Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (20): 3127-3132.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.20.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of tissue engineering adult cardiac myocytes
Bai Chen-guang1, Liu Xiao-hong2
- 1Department of Pathology, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China; 2Laboratory of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China
-
Received:2014-02-23Online:2014-05-14Published:2014-05-14 -
Contact:Liu Xiao-hong, M.D., Associate investigator, Laboratory of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China -
About author:Bai Chen-guang, Master, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Pathology, Changhai Hospital, Shanghai 200433, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30800229
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bai Chen-guang, Liu Xiao-hong. Construction of tissue engineering adult cardiac myocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(20): 3127-3132.
share this article
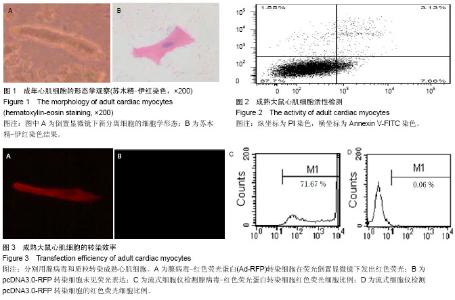
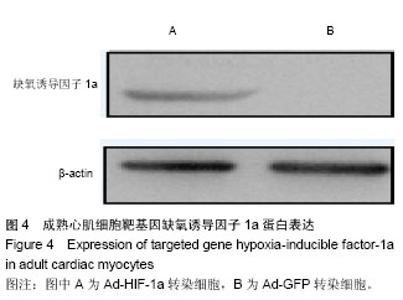
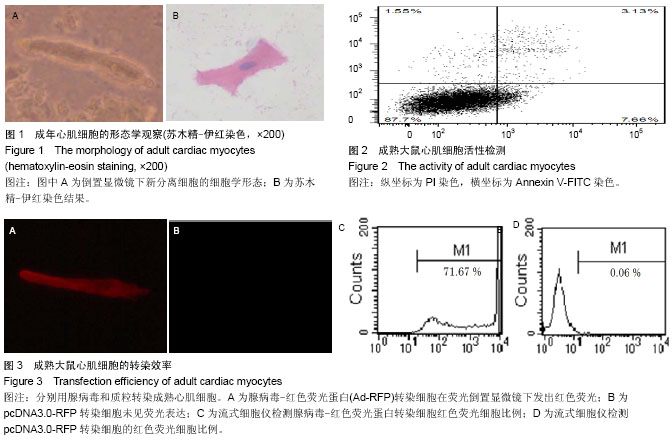
2.1 成年大鼠心肌细胞的形态 倒置显微镜下,新分离的成年大鼠心室肌细胞呈杆状或矩形,横纹清晰,菱角分明,长宽比为4-5∶1。当细胞贴壁后,苏木精-伊红染色可见明显的细胞横纹(图1)。 2.2 细胞存活效率 由于活性细胞的细胞膜完整,所以PI不能进入细胞内而拒染。死亡或损伤严重的心肌细胞则由 于细胞膜缺乏完整性,为PI所着色。根据流式细胞检测结果,实验观察到应用此分离方法可获得(87.03±0.70)%的活性成年大鼠成年心肌细胞(图2)。 2.3 组织工程化成年心肌细胞的构建效率 实验中制备的重组腺病毒以MOI值为50感染大鼠心肌细胞后,细胞未出现肿胀、漂浮、死亡等病态反应;在荧光倒置显微镜下,携带RFP的心肌细胞发出红色的荧光(图3A);流式细胞仪检测结果显示,当MOI值为50时,红色荧光细胞的百分比为(70.31±1.39)%(图3C)。说明重组腺病毒体外转染效率高,目的基因能得以有效地表达。按照Lipofectamine 2000脂质体转染说明书转染pcDNA3.0质粒,在荧光倒置显微镜下观察细胞转染效率,一直到第5天,均未见表达红色荧光的细胞(图3B);流式细胞仪检测结果亦显示红色荧光细胞比例为0(图3D),与Ad-RFP转染组相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.4 组织工程化成熟心肌细胞构建 为观察腺病毒转染的基因在成熟心肌细胞中是否能够有效表达,采用Western blot检测缺氧诱导因子1a蛋白的表达。如图4所示,当心肌细胞感染Ad-HIF-1a后,可大量表达Mr 25 000的缺氧诱导因子1a,而当心肌细胞感染Ad-GFP后,未有目标蛋白表达,说明重组腺病毒体外转染心肌细胞后,可有效表达目标蛋白,提示携带缺氧诱导因子1a基因的组织工程细胞构建成功。"
| [1] Alhabib KF, Elasfar AA, Alfaleh H,et al.Clinical features, management, and short- and long-term outcomes of patients with acute decompensated heart failure: phase I results of the HEARTS database. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014. [2] Aresti NA, Malik AA, Ihsan KM, et al. Perioperative management of cardiac disease.J Perioper Pract. 2014; 24(1-2): 9-14. [3] Harada M, Luo X, Murohara T, et al. MicroRNA Regulation and Cardiac Calcium Signaling: Role in Cardiac Disease and Therapeutic Potential. Circ Res. 2014;114(4):689-705. [4] Yin X, Subramanian S, Hwang SJ, et al. Protein Biomarkers of New-Onset Cardiovascular Disease: Prospective Study From the Systems Approach to Biomarker Research in Cardiovascular Disease Initiative. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Feb 13. [5] Hirt MN, Hansen A, Eschenhagen T. Cardiac tissue engineering: state of the art.Circ Res. 2014;114(2):354-367. [6] Subramanian M, Lim J, Dobson J. Enhanced nanomagnetic gene transfection of human prenatal cardiac progenitor cells and adult cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2013;8(7): e69812. [7] Wei Y, Peng S, Wu M, et al. Multifaceted roles of miR-1s in repressing the fetal gene program in the heart. Cell Res. 2014 Jan 31. [8] Chakraborty S, Sengupta A, Yutzey KE. Tbx20 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and persistence of fetal characteristics in adult mouse hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;62:203-213. [9] Oyama K, El-Nachef D, MacLellan WR. Regeneration potential of adult cardiac myocytes. Cell Res. 2013; 23(8): 978-979. [10] Breckenridge RA, Piotrowska I, Ng KE, et al. Hypoxic regulation of hand1 controls the fetal-neonatal switch in cardiac metabolism. PLoS Biol. 2013;11(9):e1001666. [11] Nunes SS, Miklas JW, Liu J, et al. Biowire: a platform for maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Nat Methods. 2013;10(8):781-787. [12] Petkova SB, Ashton A, Bouzahzah B, et al. Cell cycle molecules and diseases of the cardiovascular system. Front Biosci. 2000;5:D452-460. [13] Jacobson SL,Piper HM. Cell cultures of adult cardiomyocytes as models of the myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol.1986;18: 661. [14] 商立军,臧益民,臧伟进,等. 成熟心肌细胞培养的历史回顾及进展[J]. 心脏杂志,2000,12(1):37-39. [15] Wolska BM, Solaro RJ. Method for isolation of adult mouse cardiac myocytes for studies of contraction and microfluorimetry. Am J Physiol. 1996;271(3 Pt 2): H1250-1255. [16] 廖华,糜涛,涂志业,等.成年大鼠心肌细胞分离方法的改良[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复. 2009,13 (33):6536-6539. [17] Kitabayashi K, Siltanen A, Pätilä T, et al. Bcl-2 expression enhances myoblast sheet transplantation therapy for acute myocardial infarction. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(5):573-588. [18] Liu J, van Mil A, Aguor EN, Siddiqi S, Vrijsen K, Jaksani S, Metz C, Zhao J, Strijkers GJ, Doevendans PA, Sluijter JP. MiR-155 inhibits cell migration of human cardiomyocyte progenitor cells (hCMPCs) via targeting of MMP-16. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(10):2379-2386. [19] Sluijter JP, van Mil A, van Vliet P, et al. MicroRNA-1 and -499 regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(4):859-868. [20] Tian Q, Pahlavan S, Oleinikow K, et al. Functional and morphological preservation of adult ventricular myocytes in culture by sub-micromolar cytochalasin D supplement. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52(1):113-124. [21] 王慧玲,李琼,郭志坤,等. 胶原支架上体外三维培养成年大鼠心肌细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16):2961-2967. [22] 韦丽兰,莫书荣. 成年大鼠心肌细胞的急性分离方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(11):1969-1972. [23] 常惠,张琳,余志斌. 培养成年大鼠心肌细胞存活的形态标志[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2011,27(1):57-61. [24] Sheu JJ, Chang LT, Chiang CH, et al. Impact of diabetes on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and connexin43 gap junction integrity: role of pharmacological modulation. Int Heart J. 2007;48(2):233-245. [25] Liu X, Wang CY, Guo XM, et al. Experimental study of cardiac muscle tissue engineering in bioreactor. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2003;25(1):7-12. [26] Zhao YS, Wang CY, Li DX, et al. Construction of a unidirectionally beating 3-dimensional cardiac muscle construct. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005;24(8):1091-1097. [27] Holtorf HL, Jansen JA, Mikos AG. Modulation of cell differentiation in bone tissue engineering constructs cultured in a bioreactor. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;585:225-241. [28] Barron MJ, Goldman J, Tsai CJ, et al. Perfusion flow enhances osteogenic gene expression and the infiltration of osteoblasts and endothelial cells into three-dimensional calcium phosphate scaffolds. Int J Biomater. 2012;2012: 915620. [29] Du D, Furukawa KS, Ushida T. Oscillatory perfusion culture of CaP-based tissue engineering bone with and without dexamethasone. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37(1):146-155. [30] Wang Y, Uemura T, Dong J, et al. Application of perfusion culture system improves in vitro and in vivo osteogenesis of bone marrow-derived osteoblastic cells in porous ceramic materials. Tissue Eng. 2003;9(6):1205-1214. [31] 张燕,薛晓维,赵晓琴,等. 高糖高脂对培养成年大鼠心肌细胞损伤观察及机制初探[J]. 中国心血管病研究杂志, 2011,8(1): 56-59. [32] 郎明健,曾秋棠,郭敏,杨汉东,闵新文. 靶向大鼠CTGF的shRNA表达载体的构建和作用分析[J].第四军医大学学报,2008,29(1): 59-63. [33] Sasaki T, Tazawa H, Hasei J, et al. A simple detection system for adenovirus receptor expression using a telomerase-specific replication-competent adenovirus. Gene Ther. 2013;20(1):112-118. [34] Kaji K, Norrby K, Paca A, et al.Virus-free induction of pluripotency and subsequent excision of reprogramming factors. Nature. 2009;458(7239):771-775. [35] Chen Z, Wang Q, Sun J, et al. Expression of the coxsackie and adenovirus receptor in human lung cancers.Tumour Biol. 2013;34(1):17-24. [36] Wunder T, Schmid K, Wicklein D, et al. Expression of the coxsackie adenovirus receptor in neuroendocrine lung cancers and its implications for oncolytic adenoviral infection. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20(1):25-32. [37] Beatty MS, Curiel DT. Augmented adenovirus transduction of murine T lymphocytes utilizing a bi-specific protein targeting murine interleukin 2 receptor. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20(8): 445-452. [38] Sumbilla C, Ma H, Seth M, et al. Dependence of exogenous SERCA gene expression on coxsackie adenovirus receptor levels in neonatal and adult cardiac myocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003;415(2):178-183. [39] Senyo SE, Steinhauser ML, Pizzimenti CL, et al. Mammalian heart renewal by pre-existing cardiomyocytes. Nature. 2013; 493(7432):433-436. [40] Zhang R, Han P, Yang H, et al. In vivo cardiac reprogramming contributes to zebrafish heart regeneration. Nature. 2013;498 (7455):497-501. [41] Boström P, Frisén J. New cells in old hearts. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(14):1358-1360. [42] Buikema JW, Mady AS, Mittal NV, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling directs the regional expansion of first and second heart field-derived ventricular cardiomyocytes. Development. 2013;140(20):4165-4176. [43] Qian L, Srivastava D. Direct cardiac reprogramming: from developmental biology to cardiac regeneration. Circ Res. 2013;113(7):915-921. [44] Addis RC, Epstein JA. Induced regeneration--the progress and promise of direct reprogramming for heart repair. Nat Med. 2013;19(7):829-836. |
| [1] | Zhang Xu1, Chen Wangsheng2, Feng Jian3, Zhang Mengjiao1, Jiang Wenjie1, Liang Xuemei1. Protective effect of Ginkgolide B against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury and its underlying mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3097-3101. |
| [2] | Luo Kai, Yang Yafeng, Ma Teng, Xia Bing, Huang Liangliang, Huang Jinghui, Luo Zhuojing. Effects of perfluorotributylamine/alginate/bioglass biomaterials on viability and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 1995-2001. |
| [3] | Zhang Ni, Chen Lan-ying, Li Xue-liang, Guan Zi-yi, Fang Cong, Zhou Meng-jing, Luo Ying-ying, Liu Rong-hua. Viability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in inflammation-induced ischemia-reperfusion environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5259-5267. |
| [4] | Wang Li-ping1, Yu Qun1, Weng Xi-quan2, Lin Wen-tao2. Changes in parameters of erythrocyte and reticulocyte and erythropoietin production in a rat model of exercise-induced hemoglobin reduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3207-3212. |
| [5] | Cheng Jia-qiu1, Zhang Ting-ran2. Effects of hypoxia and vibration training on bone metabolism and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(12): 1852-1858. |
| [6] | Li Du-fang, Miao Ling-juan, Li Ning, Liang He, Ren De-qi, Guo Jian. Salvianolic acid B effects on the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of hippocampal neural stem cells in rats following oxygen-glucose deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(17): 2735-2740. |
| [7] | Zhang Wen-bo1, Zhang Xian2. Influence of M2 macrophage supernatant combined with Eucommia flavonoids on the biological behavior of osteoblasts under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(12): 1819-1825. |
| [8] | Li Guang-zhou, Wu Wei . Research progress in bone metabolism in the hypoxic environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(33): 4963-4969. |
| [9] | Suo Lei, Yang Yin-xiang, Tang Wen-yan, Luan Zuo . Dynamic expression of Lingo-1 in a model of white matter injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(27): 4043-4048. |
| [10] | Jiang Li1, Yin Wei-yao2, Liu Jian3, Guo Hui4. EPAS1 gene rs6756667 polymorphism and aerobic exercise capacity of Tibetan athletes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(20): 2957-2963. |
| [11] | Li Ying. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase in neural stem cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(6): 826-831. |
| [12] | Ma Jun-ning,Gao Jun-wei, Hou Bo-ru, Ren Hai-jun, Chen Si-hua, Liu Ji-xing, Yan Gui-zhong. Effect of oxygen-glucose deprivation on the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(6): 876-882. |
| [13] | Qian Wei, Qiu Jin, Qi Yue-hong, Yao Wen-long, Zhang Xue, Zhang Chuan-han. Expression of Cdh1 and its downstream substrates in primary neurons after oxygen-glucose deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 681-684. |
| [14] | Wang Yi-fan, Xu Yong-tao. Establishment of osteosarcoma cell models: effects of NS-398 on invasive ability of MG-63 cells under hypoxic condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6408-6412. |
| [15] | Xia Zhen-wei, Wang Ji-wen, Li Xiang-dong, Wei Guo-feng. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endothelial progenitor cells under hypoxic condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(45): 7255-7259. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||