Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2563-2569.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Icariin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammatory reaction
Cui Jing-fu, Xu Yao-zeng, Zhu Shi-jun, Zhu Feng, Fu Wen, Shao Hong-guo, Geng De-chun
- Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-03-10Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:Geng De-chun, Associate investigator, Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Cui Jing-fu, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Clinical Medicine Specific Fund of Jiangsu Province, No. BL2012004; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81101399, 81272018, 81372018; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK2011303; the Innovation Project for Graduate Culture in Jiangsu Province, No. CXZZ13_0835
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cui Jing-fu, Xu Yao-zeng, Zhu Shi-jun, Zhu Feng, Fu Wen, Shao Hong-guo, Geng De-chun. Icariin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammatory reaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2563-2569.
share this article
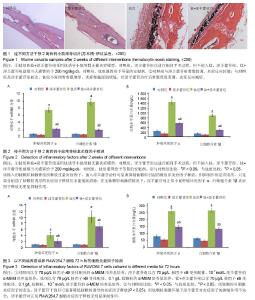
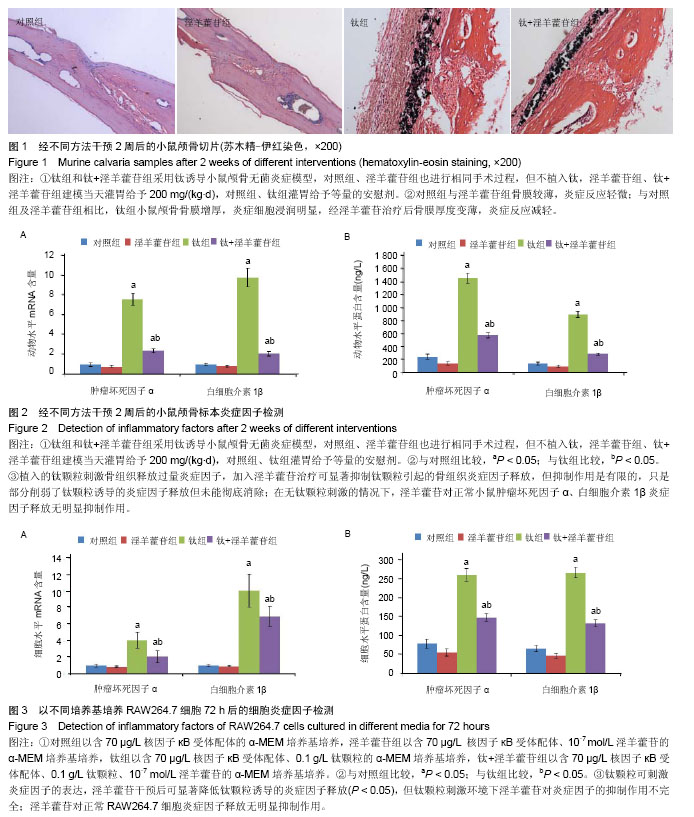
2.1 体内实验结果 2.1.1 实验动物一般情况 术后各组小鼠均在1 h内苏醒并自由活动,正常进食,精神状态佳。实验期间小鼠切口愈合佳,无红肿、渗液等不良反应。实验过程中无动物死亡。 2.1.2 淫羊藿苷抑制钛颗粒诱导的炎性细胞浸润 苏木精-伊红染色显示对照组和淫羊藿苷组小鼠颅骨骨膜内细胞总量较少,成纤维细胞较多,炎性细胞较少,骨膜较薄;与对照组相比,钛组小鼠颅骨骨膜增厚明显,骨膜内可见大量细胞浸润,炎性细胞居多,成纤维细胞较少,经淫羊藿苷后情况有所好转(图1)。Paint.NET软件测量结果表明对照组、淫羊藿苷组、钛组、钛+淫羊藿苷组颅骨骨膜厚度为分别为(0.07±0.01),(0.06±0.01),(0.28±0.04),(0.12±0.02) mm。钛组与对照组颅骨骨膜厚度比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明钛颗粒的刺激使骨膜炎性增厚明显;钛+淫羊藿苷组与钛组颅骨骨膜厚度相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明淫羊藿苷治疗后炎性增厚的骨膜显著变薄;对照组及淫羊藿苷组骨膜厚度相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);淫羊藿苷组与钛+淫羊藿苷组颅骨骨膜厚度相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这表明淫羊藿苷未能完全抑制钛颗粒诱导的炎症反应。 2.1.3 淫羊藿苷下调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因mRNA表达 设定对照组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达量为1,钛组中二者表达量分别升至7.6±0.6和9.8±0.9,两组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这表明钛颗粒显著上调肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因转录水平,钛颗粒的炎症诱导作用在基因层面表现明显;钛+淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达量分别降至2.4±0.2和2.1±0.2,与钛组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这表明淫羊藿苷抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β释放的机制涉及mRNA水平下调,这从基因层面解释了ELISA检测结果;淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因mRNA表达量分别为0.8±0.1和0.8±0.1,与对照组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),这表明对于正常小鼠淫羊藿苷不能抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因表达量(图2A)。 2.1.4 淫羊藿苷抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白的释放 对照组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白质量浓度分别为(237.1±37.4) ng/L和(133.8±19.6) ng/L;钛颗粒植入后,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β质量浓度在钛组增长明显,分别达到(1447.8±78.2) ng/L和(889.2±45.9) ng/L,与对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这说明植入的钛颗粒刺激骨组织释放过量的炎症因子;钛+淫羊藿苷组经淫羊藿苷口服治疗后肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白质量浓度下降至(568.8±42.3) ng/L和(279.3±19.4) ng/L,与钛组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),这表明淫羊藿苷可显著抑制钛颗粒引起的骨组织炎症因子释放;但与淫羊藿苷组相比,钛+淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白质量浓度仍偏高(P < 0.05),这表明淫羊藿苷的抑制作用是有限的,只是部分削弱了钛颗粒诱导的炎症因子释放但未能彻底消除,尽管抑制作用是不完全的,但炎症因子浓度的减少有利于局部反应的缓解和炎症细胞浸润减少,这与苏木精-伊红染色结果相一致;淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白质量浓度分别为(99.0±26.2) ng/L和(96.0±13.9) ng/L,与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),这表明在无钛颗粒刺激的情况下,淫羊藿苷对正常小鼠肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β炎症因子释放无明显抑制作用(图2B)。 2.2 体外细胞培养实验结果 2.2.1 淫羊藿苷下调钛颗粒诱导的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达 设定对照组RAW264.7细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达量均为1。钛组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因转录量分别为4.1±1.0和10.1±2.0,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明钛颗粒显著上调RAW264.7细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因表达量;钛+淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达量下调至2.1±0.8和7.0±1.2,与钛组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明淫羊藿苷显著抑制钛颗粒诱导的炎症因子基因表达量;淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA表达量分别为0.9±0.1和0.9±0.1,与对照组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),这表明无钛颗粒刺激的环境下,淫羊藿苷对RAW264.7细胞肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β基因表达量无明显影响,这与体内PCR结果相一致;与淫羊藿苷组相比,钛+淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β mRNA水平均显著上调(P < 0.05),这表明钛颗粒刺激环境下淫羊藿苷对炎症因子抑制作用的不完全性(图3A)。 2.2.2 淫羊藿苷抑制钛颗粒诱导的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白释放 对照组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白水平分别为(79.0±12.8) ng/L和(66.0±7.8) ng/L。钛组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白水平为(259.4±17.1) ng/L和(265.8±14.2) ng/L,与对照组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明钛颗粒刺激后炎症因子浓度上升明显;钛+淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β水平分别为(147.2±17.1) ng/L和(132.1±9.2) ng/L,与钛组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明淫羊藿苷干预可显著降低钛颗粒诱导的炎症因子释放;淫羊藿苷组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白水平分别为(56.0±9.6) ng/L和(47.0±6.3) ng/L,与对照组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),这说明淫羊藿苷对正常RAW264.7细胞炎症因子释放无明显抑制作用,这一结果与体内ELISA分析结果一致(图3B)。"
| [1] Wooley PH,Schwarz EM.Aseptic loosening.Gene Ther. 2004; 11(4):402-407. [2] Holt G,Murnaghan C,Reilly J,et al.The biology of aseptic osteolysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007;460:240-252. [3] Rao AJ,Gibon E,Ma T,et al. Revision joint replacement, wear particles, and macrophage polarization.Acta Biomater. 2012;8: 2815-2823. [4] Goodman SB,Ma T,Chiu R,et al.Effects of orthopaedic wear particles on osteoprogenitor cells. Biomaterials. 2006;27: 6096-6101. [5] Rao AJ,Nich C,Dhulipala LS,et al.Local effect of IL-4 delivery on polyethylene particle induced osteolysis in the murine calvarium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101:1926-1934. [6] Holt G,Murnaghan C,Reilly J,et al.The biology of aseptic osteolysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007;460:240-252. [7] Sundfeldt M,Carlsson LV,Johansson CB,et al.Aseptic loosening,not only a question of wear:A review of different theories.Acta Orthop.2006;77(2):177-197. [8] Schwarz EM,Campbell D,Totterman S,et al.Use of volumetric computerized tomography as a primary outcome measure to evaluate drug efficacy in the prevention of peri-prosthetic osteolysis: a 1-year clinical pilot of etanercept vs. placebo. J Orthop Res.2003;21:1049-1055. [9] Shanbhag AS.Use of bisphosphonates to improve the durability of total joint replacements.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2006;14:215-225. [10] Hsieh TP,Sheu SY,Sun JS,et al.Icariin inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by suppression of MAPKs/NF-κ β regulated HIF-1α and PGE2 synthesis. Phytomedicine.2011;18:176-185. [11] Zhao J,Ohba S,Shinkai M,et al.Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation in vitro in a BMP- and Runx2-dependent manner.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;369(2): 444-448. [12] Zhang JF,Li G,Meng CL,et al.Total flavonoidsof Herba Epimedii improves osteogenesis and inhibits osteoclastogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Phytomedicine.2009;16(6-7):521-529. [13] Nian H,Ma MH,Nian SS,et al.Antiosteoporotic activity of icariin in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 2009;16:320-326. [14] Peng S,Zhang G,Zhang BT,et al.The beneficial effect of Icaritin on osteoporotic bone is dependent on the treatment initiation timing in adult ovariectomized rats.Bone.2013;55(1):230-240. [15] Xu CQ,Liu BJ,Wu JF,et al.Icariin attenuates LPS-induced acute inflammatory responses: involvement of PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;642: 146-153. [16] von Knoch M,Jewison DE,Sibonga JD,et al.The effectiveness of polyethylene versus titanium particles in inducing osteolysis in vivo.J Orthop Res. 2004;22(2):237-43. [17] Lee SS,Woo CH,Chang JD,et al.Roles of Rac and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in the intracellular signalling in response to titanium particles.Cell Signal. 2003;15(3):339-345. [18] Livak KJ,Schmittgen TD.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC (T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402-408. [19] Wooley PH,Morren R,Andary J,et al.Inflammatory responses to orthopaedic biomaterials in the murine air pouch. Biomaterials. 2002;23:517-526. [20] Geng D,Mao H,Wang J,et al.Protective effects of COX-2 inhibitor on titanium particle induced inflammatory osteolysis via the down-regulation of RANK/RANKL. Acta Biomater. 2011;7:3216-3221. [21] Geng DC,Xu YZ,Yang HL,et al.Inhibition of titanium particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis through inactivation of cannabinoid receptor 2 by AM630. J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;95:321-326. [22] Bi Y,Seabold JM,Kaar SG,et al. Adherent endotoxin on orthopedic wear particles stimulates cytokine production and osteoclast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res.2001;16: 2082-2091. [23] Holding CA,Findlay DM,Stamenkov R,et al.The correlation of RANK, RANKL and TNFalpha expression with bone loss volume and polyethylene wear debris around hip implants. Biomaterials.2006;27:5212-5219. [24] Hamlet S,Ivanovski S.Inflammatory cytokine response to titanium chemical composition and nanoscale calcium phosphate surface modification.Acta Biomater. 2011; 7: 2345-2353. [25] Rao AJ,Nich C,Dhulipala LS,et al.Local effect of IL-4 delivery on polyethylene particle induced osteolysis in the murine calvarium.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101: 1926-1934. [26] Geng DC,Zhu XS,Mao HQ,et al.Protection against titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis by Cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitor.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;99A: 516-522. [27] Taki N,Tatro JM,Lowe R,et al.Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNFalpha in cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening.Bone.2007;40:1276-1283. [28] Holding CA,Findlay DM,Stamenkov R,et al.The correlation of RANK, RANKL and TNFalpha expression with bone loss volume and polyethylene wear debris around hip implants. Biomaterials.2006;27:5212-5219. [29] 赵旭红,伍骥,李松林,等.全膝关节置换假体松动时滑膜液中的诊断性标志物[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4782-4788. [30] Hirakawa K,Jacobs JJ,Urban R,et al.Mechanisms of failure of total hip replacements: lessons learned from retrieval studies. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;420:10-17. [31] Song L,Zhao J,Zhang X,et al.Icariin induces osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK and JNK signal activation. Eur J Pharmacol.2013;714(1-3):15-22. [32] Hsieh TP,Sheu SY,Sun JS,et al.Icariin isolated from Epimedium pubescens regulates osteoblasts anabolism through BMP-2,SMAD4,and Cbfa1 expression. Phytomedicine. 2010;17(6):414-423. |
| [1] | Song Yu-cheng, Deng Ying-jie, Liu Zhen-feng, Liang Zhi-quan, Liao Jun, Hong Han-gang, Fang Rui . Perioperative blood management combined with Bazhen Tang improves hemoglobin and hypercoagulability in senile patients after joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7925-7931. |
| [2] | Wu Xiao-guang, Qiu Zhi-fu, Meng Jie, Zu Bing-xue, Li Meng-meng, Miao Hui. Effects of Buyanghuanwu decoction on the protein expression of PI3K, Akt, Bcl-2 and BAX in brain tissue of a rat model of cerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5933-5938. |
| [3] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [4] | Li Chang-lei, Ma Bao-miao, Liu Wei, Chen Xiao-qing, Yi Hui-ling, Shu Xi-ji. Effect of nux vomica on fracture healing in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1647-1651. |
| [5] | Lin Shu-zhong, Liu Jun. Effects of different doses of puerarin on osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1658-1662. |
| [6] | Li Hong-shi, Chen Xin, Feng Yan, Yin Yin, Cao Jun-kai. Changes of cartilage matrix components, related growth factors and inflammatory factors in the temporomandibular joint under high acceleration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1663-1667. |
| [7] | Yao Ming-zhi. Effects of Jiegu Qili Tablet on proliferation and mineralization of MC-3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1694-1698. |
| [8] | Ouyang Hai-chun, Wu Wo-dong, Zhong Dong-mei, Wu Yan-xian, Li Wen-jie, Chen Xi-ming. Effects of Xingnaojing on recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-mediated tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1717-1721. |
| [9] | Li Hui-zhen, Li Meng, Li Rui-yu, Wu Li-ping. Effects of epimedium on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 979-984. |
| [10] | Wang Fang-hui, Zhang Shan-shan, Shu Jing-yuan, Gao Yan, Sun Xiao-kun, Wang Qing-shan. Effects of surface modification of titanium implants on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8491-8497. |
| [11] | Wu Tao, Wu Jin-hui, Zheng Guo-dong, Lu Zhi-qin, Zeng Hai-yan, Lv Jun, Xing Jian-zhou. Release behavior of icariin-chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8399-8404. |
| [12] | Li Dan, Hui Rui, Hu Yong-wu, Han Yan, Guo Shu-zhong. Effects of Dragon’s blood extracts on fibroblast proliferation and procollagen type III [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7437-7441. |
| [13] | Chen Ya-zhu, Guan Xiao-yan, Xiao Qian-wen, Wang Si-wei, Liu Jian-guo. The function of Chinese herbal medicine in the reconstruction of periodontal tissue during orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7477-7481. |
| [14] | Wei Biao-fang, Sun Bing-yin. Combined treatment of HUOXUEBUSHEN Decoction and bone impaction grafting for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4706-4711. |
| [15] | Zhou Zhi, Liu Kai-xiang, Xie Yue, Wang Li-ming. Protective effects of low-concentration hydrogen sulfide on rheumatoid joint disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(11): 1659-1664. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||