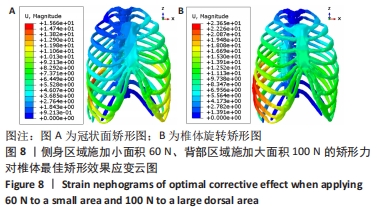
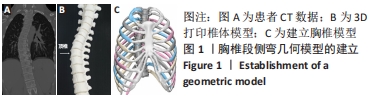
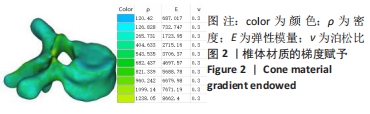
[1] 夏春,管金发,马岭,等.上海嘉定区某街道青少年脊柱侧凸患病率调查[J].上海医药,2019,40(8):53-55.
[2] FALK B, RIGBY WA, AKSEER N.Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: the possible harm of bracing and the likely benefit of exercise. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1169-1171.
[3] Hefti F. Pathogenesis and biomechanics of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). Journal J Child Orthop. 2013;7(1):17-24.
[4] CHOUDHRY MN, AHMAD Z, VERMA R. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis.Open Orthop J. 2016;10:143-154.
[5] VIVIANI GR,GHISTA DN,LOZADA PJ,et al. Biomechanical analysis and simulation of scoliosis surgical correction.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (208):40-47.
[6] 易红蕾. 新型脊柱侧凸三维矫形支具的有限元分析、顺应性监测及临床应用初探[D].上海:第二军医大学,2014.
[7] 聂文忠,房光开,闫勇增.个性化三维矫形支具的设计及其生物力学研究[J].机械设计与制造,2015(10):237-240.
[8] 许阳阳,李筱贺,李志军,等.Lenke 1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸与正常脊柱有限元模型建立与分析[J].解剖学杂志,2021,44(2):140-146.
[9] 白锦毅,李博,赵云飞,等.Lenke Ⅰ型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者生物力学在体反应特征曲线[J].第二军医大学学报,2020,41(11): 1203-1207.
[10] BARBA N, IGNASIAK D, VILLA TMT,et al.Assessment of trunk muscle activation and intervertebral load in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by musculoskeletal modelling approach. J Biomech. 2021;114:110154.
[11] 张爱平,刘羲,刘志峰,等.基于3D打印的定制脊柱侧弯矫形器设计制造与舒适度评价[J].北京工业大学学报,2017,43(4):518-525.
[12] RASMUSSEN J, TØRHOLM S, DE ZEE M. Computational analysis of the influence of seat pan inclination and friction on muscle activity and spinal joint forces. Int J Industrial Ergon. 2008;39(1):52-57.
[13] MORGAN EF, BAYRAKTAR HH, KEAVENY TM. Trabecular bone modulus–density relationships depend on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2003;36(7):897-904.
[14] 黄彦,周红海.纤维环、髓核的结构组成和生理功能[J].广西中医学院学报,1999,16(3):152-153+158.
[15] 杜瑞卿, 陈以国, 张鹏,等. 脊柱生物力学有限元分析法的概述[J].北京生物医学工程,2004,23(1):78-80.
[16] RHO JY, HOBATHO MC, ASHMAN RB.Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5): 347-355.
[17] KOPPERDAHL DL, MORGAN EF, KEAVENY TM. Quantitative computed tomography estimates of the mechanical properties of human vertebral trabecular bone. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(4):801-805.
[18] 贾少薇,张顺心,范顺成,等.脊柱侧凸腰骶椎结构的有限元分析及其变形趋势[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):235-241.
[19] GOEL VK, KONG W, HAN JS, et al. A Combined Finite Element and Optimization Investigation of Lumbar Spine Mechanics With and Without Muscles.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(11):1531-1541.
[20] ROHLMANN A, NABIL BOUSTANI H, BERGMANN G, et al. Effect of a pedicle-screw-based motion preservation system on lumbar spine biomechanics: A probabilistic finite element study with subsequent sensitivity analysis. J Biomech. 2010;43(15):2963-2969.
[21] SCHLAGER B,NIEMEYER F,GALBUSERA F,et al. Asymmetrical intrapleural pressure distribution: a cause for scoliosis? A computational analysis. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(7):1315-1329.
[22] COBETTO N, AUBIN CE, CLIN J, et al. Braces Optimized With Computer-Assisted Design and Simulations Are Lighter, More Comfortable, and More Efficient Than Plaster-Cast Braces for the Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2014;2(4):276-284.
[23] DESBIENS-BLAIS F, CLIN J, PARENT S, et al. New brace design combining CAD/CAM and biomechanical simulation for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012; 27(10):999-1005.
[24] KARAVIDAS N. Bracing In The Treatment Of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Evidence To Date.Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2019;10:153-172.
[25] 陈钵,秦大平,张晓刚,等.有限元分析法在脊柱生物力学中的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2020,26(3):208-211+216.
[26] DREISCHARF M, ZANDER T, SHIRAZI-ADL A,et al. Comparison of eight published static finite element models of the intact lumbar spine: Predictive power of models improves when combined together. J Biomech. 2014;47(8):1757-1766.
[27] CHEN YC, TU YK, ZHUANG JY,et al. Evaluation of the parameters affecting bone temperature during drilling using a three-dimensional dynamic elastoplastic finite element model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017;55(11):1949-1957.
[28] 肖进,张美超,赵卫东,等.腰椎小关节力学机制的有限元分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2008,28(10):1916-1918.
[29] 蔡志华,兰凤崇,陈吉清,等.基于汽车碰撞损伤的人体胸部有限元模型构建与验证[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(1):36-43.
|