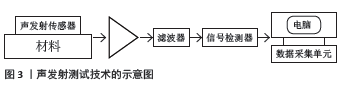
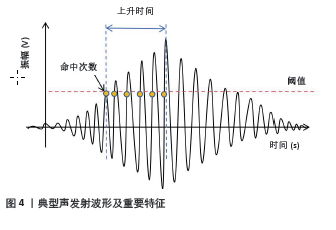
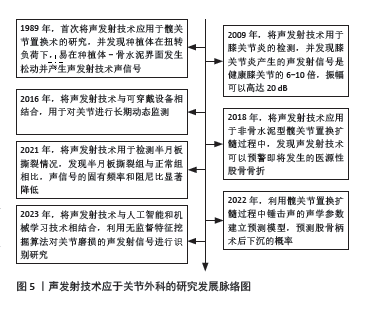
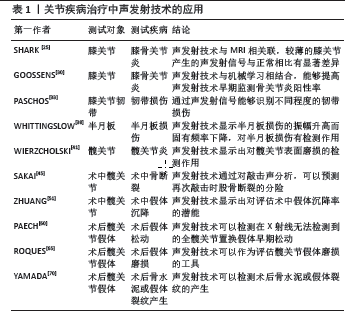
[1] 韩明睿,刘倩倩,孙洋.骨关节炎发病机制及药物调控新进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):807-812.
[2] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent Updates of Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5): 2619.
[3] LATOURTE A, KLOPPENBURG M, RICHETTE P. Emerging pharmaceutical therapies for osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(12): 673-688.
[4] VASIREDDI N, NEITZKE CC, CHANDI SK, et al. Early Periprosthetic Femur Fractures After Primary Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty: High Risk of Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Subsequent Reoperation. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39(4):1083-1087.e1.
[5] HASAN S, VAN SCHIE P, KAPTEIN BL, et al. Biomarkers to discriminate between aseptic loosened and stable total hip or knee arthroplasties: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2024;9(1):25-39.
[6] LUCENTI L, TESTA G, CALDACI A, et al. Preoperative Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Healthcare (Basel). 2024;12(6):666.
[7] 李红豫,曾祥兴,张璐.基于声子晶体的声发射波源检测概率研究[J].振动与冲击,2024,43(7):75-83.
[8] HASSANI S, DACKERMANN U. A Systematic Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Non-Destructive Testing and Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors (Basel). 2023;23(4):2204.
[9] HUTT S, CLARKE A, PULLIN R, et al. The acoustic emission from asperity interactions in mixed lubrication. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2019;475(2227):20180900.
[10] BI H, HAO M, REN B, et al. Mechanical seal friction condition monitoring based on bispectral characteristics. Industr Lubr Tribol. 2023; 75(10):1246-1252.
[11] SUGIYAMA H, WHITESIDE LA, KAISER AD. Examination of rotational fixation of the femoral component in total hip arthroplasty. A mechanical study of micromovement and acoustic emission. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(249):122-128.
[12] KHOKHLOVA L, KOMARIS DS, TEDESCO S, et al. Assessment of Hip and Knee Joints and Implants Using Acoustic Emission Monitoring: A Scoping Review. IEEE Sens J. 2021;21(13):14379-14388.
[13] KALO K, NIEDERER D, SCHMITT M, et al. Acute effects of a single bout of exercise therapy on knee acoustic emissions in patients with osteoarthritis: a double-blinded, randomized controlled crossover trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):657.
[14] TSANGOURI E, AGGELIS DG. A review of acoustic emission as indicator of reinforcement effectiveness in concrete and cementitious composites. Constr Build Mater. 2019;224:198-205.
[15] MASCARO B, PRIOR J, SHARK LK, et al. Exploratory study of a non-invasive method based on acoustic emission for assessing the dynamic integrity of knee joints. Med Eng Phys. 2009;31(8): 1013-1022.
[16] TEAGUE CN, HERSEK S, TOREYIN H, et al. Novel methods for sensing acoustical emissions from the knee for wearable joint health assessment. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2016;63(8):1581-1590.
[17] PECHON PHM, PULLIN R, EATON MJ, et al. Acoustic emission technology can warn of impending iatrogenic femur fracture during femoral canal preparation for uncemented hip replacement. A cadaveric animal bone study. J Med Eng Technol. 2018;42(2):72-87.
[18] NSUGBE E, OLORUNLAMBE K, DEARN K. On the Early and Affordable Diagnosis of Joint Pathologies Using Acoustic Emissions, Deep Learning Decompositions and Prediction Machines. Sensors (Basel). 2023;23(9):4449.
[19] 赵之栋,李众利.骨关节炎早期诊治的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2023,17(5):689-693.
[20] 莫建强, 陈康武, 仲冬艳, 等. 超声检查在早期膝关节骨关节炎诊断中的应用[J]. 山东医药,2019,59(15):64-66.
[21] 胡小丽,陈霞,黄霓,等. X线、高频超声、MRI检查对早期类风湿关节炎膝关节炎的诊断效能[J].山东医药,2018,58(39):52-54.
[22] GHAREHBAGHI S, JEONG HK, SAFAEI M, et al. A Feasibility Study on Tribological Origins of Knee Acoustic Emissions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2022;69(5):1685-1695.
[23] KALO K, NIEDERER D, SCHMITT M, et al. Acute effects of a single bout of exercise therapy on knee acoustic emissions in patients with osteoarthritis: a double-blinded, randomized controlled crossover trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):657.
[24] ASAMENE K, SUNDARESAN M. Analysis of experimentally generated friction related acoustic emission signals. Wear. 2012;296(1-2):607-618.
[25] SHARK LK, QUAN W, BOWES MA, et al. Discovering Associations between Acoustic Emission and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Biomarkers from 10 Osteoarthritic Knees. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2022;69(11):3494-3503.
[26] KHOKHLOVA L, KOMARIS DS, DAVARINOS N, et al. Non-Invasive Assessment of Cartilage Damage of the Human Knee Using Acoustic Emission Monitoring: A Pilot Cadaver Study. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023;70(9):2741-2751.
[27] SHARK LK, CHEN H, GOODACRE J. Discovering differences in acoustic emission between healthy and osteoarthritic knees using a four-phase model of sit-stand-sit movements. Open Med Inform J. 2010;4: 116-125.
[28] KHOKHLOVA L, KOMARIS DS, O’FLYNN B, et al. Acoustic emissions and age-related changes of the knee. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023;2023:1-4.
[29] 张洪波,庞月强,李小亭,等.膝关节骨性关节炎的声发射动态检测[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2021,40(7):2851-2855.
[30] GOOSSENS Q, LOCSIN M, GHAREHBAGHI S, et al. Knee acoustic emissions as a noninvasive biomarker of articular health in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a clinical validation in an extended study population. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2023;21(1):59.
[31] 王豪,陈国键,梁海波,等.膝关节前交叉韧带合并内侧副韧带损伤的诊疗新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(20):3220-3228.
[32] 汤林峰, 杨光. CT与MRI诊断膝关节韧带损伤的影像学表现与价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2024,8(1):136-138.
[33] PASCHOS NK, AGGELIS DG, BARKOULA NM, et al. An Acoustic Emission Study for Monitoring Anterior Cruciate Ligament Failure Under Tension. Exp Mech. 2013;53(5):767-774.
[34] AGGELIS DG, PASCHOS NK, BARKOULA NM, et al. Rupture of anterior cruciate ligament monitored by acoustic emission. J Acoust Soc Am. 2011;129(6):EL217-EL222.
[35] 王成伟,刘利兵,贾卫东,等.磁共振成像评价膝关节半月板损伤:与关节镜检查的对照分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(46): 7406-7411.
[36] 李晶,叶清岚,蔡磊,等.膝关节韧带、关节软骨及半月板损伤的多层螺旋CT与MRI诊断分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2023,39(8): 1314-1317.
[37] 郭吉敏,刘春霖,曹满瑞,等.MRI与关节镜诊断半月板损伤价值的对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2010,29(11):1512-1515.
[38] WHITTINGSLOW DC, JEONG HK, GANTI VG, et al. Acoustic Emissions as a Non-invasive Biomarker of the Structural Health of the Knee. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020;48(1):225-235.
[39] OZMEN GC, SAFAEI M, SEMIZ B, et al. Detection of Meniscal Tear Effects on Tibial Vibration Using Passive Knee Sound Measurements. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021;68(7):2241-2250.
[40] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[41] WIERZCHOLSKI K. Acoustic emission diagnosis for human joint cartilage diseases. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2015;17(4):139-148.
[42] LA CAMERA F, LOPPINI M, DELLA ROCCA A, et al. Total Hip Arthroplasty With a Monoblock Conical Stem in Dysplastic Hips: A 20-Year Follow-Up Study. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3242-3248.
[43] FERGUSON RJ, PALMER AJ, TAYLOR A, et al. Hip replacement. Lancet. 2018;392(10158):1662-1671.
[44] ROWLANDS A, DUCK FA, CUNNINGHAM JL. Bone vibration measurement using ultrasound: application to detection of hip prosthesis loosening. Med Eng Phys. 2008;30(3):278-284.
[45] SAKAI R, KIKUCHI A, MORITA T, et al. Hammering sound frequency analysis and prevention of intraoperative periprosthetic fractures during total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2011;21(6):718-723.
[46] FONSECA ULLOA CA, SCHREYNEMACKERS S, HARZ T, et al. Acoustical determination of primary stability of femoral short stem during uncemented hip implantation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2023;109: 106079.
[47] PECHON PHM, PULLIN R, EATON MJ, et al. Acoustic emission technology can warn of impending iatrogenic femur fracture during femoral canal preparation for uncemented hip replacement. A cadaveric animal bone study. J Med Eng Technol. 2018;42(2):72-87.
[48] LEISS F, GÖTZ JS, MEYER M, et al. Differences in femoral component subsidence rate after THA using an uncemented collarless femoral stem: full weight-bearing with an enhanced recovery rehabilitation versus partial weight-bearing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(4): 673-680.
[49] MUKHERJEE K, GHORAI TK, KUMAR A. High grade femoral stem subsidence in uncemented hip hemiarthroplasty - A radiographic analysis and an early prediction while treating femoral neck fractures. Int Orthop. 2023;47(6):1591-1599.
[50] AL-NAJJIM M, KHATTAK U, SIM J, et al. Differences in subsidence rate between alternative designs of a commonly used uncemented femoral stem. J Orthop. 2016;13(4):322-326.
[51] ZHUANG X, HOMMA Y, ISHII S, et al. Acoustic characteristics of broaching procedure for post-operative stem subsidence in cementless total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2022;46(4): 741-748.
[52] MOROHASHI I, IWASE H, KANDA A, et al. Acoustic pattern evaluation during cementless hip arthroplasty surgery may be a new method for predicting complications. SICOT J. 2017;3:13.
[53] 李志鹏,环大维,袁兆丰,等.老年股骨颈骨折全髋或半髋关节置换的中远期状态:倾向性评分匹配法评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(24):3839-3844.
[54] 陆建红,诸葛恒艳,徐娟,等.老年全髋关节置换术患者体力活动水平因素分析[J].现代预防医学,2023,50(16):3062-3066.
[55] PANEGROSSI G, CERETTI M, PAPALIA M, et al. Bone loss management in total knee revision surgery. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(2):419-427.
[56] 李儒军,陶可,寇伯龙,等.人工髋关节置换术后翻修的原因分析及处理[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(19):1729-1734.
[57] 曾懿,张德洲,易雪冰.多层螺旋CT鉴别全髋关节置换术后迟发性无菌及感染性并发症[J].放射学实践,2021,36(2):232-237.
[58] 王坤正.锥部磨损与全髋关节置换术后无菌性松动的关系[J].医学研究生学报,2018,31(4):344-349.
[59] 李占银,阿尖措,苏桂芳. SPECT/CT结合三相骨显像诊断假体周围感染的价值分析[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2019,17(12):139-142.
[60] PAECH A, CABRERA-PALACIOS H , SCHULZ AP, et al. Acoustic Tests on Hip Prosthesis Models Using Frequency Resonance Monitoring (FRM). Res J Med Sci. 2012;2(2):82-91.
[61] BROWNE M, JEFFERS JR, SAFFARI N. Nondestructive evaluation of bone cement and bone cement/metal interface failure. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;92(2):420-429.
[62] KEATY B, SUN Y, DIDEM O, et al. Early Detection of Fretting Corrosion in Hip Replacement by Acoustic Emission Non-Invasive Technique. Thin Solid Films. 2024;788:140165.
[63] 李文博,宋科官.磨损颗粒诱导髋关节置换后假体周围骨溶解的相关生物学机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(3):464-470.
[64] YUICHI O, KENGO K, YUKIO M. Effect of delamination of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on loosening behaviors of acetabular cups subjected to cyclic loading. Eng Fail Analys. 2021: 105548.
[65] ROQUES A, BROWNE M, THOMPSON J, et al. Investigation of fatigue crack growth in acrylic bone cement using the acoustic emission technique. Biomaterials. 2004;25(5):769-778.
[66] LEE C, ZHANG L, MORRIS D, et al. Non-invasive early detection of failure modes in total hip replacements (THR) via acoustic emission (AE). J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;118:104484.
[67] BACCAR D, SOEFFKER D. Wear detection by means of wavelet-based acoustic emission analysis(Article). Mech Syst Signal Process. 2015;60:198-207.
[68] 张岚峰,葛世荣,刘洪涛,等.初次承重引发骨水泥-柄界面脱粘损伤的分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(8):1081-1088.
[69] SHEARWOOD-PORTER N, BROWNE M, SINCLAIR I. Micromechanical characterisation of failure in acrylic bone cement: the effect of barium sulphate agglomerates. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012; 13:85-92.
[70] YAMADA Y, WAKAYAMA S, IKEDA J, et al. Long-Term Reliability Assessment of Ceramic Femoral Head Based on Microfracture Analysis Using Acoustic Emission Technique. IFMBE Proc. 2010;31(1):608-611.
[71] FRANKE RP, DOERNER P, SCHWALBE HJ, et al. Acoustic emission measurement system for the orthopedic diagnostics of the human femur and knee joint. J Acoust. 2004;22:236-242.
[72] KHAN-EDMUNDSON A, RODGERS GW, WOODFIELD TBF, et al. Tissue Attenuation Features of Acoustic Emission Signals for Wear and Degradation of Total Hip Arthoplasty Implants. IFAC Proc. 2012;45(18): 355-360.
[73] ZHUANG X, HOMMA Y, SATO T, et al. Factors Influence on the Broaching Hammering Sound during Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Biomed Sci Eng. 2022;15(9):229-240.
[74] FENG GH, CHEN WM. Piezoelectric-film-based acoustic emission sensor array with thermoactuator for monitoring knee joint conditions. Sensor Actuat A-Phys. 2016;246(3):180-191.
[75] FITZPATRICK AJ, RODGERS GW , HOOPER GJ, et al. Development and validation of an acoustic emission device to measure wear in total hip replacements in-vitro and in-vivo. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2017;33:281-288.
[76] MAVROGORDATO M, TAYLOR M, TAYLOR A, et al. Real time monitoring of progressive damage during loading of a simplified total hip stem construct using embedded acoustic emission sensors. Med Eng Phys. 2011;33(4):395-406.
[77] BURGO FJ, MENGELLE DE, OZOLS A, et al. The damping effect of cement as a potential mitigation factor of squeaking in ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(11): 531-537.
[78] RODGERS GW, WELSH R, KING LJ, et al. Signal processing and event detection of hip implant acoustic emissions. Control Eng Pract. 2017: 287-297.
[79] OZMEN GC, GAZI AH, GHAREHBAGHI S, et al. An Interpretable Experimental Data Augmentation Method to Improve Knee Health Classification Using Joint Acoustic Emissions. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021; 49(9):2399-2411.
[80] GHAREHBAGHI S, JEONG HK, SAFAEI M, et al. A Feasibility Study on Tribological Origins of Knee Acoustic Emissions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2022;69(5):1685-1695.
|