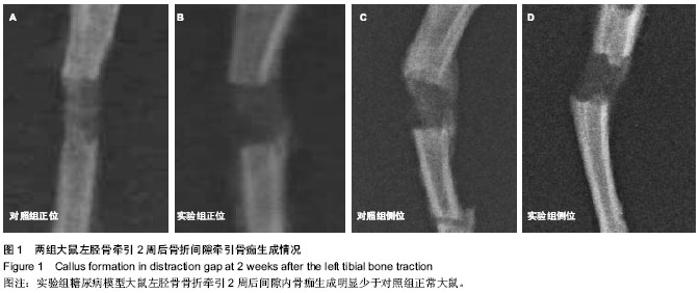
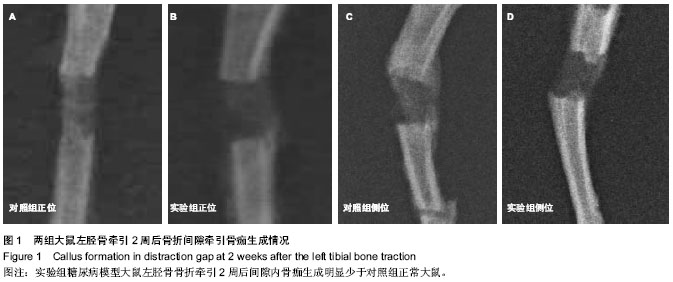
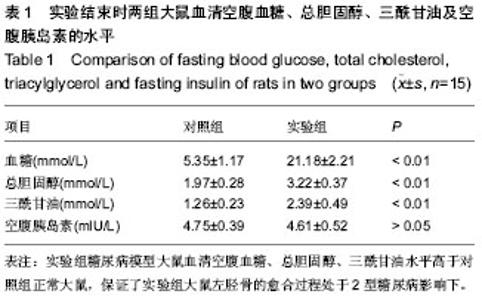
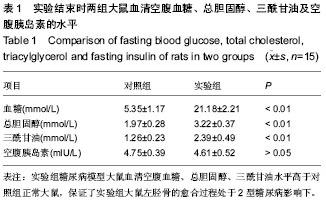
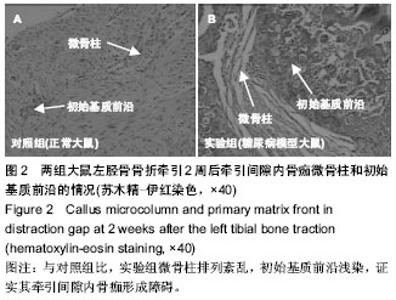
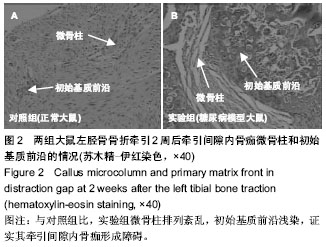
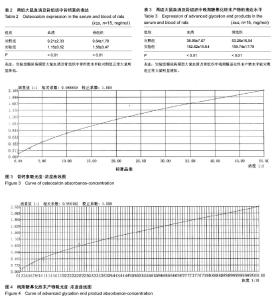
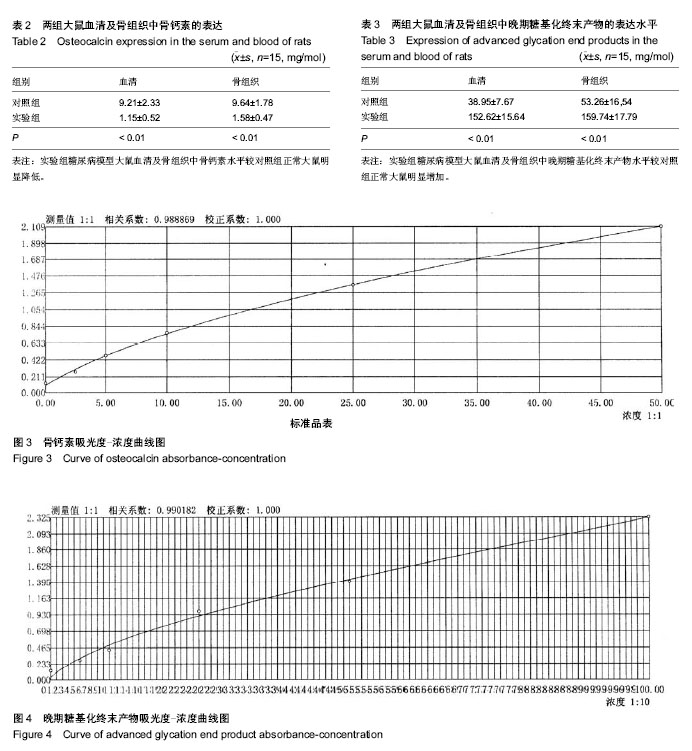
| [1] Hui SL, Epstein S, Johnston CC Jr. A prospective study of bone mass in patients with type I diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.1985;60(1):74-80.
[2] Piepkorn B, Kann P, Forst T, et al. Bone mineral density and bone metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res.1997; 29(11):584-591.
[3] Schwartz AV, Sellmeyer DE, Ensrud KE,et al.Older women with diabetes have an increased risk of fracture: a prospective study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(1):32-38.
[4] Bouillon R, Bex M, Van Herck E, et al. Influence of age, sex and insulin on osteoblast function: osteoblast dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.1995;80(4): 1194-1202.
[5] Beam HA, Parsons JR, Lin SS.The effects of blood glucose control upon fracture healing in the BB Wistar rat with diabetes mellitus.J Orthop Res. 2002;20(6):1210-1216.
[6] 孔德娟,李恩,陈永春,等.晚期糖化终末产物对大鼠成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,1999,5(3):29-32.
[7] 孔德娟.高级糖化终末产物与骨质疏松[J].国外医学:老年医学分册,1999,20(2):57-60.
[8] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the Peoples Republic of China. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals. 2006-09-30.
[9] 李丁,苏海川,赵锦荣,等.骨组织总RNA的提取[J].第四军医大学学报,1999,20(12):1056.
[10] 茂欣,权金星,朱任之,等.一种从骨组织提取RNA的新方法的研 究[J].兰州大学学报自然科学版,2000,36(5):22.
[11] 孙磊,王利群,韩一生,等.老年与青年人股骨头松质骨的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,1999,6(12):919-921.
[12] 李健,郭洪敏,聂志奎,等.2型糖尿病大鼠血清AGEs与骨代谢相关性分析[J].济宁医学院学报,2008,31(1):15-18.
[13] Liu Z, Aronson J, Wahl EC, et al. A novel rat model for the study of deficits in bone formation in type-2 diabetes. Acta Orthopaedica, 2007; 78(1):46-55.
[14] Spencer CP, Godsland IF, Cooper AJ,et al.Effects of oral and transdermal 17beta-estradiol with cyclical oral norethindrone acetate on insulin sensitivity, secretion, and elimination in postmenopausal women.Metabolism. 2000;49(6):742-747.
[15] Hein G, Weiss C, Lehmann G. Advanced glycation end product modification of bone proteins and bone remodelling: hypothesis and p reliminary immunohistochemical findings. Ann Rheum Dis.2006;65(1):101-104.
[16] Hofbauer LC, Brueck CC, Singh SK,et al.Osteoporosis in patients with diabetes mellitus.J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(9): 1317-1328. |