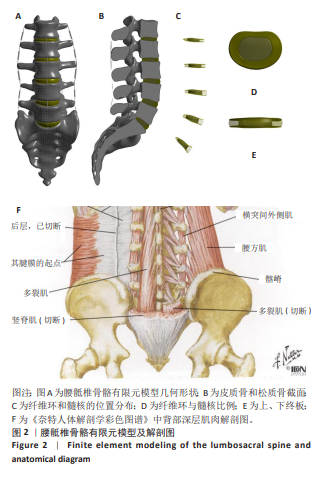
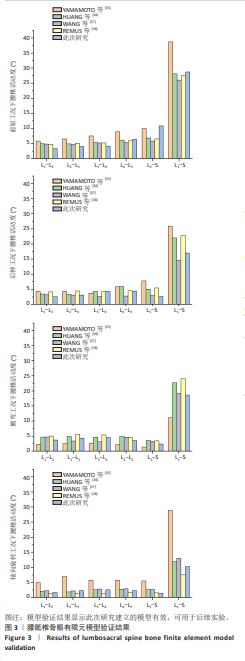
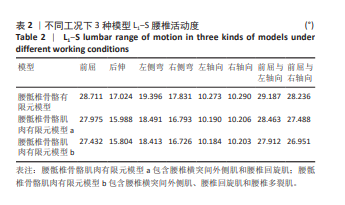
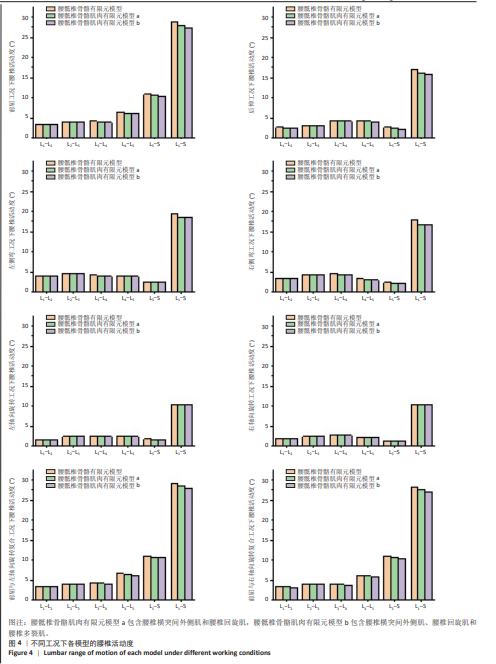
[1] YANG Y, LAI X, LI C, et al. Focus on the impact of social factors and lifestyle on the disease burden of low back pain: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):679.
[2] FERREIRA ML, DE LUCA K, HAILE LM, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(6):e316-e329.
[3] SHOKRI P, ZAHMATYAR M, FALAH TAFTI M, et al. Non-spinal low back pain: Global epidemiology, trends, and risk factors. Health Sci Rep. 2023; 6(9):e1533.
[4] GULAMOVNA DB, GUZAL AN, GULRUH A. Skeletal anatomy. Eur J Med Natural Sci. 2024;4(1-1):48-52.
[5] SIVASANKARI S, BALASUBRAMANIAN V. Influence of occupant collision state parameters on the lumbar spinal injury during frontal crash. J Adv Res. 2020;28:17-26.
[6] 曹修祥,任闻闻,巩庆雷,等.磁共振成像在胸椎和腰椎骨折中的诊断价值分析[J].影像研究与医学应用,2024,8(2):172-174.
[7] 冯良恩.经皮椎间孔镜行腰椎管减压的技术演进[J].中外医学研究, 2023,21(6):163-166.
[8] FENG N, TAN S, CHEN S, et al. A cross-sectional association study of paravertebral muscle quality and modic changes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s00586-025-09027-0.
[9] SCHÖNNAGEL L, ZHU J, CAMINO-WILLHUBER G, et al. Relationship between lumbar spinal stenosis and axial muscle wasting. Spine J. 2024;24(2): 231-238.
[10] XU S, WANG R, MA S, et al. Interventional effect of core stability training on pain and muscle function of youth with chronic non-specific lower back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32818.
[11] CHEN M, YANG C, CAI Z, et al. Lumbar posterior group muscle degeneration: influencing factors of adjacent vertebral body re-fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Front Med. 2023;9:1078403.
[12] 冯思仪,李艳娇,钟锐,等.四维牵引治疗老年退行性腰椎管狭窄症的疗效、腰肌形态学及力学性能评估[J].实用医学杂志,2025,41(10): 1525-1532.
[13] SATO K, KIKUCHI S, YONEZAWA T. In vivo intradiscal pressure measurement in healthy individuals and in patients with ongoing back problems. Spine. 1999; 24(23): 2468.
[14] POLGA DJ, BEAUBIEN BP, KALLEMEIER PM, et al. Measurement of in vivo intradiscal pressure in healthy thoracic intervertebral discs. Spine. 2004; 29(12):1320-1324.
[15] 邵翌鑫,关天民,朱晔,等.不同模量植入假体与周围骨间的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29):4612-4619.
[16] WANG X, LIU W, ZHAO Y, et al. The impact of disc degeneration on the dynamic characteristics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1384187.
[17] LI S, DU J, ZHU L, et al. Case series study and finite element analysis of a new cervicothoracic fixation device. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1): 889.
[18] WAN S, XUE B, XIONG Y. Three‐Dimensional Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Middle Aged and Elderly. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:7107702.
[19] VERMA S, CHANDA A. State-of-the-art of finite element modelling of the human spine to study the impact of vibrations: a review. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech. 2024;25(4):225-247.
[20] LONG Z, ZHOU J, XIONG L, et al. Finite element study on three osteotomy methods for treating thoracolumbar osteoporotic fracture vertebral collapse complicated with neurological dysfunction. Medicine. 2024;103(7):e36987.
[21] 张治豪,居来提·买提肉孜,张连鹏,等.新型变径全皮质骨螺纹螺钉设计以及在腰椎改良皮质骨轨迹的应用[J].医用生物力学,2024, 39(1):91-97.
[22] LI J, DU Z, CAO S, et al. Quantitative relationships between elastic modulus of rod and biomechanical properties of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025;12: 1510597.
[23] 李健,关天民,朱晔.有限元法分析骶椎腰化的力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33):5249-5253.
[24] 任东,朱晔,雷蕾,等.矫形力加载肋骨施力区对胸椎段位移及旋转角度影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2812-2816.
[25] JU C, YANG K, YANG Q, et al. Multiscale dynamics analysis of lumbar vertebral cortical bone based on the Abaqus submodel finite element method. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):6861.
[26] LI R, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The effect of suboccipital muscle dysfunction on the biomechanics of the upper cervical spine: a study based on finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1) 400.
[27] ÇELIK M, KARAOĞLU A, ÇEKINMEZ M, et al. Investigation Of The Role Of Multifidus Muscles In The Development Of Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation. Eur Health Sci J. 2025;3(1):8-16.
[28] 张连鹏,居来提·买提肉孜,张治豪,等.有限元分析改良皮质骨轨迹置钉在腰椎翻修术中的力学性能[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(3):413-420.
[29] KHUYAGBAATAR B, KIM K, KIM YH. Recent developments in finite element analysis of the lumbar spine. Int J Prec Eng Manufact. 2024;25(2):487-496.
[30] KANG I, CHOI M, LEE D, et al. Effect of passive support of the spinal muscles on the biomechanics of a lumbar finite element model. Appl Sci. 2020;10(18):6278.
[31] ZHANG XY, HAN Y. Comparison of the biomechanical effects of lumbar disc degeneration on normal patients and osteoporotic patients: A finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2023;112:103952.
[32] PASOTO SG, AUGUSTO KL, ALVARENGA JC, et al. Cortical bone density and thickness alterations by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography: association with vertebral fractures in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology. 2016;55(12):2200-2211.
[33] LIU X, MA J, PARK P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of multilevel lateral interbody fusion with and without supplementary instrumentation: a three-dimensional finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):63.
[34] ZHAO X, DU L, XIE Y, et al. Effect of lumbar lordosis on the adjacent segment in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e114-e120.
[35] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11): 1256-1260.
[36] HUANG YP, DU CF, CHENG CK, et al. Preserving posterior complex can prevent adjacent segment disease following posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgeries: a finite element analysis. PloS One. 2016;11(11): e0166452.
[37] WANG Y, MAIMAITI A, XIAO Y, et al. Hybrid cortical bone trajectory and modified cortical bone trajectory techniques in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion at L4-L5 segment: A finite element analysis. Heliyon. 2024;10(5):e26294.
[38] REMUS R, LIPPHAUS A, NEUMANN M, et al. Calibration and validation of a novel hybrid model of the lumbosacral spine in ArtiSynth–The passive structures. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0250456.
[39] LI Z, ZHANG Y, LIN Y, et al. The role of paraspinal muscle degeneration in cervical spondylosis. Eur Spine J. 2025;34(3):1187-1197.
[40] DING J, KONG C, LI X, et al. Different degeneration patterns of paraspinal muscles in degenerative lumbar diseases: a MRI analysis of 154 patients. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(3):764-773.
[41] CHOU SH, LIN SY, SHEN PC, et al. Pain control affects the radiographic diagnosis of segmental instability in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Clin Med. 2021;10(17):3984.
[42] 邹峰.慢性非特异性腰痛柔道运动员核心部位特征研究[D].南京:南京体育学院,2021.
[43] JIANG J, HUANG Y, HE B. Advances in the interaction between lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration and fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles: critical summarization, classification, and perspectives. Front Endocrinol. 2024;15:1353087.
[44] DANNEELS LA, VANDERSTRAETEN GG, CAMBIER DC, et al. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(4):266-272.
[45] KALICHMAN L, CARMELI E, BEEN E. The association between imaging parameters of the paraspinal muscles, spinal degeneration, and low back pain. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017(1):2562957.
[46] BARKER KL, SHAMLEY DR, JACKSON D. Changes in the cross-sectional area of multifidus and psoas in patients with unilateral back pain: the relationship to pain and disability. Spine. 2004;29(22):E515-E519.
[47] KIM S, KIM H, CHUNG J. Effects of spinal stabilization exercise on the cross-sectional areas of the lumbar multifidus and psoas major muscles, pain intensity, and lumbar muscle strength of patients with degenerative disc disease. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014;26(4):579-582.
[48] KANG S, PARK CH, JUNG H, et al. Analysis of the physiological load on lumbar vertebrae in patients with osteoporosis: a finite-element study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11001.
[49] PRADEEP K, PAL B. Finite element analysis of an intact lumbar spine model: Effects of loading under different coordinate systems. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2023;237(7):815-828.
[50] WARREN JM, HEY LA, MAZZOLENI AP. A finite element study of the relationship between upper body weight and the loads experienced by the human lumbosacral spine, and fusion instrumentation, in a standing upright posture. Biomed Eng Adv. 2021;2:100023.
[51] GUVEN AE, SCHÖNNAGEL L, CHIAPPARELLI E, et al. Relationship Between Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis and Multifidus Muscle Atrophy: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Spine. 2025;50(10):702-706.
[52] DE SIMONE M, CHOUCHA A, CIAGLIA E, et al. Discogenic low back pain: Anatomic and pathophysiologic characterization, clinical evaluation, biomarkers, AI, and treatment options. J Clin Med. 2024;13(19):5915.
[53] 罗金伟,徐国康,屠玉兰,等.TLIF与OLIF联合后路内固定治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效比较[J].浙江临床医学,2024,26(1):93-95.
[54] FENG C, HU Z, ZHAO M, et al. Region-specific mitophagy in nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus, and cartilage endplate of intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol. 2025;16:1579507.
[55] SCARCIA L, PILEGGI M, CAMILLI A, et al. Degenerative disc disease of the spine: from anatomy to pathophysiology and radiological appearance, with morphological and functional considerations. J Personalized Med. 2022;12(11):1810.
[56] DIWAN AD, MELROSE J. Intervertebral disc degeneration and how it leads to low back pain. JOR Spine. 2023;6(1):e1231.
[57] CHENG Z, LI Y, LI M, et al. Correlation between posterior paraspinal muscle atrophy and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in patients with chronic low back pain. Int Orthop. 2023;47(3):793-801.
[58] OEFNER C, RIEMER E, FUNKE K, et al. Determination of anisotropic elastic parameters from morphological parameters of cancellous bone for osteoporotic lumbar spine. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022;60(1):263-278.
[59] LI J, GONG H. Fatigue behavior of cortical bone: a review. Acta Mechanica Sinica. 2021;37(3):516-526.
[60] KARACAN I, TÜRKER KS. Exploring neuronal mechanisms of osteosarcopenia in older adults. J Physiol. 2024. doi: 10.1113/JP285666.
|