Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (14): 2153-2158.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.14.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of different storage solutions on the viability of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Zhou Nan1, Chen Yan2, Lei Xin1, Dong Yan-ting1, Xu Wen-jing1, Niu Yu-hu1, Niu Bo3, Cheng Niu-liang1
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Department of Biotechnology, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing 100020, China
-
Received:2014-01-26Online:2014-04-02Published:2014-04-02 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Cheng Niu-liang, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Corresponding author: Niu Bo, M.D., Doctoral supervisor, Department of Biotechnology, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing 100020, China -
About author:Zhou Nan, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Nan, Chen Yan, Lei Xin, Dong Yan-ting, Xu Wen-jing, Niu Yu-hu, Niu Bo, Cheng Niu-liang . Effects of different storage solutions on the viability of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(14): 2153-2158.
share this article
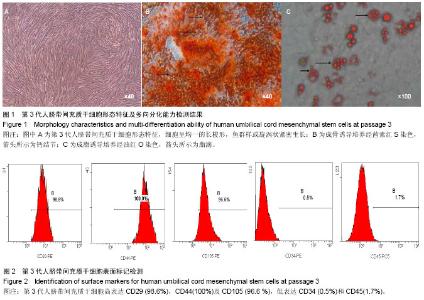
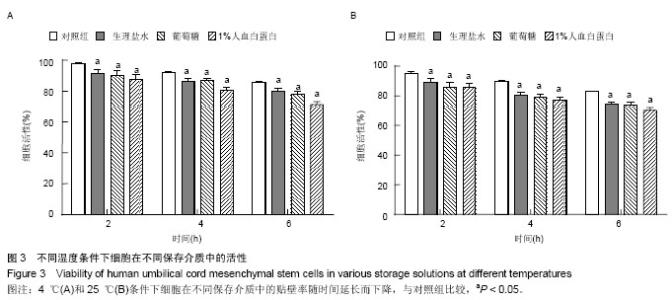
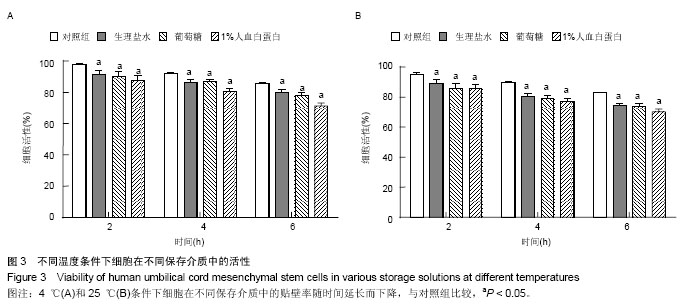
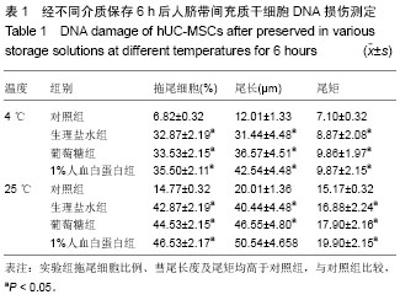
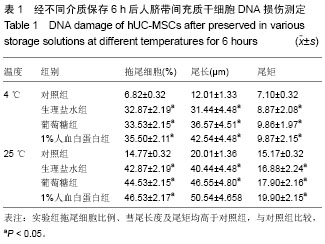
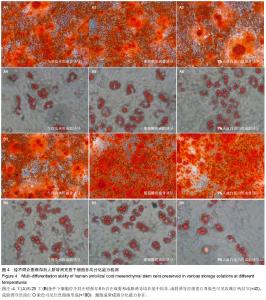
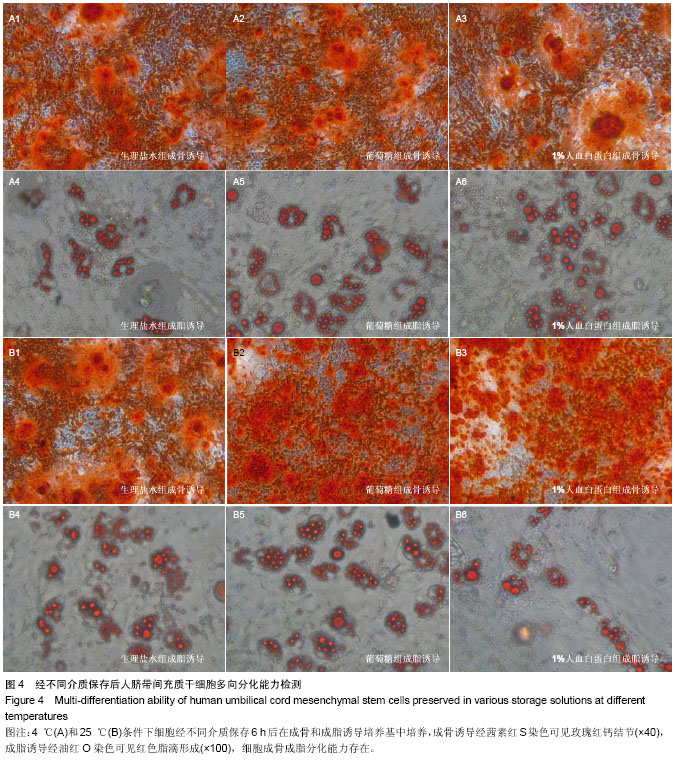
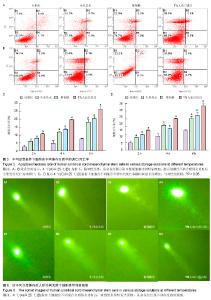
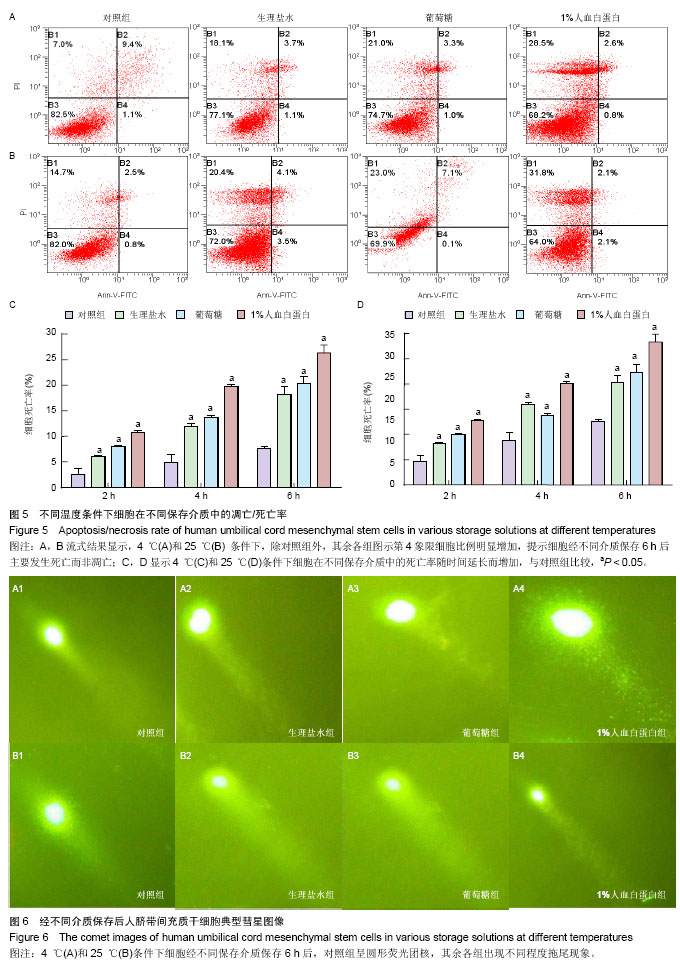
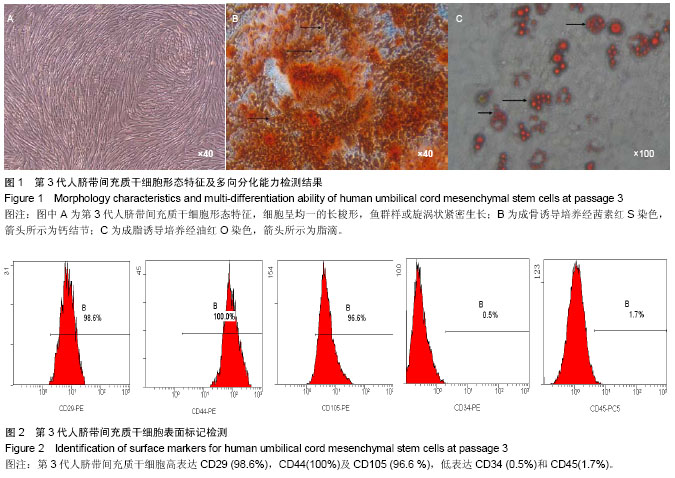
2.1 人脐带间充质干细胞形态学观察结果 倒置显微镜下观察,改良酶消化法分离脐带间充质干细胞培养12 h即见散在的长梭形贴壁细胞。原代脐带间充质干细胞融合率达80%-90%后传代培养,细胞形态趋于一致,呈鱼群样或漩涡状生长,贴壁紧密(图1A)。 2.2 人脐带间充质干细胞表面标记检测结果 流式细胞仪免疫表型鉴定结果显示(图2),分离培养的脐带间充质干细胞第3代细胞高表达基质细胞与干细胞标记CD29、CD 44与CD105,阳性率不低于95%;低表达内皮与造血干细胞标记CD34与CD45,阳性率不高于2%。 2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞多向分化能力 第3代脐带间充质干细胞在成骨细胞诱导培养基中培养23 d后,经茜素红S染色,胞浆中可见大量玫瑰红色钙结节形成(图1B);在成脂细胞诱导培养基中培养16 d后,经油红O染色呈阳性,胞浆内可见红色脂滴形成(图1C)。 2.4 不同保存介质在不同温度及不同时间点对脐带间充质干细胞活性的影响 将消化获得的脐带间充质干细胞重悬于完全培养基、生理盐水、5%葡萄糖和生理盐水+1%人血白蛋白,在4 ℃或25 ℃条件下,各组细胞活性均呈时间依赖性下降,较对照组相比,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。4 ℃条件下保存6 h,除对照组外仅生理盐水组可保持80%的细胞活性;室温组(25 ℃)保存6 h后,各组细胞活性均低于80%,远达不到临床应用的保存效果(图3)。 2.5 不同保存介质对脐带间充质干细胞多向分化能力的影响 在4 ℃和25 ℃条件下,第3代脐带间充质干细胞经不同介质保存6 h后,各组仍可贴壁的细胞依旧存在向成骨细胞和成脂细胞方向分化的能力(图4)。 2.6 不同保存介质在不同温度及不同时间点对脐带间充质干细胞凋亡/死亡率的影响 在4 ℃与25 ℃条件下保存6 h后,不同保存介质主要引起细胞不同程度的坏死而非凋亡(图5A,B)。各组间死亡率也呈时间依赖性,随时间延长死亡率增加,与对照组相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,图5C,D),进一步验证了不同保存介质对脐带间充质干细胞活性的影响。 2.7 不同保存介质在不同温度条件下对脐带间充质干细胞 DNA损伤的影响 对照组脐带间充质干细胞在4 ℃和25 ℃条件下保存6 h后细胞核均未出现明显拖尾现象,电泳后核DNA依然停留在核基质中,呈完整的圆形荧光团;其余各组细胞核DNA解旋,电泳时发生迁移,呈现不同程度的拖尾现象(图6)。数据分析结果显示各实验组拖尾细胞比例、彗尾长度及尾矩均高于对照组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,表1)。"
| [1] Eggenhofer E, Steinmann JF, Renner P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells together with mycophenolate mofetil inhibit antigen presenting cell and T cell infiltration into allogeneic heart grafts.Transplant Immunol.2011;24(3):157-163. [2] Li Lin, Tian Hui, Yue Weiming, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells play a dual role on tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol.2011;226(7):1860-1867. [3] Wu KH, Chan CK, Tsai C, et al. Effective treatment of severe steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease with umbilical cordderived mesenchymal stem cells. Transplantation. 2011; 91: 1412-1416. [4] Chen A, Siow B, Blamire AM,et al.Transplantation of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in a model of perinatal brain injury. Stem Cell Res.2010;5(3):255-266. [5] Lim JY, Park SI, Kim SM, et al.Neural differentiation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-expressing human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in culture via TrkB-mediated ERK and-catenin phosphorylation and following transplantation into the ceveloping brain. Cell Transplant.2011;11(12):1855-1866. [6] da Silva Meirelles L, Chagastelles PC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal organs and tissues. J Cell Sci.2006; 119(Pt11): 2204-2213. [7] Krampera M, Sartoris S, Liotta F, et al. Immune regulation by mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult spleen and thymus. Stem Cells.2007;16(5):797-810. [8] Tsai MS, Hwang SM, Chen KD, et al. Functional network analysis of the transcriptomes of mesenchymal stem cells derived from amniotic fluid, amniotic membrane, cord blood, and bone marrow. Stem Cells.2007;25(10):2511-2523. [9] Fridenshte?n AIa, Piatetski?-Shapiro II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol.1969; 56: 3-11. [10] Stolzing A,Jones E,McGonagle D,et al.Age-related changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: consequences for cell therapies. Mech Ageing Dev.2008; 129(3): 163-173. [11] Meyer T, Pfeifroth A, Höcht B.Isolation and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord: potent cells for cell-based therapies in paediatric surgery?Eur Surg.2008;40(5):239-244. [12] Mohyeddin-Bonab M, Mohamad-Hassani MR, Alimoghaddam K,et al. Autologous in vitro expanded mesenchymal stem cell therapy for human old myocardial infarction. Arch Iran Med.2007;10(4):467-473. [13] Müller I, Kordowich S, Holzwarth C, et al. Application of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in pediatric patients following allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Blood Cells Mol Dis.2008;40(1):25-32. [14] Troyer DL,Weiss ML. Wharton’s jelly-derived cell are a primitive stromal cell population. Stem cell.2008; 26(3): 591-599. [15] Venkataramana NK, Kumar SK, Balaraju S, et al. Open-labeled study of unilateral autologous bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in Parkinson's disease. Transl Res.2010 ;155(2):62-70. [16] Wang D, Zhang F, Shen W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell injection ameliorates the inducibility of ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction in rats. Int J Cardiol.2011;152(3): 314-320. [17] Mohamadnejad M, Alimoghaddam K, Mohyeddin-Bonab M, et al. Phase 1 trial of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. Arch Iran Med.2007;10(4):459-466. [18] Mohyeddin-Bonab M,Mohamad-Hassani MR,et al.Autologous in vitro expanded mesenchymal stem cell therapy for human old myocardial infarction. Arch Iran Med. 2007 ;10(4):467-473. [19] Song H, Cha MJ, Song BW, et al.Reactive oxygen species inhibit adhesion of mesenchymal stem cells implanted into ischemic myocardium via interference of focal adhesion complex. Stem Cells.2010; 28(3): 555-563. [20] 雷鑫,陈彦,张建林,等.评价脐带间充质干细胞移植前细胞活性的指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(32):5847-5854. [21] Sarugaser R, Lickorish D, Baksh D,et al.Human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells: a source of mesenchymal progenitors. Stem Cells.2005;23(2): 220-229. [22] Chen Y, Yu B, Xue G, et al. Effects of storage solutions on the viability of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for transplantation. Cell Transplant.2013;22(6):1075-1086. [23] Sohn HS, Heo JS, Kim HS, et al. Duration ofin vitro storage affects the key stem cell features of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical transplantation.Cytotherapy. 2013; 15: 460-466. [24] Lane TA, Garls D, Mackintosh E, et al. Liquid storage of marrow stromal cells. Transfusion. 2009; 49(7): 1471-1481. [25] Pal R, Hanwate M, Totey SM. Totey, Effect of holding time, temperature and different parenteral solutions on viability and functionality of adult bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells before transplantation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(7):436-444. [26] Cramer C, Freisinger E, Jones RK,et al. Persistent High Glucose Concentrations Alter the Regenerative Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells.2010;19(12): 1875-1884. [27] Schop D, Janssen FW, van Rijn LD,et al.Growth, metabolism, and growth inhibitors of mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A.2009 ;15(8):1877-1886. [28] Stolzing A,Coleman N,Scutt A.Glucose-induced replicative senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Rejuvenation Res. 2006;9(1):31-35. [29] Matejtschuk P, Dash CH, Gascoigne EW.Production of human albumin solution: a continually developing colloid. Br J Anaesth.2000;85(6):887-895. [30] Javazon EH, Beggs KJ , Flake AW. Mesenchymal stem cells: paradoxes of passaging. Exp Hematol.2004; 32(5):414-425. [31] Karlsson HL.The comet assay in nanotoxicology research. Anal Bioanal Chem.2010; 398(2): 651-666. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||