Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 826-831.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.06.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase in neural stem cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
Li Ying
- Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154003, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2015-01-11Online:2015-02-05Published:2015-02-05 -
About author:Li Ying, Master, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154003, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Heilongjiang Provincial Department of Education, No. 11551496
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ying. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase in neural stem cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(6): 826-831.
share this article
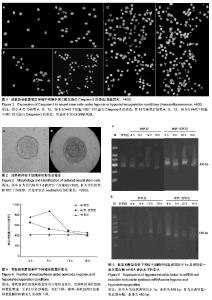
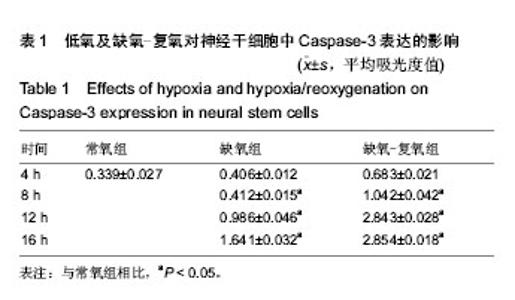
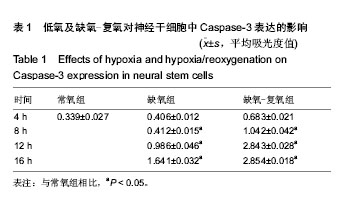
细胞表达Nestin(图2B)。 2.2 低氧及缺氧-复氧神经干细胞神经干细胞的形态及凋 亡 免疫荧光染色显示,缺氧4,8 h后神经干细胞的形态无明显变化,12 h后神经干细胞肿胀特别明显,细胞内较前浑浊,折光性差,可见小的细胞碎片,缺氧-复氧组中凋亡神经干细胞数量及平均吸光度值明显高于缺氧组,且2组凋亡神经干细胞数量及平均吸光度值均随时间的延长而增加(图3,表1)。 2.3 低氧和复氧条件下神经干细胞增殖的变化 低氧4 h后,神经干细胞球的数量略有增加;8 h后神经干细胞球的数量较常氧组增加明显,神经干细胞球密度增大,细胞球排列更为致密,且神经球数量比常氧组增多2倍;而后神经球数量逐渐减少。复氧8 h后,随着时间的增加,神经球的数量减少更加明显(图4)。 2.4 低氧和复氧条件下神经干细胞中低氧诱导因子1α与诱导型一氧化氮合酶 mRNA表达水平的变化 反转录PCR检测结果显示,各组神经干细胞中均存在低氧诱导因子1α与诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA的表达,缺氧组神经干细胞中低氧诱导因子1α与诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA的表达分别于缺氧8,12 h达到峰值,而后均逐渐下降,且分别在4-12 h和8-16 h时高于常氧组(P < 0.05);而缺氧-复氧组神经干细胞中低氧诱导因子1α与诱导型一氧化氮合酶mRNA的表达分别于缺氧8,4 h达到峰值,而后均逐渐下降,且其中低氧诱导因子1α mRNA表达在缺氧-复氧4,8 h高于常氧组(P < 0.05;图5,表2,3)。"

| [1] Chavez JC, LaManna JC. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in the rat cerebral cortex after transient global ischemia: potential role of insulin-like growth factor-1. J Neurosci. 2002;22(20):8922-8931. [2] Brownell I, Guevara E, Bai CB, et al. Nerve-derived sonic hedgehog defines a niche for hair follicle stem cells capable of becoming epidermal stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(5): 552-565. [3] Kokovay E, Temple S. Taking neural crest stem cells to new heights. Cell. 2007;131(2):234-236. [4] Kelly BD, Hackett SF, Hirota K, et al. Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ Res. 2003;93(11):1074-1081. [5] Bonaguidi MA, Song J, Ming GL, et al. A unifying hypothesis on mammalian neural stem cell properties in the adult hippocampus. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012;22(5):754-761. [6] Aprea J, Calegari F. Bioelectric state and cell cycle control of Mammalian neural stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:816049. [7] Semenza GL. HIF-1 and tumor progression: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8(4 Suppl):S62-67. [8] Resar JR, Roguin A, Voner J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha polymorphism and coronary collaterals in patients with ischemic heart disease. Chest. 2005;128(2):787-791. [9] Patkar S, Tate R, Modo M, et al. Conditionally immortalised neural stem cells promote functional recovery and brain plasticity after transient focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(1):14-25. [10] van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, et al. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature. 2002; 415(6875):1030-1034. [11] Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(5):438-445. [12] Yamamoto S, Yamamoto N, Kitamura T, et al. Proliferation of parenchymal neural progenitors in response to injury in the adult rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2001;172(1):115-127. [13] Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2001;105(1):33-41. [14] 黄庆愿,高钰琪,孙秉庸.缺氧与氧感受[J].高原医学杂志, 1999, 9(3):61-64. [15] Petit A, Castillo M, Santos M, et al. KIT expression in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: comparative immunohistochemical analysis of KIT expression in different renal cell neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28(5):676-678. [16] Grachtchouk M, Pero J, Yang SH, et al. Basal cell carcinomas in mice arise from hair follicle stem cells and multiple epithelial progenitor populations. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(5):1768-1781. [17] Millar SE. Committing to a hairy fate: epigenetic regulation of hair follicle stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(3):183-184. [18] Gu Y, Xue C, Zhu J, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) facilitates differentiation of adult dorsal root ganglia-derived neural stem cells toward Schwann cells by binding to FGFR-1 through MAPK/ERK activation. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;52(4): 538-551. [19] Losi P, Briganti E, Errico C, et al. Fibrin-based scaffold incorporating VEGF- and bFGF-loaded nanoparticles stimulates wound healing in diabetic mice. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(8):7814-7821. [20] Seidmann L, Suhan T, Unger R, et al. Imbalance of expression of bFGF and PK1 is associated with defective maturation and antenatal placental insufficiency. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170(2):352-357. [21] Wróbel T, Mazur G, Dzietczenia J, et al. VEGF and bFGF gene polymorphisms in Polish patients with B-CLL. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):456. [22] Feng DF, Wang CY, Wang H, et al. bFGF-induced human periodontal ligament fibroblasts proliferation through T-type voltage-dependent calcium channels. Acta Odontol Scand. 2013;71(1):9-14. [23] Vicario-Abejón C, Collin C, Tsoulfas P, et al. Hippocampal stem cells differentiate into excitatory and inhibitory neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12(2):677-688. [24] Nakata M, Mitsuda N, Herde M, et al. A bHLH-type transcription factor, ABA-INDUCIBLE BHLH-TYPE TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR/JA-ASSOCIATED MYC2-LIKE1, acts as a repressor to negatively regulate jasmonate signaling in arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013;25(5):1641-1656. [25] Zhang Y, Mayba O, Pfeiffer A, et al. A quartet of PIF bHLH factors provides a transcriptionally centered signaling hub that regulates seedling morphogenesis through differential expression-patterning of shared target genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003244. [26] Aguirre A, Rubio ME, Gallo V. Notch and EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and self-renewal. Nature. 2010;467(7313):323-327. [27] Draenert FG, Nonnenmacher AL, Kämmerer PW, et al. BMP-2 and bFGF release and in vitro effect on human osteoblasts after adsorption to bone grafts and biomaterials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(7):750-757. [28] Yoshimori T. Autophagy: paying Charon's toll. Cell. 2007; 128(5):833-836. [29] Kanno H, Ozawa H, Sekiguchi A, et al. Spinal cord injury induces upregulation of Beclin 1 and promotes autophagic cell death. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;33(2):143-148. [30] Rajawat YS, Bossis I. Autophagy in aging and in neurodegenerative disorders. Hormones (Athens). 2008; 7(1):46-61. [31] Yu H, Su J, Xu Y, et al. p62/SQSTM1 involved in cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells by clearing ubiquitinated proteins. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(10):1585-1594. [32] Zhang YB, Gong JL, Xing TY, et al. Autophagy protein p62/SQSTM1 is involved in HAMLET-induced cell death by modulating apotosis in U87MG cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4: e550. [33] Mehrpour M, Esclatine A, Beau I, et al. Overview of macroautophagy regulation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2010;20(7):748-762. [34] Represa A, Shimazaki T, Simmonds M, et al. EGF-responsive neural stem cells are a transient population in the developing mouse spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;14(3):452-462. [35] Song H, Stevens CF, Gage FH. Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature. 2002; 417(6884):39-44. [36] Cho T, Bae JH, Choi HB, et al. Human neural stem cells: electrophysiological properties of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuroreport. 2002;13(11):1447-1452. [37] Liberski PP, Sikorska B, Hauw JJ, et al. Ultrastructural characteristics (or evaluation) of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies or prion diseases. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2010;34(6):351-361. [38] Nixon RA. The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 2013;19(8):983-997. [39] Nassif M, Hetz C. Targeting autophagy in ALS: a complex mission. Autophagy. 2011;7(4):450-453. [40] Crippa V, Sau D, Rusmini P, et al. The small heat shock protein B8 (HspB8) promotes autophagic removal of misfolded proteins involved in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(17):3440-3456. [41] Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, et al. Autophagy- dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science. 2011;334(6062): 1573-1577. [42] Chai XQ, Kong WN, Liu LY, et al. A viral vector expressing hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibits hippocampal neuronal apoptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(11): 1145-1153. [43] Fujiwara Y, Furuta A, Kikuchi H, et al. Discovery of a novel type of autophagy targeting RNA. Autophagy. 2013;9(3): 403-409. [44] Jin J, Suzuki H, Hirai S, et al. JNK phosphorylates Ser332 of doublecortin and regulates its function in neurite extension and neuronal migration. Dev Neurobiol. 2010;70(14):929-942. [45] Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Carpentier S, et al. Role of JNK1-dependent Bcl-2 phosphorylation in ceramide-induced macroautophagy. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(5):2719-2728. |
| [1] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [2] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| [3] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [4] | Li Xiangze, Bu Xianmin, Li Dongmei, Chi Yulei, Su Qiang, Jin Xintong, Zhao Jian, Zhang Gaotian, Wu Bin, Meng Chunyang . Stem cells, cytokines, hormones, neuropeptides and genes in traumatic brain trauma to promote fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3057-3063. |
| [5] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [6] | Yu Chenghao, Zhang Yi, Qi Chao, Chen Jinli, Gao Jiake, Yu Tengbo. Effect of cytokines and platelet-rich plasma on tendon derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 133-140. |
| [7] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [8] | Wei Jianghong, Jia Aijun, Ma Libing, Wang Yueling, Qiu Lulu, Xiao Bing. Th-17 regulatory cytokines promote interleukins-17A and 17F production by neutrophils during asthma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5044-5051. |
| [9] | Wang Wenhong, Li Yanjun, Cui Caiyun. Factors influencing differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla into odontoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5071-5078. |
| [10] | Du Xiaowen, Lin Dapeng, Tu Guanjun. S100A4 promotes differentiation of neural stem cells through up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3029-3034. |
| [11] | Qian Zhouyao, Wang Yongping. Vascular endothelial growth factor intervention: a new approach for accelerating fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2759-2769. |
| [12] | Chen Ting, Li Xinzhu, Xu Wenan. Role of angiogenesis in dental pulp regeneration: exosomes and angiogenic factors#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2263-2270. |
| [13] | Liu Ting, Yang Tingting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun. Immunoregulation of allograft rejection: a role played by human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2068-2073. |
| [14] | Sun Nai, Wang Dali, Zhang Jun, Cao Jinming, Qiu Fucheng, Liu Huimiao, Li Dong, Gu Ping. Effects of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant 3 on the survival and proliferation of neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 118-123. |
| [15] | Zhang Yunqiang, Ke Xixian, Zhang Lingtao, Liang Guiyou. Research progress of mesenchymal stem cells in treating lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 148-153. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||