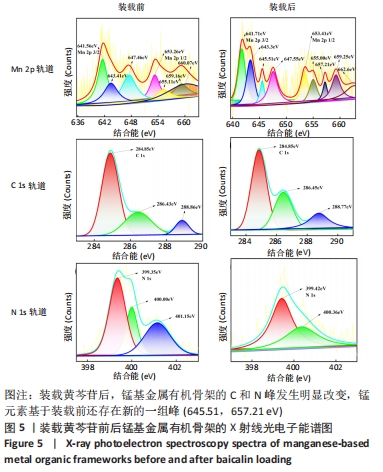
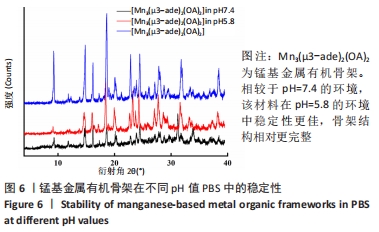
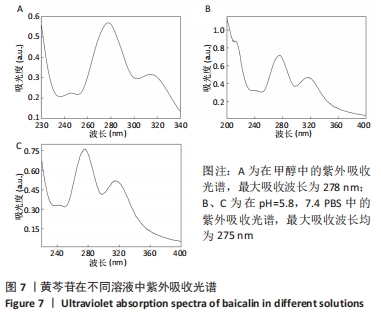
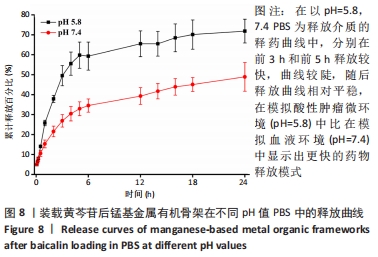
[1] SAFAEI M, FOROUGHI MM, EBRAHIMPOOR N, et al. A review on metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. Trends Analyt Chem. 2019;118:401-425.
[2] ZHOU HC, KITAGAWA S. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43(16):5415-5418.
[3] LI H, LI L, LIN RB, et al. Porous metal-organic frameworks for gas storage and separation: Status and challenges. EnergyChem. 2019;1(1):100006.
[4] LI H, WANG K, SUN Y, et al. Recent advances in gas storage and separation using metal–organic frameworks. Mater Today. 2018;21(2): 108-121.
[5] LI D, XU HQ, JIAO L, et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Catalysis: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Opportunities. EnergyChem. 2019; 1(1):100005.
[6] YANG D, GATES BC. Catalysis by Metal Organic Frameworks: Perspective and Suggestions for Future Research. ACS Catalysis. 2019;9(3):1779-1798.
[7] ZHOU J, LI Y, WANG W, et al. Metal-organic frameworks-based sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;164: 112332.
[8] LV M, ZHOU W, TAVAKOLI H, et al. Aptamer-functionalized metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021; 176:112947.
[9] YANG J, YANG YW. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Applications. Small. 2020;16(10): 1906846.
[10] PHAM H, RAMOS K, SUA A, et al. Tuning Crystal Structures of Iron-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery Applications. ACS Omega. 2020;5(7):3418-3427.
[11] GAO X, CUI R, SONG L, et al. Hollow structural metal–organic frameworks exhibit high drug loading capacity, targeted delivery and magnetic resonance/optical multimodal imaging. Dalton Trans. 2019;48(46):17291-17297.
[12] WEI LQ, LI Y, MAO LY, et al. A series of porous metal–organic frameworks with hendecahedron cage: Structural variation and drug slow release properties. J Solid State Chem. 2018;257:58-63.
[13] BAHRANI S, HASHEMI SA, MOUSAVI SM, et al. Zinc-based metal–organic frameworks as nontoxic and biodegradable platforms for biomedical applications: review study. Drug Metab Rev. 2019;51(3): 356-377.
[14] HORCAJADA P, CHALATI T, SERRE C, et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat Mater. 2010;9:172-178.
[15] HORCAJADA P, SERRE C, MAURIN G, et al. Flexible porous metal-organic frameworks for a controlled drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2008; 130(21):6774-6780.
[16] LENG X, DONG X, WANG W, et al. Biocompatible Fe-Based Micropore Metal-Organic Frameworks as Sustained-Release Anticancer Drug Carriers. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2490.
[17] MIRI B, MOTAKEF-KAZEMI N, SHOJAOSADATI SA, et al. Application of a Nanoporous Metal Organic Framework Based on Iron Carboxylate as Drug Delivery System. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018;17(4):1164-1171.
[18] WYSZOGRODZKA G, DOROŻYŃSKI P, GIL B, et al. Iron-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks as a Theranostic Carrier for Local Tuberculosis Therapy. Pharm Res. 2018;35(7):144.
[19] WANG L, ZHU H, SHI Y, et al. Novel catalytic micromotor of porous zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 for precise drug delivery. Nanoscale. 2018;10(24):11384-11391.
[20] LI J, LV F, LI J, et al. Cobalt-based metal–organic framework as a dual cooperative controllable release system for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Nano Res. 2020;13(8):2268-2279.
[21] XIAO J, ZHU Y, HUDDLESTON S, et al. Copper Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles Stabilized with Folic Acid Improve Wound Healing in Diabetes. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1023-1032.
[22] LIU W, ZHONG Y, WANG X, et al. A porous Cu(II)-based metal-organic framework carrier for pH-controlled anticancer drug delivery. Inorg Chem Commun. 2020;111:107675.
[23] CHEN G, LUO J, CAI M, et al. Investigation of Metal-Organic Framework-5 (MOF-5) as an Antitumor Drug Oridonin Sustained Release Carrier. Molecules. 2019;24(18):3369.
[24] JAVANBAKHT S, HEMMATI A, NAMAZI H, et al. Carboxymethylcellulose-coated 5-fluorouracil@MOF-5 nano-hybrid as a bio-nanocomposite carrier for the anticancer oral delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;155: 876-882.
[25] JAVANBAKHT S, POORESMAEIL M, NAMAZI H. Green one-pot synthesis of carboxymethylcellulose/Zn-based metal-organic framework/graphene oxide bio-nanocomposite as a nanocarrier for drug delivery system. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;208:294-301.
[26] XU Q, ZHAN G, ZHANG Z, et al. Manganese porphyrin-based metal-organic framework for synergistic sonodynamic therapy and ferroptosis in hypoxic tumors. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1937-1952.
[27] AL HAYDAR M, ABID H R, SUNDERLAND B, et al. Multimetal organic frameworks as drug carriers: aceclofenac as a drug candidate. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;13:23-35.
[28] CHEN X, YANG G, ZHANG B, et al. Effects of manganese-supplemented diets on growth performance, blood biochemistry, nitrogen metabolism and skeletal development of rex rabbits. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020; 61:126543.
[29] CONSTANTOPOULOS G. Lipid Metabolism of Manganese-deficient Algae: I. Effect of Manganese Deficiency on the Greening and the Lipid Composition of Euglena Gracilis Z. Plant Physiol. 1970;45(1):76-80.
[30] COASSIN M, URSINI F, BINDOLI A. Antioxidant effect of manganese. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992;299(2):330-333.
[31] KE M, ZHANG Z, XU B, et al. Baicalein and baicalin promote antitumor immunity by suppressing PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105824.
[32] JIANG H, YAO Q, AN Y, et al. Baicalin suppresses the progression of Type 2 diabetes-induced liver tumor through regulating METTL3/m6A/HKDC1 axis and downstream p-JAK2/STAT1/clevaged Capase3 pathway. Phytomed. 2022;94:153823.
[33] KONG N, CHEN X, FENG J, et al. Baicalin induces ferroptosis in bladder cancer cells by downregulating FTH1. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.036
[34] IKEMOTO S, SUGIMURA K, YOSHIDA N, et al. Antitumor effects of Scutellariae radix and its components baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin on bladder cancer cell lines. Urology. 2000;55(6): 951-955.
[35] HUANG Q, ZHANG J, PENG J, et al. Effect of baicalin on proliferation and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(9): 5645-5654.
[36] HUANG Y, HU J, ZHENG J, et al. Down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and induction of apoptosis in CA46 Burkitt lymphoma cells by baicalin. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31(1):48.
[37] XING J, CHEN X, ZHONG D. Absorption and enterohepatic circulation of baicalin in rats. Life Sci. 2005;78(2):140-146.
[38] ZHAO H, HE H, WANG X, et al. Four unprecedented 2D trinuclear Mn(II)-complexes with adenine nucleobase controlled by solvent or co-ligand: Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic behaviour. J Mol Struct. 2018;1155:687-694.
[39] PAGLIAI M, CAPORALI S, MUNIZ-MIRANDA M, et al. SERS, XPS, and DFT Study of Adenine Adsorption on Silver and Gold Surfaces. J Phys Chem Lett. 2012;3(2):242-245.
[40] STOCK N, BISWAS S. Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Routes to Various MOF Topologies, Morphologies, and Composites. Chem Rev. 2012;112(2):933-969.
[41] KUMAR S, JAIN S, NEHRA M, et al. Green synthesis of metal–organic frameworks: A state-of-the-art review of potential environmental and medical applications. Coord Chem Rev. 2020;420:213407.
[42] GAO X, GE F, ZHENG H. Improving the Stability and Visualizing the Structural Transformation of the Stimuli-Responsive Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Inorg Chem. 2020;59(7):5093-5098.
[43] YIN Z, ZHOU YL, ZENG MH, et al. The concept of mixed organic ligands in metal–organic frameworks: design, tuning and functions. Dalton Trans. 2015;44(12):5258-5275.
|