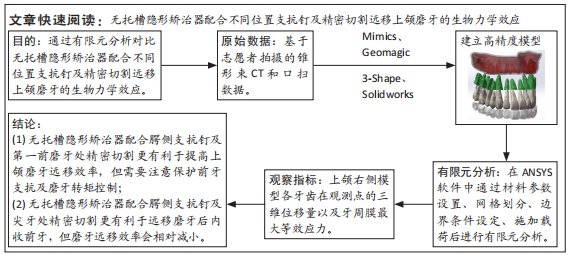
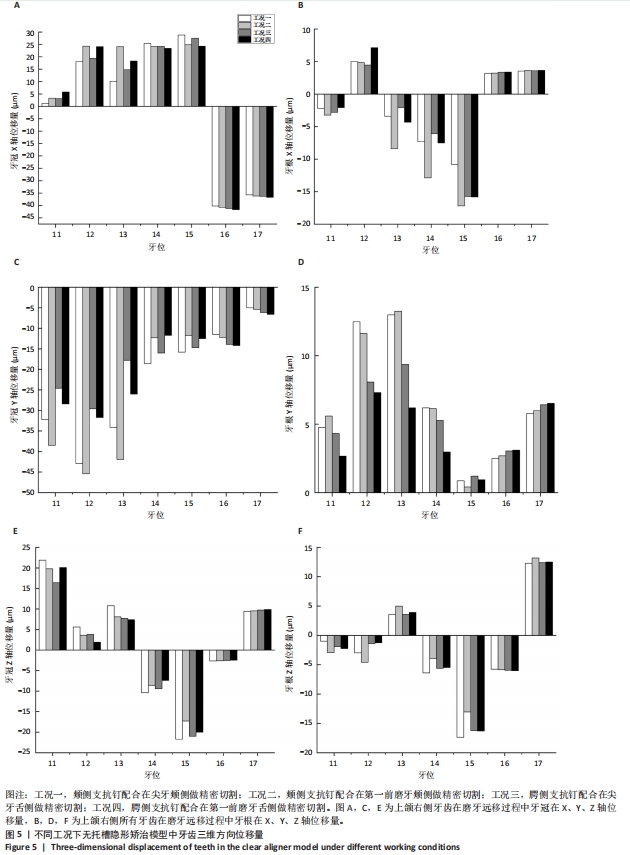
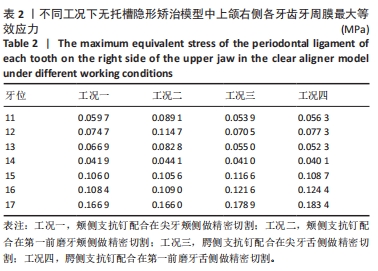
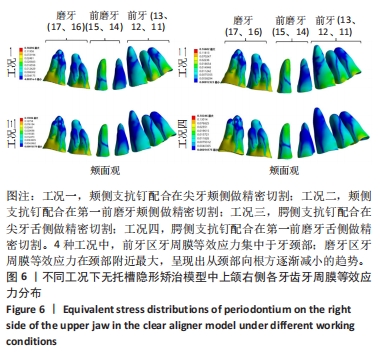
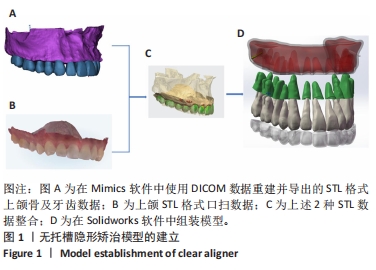
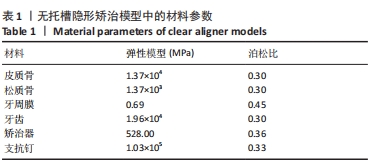
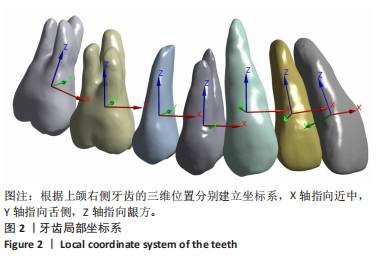
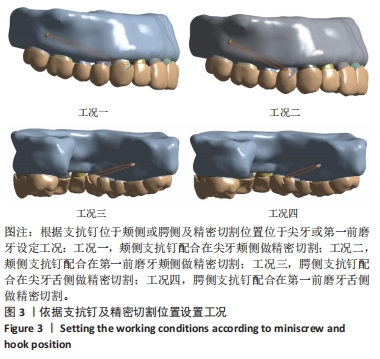
[1] CHENG L, FENG Z, HAO Z, et al. Molar distalization in orthodontics: a bibliometric analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(2):123.
[2] WEIR T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust Dent J. 2017;62 Suppl 1:58-62.
[3] RAVERA S, CASTROFLORIO T, GARINO F, et al. Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: a multicenter retrospective study. Prog Orthod. 2016;17:12.
[4] 经典,王瑞清,房兵.口腔正畸生物力学的研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2023,38(5):864-873.
[5] 任玉仲秀,张继武,马俐丽,等.无托槽隐形矫治技术推上颌第二磨牙向远中的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2018, 25(2):108-112.
[6] BOWMAN S J, CELENZA F, SPARAGA J, et al. Creative adjuncts for clear aligners, part 1: class II treatment. J Clin Orthod. 2015; 49(2):83-94.
[7] 刘洪,牟雁东,于晓光,等.口腔正畸治疗中微型种植体支抗的稳定和安全性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(8):1159-1164.
[8] 任亚男,宋保龙,封颖丽,等.无托槽隐形矫治器结合微种植体支抗远移上颌磨牙效率的三维重叠研究 [J].中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2018,25(2):92-97.
[9] 马静,赵红芳,叶茜,等.微螺钉种植体支抗辅助全牙列整体远移的研究进展[J].兰州大学学报(医学版),2021,47(6):96-101.
[10] PARK HS, BAE SM, KYUNG HM, et al. Simultaneous incisor retraction and distal molar movement with microimplant anchorage. World J Orthod. 2004;5(2):164-171.
[11] AL AMRI MS, SABBAN HM, ALSAGGAF DH, et al. Anatomical consideration for optimal position of orthodontic miniscrews in the maxilla: a CBCT appraisal. Ann Saudi Med. 2020;40(4):330-337.
[12] KOOK YA, BAYOME M, TRANG VT, et al. Treatment effects of a modified palatal anchorage plate for distalization evaluated with cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;146(1):47-54.
[13] XIN Y, WU Y, CHEN C, et al. Miniscrews for orthodontic anchorage: analysis of risk factors correlated with the progressive susceptibility to failure. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022; 162(4):e192-e202.
[14] PARK J, CHO HJ. Three-dimensional evaluation of interradicular spaces and cortical bone thickness for the placement and initial stability of microimplants in adults. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(3):314.e1-315.
[15] JIA L, WANG C, LI L, et al. The effects of lingual buttons, precision cuts, and patient-specific attachments during maxillary molar distalization with clear aligners: Comparison of finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;163(1):e1-e12.
[16] OH S, CHOI YK, KIM SH, et al. Biomechanical analysis for different mandibular total distalization methods with clear aligners: A finite element study. Korean J Orthod. 2023;53(6):420-430.
[17] LIU X, CHENG Y, QIN W, et al. Effects of upper-molar distalization using clear aligners in combination with Class II elastics: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):546.
[18] 王诗语,黄钖钖,刘浩,等.不同牙弓形态和第二前磨牙缺失对上颌磨牙远移中支抗的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28): 4541-4546.
[19] 杨建浩,韩璐,李亚茹,等.颧下嵴区微植体不同高度支抗远移上牙列位移的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(10): 1523-1528.
[20] LIU H, WU X, YANG L, et al. Safe zones for miniscrews in maxillary dentition distalization assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2017;151(3):500-506.
[21] LEO M, CERRONI L, PASQUANTONIO G, et al. Temporary anchorage devices(TADs)in orthodontics:review of the factors that influence the clinical success rate of the mini- implants. Clin Ter. 2016;167(3): e70-e77.
[22] 林泉宏,赵桂芝,柯杰.微种植体支抗整体远中移动下牙列的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2015,23(6):355-357.
[23] RAVERA S, CASTROFLORIO T, GARINO F, et al. Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: a multicenter retrospective study. Prog Orthod. 2016;17:12.
[24] MOHAMED RN, BASHA S, AL-THOMALI Y. Maxillary molar distalization with miniscrew-supported appliances in Class II malocclusion: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2018;88(4):494-502.
[25] GUO R, LAM XY, ZHANG L, et al. Biomechanical analysis of miniscrew-assisted molar distalization with clear aligners: a three-dimensional finite element study. Eur J Orthod. 2024;46(1):cjad077.
[26] JI L, LI B, WU X. Evaluation of biomechanics using different traction devices in distalization of maxillary molar with clear aligners: a finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023;26(5): 559-567.
[27] ZHOU X, GAN Y, XIONG J, et al. A Method for Tooth Model Reconstruction Based on Integration of Multimodal Images. J Healthc Eng. 2018;2018:4950131.
[28] 王勇.口内数字印模技术[J].口腔医学,2015,35(9):705-709,743.
[29] 朱玉佳,蒋博,孙玉春,等.口腔三维冠根整合模型构建方法的研究进展[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2020,55(4):280-280.
[30] 陈妍曲,唐敏,黄旋平,等.高精度三维整合牙颌模型个体化微种植体手术导板的计算机辅助设计与制作[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(10):1529-1533.
[31] TAKAHASHI N, KITAGAMI T, KOMORI T. Behaviour of teeth under various loading conditions with finite element method. J Oral Rehabil. 1980;7(6):453-461.
[32] ELSHAZLY TM, BOURAUEL C, ALDESOKI M, et al. Computer-aided finite element model for biomechanical analysis of orthodontic aligners. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(1):115-124.
[33] DERMAUT LR, KLEUTGHEN JP, DE CLERCK HJ. Experimental determination of the center of resistance of the upper first molar in a macerated, dry human skull submitted to horizontal headgear traction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1986;90(1):29-36.
[34] KE Y, ZHU Y, ZHU M. A comparison of treatment effectiveness between clear aligner and fixed appliance therapies. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):24.
[35] LI L, GUO R, ZHANG L, et al. Maxillary molar distalization with a 2-week clear aligner protocol in patients with Class II malocclusion: A retrospective study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;164(1): 123-130.
[36] MIN HJ,KIM TW.Biomechanical considerations in treatment with miniscrew anchorage.Part 1: the sagittal plane. J Clin Orthod. 2008; 42(6):329-337.
[37] LEE SK, ABBAS NH, BAYOME M, et al. A comparison of treatment effects of total arch distalization using modified C-palatal plate vs buccal miniscrews. Angle Orthod. 2018;88(1):45-51.
[38] MCCORMACK SW, WITZEL U, WATSON PJ, et al.The biomechanical function of periodontal ligament fibres in orthodontic tooth movement. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102387.
[39] VIECILLI RF, BURSTONE CJ. Ideal orthodontic alignment load relationships based on periodontal ligament stress. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2015;18 Suppl 1:180-186.
[40] MAO B, TIAN Y, XIAO Y ,et al. The effect of maxillary molar distalization with clear aligner: a 4D finite-element study with staging simulation. Prog Orthod. 2023;24(1):16.
|