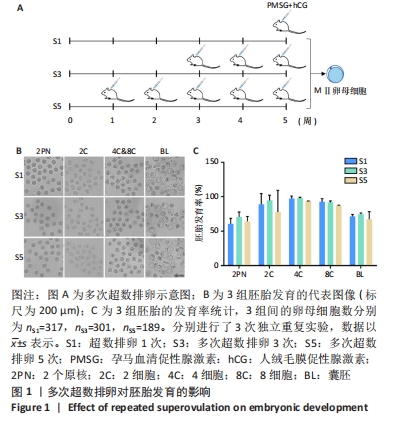
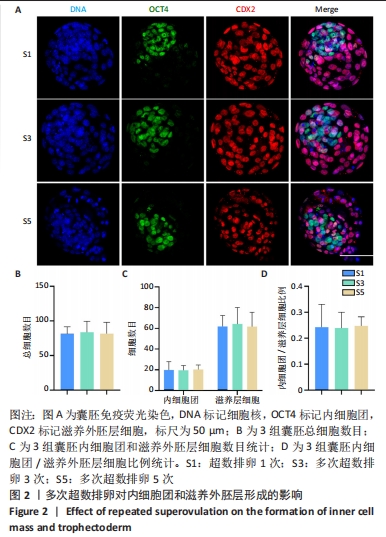
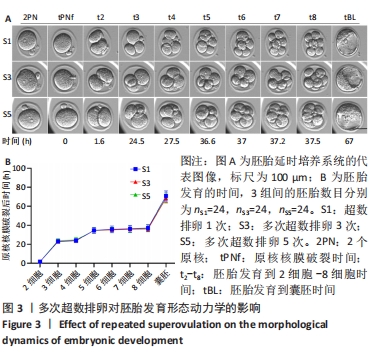
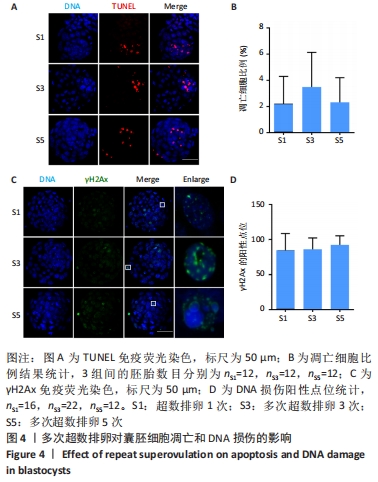
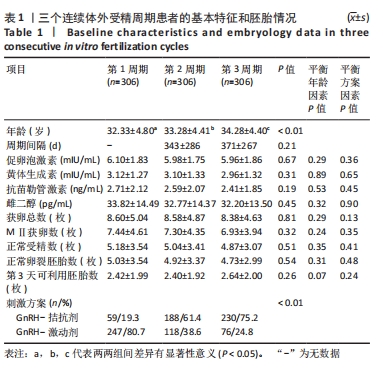
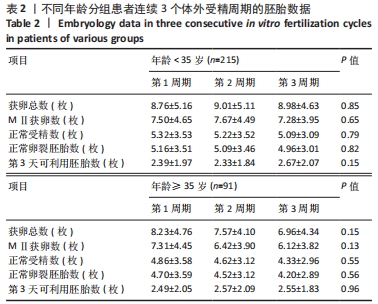
[1] LUO XF, WU HL, JI XR, et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes, Risks, and Costs for 20,910 Donor In Vitro Fertilization and 16,850 Donor Artificial Insemination Treatment Cycles: A Retrospective Analysis in China. J Clin Med. 2023;12(3):954.
[2] QIAO J, WANG Y, LI X, et al. A Lancet Commission on 70 years of women’s reproductive, maternal, newborn, child, and adolescent health in China. Lancet. 2021;397(10293):2497-2536.
[3] SUNDERAM S, KISSIN DM, CRAWFORD SB, et al. Assisted Reproductive Technology Surveillance - United States, 2015. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2018;67(3):1-28.
[4] DONG G, GUO Y, CAO H, et al. Long-term effects of repeated superovulation on ovarian structure and function in rhesus monkeys. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(5):1452-1457.e1.
[5] HOLT-KENTWELL A, GHOSH J, DEVALL A, et al. Evaluating interventions and adjuncts to optimize pregnancy outcomes in subfertile women: an overview review. Hum Reprod Update. 2022;28(4):583-600.
[6] ALLEN C, MCLERNON D, BHATTACHARYA S, et al. Early pregnancy outcomes of IVF cycles using donor versus partner sperm: analysis of 1 376 454 cycles recorded by the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (1991-2016). Hum Reprod. 2023. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead057. Online ahead of print.
[7] VUONG LN, NGUYEN LK, LE AH, et al. Fresh embryo transfer versus freeze-only after in vitro maturation with a pre-maturation step in women with high antral follicle count: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021;38(6):1293-1302.
[8] PARK SR, KIM SK, KIM SR, et al. Novel roles of luteinizing hormone (LH) in tissue regeneration-associated functions in endometrial stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):605.
[9] WANG Q, ZHAO SX, HE JN, et al. Repeated Superovulation Accelerates Primordial Follicle Activation and Atresia. Cells. 2022;12(1):92.
[10] PARK SJ, KIM TS, KIM JM, et al. Repeated Superovulation via PMSG/hCG Administration Induces 2-Cys Peroxiredoxins Expression and Overoxidation in the Reproductive Tracts of Female Mice. Mol Cells. 2015;38(12):1071-1078.
[11] ZHANG J, LAI Z, SHI L, et al. Repeated superovulation increases the risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases by accelerating ovarian aging in mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(5):1089-1102.
[12] LIU B, WANG JL, WANG XM, et al. Reparative effects of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on mouse ovarian injuries induced by repeated superovulation. Theriogenology. 2020;145:115-125.
[13] CHAO HT, LEE SY, LEE HM, et al. Repeated ovarian stimulations induce oxidative damage and mitochondrial DNA mutations in mouse ovaries. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1042:148-156.
[14] XIE JK, WANG Q, ZHANG TT, et al. Repeated superovulation may affect mitochondrial functions of cumulus cells in mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31368.
[15] TANG SB, YANG LL, ZHANG TT, et al. Multiple superovulations alter histone modifications in mouse early embryos. Reproduction. 2019; 157(6):511-523.
[16] XIAO P, NIE J, WANG X, et al. Melatonin alleviates the deterioration of oocytes from mice subjected to repeated superovulation. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):13413-13422.
[17] JAIN A, ROBINS JC, WILLIAMS DB, et al. The effect of multiple cycles in oocyte donors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(5):1382-1384.
[18] LUK J, ARICI A. Does the ovarian reserve decrease from repeated ovulation stimulations? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;22(3):177-182.
[19] PAUL LT, ATILAN O, TULAY P. The effect of repeated controlled ovarian stimulation cycles on the gamete and embryo development. Zygote. 2019;27(5):347-349.
[20] KHODADADI A, NIASARI-NASLAJI A, NIKJOU D, et al. Superovulation of high-producing Holstein lactating dairy cows with human recombinant FSH and hMG. Theriogenology. 2022;191:239-244.
[21] GONZALEZ-RAMIRO H, CUELLO C, CAMBRA JM, et al. A Short-Term Altrenogest Treatment Post-weaning Followed by Superovulation Reduces Pregnancy Rates and Embryo Production Efficiency in Multiparous Sows. Front Vet Sci. 2021;8:771573.
[22] BRUNO-GALARRAGA MM, FERNANDEZ J, LACAU-MENGIDO IM, et al. A simple method to select high superovulatory responder goats. Theriogenology. 2023;195:187-191.
[23] XIA X, ZHANG Y, CAO M, et al. Adverse effect of assisted reproductive technology-related hyperoestrogensim on the secretion and absorption of uterine fluid in superovulating mice during the peri-implantation period. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:859204.
[24] ALJAHDALI A, AIRINA RKRI, VELAZQUEZ MA, et al. The duration of embryo culture after mouse IVF differentially affects cardiovascular and metabolic health in male offspring. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(11):2497-2514.
[25] KIRKEGAARD K, INGERSLEV HJ. Clinical outcomes following selection of human preimplantation embryos with time-lapse monitoring: a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(5):802.
[26] TRUONG TT, SOH YM, GARDNER DK. Antioxidants improve mouse preimplantation embryo development and viability. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(7):1445-1454.
[27] WARSHAVIAK M, KALMA Y, CARMON A, et al. The Effect of Advanced Maternal Age on Embryo Morphokinetics. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:686.
[28] WANG Y, YUAN P, YAN Z, et al. Single-cell multiomics sequencing reveals the functional regulatory landscape of early embryos. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1247.
[29] CHI F, SHARPLEY MS, NAGARAJ R, et al. Glycolysis-Independent Glucose Metabolism Distinguishes TE from ICM Fate during Mammalian Embryogenesis. Dev Cell. 2020;53(1):9-26.e4.
[30] DIETRICH JE, HIIRAGI T. Stochastic patterning in the mouse pre-implantation embryo. Development. 2007;134(23):4219-4231.
[31] STRUMPF D, MAO CA, YAMANAKA Y, et al. Cdx2 is required for correct cell fate specification and differentiation of trophectoderm in the mouse blastocyst. Development. 2005;132(9):2093-2102.
[32] FOGARTY NME, MCCARTHY A, SNIJDERS KE, et al. Genome editing reveals a role for OCT4 in human embryogenesis. Nature. 2017; 550(7674):67-73.
[33] SIMMET K, ZAKHARTCHENKO V, PHILIPPOU-MASSIER J, et al. OCT4/POU5F1 is required for NANOG expression in bovine blastocysts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(11):2770-2775.
[34] PONTIS J, PULVER C, PLAYFOOT CJ, et al. Primate-specific transposable elements shape transcriptional networks during human development. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7178.
[35] NIE X, DAI Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Establishment of a Mouse Model of Premature Ovarian Failure Using Consecutive Superovulation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2341-2358.
[36] ZHAO Y, CHEN Y, MIAO C, et al. He’s Yangchao Recipe Ameliorates Ovarian Oxidative Stress of Aging Mice under Consecutive Superovulation Involving JNK- And P53-Related Mechanism. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:7705194.
[37] YANG G, CHEN J, HE Y, et al. Neddylation Inhibition Causes Impaired Mouse Embryo Quality and Blastocyst Hatching Failure Through Elevated Oxidative Stress and Reduced IL-1β. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 925702.
[38] MARTIN JH, AITKEN RJ, BROMFIELD EG, et al. DNA damage and repair in the female germline: contributions to ART. Hum Reprod Update. 2019;25(2):180-201.
[39] WILSON Y, MORRIS ID, KIMBER SJ, et al. The role of Trp53 in the mouse embryonic response to DNA damage. Mol Hum Reprod. 2019; 25(7):397-407.
[40] LAI XL, XIONG WJ, LI LS, et al. Zinc deficiency compromises the maturational competence of porcine oocyte by inducing mitophagy and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;252:114593.
[41] TSUI KH, LI CJ. Mitoquinone shifts energy metabolism to reduce ROS-induced oxeiptosis in female granulosa cells and mouse oocytes. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(1):246-260.
[42] HE YC, SU KZ, CAI J, et al. Serum anti-Müllerian hormone levels are associated with perinatal outcomes in women undergoing IVF/ICSI: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1081069.
[43] FRIIS WANG N, BOGSTAD JW, PORS SE, et al. Eight weeks of androgen priming by daily low-dose hCG injections before ICSI treatment in women with low ovarian reserve. Hum Reprod. 2023;38(4):716-725.
[44] GUI J, NI Y, LIU Q, et al. Comparison of clinical effects between early follicular prolonged GnRH agonist protocol and GnRH antagonist protocol in 3310 cycles: a retrospective study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022;22(1):942.
[45] TARÍN JJ, PASCUAL E, PÉREZ-HOYOS S, et al. Cumulative probabilities of live birth across multiple complete IVF/ICSI cycles: a call for attention. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020;37(1):141-148.
|