[1] 刘慧,沈国权,张喜林,等.肌肉加载下腰椎间盘突出的有限元研究[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):493-499.
[2] 陈贤艺,陈扬,陈显辉,等.单侧与双侧穿刺PKP术后相邻节段生物力学的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(1): 56-58.
[3] 迟鹏飞,王征,吴兵,等. 成人退行性脊柱侧凸患者椎旁肌和腰大肌退变的不对称性及其与脊柱-骨盆冠状位参数的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(1):1-7.
[4] 赵鹏飞,陈玲,门玉涛.有限元分析肌肉力对腰椎内固定系统的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3654-3658.
[5] LIU YK, RAY G, HIRSCH C. The resistance of the lumbar spine to direct shear. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975;6(1):33.
[6] 秦计生,王昱,彭雄奇,等.全腰椎三维有限元模型的建立及其有效性验证[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(3):321-325.
[7] 项嫔,都承斐,赵美雅,等.全腰椎有限元模态分析[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(2):154-160.
[8] 贾少薇,张顺心,范顺成,等.脊柱侧凸腰骶椎结构的有限元分析及其变形趋势[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):235-241.
[9] 刘巍,吴会东,刘垚,等.矫形器和运动训练对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的效果比较[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(8):869-874.
[10] RASMUSSEN J, TRHOLM S, ZEE MD. Computational analysis of the influence of seat pan inclination and friction on muscle activity and spinal joint forces. Int J Industr Ergon. 2009;39(1):52-57.
[11] 刘艺,陈金传,程辰,等. 单侧与双侧经皮椎弓根螺钉固定融合术治疗退行性腰椎不稳症的有限元分析[J]. 山东医药,2019,59(24): 52-55.
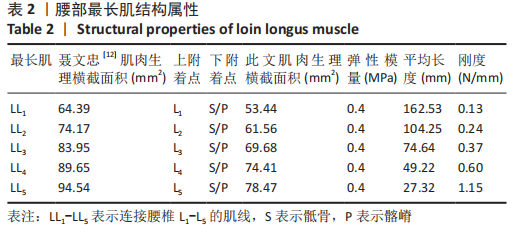
[12] 聂文忠.脊柱胸腰部的生物力学建模与应用研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2009.
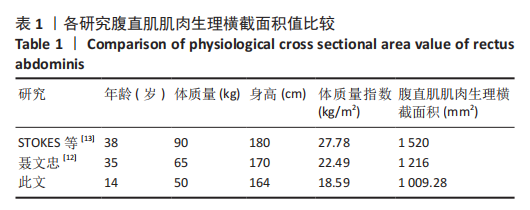
[13] STOKES IAF, GARDNER-MORSE M. Quantitative anatomy of the lumbar musculature. J Biomech. 1999;32(3):311-316.
[14] SHINOHARA M, SABRA K, GENNISSON JL, et al. Real-time visualization of muscle stiffness distribution with ultrasound SWI during muscle contractions. Muscle Nerve. 2010;42(3):438-441.
[15] 温朝阳,范春芝,袭九春,等. 实时定量超声弹性成像技术检测肱二头肌松弛和紧张状态下弹性模量值差异[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2011,8(1):61-63.
[16] 边蔷,胡海威,温建民, 等. 足部相关肌肉、肌腱组织材料弹性模量的测定[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(12):1919-1923.
[17] WEIJS WA, HILLEN B. Cross-sectional areas and estimated intrinsic strength of the human jaw muscles. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. 1985; 23(3):267.
[18] 罗林聪, 马立敏, 林泽,等. 基于AnyBody骨骼肌肉多体动力学分析的有限元仿真[J]. 医用生物力学,2019,34(3):237-242,250.
[19] WU JZ, SINSEL EW, SHROYER JF, et al. Analysis of the musculoskeletal loading of the thumb during pipetting – A pilot study. J Biomech. 2014; 47(2):392-399.
[20] 王欣文,刘继军,王文涛,等.3D打印技术在经皮椎体成形术中的临床应用[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2017,21(5): 321-326.
[21] BROWN T, HANSEN RJ, YORRA AJ. Some mechanical tests on the lumbosacral spine with particular reference to the intervertebral discs; a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39(5):1135-1164.
[22] 赵迪. 成人退变性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的建立及后路三维矫形生物力学研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2010.
[23] 唐勇.脊柱腰段活动度正常值的测量[J].国外医学(物理医学与康复学分册),2002,22(2):67-68.
[24] 苏晋. 腰椎有限元模型的建立与生物力学分析[D].大连:大连医科大学,2010.
[25] EKICI G, UNAL E, AKBAYRAK T, et al. Effects of active/passive interventions on pain, anxiety, and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: Randomized controlled pilot trial. Women Health. 2017; 57(1):88-107.
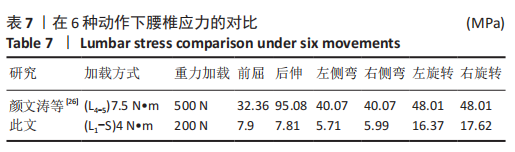
[26] 颜文涛,赵改平,方新果,等.人体腰椎L_(4-5)节段有限元建模及分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2014,31(3):612-618.
[27] 温建民,孙卫东,成永忠,等. 基于CT图像外翻足有限元模型的建立与临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(11):1026-1029.
[28] 张聪,赵岩,杜小宇,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸腰主弯患者腰椎-骨盆的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1155-1161.
|
 文题释义:
文题释义: