Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2570-2575.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
The preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4/SiO2-polyethyleneimine composite particles and their applications in gene delivery
Zhang Qing-yun1, Li Rong-rong2, Deng Gui-ru1, Zhu Hui1, Yang Xiao-ying2
- 1Department of Chemistry, Basic Section, Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300309, China; 2Tianjin Key Laboratory on Technologies Enabling Development of Clinical Therapeutics and Diagnostics (Theranostics), School of Pharmacy, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
-
Revised:2014-04-01Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:Yang Xiao-ying, Professor, Tianjin Key Laboratory on Technologies Enabling Development of Clinical Therapeutics and Diagnostics (Theranostics), School of Pharmacy, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
About author:Zhang Qing-yun, Master, Associate professor, Department of Chemistry, Basic Section, Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300309, China -
Supported by:Innovation Team Fund of the Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, No. WHTD201307-2; the General Program of Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, No. WHM201203
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qing-yun, Li Rong-rong, Deng Gui-ru, Zhu Hui, Yang Xiao-ying. The preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4/SiO2-polyethyleneimine composite particles and their applications in gene delivery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2570-2575.
share this article

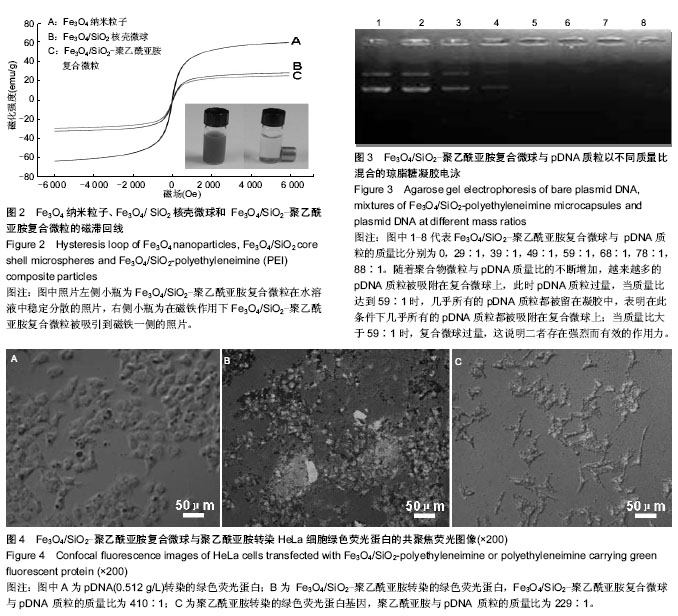
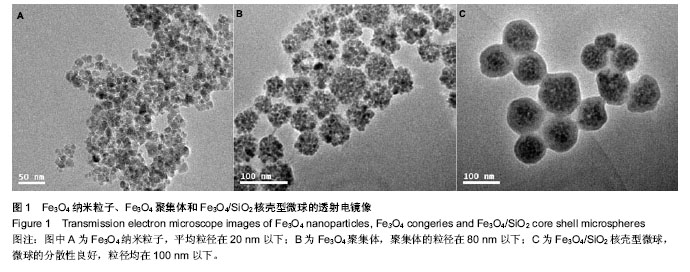
2.1 Fe3O4/SiO2核壳型微球的制备及表征 如图1所示,采用化学沉积法合成Fe3O4纳米粒子,平均粒径在20 nm以下;通过乳化溶剂挥发法制备了Fe3O4纳米粒子聚集体,该聚集体的粒径在80 nm以下;经吐温-80修饰该Fe3O4纳米粒子聚集体后,采用改进的stober法,在碱性环境下催化正硅酸四乙酯水解制备 Fe3O4/SiO2核壳结构微球,该微球的分散性良好,粒径均在100 nm以下,透射电镜表示二氧化硅成功的包裹在Fe3O4聚集体表面。由于SiO2的具有良好的生物稳定性和亲水性,使得复合微球的生物稳定性和相容性变的更好,整个壳层不容易被破坏,同时也更易于修饰。 Fe3O4/SiO2微球经丁二酸酐修饰后后,得到羧基化的Fe3O4/SiO2,Zeta电位检测表明其表面电荷为-29.04 mV,与阳离子聚合物聚乙酰亚胺反应后得到的 Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球的Zeta电位为+21.07 mV,这说明阳离子聚合物聚乙酰亚胺与Fe3O4/SiO2微球表面的羧基阴离子(-COO-)通过静电引力相互作用,聚乙酰亚胺已经成功的修饰到Fe3O4/SiO2微球的氧化硅壳层表面上。在微球表面引入亲水性阳离子聚合物聚乙酰亚胺不仅提供了运输和解离基因的能力,也提高了在水中的稳定性。 纳米粒子容易发生聚集和团聚,难以形成稳定的分散体系,磁性纳米粒子还具备强烈的各向异性的偶极距相互作用,更容易团聚。因此,制备分散性良好的磁性纳米粒子是磁性纳米材料研究领域不可避免的话题。克服这一问题常采用纳米粒子包裹修饰,这样就有效阻止了粒子之问的团聚,增加了分散稳定性。经典的stober法是用于制备无机-无机复合材料的方法之一。在醇溶剂中,将SiO2包裹在一定量的金属粒子表面,利用氨水作催化剂及形貌控制剂,催化TEOS发生水解和缩合反应,生成的二氧化硅沉积在粒子表面,得到核壳结构的复合粒子。通过改变反应氨水、种子和TEOS含量可以改变复合颗粒的形貌及尺寸。 早在1992年,Hmori等[31]就利用TEOS的水解在锭子状α-Fe2O3表面覆盖了一层均匀厚度的二氧化硅。此法制得的二氧化硅磁性复合微球兼具磁性纳米粒子优异的磁性和二氧化硅的生物相容性和稳定性,在生物学和药学方面有着广泛的应用。而包裹上二氧化硅的最大优点是能够很容易地在二氧化硅表面连接上所需要的基团。实验通过活化羧基Fe3O4/SiO2微球与聚乙酰亚胺发生酰胺化反应,从而成功地将聚乙酰亚胺修饰到Fe3O4/SiO2微球上,微球带正电荷,为其通过静电作用吸附pDNA进而将其转运到靶向部位并成功表达相应产物奠定了基础。 2.2 磁性复合微球的磁性能的测试 图2磁滞回线所示,Fe3O4纳米粒子的饱和磁化强度为61.48 emu/g,SiO2包裹后磁性纳米粒子的饱和磁化强度下降为30.48 emu/g;Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺的饱和磁化强度为28.05 emu/g。3种粒子的矫顽力基本保持一致,均趋近于零,几乎没有磁滞,表明其均具有较好的超顺磁性。这个研究结果和以往的文献结果类似,当包裹上非磁性材料后,Fe3O4磁性纳米粒子的饱和磁化强度均表现出下降。 2.3 体外转染实验 2.3.1 电泳实验 由图3显示:随着聚合物微粒与pDNA质量比的不断增加,越来越多的pDNA质粒被吸附在Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球上,此时pDNA质粒过量,当质量比达到59∶1时,几乎所有的pDNA质粒都被留在凝胶中如第5孔,表明在此条件下几乎所有的pDNA质粒都被吸附在Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球上;当质量比大于59∶1时,Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球过量,这说明二者存在强烈而有效的作用力。由此可见,聚合物微粒与pDNA的质量比为59∶1时结果较好,在此条件下,所有的pDNA质粒正好被吸附在所有Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球上,二者均无过量,因此将使用这一比例计算负载量以指导转染实验。 2.3.2 转染实验 通过Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球与聚乙酰亚胺对HeLa细胞绿色荧光蛋白基因转染能力的比较,可清晰地看出图4A中无载体转染的绿色荧光蛋白,几乎无绿色存在;图4B显示Fe3O4/SiO-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球转染绿色荧光蛋白的图像,绿色荧光明显,细胞存活状况良好;图4C显示聚乙酰亚胺转染的绿色荧光蛋白,能看到少量绿色荧光,但细胞凋亡明显。由此说明当Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球与pDNA 质粒的质量比为410∶1时Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球有好的转染效率,这可能是由于Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球表面剩余的正电荷与绿色荧光蛋白表面的负电荷之间的静电作用使之形成更为紧密的复合物,这些结果显示Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球能使pDNA的转染效率显著增强,并且Fe3O4/SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球具有一定的生物安全性。同时与聚乙酰亚胺相比,Fe3O4-SiO2-聚乙酰亚胺复合微球可显著提高pDNA的转染效率。"
| [1] Zhao N,Roesler S,Kissel T.Synthesis of a new potential biodegradable disulfide containing poly(ethylene imine)- poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer cross-linked with click cluster for gene delivery.Int J Pharm.2011;411(1-2):197-205. [2] Zhang G,Liu J,Yang Q,et al.Disulfide-Containing Brushed Polyethylenimine Derivative Synthesized by Click Chemistry for Nonviral Gene Delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23(6): 1290-1299. [3] Lungwitz U,Breunig M,Blunk T,et al.Polyethylenimine-based non-viral gene delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005; 60(2):247-266. [4] Breunig M, Lungwitz U, Liebl R, et al. Gene delivery with low molecular weight linear polyethylenimines.J Gene Med. 2005; 7(10):1287-1298. [5] Neu M,Fischer D,Kissel T.Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly(ethylene imine) and its derivatives.J Gene Med.2005;7(8):992-1009. [6] Lungwitz U,Breunig M,Liebl R,et al.Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)--low molecular weight linear polyethylenimine-derived copolymers enable polyplex shielding.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69(1):134-148. [7] Peng Q,Zhong Z,Zhuo R.Disulfide cross-linked polyethylenimines (PEI) prepared via thiolation of low molecular weight PEI as highly efficient gene vectors. Bioconjug Chem.2008;19(2):499-506. [8] Son S,Singha K,Kim WJ.Bioreducible BPEI-SS-PEG-cNGR polymer as a tumor targeted nonviral gene carrier. Biomaterials.2010;31(24):6344-6354. [9] Koo H,Jin GW,Kang H,et al.Biodegradable branched poly(ethylenimine sulfide) for gene delivery. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(5):988-997. [10] Choi S,Lee KD.Enhanced gene delivery using disulfide-crosslinked low molecular weight polyethylenimine with listeriolysin o-polyethylenimine disulfide conjugate. J Control Release.2008;131(1):70-76. [11] Feng FL,Li RR,Zhang QY,et al.Preparation of reduction- triggered degradable microcapsules for intracellular delivery of anti-cancer drug and gene.Polymer. 2014; 55(1):110-118. [12] Yang M,Cheng K,Qi S,et al.Affibody modified and radiolabeled gold-iron oxide hetero-nanostructures for tumor PET, optical and MR imaging. Biomaterials.2013;34(11):2796-2806. [13] Guo J,Yang W,Wang C.Magnetic colloidal supraparticles: design, fabrication and biomedical applications.Adv Mater. 2013;25(37):5196-5214. [14] Santhosh PB,Ulrih NP.Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promising tools in cancer theranostics. Cancer Lett.2013;336(1):8-17. [15] Xiong F,Chen Y,Chen J,et al.Rubik-like magnetic nanoassemblies as an efficient drug multifunctional carrier for cancer theranostics.J Control Release.2013;172(3):993-1001. [16] Chertok B,David AE,Yang VC.Magnetically-enabled and MR-monitored selective brain tumor protein delivery in rats via magnetic nanocarriers.Biomaterials.2011;32(26): 6245-6253. [17] Yu JH,Li XY,Luo Y,et al.Poly(ethylene glycol) shell-sheddable magnetic nanomicelle as the carrier of doxorubicin with enhanced cellular uptake. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013; 107:213-219. [18] Chertok B,Moffat BA,David AE,et al.Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors.Biomaterials.2008;29(4):487-496. [19] Narayanan S,Sathy BN,Mony U,et al.Biocompatible magnetite/gold nanohybrid contrast agents via green chemistry for MRI and CT bioimaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(1):251-260. [20] Qu JB,Shao HH,Jing GL,et al.PEG-chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles with high saturated magnetization as carriers of 10-hydroxycamptothecin: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2013;102: 37-44. [21] Cai H,An X,Cui J,et al.Facile hydrothermal synthesis and surface functionalization of polyethyleneimine-coated iron oxide nanoparticlesfor biomedical applications.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2013;5(5):1722-1731. [22] Yu J,Li X,Luo Y,et al.Poly(ethylene glycol) shell-sheddable magnetic nanomicelle as the carrier of doxorubicin with enhanced cellularuptake.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;107:213-219. [23] Kim J,Kim HS,Lee N,et al.Multifunctional Uniform Nanoparticles Composed of a Magnetite Nanocrystal Core and a Mesoporous Silica Shell for Magnetic Resonance and Fluorescence Imaging and for Drug Delivery.Angew Chem Int Ed.2008;47(44): 8438-8441. [24] Law WC,Yong KT,Roy I,et al.Optically and Magnetically Doped Organically Modified Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Magnetically Guided Biomarkers for Two-Photon Imaging of Live Cancer Cells.J Phys Chem C.2008;112(21):7972-7977. [25] Kempe M,Kempe H,Snowball I,et al.The use of magnetite nanoparticles for implant—assisted magnetic drug targeting in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(36): 9499-9510. [26] Teng ZG,Li J,Yan F,et al.Highly magnetizable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embedded mesoporous silica spheres and their application for efficient recovery of DNA from agarose gel.J Mater Chem. 2009; 19(13): 1811-1815. [27] Piao Y,Kim J,Na HB,et al.Wrap-bake-peel process for nanostructural transformation from β-FeOOH nanorods to biocompatible iron oxide nanocapsules.Nat Mater. 2008;7: 242-247. [28] Kim J,Piao Y,Hyeon T.Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy.Chem Soc Rev.2009;38:372-390. [29] Liu YY, Shi MR, Xu MM,et al.Multifunctional nanoparticles of Fe3O4@SiO2(FITC)/PAH conjugated the recombinant plasmid of pIRSE2-EGFP/VEGF(165) with dual functions for gene delivery and cellular imaging.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012; 9(10):1197-1207. [30] Fu R,Jin XM,Liang JL,et al.Preparation of nearly monodispersed Fe3O4/SiO2 composite particles from aggregates of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.J Mater Chem.2011; 21(39): 15352-15356. [31] Hmori MO,Atijevic EM.Preparation and Properities of uniform coated colloidal Particles. Ⅶ sillica on hematite.J Colloid Interface Sci.1992;150:594. |
| [1] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [2] | Shi Zhengliang, Zhang Hua, Fan Zhiyong, Ma Wei, Yuan He, Yang Bing. Nerve conduits of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol with brain-derived neurotrophic factor microspheres for peripheral nerve defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1555-1559. |
| [3] | Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua. Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 511-516. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan, Cao Jinxing, Jiang Xiaohong. Porous beta-tricalcium phosphate-polypyrrole-biotin-icariin composite scaffold promotes recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5532-5537. |
| [5] | Liu Hao, Liu Jun, Rui Yongjun, Tang Fenglin, Lu Miao, Ding Tao. Co-transfection by Nell-1 and Noggin-shRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4966-4970. |
| [6] | Wang Wenhong, Li Yanjun, Cui Caiyun. Factors influencing differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla into odontoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5071-5078. |
| [7] | Wang Le, Hui Min, Dong Xiling, Zhou Han, Dong Hongliang, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Effects of sustained-release atorvastatin calcium nanofiber scaffold on cell adhesion and proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4492-4497. |
| [8] | Yang Zhen, Li Hao, Gao Cangjian, Fu Liwei, Tian Guangzhao, Zha Kangkang, Sun Zhiqiang, Li Xu, Guo Weimin, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Shibi, Guo Quanyi . Regulation of stem cells by transforming growth factor β3/polylactic acid-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4540-4546. |
| [9] |
Wang Ning, Chen Junyi, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Li Zhijun, Bei Chaoyong.
Lentivirus-mediated P75 neurotrophin receptor silencing combined with nerve growth factor overexpression promotes proliferation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3988-3993. |
| [10] | He Jianwei, Zheng Hanshan, Xu Jian, Zhang Ying. Changes in three physical indicators of the muscle after far-infrared ceramic microsphere intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3527-3533. |
| [11] | Zou Gang, Zhang Jun, You Qi, Tang Jingfeng, Jin Ying, Yang Jibin, Zhu Xizhong, Liu Yi. Scleraxis lentivirus-transfected human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promote tendon-bone healing in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2080-2086. |
| [12] | Sun Li, Zong Yanyan, Wei Jianfeng. Comparison of two passage methods affecting the transfection efficiency of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 72-76. |
| [13] | Xu Huijun, Shi Dongmei, Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Effect of sex combing protein 1 on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in inflammatory microenvironment#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 130-135. |
| [14] | Xiang Bingyan, Li Peng, Bo Fan, Zhou Sirui . Repair of bone defects due to chronic osteomyelitis in rabbits using nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan scaffold carrying vancomycin/polyactic-co-glycolic acid sustained-release microspheres combined with autologous red bone marrow [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 843-848. |
| [15] | Wang Yang, Nie Jinshan, Gu Zhun, Zhu Kai. Construction and in vitro evaluation of a biodegradable cationic gene delivery system based on hyperbranched polyamidoamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 936-944. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||