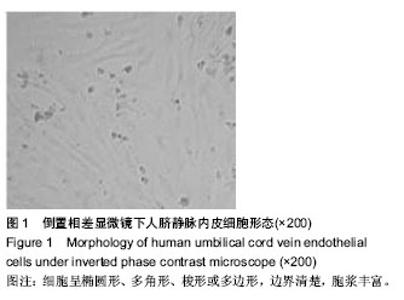
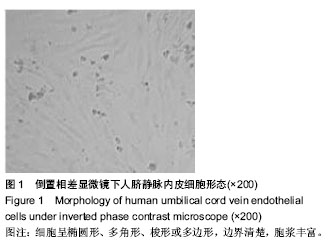
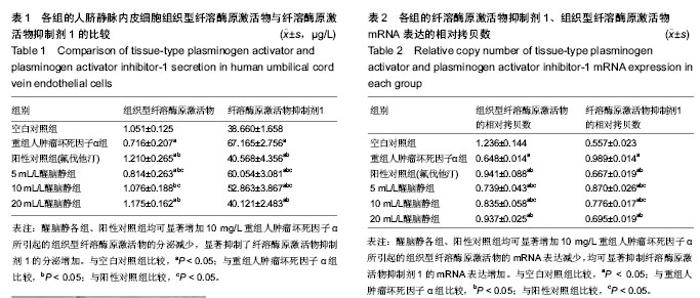
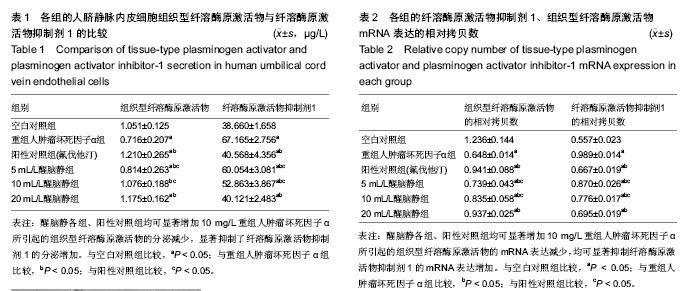
| [1] Marini MG, Sonnino C, Previtero M, et al,Targeting inflammation:impact on atherothrombosis.J Cardiovasc Transl Res.2014;7(1):9-18.
[2] Cho HC,Yu G,Lee MY,et al.TNF-α polymorphisms and coronary artery disease: Association study in the Korean population.Cytokine.2013;62(1):104-109.
[3] Biswas S,Ghoshal PK,Mandal SC,et al.Relation of anti-to pro-inflammatory cytokine ratios with acute myocardial infarction. Korean J Intern Med.2010; 25(1):44-50.
[4] Ku SK,Kim TH,Lee S,et al.Antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activities of isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside and hyperoside. Food Chem Toxicol.2013;53:197-204.
[5] Tian J,Gu X,Sun Y,et al.Effect of statin therapy on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord.2012;12:70.
[6] Bergh N,Larsson P,Ulfhammer E,et al.Effect of shear stress,statins and TNF-a on hemostatic genes in human endothelial cells,Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2012; 420(1):166-171.
[7] Liu L,Zhao SP,Zhou HN,et al.Effect of fluvastatin and valsartan,alone and in combination,on postprandial vascular inflammation and fibrinolytic activity in patients with essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.2007;50(1):50-55.
[8] 欧阳海春,吴沃栋,钟冬梅,等,醒脑静抑制重组人肿瘤坏死因子介导的人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(2):239-242.
[9] 李昶,茹雪莹,吴泰相,等,醒脑静注射液治疗急性脑梗死随机对照试验的系统评价[J].临床荟萃.2013,28(9):1006-1013.
[10] 欧阳海春,吴沃栋,钟冬梅,等.安宫牛黄丸及类方预处理对兔心肌缺血及再灌注损伤保护的作用研究[J].现代医院,2008,7(8),25-28.
[11] 李文杰,陈晞明,吴沃栋,等,醒脑静注射液治疗急性心肌梗死的临床疗效研究[J].中国急救医学,2007,27(8):682-684.
[12] Jaffe EA,Nachman RL,Becker CG,et al.Culture of human endothelial cell derived from umbilical veins.identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest.1973; 52(11):2745-2756.
[13] Bai H,Nangia S,Parmer RJ.The plasminogen activation system and the regulation of catecholaminergic function.J Biomed Biotechnol.2012;2012:721657.
[14] Walter T,Szabo S,Suselbeck T,et al.Effect of atorvastatin on haemostasis, fibrinolysis and inflammation in normocholesterolaemic patients with coronary artery disease:a post hoc analysis of data from a prospective,randomized, double-blind study.Clin Drug Investig.2010;30(7):453-60.
[15] Shantsila E,Montoro-García S,Tapp LD,et al.Fibrinolytic status in acute coronary syndromes:evidence of differences in relation to clinical features and pathophysiological pathways. Thromb Haemost.2012;108(1):32-40.
[16] Robinson R,Ho CE,Tan QS,et al.Fluvastatin downregulates VEGF-A expression in TNF-α-induced retinal vessel tortuosity.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2011;52(10):7423-7431.
[17] Wiesbauer F,Kaun C,Zorn G,et al.HMG CoA reductase inhibitors affect the fibrinolytic system of human vascular cells in vitro: a comparative study using different statins. Br J Pharmacol.2002;135(1):284-292.
[18] Kunieda Y,Nakagawa K,Nishimura H,et al.HMG CoA reductase inhibitor suppresses the expression of tissue factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induced by angiotensin II in cultured rat aortic endothelial cells.Thromb Res.2003; 110(4):227-234.
[19] Dunoyer-Geindre S,Fish RJ,Kruithof EK.Regulation of the endothelial plasminogen activator system by fluvastatin.Role of Rho family proteins,actin polymerisation and p38 MAP kinase.Thromb Haemost.2011;105(3):461-472. |