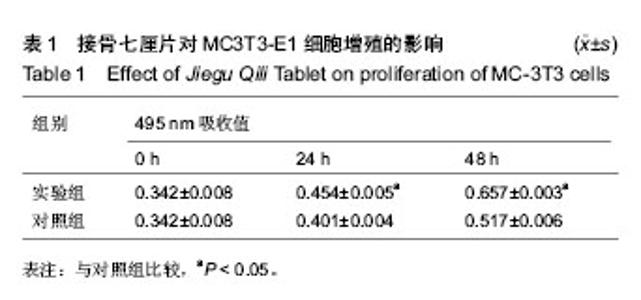
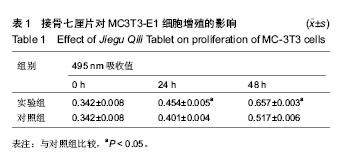
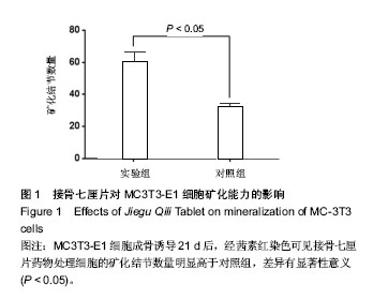
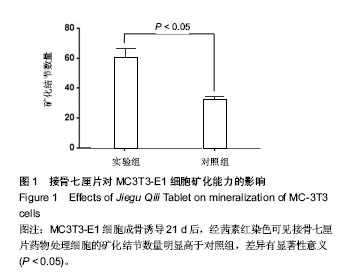
| [1] 胡蕴玉.骨折愈合的分子生物学进展[J].当代医学,2002,8(1): 27-32.
[2] 王慧,李玉坤.成骨细胞分化调控因子研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):377-379.
[3] 于明圣,黄东,刘晓春,等.炎性因子对骨折愈合过程中Runx2信号通道影响的研究进展[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(29): 322-324.
[4] 王保仓,张立峰,于永林,等.骨折愈合研究进展[J].局解手术学杂志, 2003,12(5):374-376.
[5] Manolagas SC, Jilka RL. Bone marrow, cytokines, and bone remodeling. Emerging insights into the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(5):305-311.
[6] Owen TA, Aronow M, Shalhoub V, et al. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vitro: reciprocal relationships in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990;143(3):420-430.
[7] Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, et al. In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J Cell Biol. 1983;96(1): 191-198.
[8] 朱建林,于跃爱,王玉霞.接骨七厘片治疗创伤骨折临床疗效观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2000,8(5):29-30.
[9] 王力,郑甦,杨风云,等.壮筋续骨汤促进大鼠胫骨骨折愈合:RT-PCR法检测核心结合子α1基因表达的验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(20):3678-3681.
[10] 魏合伟,林一峰,曲崇正,等.中药骨康含药血清对骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程中血小板衍生生长因子表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(37):7290-7293.
[11] 杨彦君,熊屹,程志刚,等. 苗药九仙罗汉接骨汤干预胫骨干骨折不同时相点的X射线比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(50): 9311-9315.
[12] 邱宇,高仕长,倪卫东,等. 中药接骨Ⅰ号治疗超声透入桡骨骨折愈合过程中骨形态发生蛋白7的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(15):2781-2785.
[13] 龙涛.接骨七厘片治疗四肢骨折的临床疗效及安全性分析[J].中国处方药,2014,12(4):123.
[14] 李遐方.接骨七厘片治疗胫腓骨下段骨折延迟愈合的临床观察[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(12):10-11.
[15] 罗毅文,段戡.接骨七厘片促进骨折愈合临床实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1997,5(3):13-16.
[16] Tang DZ, Hou W, Zhou Q, et al. Osthole stimulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation by activation of beta-catenin-BMP signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(6): 1234-1245.
[17] Tang DZ, Yang F, Yang Z, et al. Psoralen stimulates osteoblast differentiation through activation of BMP signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;405(2): 256-261.
[18] Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Chang CH, et al. Osthole-mediated cell differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in human osteoblast cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;314(3): 1290-1299.
[19] Hsu YL, Chang JK, Tsai CH, et al. Myricetin induces human osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007; 73(4):504-514.
[20] Hsu YL, Liang HL, Hung CH, et al. Syringetin, a flavonoid derivative in grape and wine, induces human osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009; 53(11):1452-1461.
[21] Kuo PL, Huang YT, Chang CH, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 (BMP-2 and -4) mediates fraxetin-induced maturation and differentiation in human osteoblast-like cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006; 29(1):119-124.
[22] Chang JK, Hsu YL, Teng IC, et al. Piceatannol stimulates osteoblast differentiation that may be mediated by increased bone morphogenetic protein-2 production.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006; 551(1-3):1-9.
[23] Jia TL, Wang HZ, Xie LP, et al. Daidzein enhances osteoblast growth that may be mediated by increased bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) production. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65(5):709-715.
[24] Jørgensen NR, Henriksen Z, Sørensen OH, et al. Dexamethasone, BMP-2, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D enhance a more differentiated osteoblast phenotype: validation of an in vitro model for human bone marrow-derived primary osteoblasts.Steroids. 2004;69(4):219-226.
[25] Spinella-Jaegle S, Roman-Roman S, Faucheu C, et al. Opposite effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-beta1 on osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2001;29(4):323-330.
[26] Kuo PL, Huang YT, Chang CH, et al. Fraxetin inhibits the induction of anti-Fas IgM, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta-mediated apoptosis by Fas pathway inhibition in human osteoblastic cell line MG-63.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006;6(7):1167-1175.
[27] Tang CH, Yang RS, Chien MY, et al. Enhancement of bone morphogenetic protein-2 expression and bone formation by coumarin derivatives via p38 and ERK-dependent pathway in osteoblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;579(1-3):40-49.
[28] 李恒,沈霖,李丽琴,等. 骨折愈合过程中生长因子表达与中药阿胶复方的干预效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(23):4634-4637.
[29] 张继东,祝汉忠,纪晓军,等.壮筋续骨汤对骨折大鼠血清BMP-7和IGF-1水平的影响和意义[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(24):8-10.
[30] 黄有荣,高冠群,杨丽平,等. 白脉软膏对家兔桡骨骨折愈合过程及骨痂骨形态发生蛋白2、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子水平的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(13):112-114.
[31] 王琴,易美彤,曾敏. 愈骨胶囊促进兔骨折愈合的分子机制初探[J].中成药,2013,35(11):2337-2341.
[32] 冯伟,傅文彧,魏义勇,等.单味中药对成骨相关基因表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2004,16(3):6-8.
[33] Frost HM.The biology of fracture healing. An overview for clinicians. Part I. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248):283-293.
[34] Grigor'ev AI, Larina IM, Morukov BV. Calcium metabolism characteristics in microgravity. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 1999;85(6):835-846.
[35] Buckey JC Jr. Preparing for Mars: the physiologic and medical challenges. Eur J Med Res. 1999;4(9):353-356.
[36] 卢国华,查细国.接骨七厘片治疗四肢骨折45例[J].中国药业, 2013,22(4):66-67.
[37] 罗毅文,段戡,刘向前,等.接骨七厘片促进骨折愈合临床实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科,1997,5(3):15-18.
[38] 陈玲,杨云洲,陈继革.接骨七厘片促进大鼠骨折愈合的实验研究[J].湖北中医杂志,2005,27(1):50-52.
[39] 王军跃,成扶真,庹元斌,等.接骨七厘片对实验性骨折愈合的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科,1997,5(2):3-5,67.
[40] 张家军,周保国,张景州,等.接骨七厘片治疗新鲜骨折150例临床观察(一等奖)[J].湖南中医杂志,2000,16(5):44.
[41] 吴华,陈继革,陈超. 接骨七厘片治疗骨折的实验研究[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2003,32(1):92-94,104.
[42] 周铜水,刘晓东,周荣汉.骨碎补对大鼠实验性骨伤愈合的影响[J].中草药,1994,25(5):249.
[43] 宋钦兰.骨碎补、续断、西洋参对成骨细胞MC3T3-E1细胞增殖的影响[J].山东中医药大学学报,2007,31(4):332-333. |