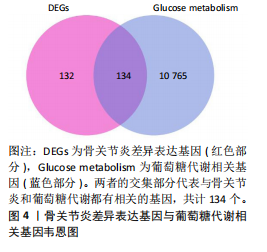
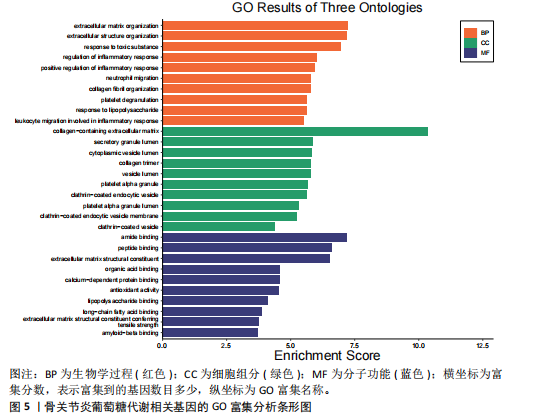
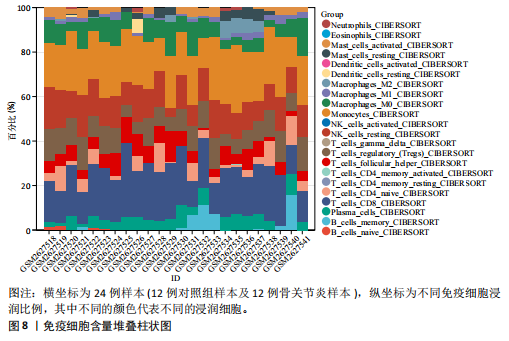
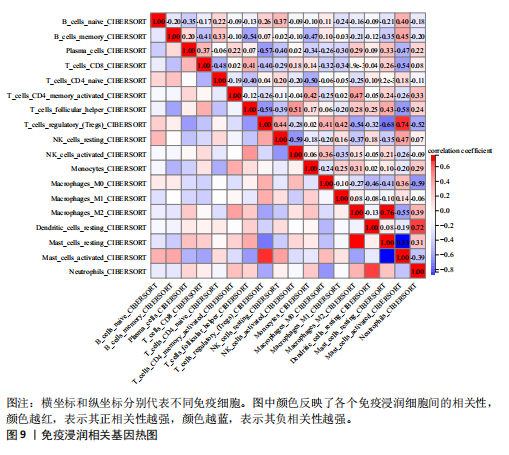
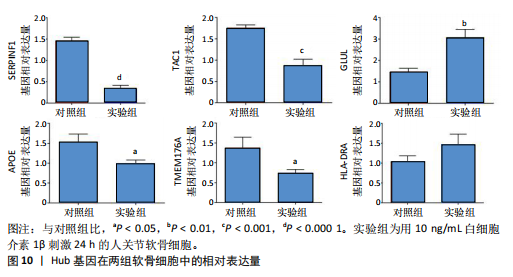
[1] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent Updates of Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619.
[2] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195.
[3] DUONG V, OO W M, DING C, et al. Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Pain: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(16):1568-1580.
[4] 钱燕,刘启颂.调整细胞培养条件提高间充质干细胞外泌体治疗骨关节炎的潜能[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(1):164-174.
[5] YU M, XU Y, WENG X, et al. Clinical outcome and survival rate of condylar constrained knee prosthesis in revision total knee arthroplasty: an average nine point six year follow-up. Int Orthop. 2024;48(5):1179-1187.
[6] HOLLANDER JM, ZENG L. The Emerging Role of Glucose Metabolism in Cartilage Development. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(2):59-69.
[7] ZLACKÁ J, ZEMAN M. Glycolysis under Circadian Control. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(24):13666.
[8] OHASHI Y, TAKAHASHI N, TERABE K, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in chondrocytes to promote mitochondrial respiration reduces downstream features of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15131.
[9] KONG P, CHEN R, ZOU FQ, et al. HIF-1α repairs degenerative chondrocyte glycolytic metabolism by the transcriptional regulation of Runx2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1206-1214.
[10] ARRUDA AL, HARTLEY A, KATSOULA G, et al. Genetic underpinning of the comorbidity between type 2 diabetes and osteoarthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 2023;110(8):1304-1318.
[11] PEMMARI A, LEPPÄNEN T, HÄMÄLÄINEN M, et al. Widespread regulation of gene expression by glucocorticoids in chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis as determined by RNA-Seq. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):271.
[12] UESAKA K, OKA H, KATO R, et al. Bioinformatics in bioscience and bioengineering: Recent advances, applications, and perspectives. J Biosci Bioeng. 2022;134(5):363-373.
[13] BARRETT T, WILHITE SE, LEDOUX P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D991-995.
[14] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):422-432.
[15] 周亮,陈兴真,李振宇,等. lncRNA HOTAIR在白细胞介素1β介导骨关节炎中的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(35):5607-5613.
[16] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):3-6.
[17] LONG H, LIU Q, YIN H, et al. Prevalence Trends of Site-Specific Osteoarthritis From 1990 to 2019: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(7):1172-1183.
[18] LI K, JI X, SEELEY R, et al. Impaired glucose metabolism underlies articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Faseb J. 2022;36(6):e22377.
[19] MEINI S, CUCCHI P, CATALANI C, et al. Bradykinin and B₂ receptor antagonism in rat and human articular chondrocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162(3):611-622.
[20] ARELLANO H, NARDELLO-RATAJ V, SZUNERITS S, et al. Saturated long chain fatty acids as possible natural alternative antibacterial agents: Opportunities and challenges. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;318:102952.
[21] RIEGGER J, SCHOPPA A, RUTHS L, et al. Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):76.
[22] HUANG Z, KRAUS VB. Does lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation have a role in OA?. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(2):123-129.
[23] AN X, WANG T, ZHANG W, et al. Chondroprotective Effects of Combination Therapy of Acupotomy and Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis Rabbits via the GSK3β-Cyclin D1-CDK4/CDK6 Signaling Pathway. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1116-1132.
[24] BHOGE SS, SAMAL S. Physiotherapeutic Approach for Septic Arthritis of Knee Joint. Cureus. 2023;15(9):e45550.
[25] 冯方,刘英,彭毅,等.膝骨关节炎患者关节滑液中IL-17水平与疾病严重程度的相关性[J].西部医学,2020,32(6):845-848.
[26] IIJIMA H, GILMER G, WANG K, et al. Meta-analysis Integrated With Multi-omics Data Analysis to Elucidate Pathogenic Mechanisms of Age-Related Knee Osteoarthritis in Mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022;77(7):1321-1334.
[27] 徐以明,薛松,桑伟林,等.巨噬细胞极化在骨关节炎中的作用[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(9):689-694.
[28] BARBOZA E, HUDSON J, CHANG WP, et al. Profibrotic Infrapatellar Fat Pad Remodeling Without M1 Macrophage Polarization Precedes Knee Osteoarthritis in Mice With Diet-Induced Obesity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(6):1221-1232.
[29] HAUBRUCK P, PINTO MM, MORADI B, et al. Monocytes, Macrophages, and Their Potential Niches in Synovial Joints - Therapeutic Targets in Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis? Front Immunol. 2021;12: 763702.
[30] ROMERA-CáRDENAS G, THOMAS LM, LOPEZ-COBO S, et al. Ionomycin Treatment Renders NK Cells Hyporesponsive. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150998.
[31] SOHN HS, CHOI JW, JHUN J, et al. Tolerogenic nanoparticles induce type II collagen-specific regulatory T cells and ameliorate osteoarthritis. Sci Adv. 2022; 8(47):eabo5284.
[32] HSIEH JL, SHIAU AL, LEE CH, et al. CD8+ T cell-induced expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinses-1 exacerbated osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(10):19951-19970.
[33] BECKER J, SEMLER O, GILISSEN C, et al. Exome sequencing identifies truncating mutations in human SERPINF1 in autosomal-recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;88(3):362-371.
[34] MALEK N, MLOST J, KOSTRZEWA M, et al. Description of Novel Molecular Factors in Lumbar DRGs and Spinal Cord Factors Underlying Development of Neuropathic Pain Component in the Animal Model of Osteoarthritis. Mol Neurobiol. 2024; 61(3):1580-1592.
[35] JONES AG, AQUILINO M, TINKER RJ, et al. Clustered de novo start-loss variants in GLUL result in a developmental and epileptic encephalopathy via stabilization of glutamine synthetase. Am J Hum Genet. 2024;111(4):729-741.
[36] YANG LG, MARCH ZM, STEPHENSON RA, et al. Apolipoprotein E in lipid metabolism and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34(8):430-445.
[37] RAULIN C, DOSS SV, TROTTIER ZA, et al. ApoE in Alzheimer’s disease: pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Mol Neurodegener. 2022;17(1):72. |