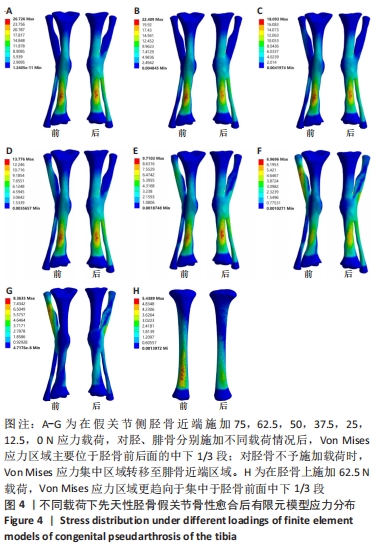
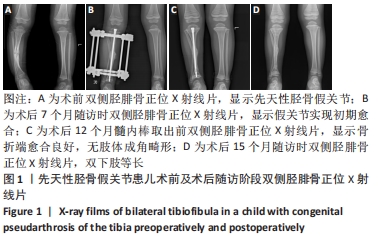
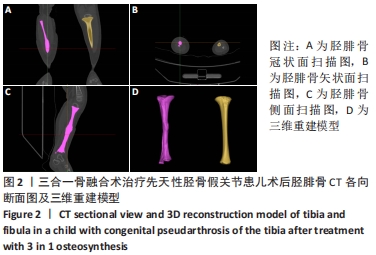
[1] HEFTI F, BOLLINI G, DUNGL P, et al. Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia: History, Etiology, Classification, and Epidemiologic Data. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2000;9(1):11-15.
[2] CANAVESE F, SHAH H, ROUSSET M. Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia: Management and complications. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(6): 616-626.
[3] KHAN T, JOSEPH B. Controversies in the management of congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia and fibula. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(8):1027-1034.
[4] 刘尧喜,梅海波.先天性胫骨假关节治疗进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2014(5):302-305.
[5] PANNIER S. Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(7):750-761.
[6] CHOI IH, CHO T, MOON HJ. Ilizarov Treatment of Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia: A Multi-Targeted Approach Using the Ilizarov Technique. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(1):1-8.
[7] CHO T, CHOI IH, LEE SM, et al. Refracture after Ilizarov osteosynthesis in atrophic-type congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia. J Bone Joint surg Br. 2008;90(4):488-493.
[8] SHANNON CE, HUSER AJ, PALEY D. Cross-Union Surgery for Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia. Children (Basel). 2021;8(7):547-571.
[9] LIU Y, YANG G, LIU K, et al. Combined surgery with 3-in-1 osteosynthesis in congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia with intact fibula. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020;15(1):62-70.
[10] 伍江雁,梅海波,刘尧喜,等.三合一骨融合术在儿童先天性胫骨假关节联合手术中的应用[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2017,38(9):691-697.
[11] 刘尧喜,梅海波,刘昆,等.四合一骨融合术在儿童先天性胫骨假关节联合手术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(12):770-777.
[12] CHOI IH, LEE SJ, MOON HJ, et al. “4-in-1 Osteosynthesis” for Atrophic-type Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011; 31(6):697-704.
[13] ZHANG M, HAO Z, TINGSHENG T. Finite Element Analysis in Orthopedic Biomechanics Research. Digital Orthopedics, 2018:147-164.
[14] 倪鹏辉,张鹰,杨晶,等.临床骨科中应用的有限元分析法:新理论与新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(31):4693-4699.
[15] RICHARDS BS, WILKES D, DEMPSEY M, et al. A radiographic scoring system to assess healing in congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2015;24(2):118-122.
[16] 张国栋,廖维靖,陶圣祥,等.股骨颈有限元分析的赋材料属性方法探讨及有效性验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(52):10263-10268.
[17] 荀福兴,刘雄,张美超.材料属性分配梯度对椎体有限元模型力学性能的影响[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(4):432-435.
[18] TAYLOR WR, ROLAND E, PLOEG H, et al. Determination of orthotropic bone elastic constants using FEA and modal analysis. J Biomech. 2002; 35(6):767-773.
[19] HOBATHO MC, RHO JY, ASHMAN RB. Anatomical variation of human cancellous bone mechanical properties in vitro. Stud Health Technol Inform. 1997;40(40):157-173.
[20] 赵英红,平杰,吴仁愿,等.胫骨骨折有限元模型建立及生物力学分析[J].军事医学,2016,40(12):988-993.
[21] DONAHUE TLH, HULL ML, RASHID MM, et al. A finite element model of the human knee joint for the study of tibio-femoral contact. J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(3):273-280.
[22] LENGSFELD M, SCHMITT J, ALTER P, et al. Comparison of geometry-based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(7):515-522.
[23] LOVE SM, GANEY T, OGDEN JA. Postnatal Epiphyseal Development: The Distal Tibia and Fibula. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990;10(3):298-305.
[24] MAKIN M. tibio-fibular relationship in paralysed limbs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965;47-B(3):500-506.
[25] OKEN OF, YILDIRIM AO, ASILTURK M. Finite element analysis of the stability of AO/OTA 43-C1 type distal tibial fractures treated with distal tibia medial anatomic plate versus anterolateral anatomic plate. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(5):404-408.
[26] HERRERA A. Applications of finite element simulation in orthopedic and trauma surgery. World J Orthop. 2012;3(4):25-41.
[27] 黄若昆,谢鸣,勘武生,等.数字骨科学研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(12):1003-1005.
[28] SHYAM SUNDAR S, NANDLAL B, SAIKRISHNA D, et al. Finite Element Analysis: A Maxillofacial Surgeon’s Perspective. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11(2):206-211.
[29] CAI X, SANG D, YUCHI C, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519-103531.
[30] SUN J, YAN S, JIANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the valgus knee joint of an obese child. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(S2):309-321.
[31] 廖东华,韩海潮,匡震邦.离体胫骨的有限元分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,1998(1):55-59.
[32] PALEY D. Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia: biological and biomechanical considerations to achieve union and prevent refracture. J Child Orthop. 2019;13(2):120-133.
[33] FROST HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):3-15.
|