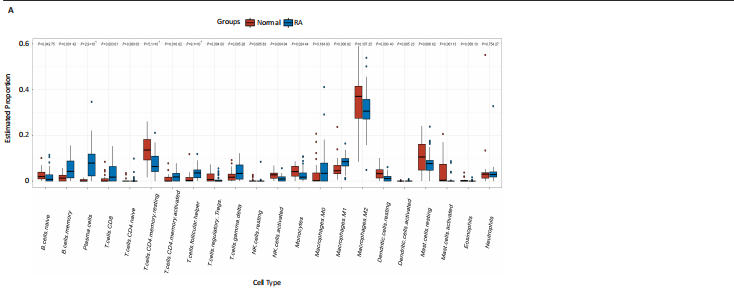
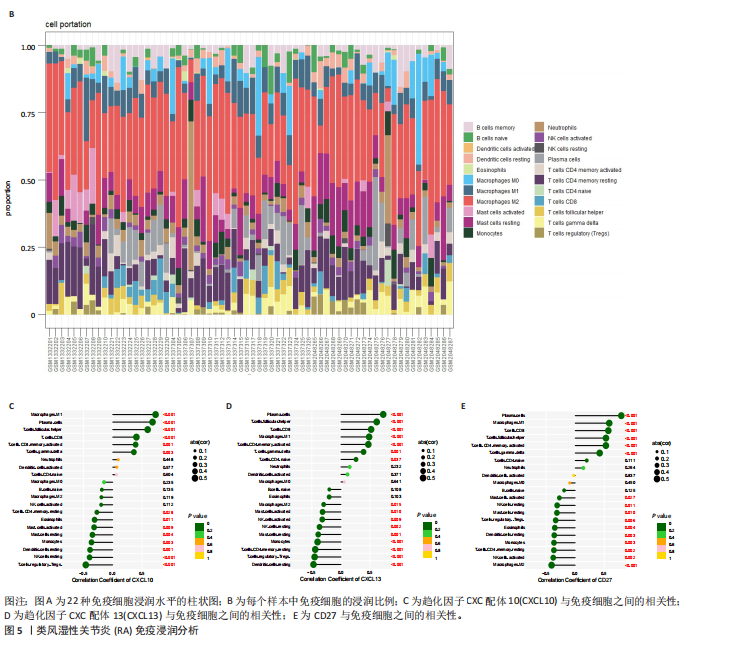
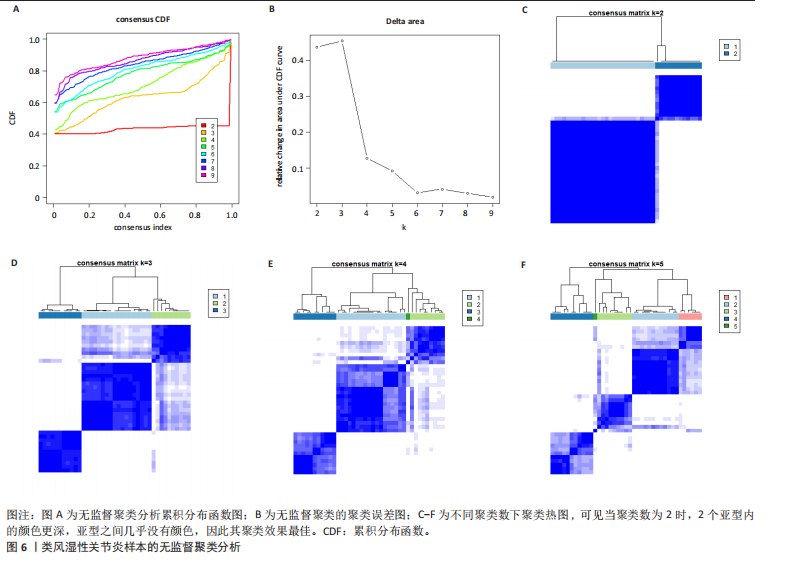
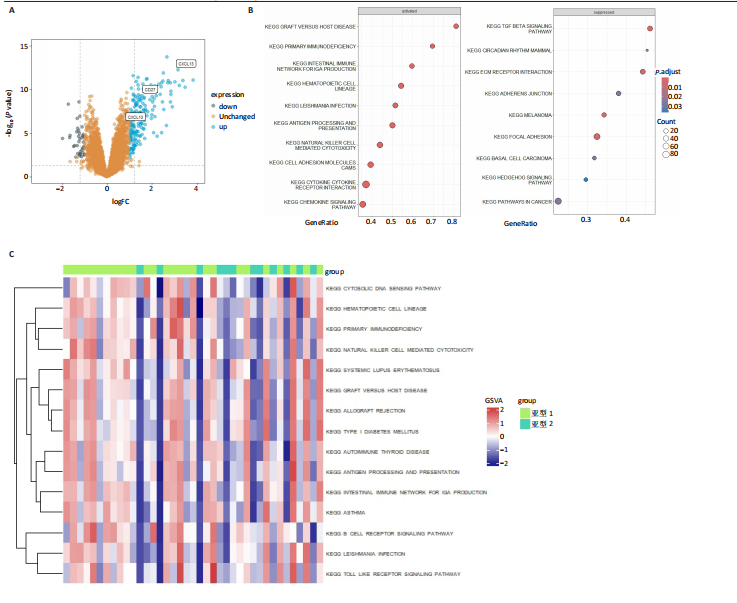
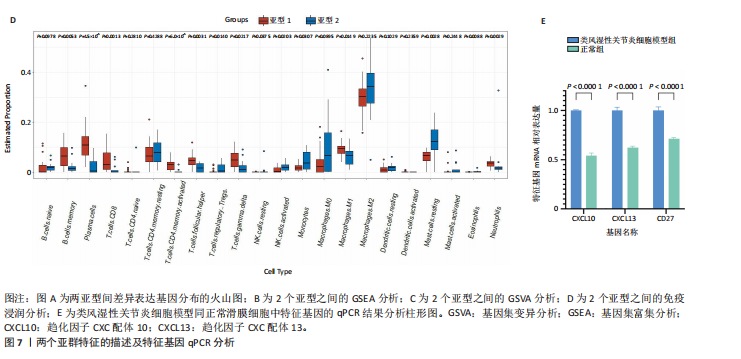
[1] ZHOU S, LU H, XIONG M. Identifying Immune Cell Infiltration and Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12726747.
[2] WU YK, LIU CD, LIU C, et al. Machine learning and weighted gene co-expression network analysis identify a three-gene signature to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1387311.
[3] YU F, HU G, LI L, et al. Identification of key candidate genes and biological pathways in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2022; 23(6):368.
[4] BRZUSTEWICZ E, BRYL E. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis--Practical and potential application of cytokines as biomarkers and targets of personalized therapy. Cytokine. 2015;76(2):527-356.
[5] SULLIVAN DI, ASCHERMAN DP. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD): Update on Prevalence, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Therapy. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024;26(12):431-449.
[6] DINARELLO CA. The IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(10):612-632.
[7] BROWN P, PRATT AG, HYRICH KL. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. Bmj. 2024;384:e070856.
[8] LIU X, PING G, JI D, et al. Reclassify High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Patients Into Different Molecular Subtypes With Discrepancy Prognoses and Therapeutic Responses Based on Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Enriched Prognostic Genes. Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2024;15:11795972241274024.
[9] DU G, CHEN J, ZHU X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis identifies TGF-β signaling pathway-associated molecular subtypes and gene signature in diabetic foot. iScience. 2024; 27(3):109094.
[10] ZHAO J, HE K, DU H, et al. Bioinformatics prediction and experimental verification of key biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease based on transcriptome sequencing in mice. Peer J. 2022;10:e13932.
[11] KANG J, CHOI YJ, KIM IK, et al. LASSO-Based Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in T1 Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2021;53(3):773-783.
[12] LV JH, HOU AJ, ZHANG SH, et al. WGCNA combined with machine learning to find potential biomarkers of liver cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(50):e36536.
[13] SANZ H, VALIM C, VEGAS E, et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(1):432.
[14] HAMIDI F, GILANI N, ARABI BELAGHI R, et al. Identifying potential circulating miRNA biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of ovarian cancer using machine-learning approach: application of Boruta. Front Digit Health. 2023;5:1187578.
[15] LIU K, CHEN S, LU R. Identification of important genes related to ferroptosis and hypoxia in acute myocardial infarction based on WGCNA. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):7950-7963.
[16] CHEN T, HUA W, XU B, et al. Robust rank aggregation and cibersort algorithm applied to the identification of key genes in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Math Biosci Eng. 2021;18(4):4491-4507.
[17] WANG Q, GAO QC, WANG QC, et al. A compendium of mitochondrial molecular characteristics provides novel perspectives on the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):561.
[18] RADU AF, BUNGAU SG. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells. 2021;10(11):2857.
[19] CONFORTI A, DI COLA I, PAVLYCH V, et al. Beyond the joints, the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(2):102735.
[20] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880.
[21] GUO D, ZHANG B, WU D, et al. Identification of PRTN3 as a novel biomarker for the diagnosis of early gastric cance. J Proteomics. 2023;277:104852.
[22] ZHOU Y, LIN Z, XIE S, et al. Interplay of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and colorectal cancer development: unravelling the mediating role of fatty acids through a comprehensive multi-omics analysis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):587.
[23] ZHOU Z, ZHOU X, JIANG X, et al. Single-cell profiling identifies IL1B(hi) macrophages associated with inflammation in PD-1 inhibitor-induced inflammatory arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2107.
[24] LARAGIONE T, BRENNER M, SHERRY B, et al. CXCL10 and its receptor CXCR3 regulate synovial fibroblast invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(11):3274-3283.
[25] PAN Z, ZHU T, LIU Y, et al. Role of the CXCL13/CXCR5 Axis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;13:850998.
[26] BUGATTI S, MANZO A, VITOLO B, et al. High expression levels of the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13 in rheumatoid synovium are a marker of severe disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(10):1886-1895.
[27] STARZER AM, BERGHOFF AS. New emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy: CD27 (TNFRSF7). ESMO Open. 2020;4(Suppl 3): e000629.
[28] MERINO-VICO A, FRAZZEI G, VAN HAMBURG JP, et al. Targeting B cells and plasma cells in autoimmune diseases: From established treatments to novel therapeutic approaches. Eur J Immunol. 2023;53(1):e2149675.
[29] DI BENEDETTO P, RUSCITTI P, VADASZ Z, et al. Macrophages with regulatory functions, a possible new therapeutic perspective in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(10):102369.
[30] GENSOUS N, CHARRIER M, DULUC D, et al. T Follicular Helper Cells in Autoimmune Disorders. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1637.
[31] LI Y, BAI S, ZHANG J, et al. [T follicular helper cells and their related molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: A review]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;35(3):281-286. |