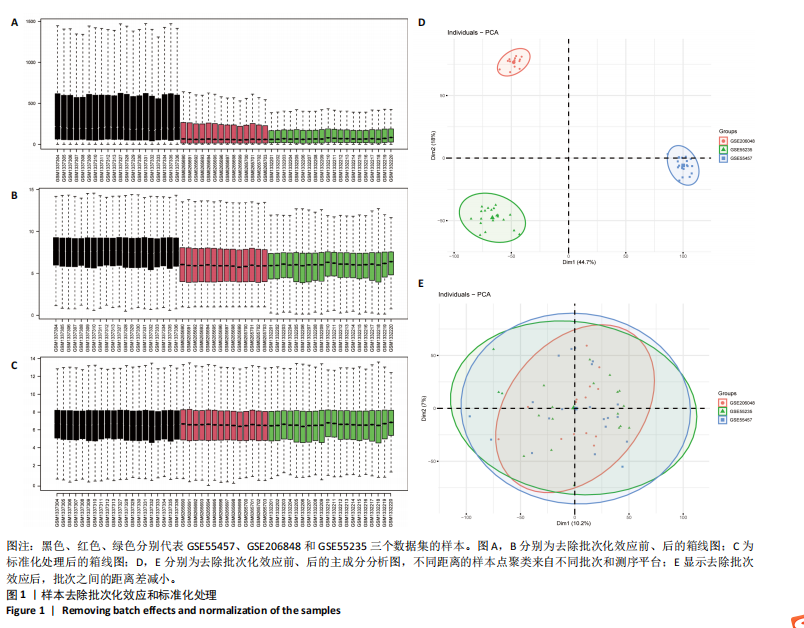
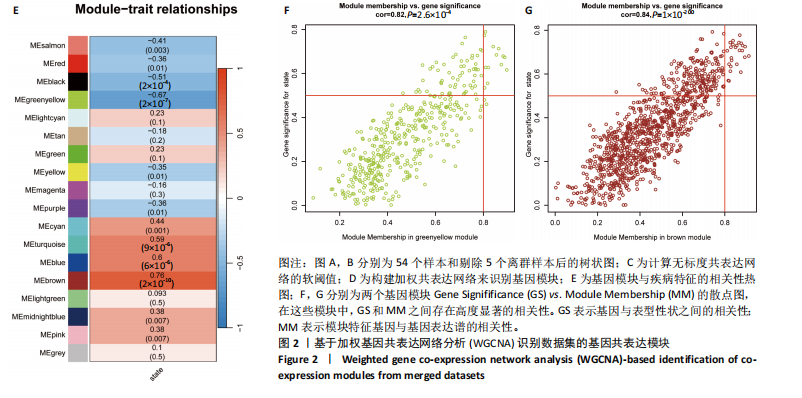
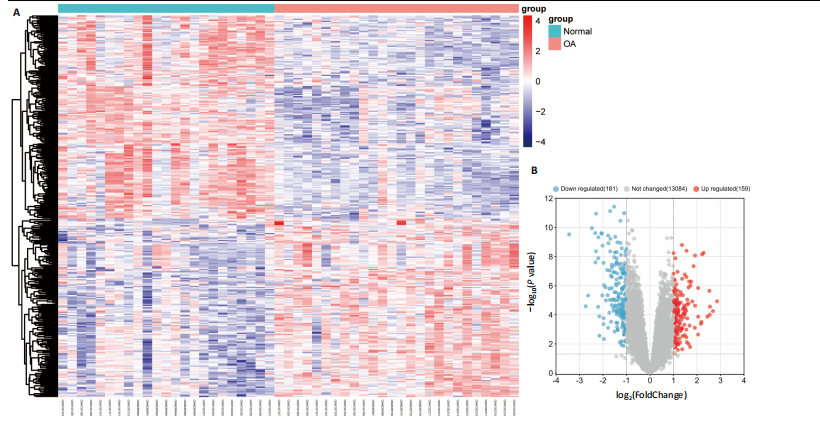
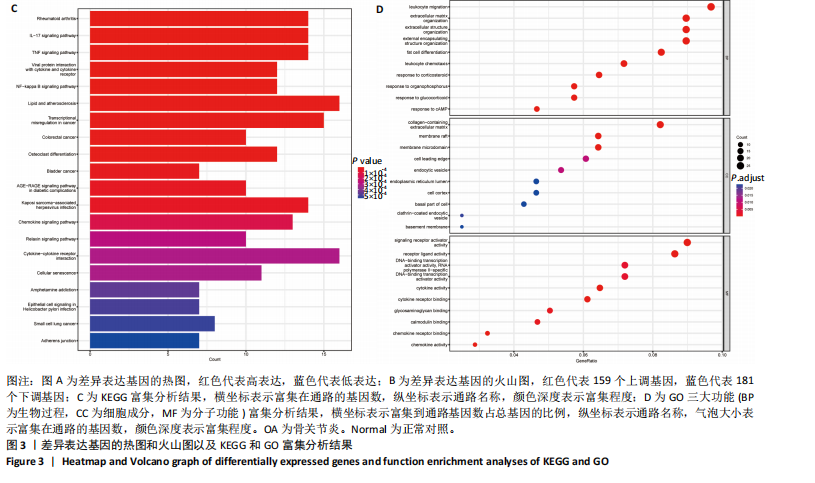
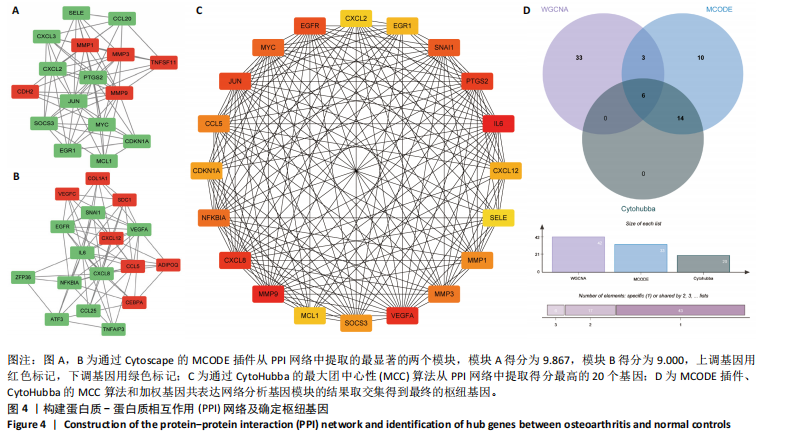
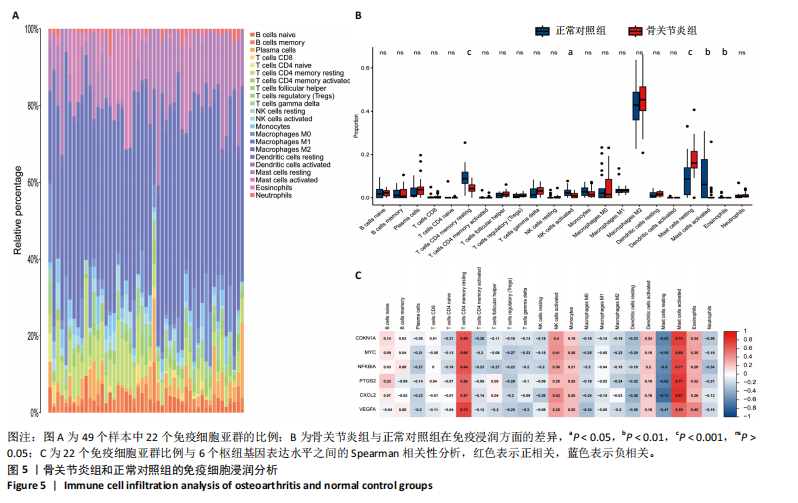
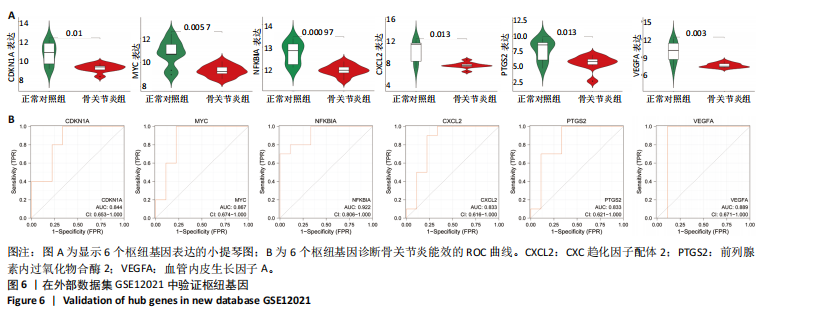
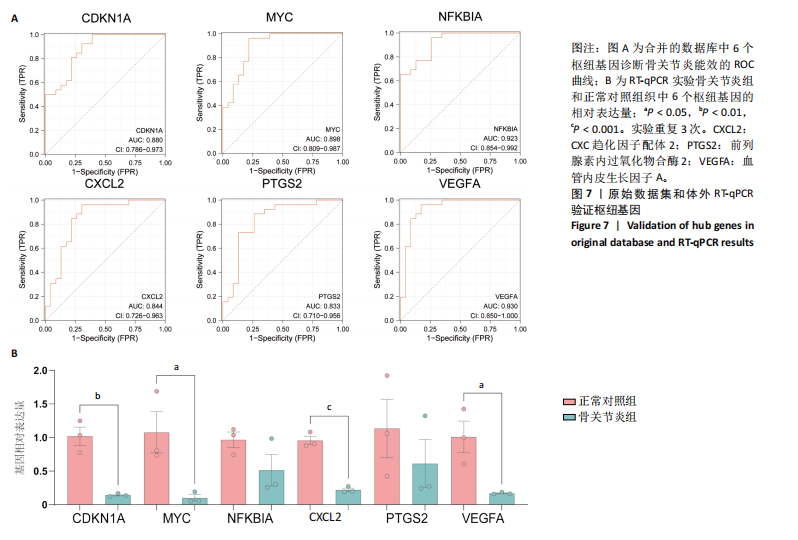
[1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[2] BARNETT R. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2018;391(10134):1985.
[3] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[4] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院), 等. 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314.
[5] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options.Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[6] CHO Y, JEONG S, KIM H, et al. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: current status and future directions. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1689-1696.
[7] YUE L, BERMAN J. What Is Osteoarthritis? JAMA. 2022;327(13):1300.
[8] JANSEN MP, MASTBERGEN SC. Joint distraction for osteoarthritis: clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):35-46.
[9] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208.
[10] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10):580-592.
[11] ZHANG R, YANG X, WANG J, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome‑wide gene expression profiling analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(1):30-40.
[12] LOUGHLIN J. Translating osteoarthritis genetics research: challenging times ahead. Trends Mol Med. 2022;28(3):176-182.
[13] WANG T, DAI L, SHEN S, et al. Comprehensive Molecular Analyses of a Macrophage-Related Gene Signature With Regard to Prognosis, Immune Features, and Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on WGCNA and the LASSO Algorithm.Front Immunol. 2022;13:843408.
[14] POSTLER AE, LÜTZNER C, GORONZY J, et al. When are patients with osteoarthritis referred for surgery?. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2023;37(2):101835.
[15] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969.
[16] WARMINK K, VINOD P, KORTHAGEN NM, et al. Macrophage-Driven Inflammation in Metabolic Osteoarthritis: Implications for Biomarker and Therapy Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6112.
[17] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090.
[18] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44.
[19] SCHAIBLE HG.Nociceptive neurons detect cytokines in arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):470.
[20] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6(11):625-635.
[21] ZHENG W, ZHOU T, ZHANG Y, et al. Simplified α2-macroglobulin as a TNF-α inhibitor for inflammation alleviation in osteoarthritis and myocardial infarction therapy. Biomaterials. 2023;301:122247.
[22] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al.Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[23] LIAO CR, WANG SN, ZHU SY, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products increase TNF-α and IL-1β expression in chondrocytes via NADPH oxidase 4 and accelerate cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis progression. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101306.
[24] LI Z, HUANG Z, BAI L. Cell Interplay in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:720477.
[25] RUAL JF, VENKATESAN K, HAO T, et al.Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature. 2005; 437(7062):1173-1178.
[26] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):56.
[27] YANG W, LI J, ZHANG M, et al. Elevated expression of the rhythm gene NFIL3 promotes the progression of TNBC by activating NF-κB signaling through suppression of NFKBIA transcription. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):67.
[28] KIHARA S, HAYASHI S, HASHIMOTO S, et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor-1-Deficient Mice are Susceptible to Osteoarthritis Associated with Enhanced Inflammation. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(5):991-1001.
[29] RODRIGUEZ-FONTENLA C, CALAZA M, EVANGELOU E, et al. Assessment of osteoarthritis candidate genes in a meta-analysis of nine genome-wide association studies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):940-949.
[30] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924.
[31] YOO SA, BAE DG, RYOO JW, et al. Arginine-rich anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) hexapeptide inhibits collagen-induced arthritis and VEGF-stimulated productions of TNF-alpha and IL-6 by human monocytes. J Immunol. 2005;174(9):5846-5855.
[32] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):909-920.
[33] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105.
[34] CHEN Z, WANG W, HUA Y. Identification and validation of BCL6 and VEGFA as biomarkers and ageing patterns correlating with immune infiltrates in OA progression. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2558.
[35] LI HY, PAN L, KE YS, et al.Daidzein suppresses pro-inflammatory chemokine Cxcl2 transcription in TNF-α-stimulated murine lung epithelial cells via depressing PARP-1 activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014; 35(4):496-503.
[36] CAI W, LI H, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2020;8:e8390.
[37] DUFFY MJ, O’GRADY S, TANG M, et al. MYC as a target for cancer treatment.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;94:102154.
[38] LIU J, HUANG X, LIU D, et al. Demethyleneberberine induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence of NSCLC cells via c-Myc/HIF-1α pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153678.
[39] LI X, ZHANG Z, GAO F, et al. c-Myc-Targeting PROTAC Based on a TNA-DNA Bivalent Binder for Combination Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145(16):9334-9342.
[40] EZAWA K, YAMAMURA M, MATSUI H, et al. Comparative analysis of CD45RA- and CD45RO-positive CD4+T cells in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Acta Med Okayama. 1997;51(1):25-31.
[41] QI C, SHAN Y, WANG J, et al. Circulating T helper 9 cells and increased serum interleukin-9 levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(5):528-534.
[42] BENIGNI G, DIMITROVA P, ANTONANGELI F, et al. CXCR3/CXCL10 Axis Regulates Neutrophil-NK Cell Cross-Talk Determining the Severity of Experimental Osteoarthritis. J Immunol. 2017;198(5):2115-2124.
[43] CHOU CH, JAIN V, GIBSON J, et al. Synovial cell cross-talk with cartilage plays a major role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):10868.
[44] KULKARNI P, HARSULKAR A, MÄRTSON AG, et al. Mast Cells Differentiated in Synovial Fluid and Resident in Osteophytes Exalt the Inflammatory Pathology of Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):541.
[45] ZHAO X, YOUNIS S, SHI H, et al. RNA-seq characterization of histamine-releasing mast cells as potential therapeutic target of osteoarthritis.Clin Immunol. 2022;244:109117. |