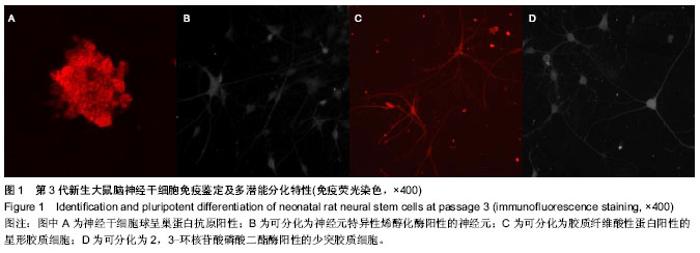
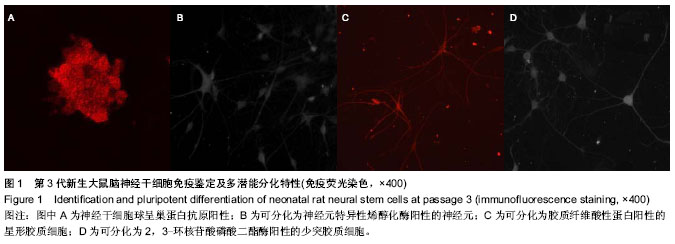
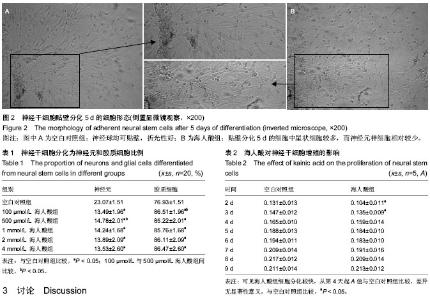
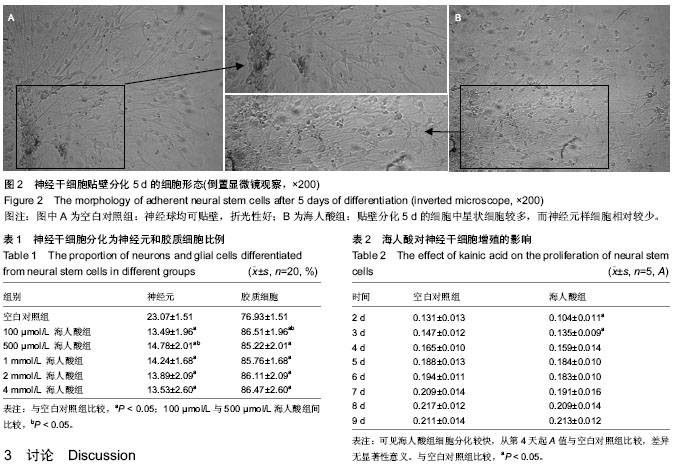
| [1] Nochi R, Kato T, Kaneko J,et al. Involvement of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling in activity-related proliferation of adult hippocampalneural stem cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2012; 36(3):2273-2283.
[2] Bunk EC, König HG, Bonner HP, et al.NMDA-induced injury of mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures triggers delayed neuroblast proliferation in the dentate gyrus: an in vitro model for the study of neural precursor cell proliferation. Brain Res. 2010;1359:22-32.
[3] Ciceroni C, Mosillo P, Mastrantoni E, et al. mGLU3 metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate the differentiation of SVZ-derived neural stem cells towards the astrocytic lineage. Glia. 2010;58(7):813-822.
[4] Kantrowitz JT, Javitt DC. N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor dysfunction or dysregulation: the final common pathway on the road to schizophrenia? Brain Res Bull. 2010; 83(3-4):108-121.
[5] Yamashita T, Ninomiya M, Hernandez Acosta P, et al. Subventricular zone-derived neuroblasts migrate and differentiate into mature neurons in the post-stroke adult striatum. J Neurosci. 2006;26(24):6627-6636.
[6] Tania Aguado, Eva Romero, Krisztina Monory, et al. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediates excitotoxicity-induced neural progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis. Biol Chem. 2007; 282:23892-23898.
[7] Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, et al. Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc Natl Aead Sci.2001;98: 4710-4715.
[8] Jin K, Peel AL, Mao XO, et al. Increased hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(1):343-347.
[9] Azami Tameh A, Clarner T, et al. Regional regulation of glutamate signaling during cuprizone-induced demyelination in the brain. Ann Anat. 2013;195(5):415-423.
[10] Gu N, Jackson J, Goutagny R, et al.NMDA-dependent phase synchronization between septal and temporal CA3 hippocampal networks. J Neurosci. 2013;33(19):8276-8287.
[11] Kim HJ, Kim TH, Choi SJ, et al. Fluoxetine suppresses synaptically induced[Ca2+]i spikes and excitotoxicity in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 2013;1490: 23-34.
[12] Gibson CJ, Meyer RC, Hamm RJ. Traumatic brain injury and the effects of diazepam, diltiazem, and MK-801 on GABA-A receptor subunit expression in rat hippocampus. J Biomed Sci. 2010;17(1): 38.
[13] Shacka JJ, Lu J, Xie ZL, et al. Kanic acid induces early and transient autophagic stress in mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2007; 414(1):57-60.
[14] Koga K, Sim SE, Chen T,et al. Kainate receptor-mediated synaptic transmissions in the adult rodent insular cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2012;108(7):1988-1998.
[15] Meade AJ, Meloni BP, Mastaglia FL, et al. AP-1 inhibitory peptides attenuate in vitro cortical neuronal cell death induced by kainic acid. Brain Res. 2010;1360:8-16.
[16] Sun Y, Jin K, Childs JT, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B ( VEGFB ) stimulates neurogenesis: evidence from knockout mice and growth factor administration. Dev Biol. 2006;289(2):329-335.
[17] Li Hua, Chen ZJ, Zhou SP. Apoptos,s in glioma-bearing rats after neural stem cell transplantation. Neural Regeneration Research. 2013,8(19):1793-1802.
[18] 张军,张琰君,贾云嶂,等. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对放射性诱导小鼠C17.2神经干细胞凋亡的影晌[J].神经解剖学杂志,2014, 30(1):98-102.
[19] 邓鑫,宋来君,郭新宾.血管内皮生长因子165对神经干细胞生长及分化的影响[J].中华脑科疾病与康复杂志(电子版),2013,3(3): 23-26.
[20] 张君度,龙大宏,陈艳,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子诱导神经干细胞分化过程中bHLH转录因子的表达变化[J].解剖学研究, 2013, 35(6):427-430.
[21] Sharma S, Rakoczy S, Dahlheimer K, et al.The hippocampus of Ames dwarf mice exhibits enhanced antioxidative defenses following kainic acid-induced oxidative stress. Exp Gerontol. 2010;45(12):936-949.
[22] Spaethling J, Le L, Meaney DF. NMDA receptor mediated phosphorylation of GluR1 subunits contributes to the appearance of calcium-permeableAMPA receptors after mechanical stretch injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46(3):646-654.
[23] Lee KH, Cho JH, Choi IS, et al. Pregnenolone sulfate enhances spontaneous glutamate release by inducing presynaptic Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release. Neuroscience. 2010;171(1):106-116.
[24] Santiago AR, Carvalho CM, Carvalho AP, et al. Differential contribution of L-, N-, and P/Q-type calcium channels to [Ca2+]i changes evoked by kainate in hippocampal neurons. Neurochem Res, 2008;33(8):1501-1508.
[25] Pilli J, Kumar SS. Triheteromeric N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors differentiate synaptic inputs onto pyramidal neurons in somatosensory cortex: involvement of the GluN3A subunit. Neuroscience. 2012;222:75-88.
[26] Tsang SW, Vinters HV, Cummings JL, et al. Alterations in NMDA receptor subunit densities and ligand binding to glycine recognition sites are associated with chronic anxiety in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29(10): 1524-1532.
[27] Rangel A, Burgaya F, Gavín R, et al. Enhanced susceptibility of Prnp-deficient mice to kainate-induced seizures, neuronal apoptosis, and death: Role of AMPA/kainate receptors. J Neurosci Res. 2007 ;85(12):2741-2755.
[28] Li Y, Chopp M. Temporal profile of nestin expression after focal cerebralischemia in adult rat. Brain Res. 1999;838 (1-2): 1-10.
[29] Panaqiotakos G, ALshamy G, Chan B, et al. Long-term impact of radiation on the stem cell and oligodendrocyte precursors in the brain. PLoS ONE. 2007;2(7): e588.
[30] Ruocco LA, Gironi Carnevale UA, Sica A, et al. Differential prepuberal handling modifies behaviour and excitatory amino acids in the forebrain of the Naples High-Excitability rats. Behav Brain Res. 2009;198(1):29-36.
[31] Daadi MM, Davis AS, Arac A,et al. Human neural stem cell grafts modify microglial response and enhance axonal sprouting in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 2010;41(3):516-523.
[32] Csoknya M, Dénes V, Wilhelm M. Glial cells in the central nervous system of earthworm, Eisenia fetida.Acta Biol Hung. 2012;63 Suppl 1:114-128.
[33] Sivakumar V, Ling EA, Lu J, et al. Role of glutamate and its receptors and insulin-like growth factors in hypoxia induced periventricular white matter injury.Glia. 2010;58(5):507-523.
[34] Park DH, Eve DJ, Sanberg PR, et al. Increased neuronal proliferation in the dentate gyrus of aged rats following neural stem cell implantation. Stem Cells Dev.2010;19(2):175-180.
[35] Daadi MM, Davis AS, Arac A, et al. Human neural stem cell grafts modify microglial response and enhance axonal sprouting in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 2010 ;41(3):516-523. |