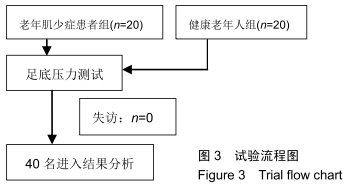
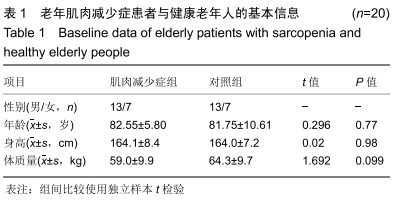
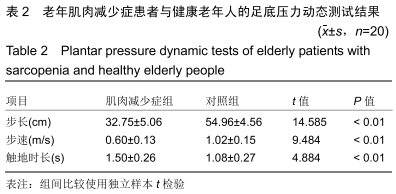
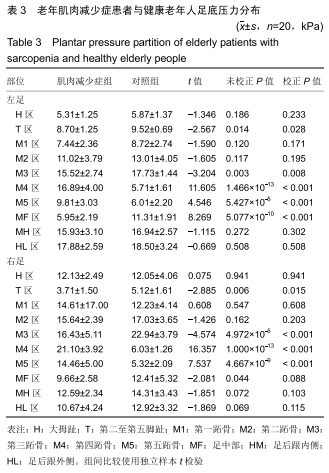
[1] SHAW FE, BOND J, RICHARDSON DA, et al. Multifactorial intervention after a fall in older people with cognitive impairment and dementia presenting to the accident and emergency department: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2003;326(7380):73.
[2] WOLFE RR. The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(3):475-482.
[3] SCOTT D, HAYES A, SANDERS KM, et al. Operational definitions of sarcopenia and their associations with 5-year changes in falls risk in community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(1):187-193.
[4] 中国老年保健医学研究会老龄健康服务与标准化分会,中国老年保健医学》杂志编辑委员会.中国老年人跌倒风险评估专家共识(草案) J].中国老年保健医学,2019,17(4):47-48,50.
[5] 王明鑫,俞光荣.正常人足底压力分析的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(22):1722-1724.
[6] DE COCK A, VANRENTERGHEM J, WILLEMS T, et al. The trajectory of the centre of pressure during barefoot running as a potential measure for foot function. Gait Posture. 2008; 27(4): 669-675.
[7] GOFFAR SL, REBER RJ, CHRISTIANSEN BC, et al. Changes in dynamic plantar pressure during loaded gait. Phys Ther. 2013;93(9):1175-1184.
[8] 徐凌杰,程雯,赵柯湘,等.肌肉减少症筛查方法研究进展[J].现代临床医学,2015,41(2):96-98.
[9] 周明.骨骼肌质量、肌力和功能性活动测试在肌少症和跌倒中的筛查研究[D].北京:解放军医学院,2014.
[10] 段宗宇,张全兵,周云,等.前交叉韧带重建术后患者足底压力变化的初步临床观察[J].生物医学工程与临床,2019,23(5):570-575.
[11] 章琴,罗志增.视觉和本体感觉对人体静态平衡稳定性的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(S1):396-400
[12] LANDI F, CHERUBINI A, CESARI M, et al. Sarcopenia and frailty: From theoretical approach into clinical practice. European Geriatric Medicine. 2016;7(3):197-200.
[13] MORLEY JE. Sarcopenia: diagnosis and treatment. J Nutr Health Aging. 2008;12(7):452-456.
[14] TINETTI ME, KUMAR C. The patient who falls: "It's always a trade-off". JAMA. 2010;303(3):258-266.
[15] BATSIS JA, MACKENZIE TA, BARRE LK, et al. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and mortality in older adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014;68(9):1001-1007.
[16] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(2):95-101.
[17] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.肌少症共识[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):215-227.
[18] 韩佩佩,郭琪,潘翔,等.老年人肌肉衰减综合征的诊断标准与运动疗法[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(3):290-294.
[19] GANZ DA, BAO Y, SHEKELLE PG, et al. Will my patient fall?. JAMA. 2007;297(1):77-86.
[20] KO SU, LING SM, SCHREIBER C, et al. Gait patterns during different walking conditions in older adults with and without knee osteoarthritis--results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Gait Posture. 2011;33(2):205-210.
[21] 毛宾尧,贾学文,郑菲蓉,等.行走和站立时足底应力分布研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(12):68-70.
[22] DE COCK A, WILLEMS T, WITVROUW E, et al. A functional foot type classification with cluster analysis based on plantar pressure distribution during jogging. Gait Posture. 2006;23(3): 339-347.
[23] STINS JF, MICHIELSEN ME, ROERDINK M, et al. Sway regularity reflects attentional involvement in postural control: effects of expertise, vision and cognition. Gait Posture. 2009; 30(1):106-109.
[24] 马天亮,毛志勇,王典,等.平衡功能测试与评估系统数据预处理方法研究[J].宇航计测技术,2017,37(2):22-25.
[25] CAVANAUGH JT, GUSKIEWICZ KM, STERGIOU N. A nonlinear dynamic approach for evaluating postural control: new directions for the management of sport-related cerebral concussion. Sports Med. 2005;35(11):935-950.
[26] TSANG WW, HUI-CHAN CW. Comparison of muscle torque, balance, and confidence in older tai chi and healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(2):280-289.
[27] HESSERT MJ, VYAS M, LEACH J, et al. Foot pressure distribution during walking in young and old adults. BMC Geriatr. 2005;5:8.
[28] STREEPEY JW, ANGULO-KINZLER RM. The role of task difficulty in the control of dynamic balance in children and adults. Hum Mov Sci. 2002;21(4):423-438.
[29] 李正宇,张盘德.踝背屈延迟预测老年人跌倒[J].国外医学(物理医学与康复学分册),2004,24(1):39-40.
[30] ROSE DJ, HERNANDEZ D. The role of exercise in fall prevention for older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 2010;26(4): 607-631.
[31] SHERRINGTON C, WHITNEY JC, LORD SR, et al. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56(12):2234-2243.
[32] RYAN-WENGER NA, KIMCHI-WOODS J, ERBAUGH MA, et al. Challenges and conundrums in the validation of Pediatric Fall Risk Assessment tools. Pediatr Nurs. 2012;38(3): 159-167.
|