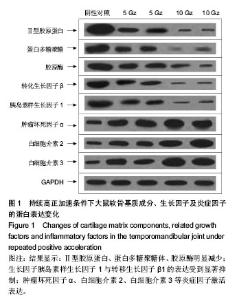
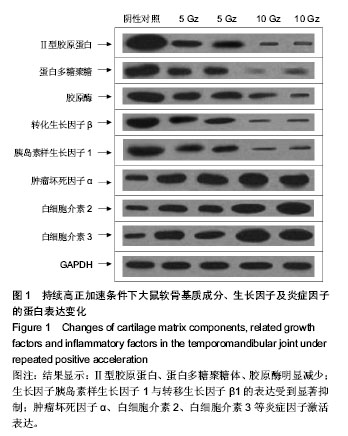
| [1] Krafte DS, Bannon AW.Sodium channels and nociception: recent concepts and therapeutic opportunities.Curr Opin Pharmacol.2008;8(1):50-56.
[2] Chen JT ,Adelson DW, Pecson B. Changes in head withdrawal response to pressure stimuli following induction of acutearthritis in the guineeapig.J Orofac Pain. 1998;12:164.
[3] Chen J, Zhang J, Zhao Y. Hyperalgesia in response to traumatic occlusion and GFAP expression in ratparabrachial [correction of parabranchial] nucleus: modulation with fluorocitrate. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;329(2):231-237.
[4] Ortega AO,Guimarães AS,Ciamponi AL, et al.Frequency of temporomandibular disorder signs in individuals with cerebral palsy.J Oral Rehabil.2008; 35(3):191-195.
[5] Al-Jabrah OA, Al-Shumailan YR.Prevalence of temporomandibular disorder signs in patients with complete versus partial dentures.Clin Oral Investig.2006; 10(3):167-173.
[6] 刘洪臣,刘宁,周继林.老年无牙颌颞颌关节紊乱综合征的特点[J]. 现代口腔医学,1992; 4:198.
[7] 尹音,田慧颖,孙振宇,等.不同机种飞行员飘颌关节病发病情况比较[J].解放军医学杂志,2001.26(7) :517-518.
[8] 刘肖平.现代疼痛学[M].石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社, 1999: 150-159.
[9] 尹音,田慧颖,李东霞,等.空勤人员与地勤人员口腔疾病发病比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2001,11(3):202-205.
[10] Victoria V. findings of a working group on chronic health effects ofsustained high-G exposure. Military Medicine. 1995; 160(1):26.
[11] 孙振宇,胡敏,尹音.持续性高正加速度与颞下颌关节[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2001,04:310-312.
[12] 孙振宇,胡敏,马良.持续性高正加速度重复作用对咀嚼肌的影响分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2002,37(5):327-329.
[13] 孙荃,李恺得,刘磊.人工颞下颌关节的研究进展[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2014,36(4):422-423.
[14] 张婧.持续性高正加速度对大鼠口腔组织影响及丹参多酚酸盐作用研究[D].安徽医科大学,2014.
[15] 胡开进,王大章,李明哲,等. 间接性TMJ 损伤后髁突软骨增殖能力的改变[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,1998 ,8 (4):250-252.
[16] 陈新,熊亚茸,刘洪臣,等.三种模拟咬合板对髁突表面应力影响的比较[J].中国现代实用医学杂志,2005,4(2):27-28.
[17] 陈新,熊亚茸,刘洪臣,等.两种模拟咬合板对髁突表面应力影响的三维有限元研究[J].中国现代临床医学杂志,2005,4(3):24-26.
[18] 邓廉夫,柴本甫,李慧,等. 骨关节炎滑液中肿瘤坏死因子活性检测及滑膜组织超微结构观察[J].中华外科杂志, 1998,36(2): 77-79.
[19] 段丽红,张靖霄,宋春红,等.脐血中胰岛素、胰岛素样生长因子-Ⅰ及胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-2与胎儿生长受限的关系[J].河北医药,2013,35(8):1143-1144.
[20] 裴刘成,赵杰,刘芳,等. 胰岛素样生长因子在PCOS病人卵泡液及颗粒细胞中的表达[J].内蒙古医学院学报,2012,34(3): 225-228.
[21] 张志芳,肖卫华,周未艾. 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白3在疾病诊断与风险评估中的潜在价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(38): 6210-6221.
[22] 贾鹏,赵文国,王勇贵.瘦素对骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨转移生长因子β表达的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2013,30(7): 518-521.
[23] 李奇,华晓萍,邹雅丹,等.转移生长因子β在免疫应答和自身免疫中的作用[J].沈阳医学院学报,2012,14(1): 58-60.
[24] 吕志敢,郭政.肿瘤坏死因子的研究进展[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2006; 37(3):311-314.
[25] 王一蓉,毛海峰,陈嘉勤.虎纹捕鸟蛛毒素对脑缺血模型大鼠海马肿瘤坏死因子凋亡通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(36): 5813-5818.
[26] 李辉.瘦素与肿瘤坏死因子检测在结核性与恶性胸腔积液中的诊断价值[J].当代医学,2012,18(15): 67-68.
[27] 李永忠,闵华,刘超,等.骨关节炎疾病中白细胞介素17协同肿瘤坏死因子α调节诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,18(24): 4393-4412.
[28] 不同类型咬合板对髁突表面应力影响的比较陈新 熊亚茸 刘洪臣 等空军总医院学报2005年第21卷第2期77-80.
[29] 尹音,孙振宇,胡敏,等.持续性高正加速度重复作用对大鼠颞下颌关节的影响[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,2001,12 (2):81-83.
[30] 陈新,刘洪臣,王延荣.单侧咬合接触对颞颌关节髁突应力分布的影响[J].医学临床研究,2010,27(5):769-771.
[31] 尹音,孙振宇, 胡敏.等. 高正加速度对蕞下镊关节影响的动物模型的建立[J].解放军医学杂志,2000,25(6):404.
[32] 柯珂,余云熹.黄芪注射液与白细胞介素2增强树突细胞抗肿瘤转移作用价值比较[J].亚太传统医药,2014,14: 14-16.
[33] 陈晶晶.IL-1及其基因多态性在颞下颌关节紊乱病中的研究[D].天津医科大学,2007.
[34] 尹音, 田慧颖, 胡敏,等.+Gz对颢下颌关节影晌的动物实验模型[J].军医进修学院学报.2001,22(4):265-267.
[35] Pelletier JP, Mart el-Pelletier J .Evidence for the involvement of interleukin-1 in human osteoarthritic cartilage degradation: protective effect of NSAID.J Rheumatology. 1989;18(15): 19-27.
[36] 潘光华,李春洁,李双君.椅旁循证在颞下颌关节骨关节炎治疗中的应用研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2012,34(6):624-626.
[37] 龙星.颞下颌关节疾病的外科治疗[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2013, 23(2): 79-81.
[38] Gedrange T, Luck O, Hesske G,et al.Differential expression of myosin heavy-chain mRNA in muscles of mastication during functional advancement of the mandible in pigs. Arch Oral Biol. 2001;46(3):215-220.
[39] Gedrange T, Lupp A, Kirsch C,et al.Influence of the sagittal advancement of mandibulae on myofibrillar ATPase activity and myosin heavy chain content in the masticatory muscles of pigs. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2002;40(3):277-284.
[40] Zhan H, Dong HJ, Xin YM, et al.Effects of Tea Polyphenols on Cardiac Function and Myocardial Ultrastructure in Rats af2ter repeated +Gz stress. Space Medicine &Medical Engineer. 1999;12(2):79.
[41] Anderson HT. Neck injury sustained during exposure to high-G forces in the F-16B. Aviat Space Environ Med.1988; 59:356 -358.
[42] Hämäläinen O, Toivakka-Hämäläinen SK, Kuronen P. +Gz associated stenosis of the cervical spinal canal in fighter pilots. Aviat Space Environ Med.1999;70(4):330-334.
[43] Ma L, Hu M, Sun ZY. The post-injury regenerating ability of temporomandibular joint of rats exposed to the repeated +Gz forces Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006;41(6): 364-367.
[44] Sun Z, Hu M, Yin Y.Effects of repeated + Gz forces on masticatory muscles. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002 Sep;37(5):327-329.
[45] 胡敏,周继林,洪民,等.小型猪与颞下颌关节实验研究:咀嚼肌解剖、组织学、酶组织化学及超微结构比较[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,1998, (4):264-267.
[46] Abe S,Hiroki E, Iwanuma O, et al.Relationship between function of masticatory muscle in mouse and properties of muscle fibers. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2008;49(2):53-58.
[47] Stauber WT,Miller GR,Juanita G.Adaptation of rat Gastrocnemlus muscles to 2 weeks of centrifugation: Myofibers and extracellular matrix. Aviat Space Environ Med.1998;69 (6 sectionⅡ):A45 - A48.
[48] 马良,孙振宇,胡敏.持续性高正加速度对咀嚼肌纤维酶组织化学特性的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2004,5(2):96-98.
[49] 蒋萍,蔚芃,赵明才.Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白对人软骨细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(30): 4845-4847.
[50] 张猛,周嘉俊,罗宗平.软骨损伤后Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(51): 8305-8307.
[51] 常嘉,马绪臣,马大龙.颞下颌关节骨关节病髁突软骨细胞及基质合成代谢特性的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2004,39(4): 309-312.
[52] 王盛姬,殷新民,胡建.颞下颌关节骨关节病中蛋白多糖的组织化学研究[J].口腔医学,2006,26(4): 257-260. |