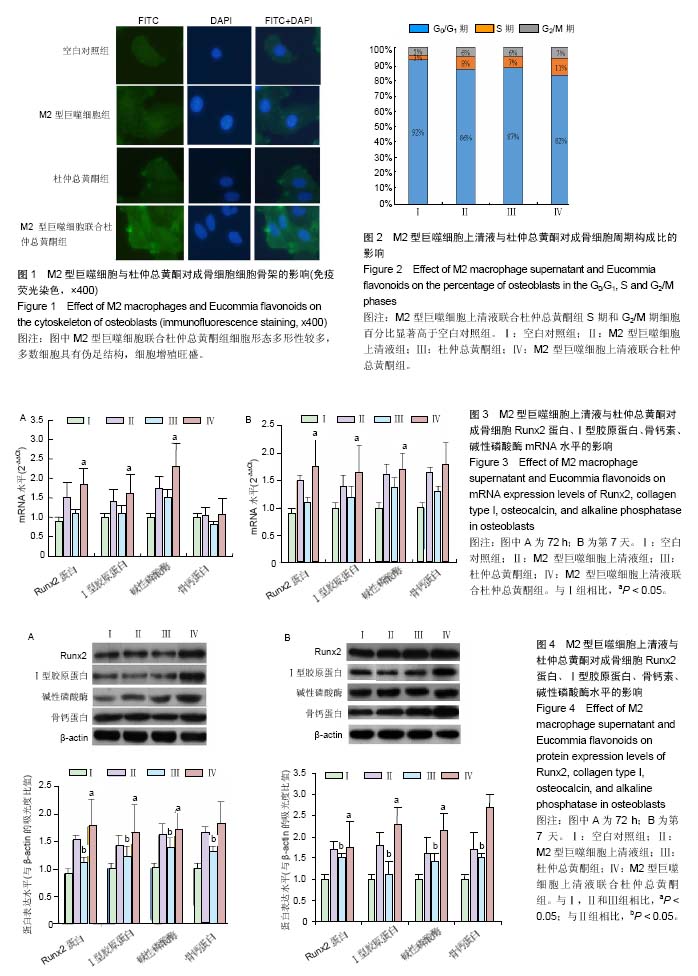
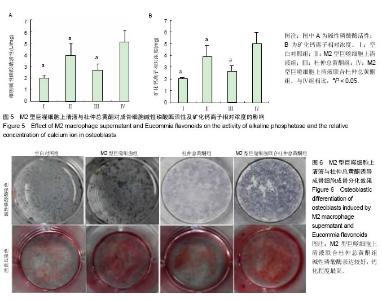
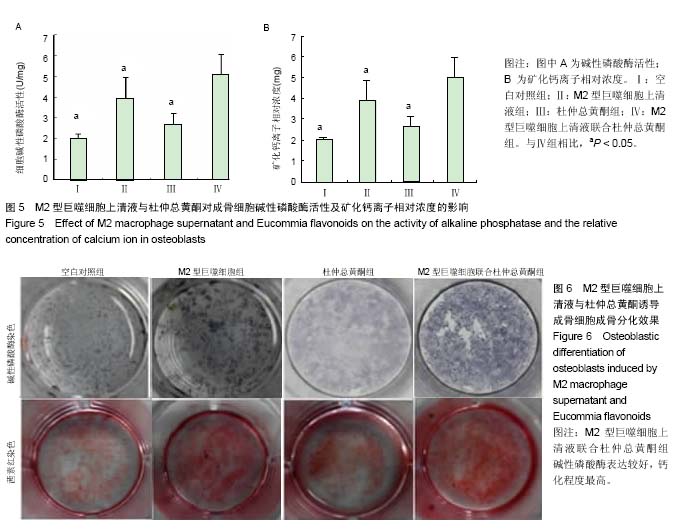
| [1] Cox SC, Thornby JA, Gibbons GJ, et al. 3D printing of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds intended for use in bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;47:237-247. [2] Melinte P R, Dragoi G S, Croitoru R. Anatomic phenotyping of osseous progenitor cells. Implications in tissue engineering and bone remodeling. Rom J Leg Med. 2015;23(1):61-68.[3] Venkatesan J, Bhatnagar I, Manivasagan P, et al. Alginate composites for bone tissue engineering: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:269-281. [4] Farshid B, Lalwani G, Shir Mohammadi M, et al. Boron nitride nanotubes and nanoplatelets as reinforcing agents of polymeric matrices for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(2):406-419.[5] de la Croix Ndong J, Stevens DM, Vignaux G, et al. Combined MEK inhibition and BMP2 treatment promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone healing in Nf1Osx -/- mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(1):55-63. [6] Baik SW, Park BS, Kim YH, et al. Effects of Remifentanil Preconditioning on Osteoblasts under Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Condition. Int J Med Sci. 2015;12(7): 583-589. [7] Dickson G, Buchanan F, Marsh D, et al. Orthopaedic tissue engineering and bone regeneration. Technol Health Care. 2007;15(1):57-67.[8] Abdallah BM, Jafari A, Zaher W, et al. Skeletal (stromal) stem cells: an update on intracellular signaling pathways controlling osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2015;70:28-36. [9] Mills CD. Anatomy of a discovery: m1 and m2 macrophages. Front Immunol. 2015;6:212.[10] Zhu D, Mackenzie NC, Shanahan CM, et al. BMP-9 regulates the osteoblastic differentiation and calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells through an ALK1 mediated pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(1):165-174. [11] Chang HY, Lee HN, Kim W, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid induces M2 macrophage polarization through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ activation. Life Sci. 2015; 120:39-47.[12] 李三华,陈全利,何志全,等.杜仲总黄酮对大鼠成骨细胞护骨素表达的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(25):15279-15280.[13] 李三华,何志全,陈全利,等.杜仲总黄酮对成骨细胞增殖及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达的影响[J].西北药学杂志,2011,26(4):272-274.[14] Reiner, Neil E. Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Humana Press, 2009.[15] Lalwani G, Gopalan A, D'Agati M, et al. Porous three-dimensional carbon nanotube scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(10): 3212-3225.[16] Liu Y, Chan JK, Teoh SH. Review of vascularised bone tissue-engineering strategies with a focus on co-culture systems. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(2):85-105. [17] Lv H, Che T, Tang X, et al. Puerarin enhances proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells via a nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 12(2):2283-2290. [18] 赵光宗,方军,丁刚,等.拉喹莫德抑制成骨细胞中缺氧诱导因子2α的表达及其功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(7):917-924.[19] Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Tanaka A, et al. Preferential M2 macrophages contribute to fibrosis in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz's disease. Clin Immunol. 2015;156(1):9-18.[20] Brenner C, Franz WM, Kühlenthal S, et al. DPP-4 inhibition ameliorates atherosclerosis by priming monocytes into M2 macrophages. Int J Cardiol. 2015;199:163-169. [21] Kambara K, Ohashi W, Tomita K, et al. In vivo depletion of CD206+ M2 macrophages exaggerates lung injury in endotoxemic mice. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(1):162-171.[22] Satoh T, Takeuchi O, Vandenbon A, et al. The Jmjd3-Irf4 axis regulates M2 macrophage polarization and host responses against helminth infection. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(10): 936-944.[23] R?szer T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:816460. [24] Vi L, Baht GS, Whetstone H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015; 30(6):1090-1102. [25] 肖静,李三华,莫宁萍,等.杜仲总黄酮对体外培养大鼠成骨细胞增殖的影响[J].遵义医学院学报,2008,31(3):238-240.[26] 杜鹏,肖润梅,陈勇.淫羊藿总黄酮、杜仲总黄酮对维甲酸所致小鼠骨质疏松的实验研究[J].湖北大学学报:自然科学版,2005, 27(4):392-394.[27] Lin L, Qiu Q, Zhou N, et al. Dickkopf-1 is involved in BMP9-induced osteoblast differentiation of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2016;49(3):179-184.[28] Kang IH, Jeong BC, Hur SW, et al. MicroRNA-302a stimulates osteoblastic differentiation by repressing COUP-TFII expression. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(4):911-921. [29] Huang Y, Zheng Y, Jia L, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation Via TGF-β1/Smad3/HDAC Signaling Pathway by Deriving miR-675. Stem Cells. 2015;33(12):3481-3492. [30] Kang IH, Jeong BC, Hur SW, et al. MicroRNA-302a stimulates osteoblastic differentiation by repressing COUP-TFII expression. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(4):911-921. [31] Sowmya S, Chennazhi KP, Arzate H, et al. Periodontal Specific Differentiation of Dental Follicle Stem Cells into Osteoblast, Fibroblast, and Cementoblast. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(10):1044-1058. |