Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (14): 2244-2249.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.14.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Placental hematopoietic stem cells: from basic research to clinical applications
Mo Zheng, Zhang Bin, Chen Hu
- Department of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, the 307 Hospital of PLA, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100071, China
-
Received:2014-01-26Online:2014-04-02Published:2014-04-02 -
Contact:Zhang Bin, M.D., Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, the 307 Hospital of PLA, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100071, China Corresponding author: Chen Hu, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Department of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, the 307 Hospital of PLA, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100071, China -
About author:Mo Zheng, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, the 307 Hospital of PLA, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100071, China -
Supported by:The “863 Projects” of Ministry of Science and Technology of China, No. 2013AA020103; Military Clinical High-Tech Key Program, No. 2010gxjs100
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mo Zheng, Zhang Bin, Chen Hu . Placental hematopoietic stem cells: from basic research to clinical applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(14): 2244-2249.
share this article
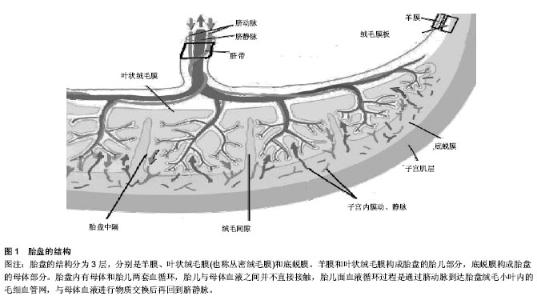
2.1 造血干细胞的胚胎起源 在胚胎形成过程中,受精卵经最初几次有丝分裂后产生胚胎干细胞,这是一种能在体外培养并且高度未分化的全能干细胞,具有向各种组织细胞分化的潜能。在胎儿造血系统的发育过程中,最先出现的是来自胚胎干细胞的成血-血管细胞[1]。该细胞的存在已经证实,但目前尚未建立起分离纯化技术[2]。随后成血-血管细胞又可向成血管细胞和造血干细胞分化[3]。但是,Lancrin等[4]认为,小鼠胚胎的成血-血管细胞先向生血内皮发育,再由生血内皮生成造血干细胞。造血干细胞是造血系统细胞的鼻祖,它具有向各种髓系细胞和淋巴系细胞发育的潜能,也具有自我更新能力,可通过移植重建造血和免疫系统[5]。 2.2 人类胎盘的发生、结构与功能 人类胚胎包括胎盘发育先后经历受精、卵裂、胚泡形成与植入、三胚层分化、器官发育等复杂过程,胚胎发育过程中伴随着胎盘的发生。胚泡植入子宫后数小时,滋养细胞分化,外层融合形成合体滋养细胞,内层为细胞滋养细胞。在以后的5周内,胎盘胎儿循环逐渐建立,绒毛形成,绒毛可分为游离绒毛、锚状固定于母体蜕膜的固定绒毛及绒毛外的细胞滋养细胞。妊娠10周左右,由合体细胞滋养细胞、细胞滋养细胞、结缔组织及胎儿毛细血管内皮组成的胎盘屏障形成。妊娠16-20周,绒毛外的细胞滋养细胞完成对子宫螺旋小动脉的侵蚀,并部分代替内皮细胞。妊娠中期,细胞滋养细胞逐渐消失,合体细胞滋养细胞层变薄,使胎盘两侧母儿物质交换更加便利。 胎盘分为胎儿面和母体面(图1),胎盘的胎儿面光滑,覆盖一层透明的羊膜,是胎盘的最内层;母体面粗糙,是剥离后的底蜕膜,由不规则的浅沟将其分成15-30个胎盘小叶。胎盘的结构分为3层,分别是羊膜、叶状绒毛膜(也称丛密绒毛膜)和底蜕膜。羊膜和叶状绒毛膜构成胎盘的胎儿部分,底蜕膜构成胎盘的母体部分。胎盘是子宫所包绕的最重要的器官之一,在怀孕期间发挥多种功能,包括供能,排除废弃物,分泌及免疫调节作用,也可以产生大量激素、生长因子、细胞因子及转录因子,因此对于胚胎的存活及生长至关重要。 2.3 胎盘造血及胎盘中造血干/祖细胞的发现 哺乳动物体内全部血细胞均来源于胚胎时期产生的造血干细胞[6]。胚胎期造血分为原始造血和永久造血,后者以多时间点和连续性为主要特征[7]。原始造血是血细胞发育的最早阶段,在小鼠胚胎7.5 d(人胚16 d)首先见于胚外的卵黄"
| [1] Huber TL, Kouskoff V, Fehling HJ,et al. Haemangioblast commitment is initiated in the primitive streak of the mouse embryo.Nature. 2004;432(7017):625-630. [2] Lacaud G, Robertson S, Palis J,et al. Regulation of hemangioblast development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;938: 96-107. [3] Doetschman TC, Eistetter H, Katz M,et al. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985;87:27-45. [4] Lancrin C, Sroczynska P, Stephenson C,et al.The haemangioblast generates haematopoietic cells through a haemogenic endothelium stage.Nature. 2009;457(7231): 892-895. [5] Marshall CJ, Thrasher AJ.The embryonic origins of human haematopoiesis.Br J Haematol. 2001;112(4):838-850. [6] Lee LK, Ueno M, Van Handel B, et al.Placenta as a newly identified source of hematopoietic stem cells.Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(4):313-318. [7] Dzierzak E, Speck NA.Of lineage and legacy: the development of mammalian hematopoietic stem cells.Nat Immunol. 2008;9(2):129-136. [8] Orkin SH, Zon LI.Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology.Cell. 2008;132(4):631-644. [9] Klimchenko O, Mori M, Distefano A,et al. A common bipotent progenitor generates the erythroid and megakaryocyte lineages in embryonic stem cell-derived primitive hematopoiesis. Blood. 2009;114(8):1506-1517. [10] Peeters M, Ottersbach K, Bollerot K,et al.Ventral embryonic tissues and Hedgehog proteins induce early AGM hematopoietic stem cell development.Development. 2009; 136(15):2613-2621. [11] Cumano A, Godin I.Ontogeny of the hematopoietic system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:745-785. [12] Chen S, Liu S, Xu L,et al.The characteristic expression pattern of BMI-1 and SALL4 genes in placenta tissue and cord blood.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(2):49. [13] Kataoka K, Sato T, Yoshimi A,et al. Evi1 is essential for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal, and its expression marks hematopoietic cells with long-term multilineage repopulating activity.J Exp Med. 2011;208(12):2403-2416. [14] Till JE, McCulloch EA.A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells.Radiat Res. 1961;14:213-222. [15] Dancis J, Jansen V, Brown GF,et al.Treatment of hypoplastic anemia in mice with placental transplants.Blood. 1977; 50(4): 663-670. [16] 刘玉峰,张永卓,张传新,等.人胎盘组织源造血干/祖细胞的初步研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2006,14(1):98-101. [17] 周胜利,宋剑秋,旭日.胎盘组织及血液中含有丰富的造血干/祖细胞[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2002,10(2):142-147. [18] Wang Y, Nathanson L, McNiece IK.Differential hematopoietic supportive potential and gene expression of stroma cell lines from midgestation mouse placenta and adult bone marrow. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(5):707-726. [19] Zeigler BM, Sugiyama D, Chen M,et al.The allantois and chorion, when isolated before circulation or chorio-allantoic fusion, have hematopoietic potential.Development. 2006; 133(21):4183-4192. [20] Corbel C, Salaün J, Belo-Diabangouaya P,et al. Hematopoietic potential of the pre-fusion allantois.Dev Biol. 2007;301(2):478-488. . [21] Rhodes KE, Gekas C, Wang Y,et al.The emergence of hematopoietic stem cells is initiated in the placental vasculature in the absence of circulation.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(3):252-263. [22] Chen MJ, Yokomizo T, Zeigler BM,et al.Runx1 is required for the endothelial to haematopoietic cell transition but not thereafter.Nature. 2009;457(7231):887-891. [23] Sugiyama D, Inoue-Yokoo T, Fraser ST,et al.Embryonic regulation of the mouse hematopoietic niche. Scientific World J. 2011;11:1770-1780. [24] Sasaki T, Mizuochi C, Horio Y,et al.Regulation of hematopoietic cell clusters in the placental niche through SCF/Kit signaling in embryonic mouse.Development. 2010; 137(23):3941-3952. [25] Chhabra A, Lechner AJ, Ueno M,et al.Trophoblasts regulate the placental hematopoietic niche through PDGF-B signaling. Dev Cell. 2012;22(3):651-659. [26] Su?man S, Sori??u O, Rus-Ciuc? D,et al.Placental stem cell differentiation into islets of Langerhans-like glucagon- secreting cells.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010; 51(4):733-738. [27] 章涛,陈代雄,方宁,等.人胎盘组织造血干/祖细胞的分离富集[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2006,14(5):955-958. [28] Tsagias N, Koliakos I, Lappa M,et al.Placenta perfusion has hematopoietic and mesenchymal progenitor stem cell potential. Transfusion. 2011;51(5):976-985. [29] Gekas C, Rhodes KE, Van Handel B,et al.Hematopoietic stem cell development in the placenta.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7): 1089-1098. [30] 王敬龙,金巨楼,杜冰,等.胎盘源间充质干细胞的分子生物学特性[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2013,3(1):27-30. [31] 韩之波,王有为,王涛,等.人胎盘底蜕膜间充质干细胞的分离及其生物学特性研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(3):754-759. [32] 刘丽,黎渊明,刘琴,等.三种胎盘间充质干细胞的分离培养及生物学特性对比研究[J].中国热带医学,2012,12(12):1528-1529. [33] Ottersbach K, Dzierzak E.The placenta as a haematopoietic organ.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7):1099-1106. [34] Robin C, Ottersbach K, Boisset JC,et al.CD41 is developmentally regulated and differentially expressed on mouse hematopoietic stem cells.Blood. 2011;117(19): 5088-5091. [35] 陈冬波. CD43表达与造血干细胞发育的相关性研究[D].北京:解放军军事医学科学院, 2011. [36] Bárcena A, Muench MO, Kapidzic M,et al.Human placenta and chorion: potential additional sources of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation.Transfusion. 2011;51 Suppl 4: 94S-105S. [37] 《中国组织工程研究与临床康复》杂志社学术部.造血干细胞移植的临床应用:现状与概况及未来[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(1):140-141. [38] 张永卓.人胎盘组织源造血干/祖细胞的初步研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2005. [39] Miki T.Amnion-derived stem cells: in quest of clinical applications.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;2(3):25. [40] 章涛,方宁,陈代雄,等.人胎盘组织来源造血干/祖细胞及其特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(21):4172-4176. [41] Robin C, Bollerot K, Mendes S,et al. Human placenta is a potent hematopoietic niche containing hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells throughout development.Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(4):385-395. [42] Murphy SV, Atala A. Amniotic fluid and placental membranes: unexpected sources of highly multipotent cells.Semin Reprod Med. 2013;31(1):62-68. [43] 张瑞锋,吴金英,姚金凤,等.间充质干细胞的来源[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(15):2968-2970. [44] 耿娟娟,崔勇,邱书奇.羊膜上皮细胞的体外培养及干细胞特性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2012, 28(2):172-174. [45] Parolini O, Alviano F, Bergwerf I,et al.Toward cell therapy using placenta-derived cells: disease mechanisms, cell biology, preclinical studies, and regulatory aspects at the round table.Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(2):143-154. [46] 喻晓丹.人胎盘AC133+造血干/祖细胞的集落形成能力[J]. 遵义师范学院学报,2013,15(3): 83-86. [47] 丁红芳,丁慧芳,高欣义,等.胎盘间充质干细胞治疗大鼠缺氧缺血性脑病的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(5):711-714. [48] 韩忠朝.胎盘间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足安全有效[J].中华医学信息导报,2012,27(22):19. [49] 彭海林,苗宗宁,蒋霖,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞移植治疗局灶性脑缺血[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(3):477. [50] 肖振勇,卢国辉,殷志林,等.人胎盘底蜕膜间充质干细胞抗炎特性对帕金森病模型大鼠的神经保护作用[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2013,12(5):448-453. [51] 杨立枫,刘伟,周晔,等.人胎盘来源间充质干细胞移植促进肌腱移植物在骨隧道内的愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(49): 8539-8544. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||