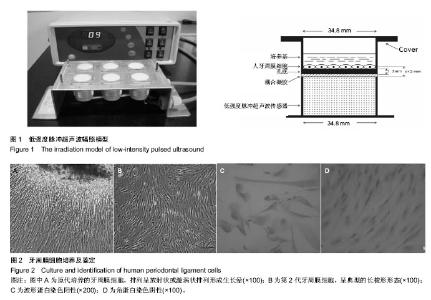
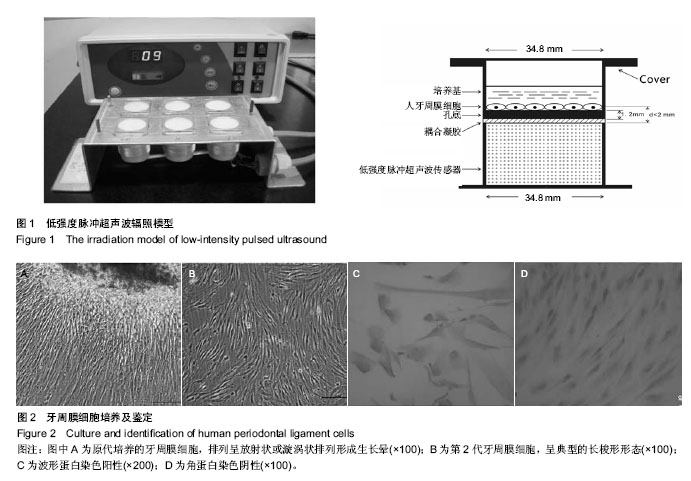
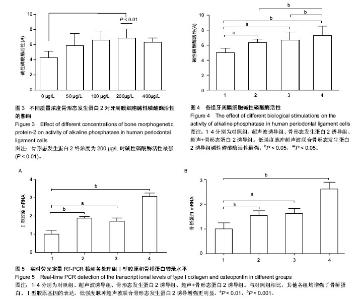
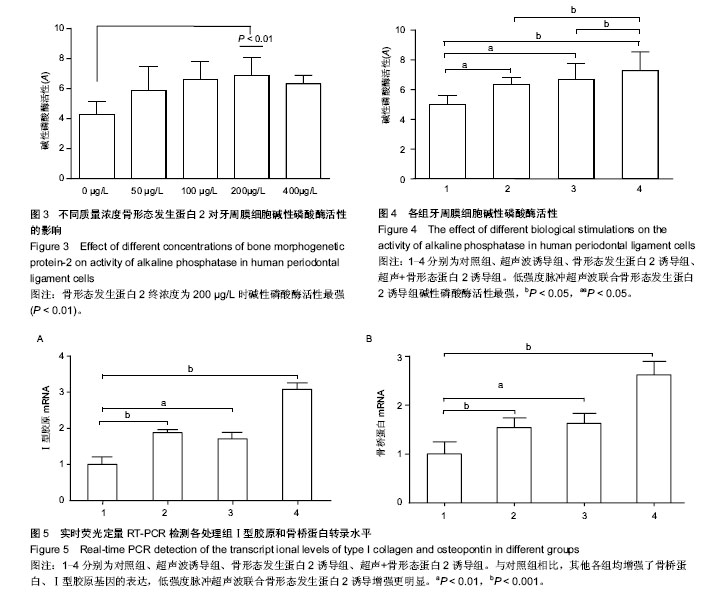
| [1] Mi HW, Lee MC, Fu E, et al. Highly efficient multipotent differentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts induced by combined BMP4 and hTERT gene transfer. Gene Ther.2011;18(5):452-461.
[2] Pitaru S, McCulloch CA, Narayanan SA. Cellular origins anddifferentiation control mechanisms during periodontal development and wound healing. J Periodontal Res. 1994; 29(2): 81-94.
[3] Iwata T, Yamato M, Ishikawa I, et al. Tissue engineering in periodontal tissue. Anat Rec.2014;297(1):16-25.
[4] Hu B,Zhang Y,Zhou J,et al.Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation Facilitates Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. PLoS ONE.2014;9(4):e95168.
[5] E lingling, Xu lulu, Wu xia, et al.The interactions between rASCs, rhBMP-2 and β-TCP play an important role in bone tissue engineering. Tissue Engineering Part A.2010;16(9):2927-2940.
[6] Ferrandis E,Pradhananga S,Touvay C,et al.Immunogenicity, toxicology, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of growth hormone ligand-receptor fusions. Clin Sci.2010; 119(11):483-491.
[7] Rego EB,Takata T,Tanne K,et al.Current Status of Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound for Dental Purposes. Open Dent J .2012;6:220-225.
[8] Romano CL, Romano D, Logoluso N . Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for the treatment of bone delayed union or nonunion: a review. Ultrasound Med Biol.2009; 35(4):529-536.
[9] Ikai H, Tamura T, Watanabe T, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates periodontal wound healing after flap surgery. J Periodontal Res.2008;43(2):212-216.
[10] 高翔,宋锦璘,邓锋,等.低强度脉冲超声波联合引导骨再生术对Beagle犬牙周骨开窗缺损修复效应的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2012,31(6):895-901.
[11] Zhao M,Xiao G,Berry JE,et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 induces dental follicle cells to differentiate toward a cementoblast/osteoblast phenotype. J Bone Miner Res. 2002; 17(8):1441-1451.
[12] Ren L, Yang Z, Song J, et al. Involvement of p38 MAPK pathway in low intensity pulsed ultrasound induced osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Ultrasonics.2013;539(3):686-690. |