Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1755-1767.doi: 10.12307/2026.640
Previous Articles Next Articles
Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis
Han Teng1, Ma Hong1, Yang Ruoyi1, Luo Yi2, Li Chao1, 3
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, and Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Thyroid-Oral and Maxillofacial Head and Neck Surgery, Sichuan Cancer Clinical Medical Research Center, Sichuan Cancer Hospital · Research Institute, Sichuan Cancer Prevention and Control Center, Tumor Hospital Affiliated to University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2025-01-02Revised:2025-07-03Accepted:2025-07-14Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-20 -
Contact:Li Chao, MD, Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, and Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Thyroid-Oral and Maxillofacial Head and Neck Surgery, Sichuan Cancer Clinical Medical Research Center, Sichuan Cancer Hospital · Research Institute, Sichuan Cancer Prevention and Control Center, Tumor Hospital Affliated to University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Han Teng, Master candidate, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, and Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, No. 2023NSFSC1501, 2024ZYD0051, 2024YFHZ0215 (to LC); National Key Laboratory for the Prevention and Treatment of Oral Diseases, No. SKLOD2024OF02 (to LC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
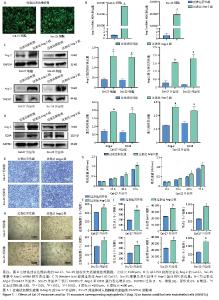
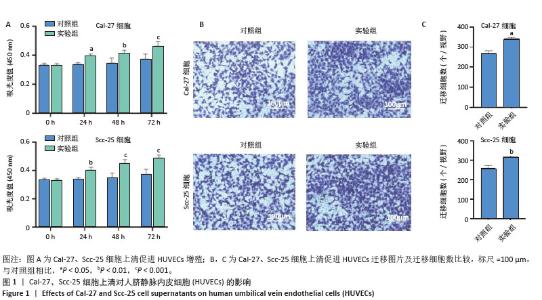
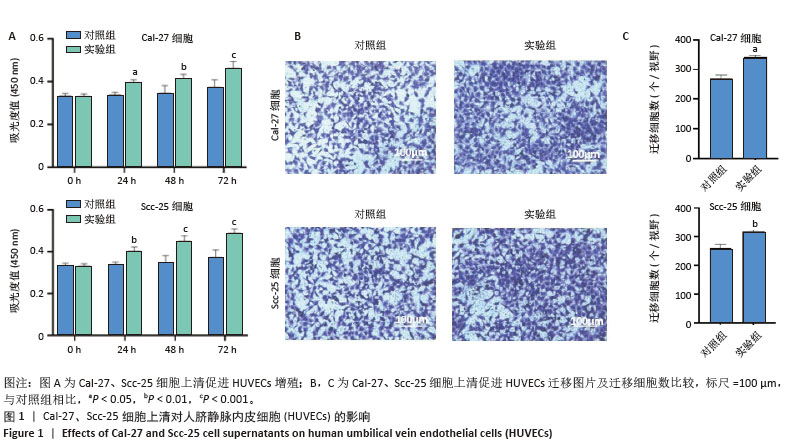
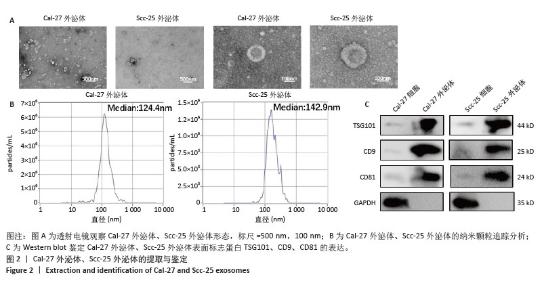
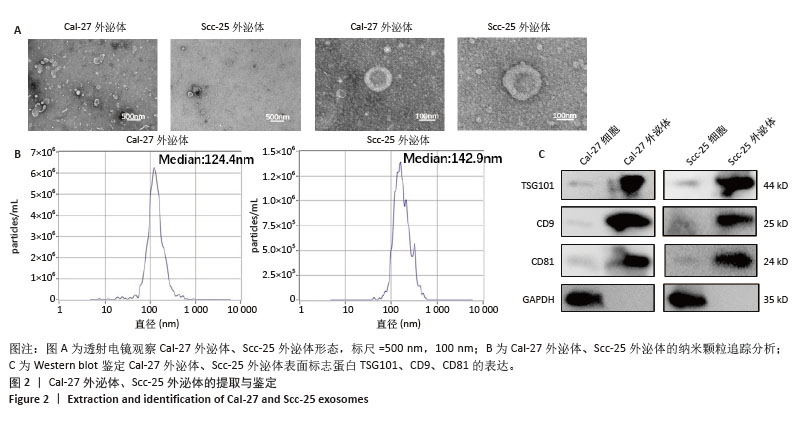
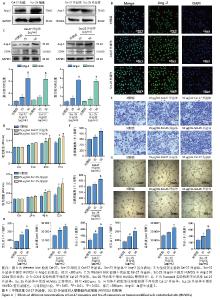
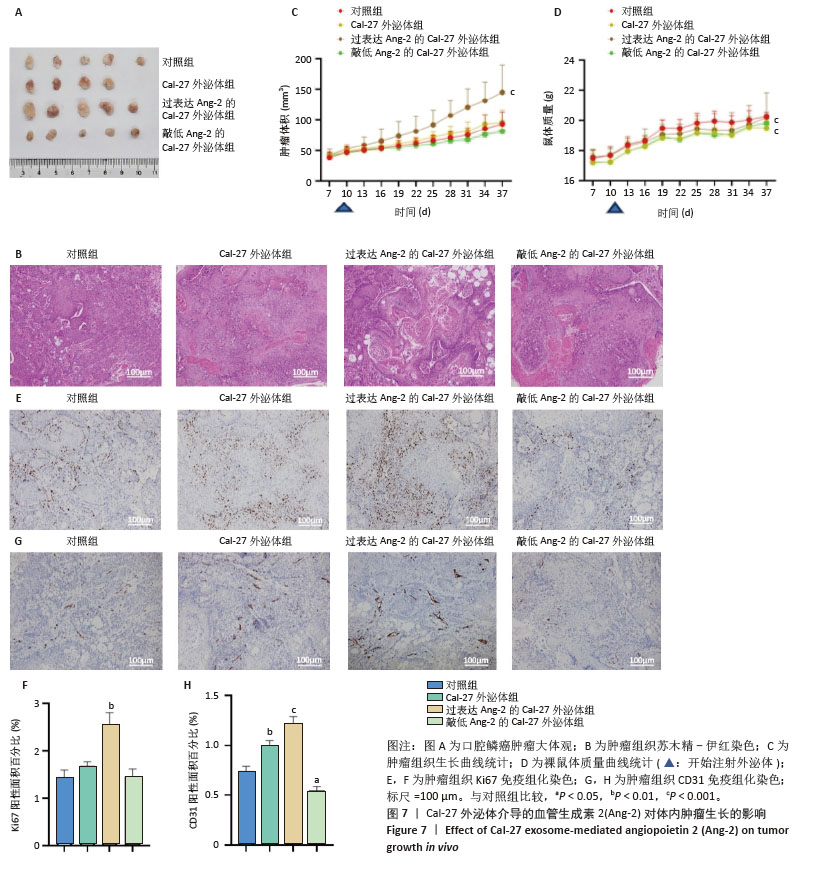
2.5 过表达Ang-2的Cal-27外泌体、Scc-25外泌体对HUVECs的影响 过表达慢病毒转染Cal-27、Scc-25细胞,荧光显微镜下见明显绿色荧光,见图5A。qRT-PCR检测结果显示,与过表达阴性组相比,过表达Ang-2组Cal-27、Scc-25细胞中Ang-2表达显著增多,见图5B。Western blot检测结果显示,与过表达阴性组相比,过表达Ang-2组Cal-27、Scc-25细胞及外泌体中Ang-2蛋白表达明显升高,见图5C。Western blot检测结果显示,与过表达阴性组相比,过表达Ang-2的Cal-27外泌体、Scc-25外泌体处理HUVECs后,Ang-2和CD34蛋白表达明显增多,见图5D。Transwell、CCK-8和细胞管腔形成实验结果显示,与过表达阴性组相比,过表达Ang-2的Cal-27外泌体、Scc-25外泌体可以明显促进HUVECs的迁移、增殖和管形成(P < 0.05),见图5E-I。"
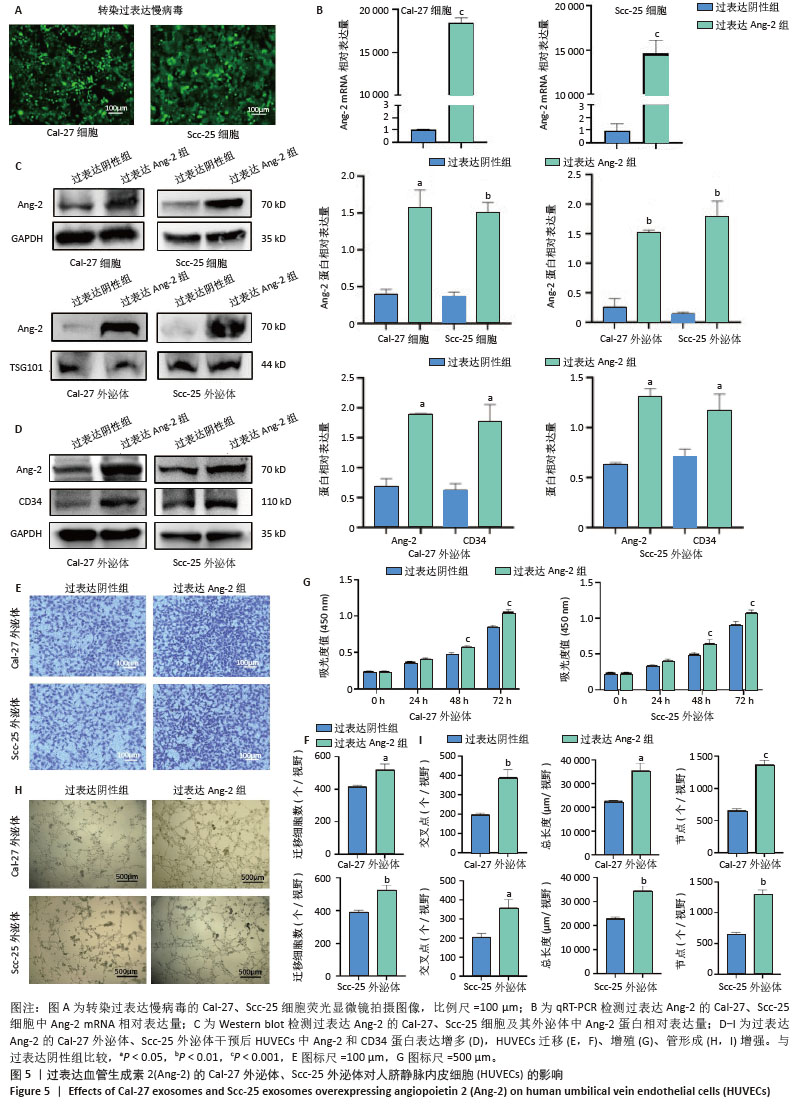
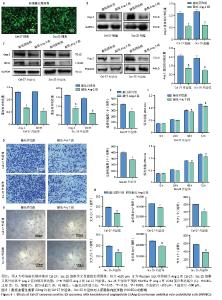
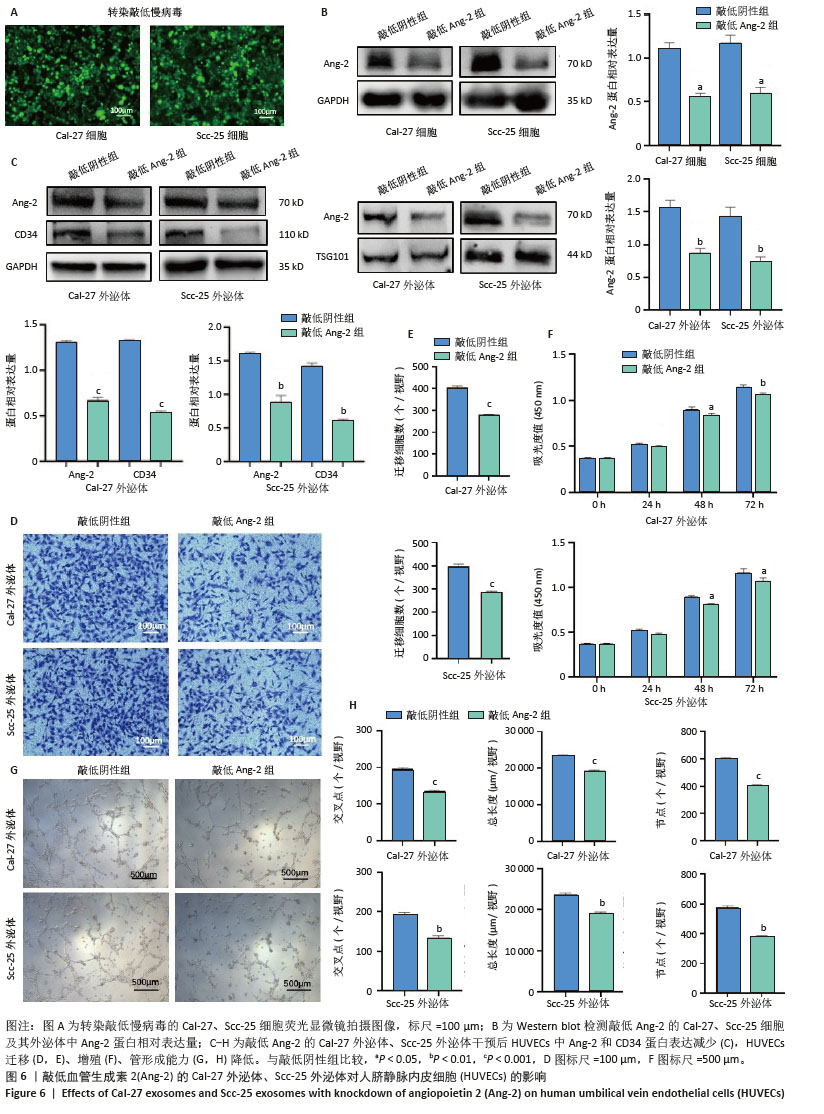
2.6 敲低Ang-2的Cal-27、Scc-25外泌体对HUVECs的影响 敲低慢病毒转染Cal-27、Scc-25细胞,荧光显微镜下见明显绿色荧光,见图6A。Western blot检测结果显示,与敲低阴性组相比,敲低Ang-2组Cal-27、Scc-25细胞及其外泌体中Ang-2蛋白表达降低,见图6B。Western blot检测结果显示,与敲低阴性组相比,敲低Ang-2的Cal-27外泌体、Scc-25外泌体处理HUVECs后,Ang-2和CD34蛋白表达减少,见图6C。CCK-8、Transwell和细胞管腔形成实验结果显示,与敲低阴性组相比,敲低Ang-2的Cal-27外泌体、Scc-25外泌体的促HUVECs迁移、增殖和管形成能力减弱(P < 0.05),见图6D-H。"
| [1] STASIEWICZ M, KARPIŃSKI TM. The oral microbiota and its role in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 3):633-642. [2] YANG M, LUO Q, CHEN X, et al. Bitter melon derived extracellular vesicles enhance the therapeutic effects and reduce the drug resistance of 5-fluorouracil on oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):259. [3] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [4] LIU H, HUANG Y, HUANG M, et al. Current Status, Opportunities, and Challenges of Exosomes in Oral Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:2679-2705. [5] XIA C, DONG X, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(5):584-590. [6] LIU TPJ, FISHER BM, CHUA B, et al. Survival outcomes following modern multidisciplinary management of oral squamous cell carcinoma in Australia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021;131(1): 92-98. [7] KUGERATSKI FG, KALLURI R. Exosomes as mediators of immune regulation and immunotherapy in cancer. FEBS J. 2021;288(1):10-35. [8] GUELFI S, HODIVALA-DILKE K, BERGERS G. Targeting the tumour vasculature: from vessel destruction to promotion. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024;24(10):655-675. [9] BATISTELLA EA, MIGUEL AFP, NASCIMENTO NL, et al. Microvascular density analysis and histological parameters of oral cancer progression. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2110-2121. [10] MAMILOS A, LEIN A, WINTER L, et al. Immunohistochemical Assessment of Microvessel Density in OSCC: Spatial Heterogeneity of Angiogenesis and Its Impact on Survival. Biomedicines. 2023;11(10):2724. [11] CHEN YF, LUH F, HO YS, et al. Exosomes: a review of biologic function, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications, and clinical trials. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):67. [12] LI SR, MAN QW, GAO X, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: Present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175. [13] YU D, LI Y, WANG M, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):56. [14] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [15] MA X, YANG R, LI H, et al. Role of exosomes in the communication and treatment between OSCC and normal cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(7): e28148. [16] ZHANG X, LI B. Updates of liquid biopsy in oral cancer and multiomics analysis. Oral Dis. 2023;29(1):51-61. [17] CHEN Y, LI Z, LIANG J, et al. CircRNA has_circ_0069313 induced OSCC immunity escape by miR-325-3p-Foxp3 axes in both OSCC cells and Treg cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(10):4376-4389. [18] HE L, PING F, FAN Z, et al. Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109553. [19] SUN YQ, WANG B, ZHENG LW, et al. Oral cancer cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miR-21/RMND5A pathway. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):82. [20] KINANE DF, GABERT J, XYNOPOULOS G, et al. Strategic approaches in oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostics using liquid biopsy. Periodontol 2000. 2024;96(1):316-328. [21] PASQUIER J, GHIABI P, CHOUCHANE L, et al. Angiocrine endothelium: from physiology to cancer. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):52. [22] ORIA VO, ERLER JT. Tumor Angiocrine Signaling: Novel Targeting Opportunity in Cancer. Cells. 2023;12(20):2510. [23] SUN R, KONG X, QIU X, et al. The Emerging Roles of Pericytes in Modulating Tumor Microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 676342. [24] SAHARINEN P, LEPPÄNEN VM, ALITALO K. SnapShot: Angiopoietins and Their Functions. Cell. 2017;171(3):724-724.e1. [25] DAVIS S, ALDRICH TH, JONES PF, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996;87(7):1161-1169. [26] GHALEHBANDI S, YUZUGULEN J, PRANJOL MZI, et al. The role of VEGF in cancer-induced angiogenesis and research progress of drugs targeting VEGF. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;949:175586. [27] TEICHERT-KULISZEWSKA K, MAISONPIERRE PC, JONES N, et al. Biological action of angiopoietin-2 in a fibrin matrix model of angiogenesis is associated with activation of Tie2. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;49(3):659-670. [28] FELCHT M, LUCK R, SCHERING A, et al. Angiopoietin-2 differentially regulates angiogenesis through TIE2 and integrin signaling. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(6):1991-2005. [29] SCHOLZ A, PLATE KH, REISS Y. Angiopoietin-2: a multifaceted cytokine that functions in both angiogenesis and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1347:45-51. [30] XIE JY, WEI JX, LV LH, et al. Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis via exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):46. [31] TAKAMURA Y, YAMADA Y, MORIOKA M, et al. Turnover of Microaneurysms After Intravitreal Injections of Faricimab for Diabetic Macular Edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023;64(13):31. [32] MCCORD C, KISS A, MAGALHAES MA, et al. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Precursor Lesions. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021;14(9):873-884. [33] SHARMA A, NATARAJAN S, MANAKTALA N, et al. Prognostic Nomogram for Lymph-Node Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Using Immunohistochemical Marker D2-40. Cancer Manag Res. 2023; 15:929-936. [34] HUI L, CHEN Y. Tumor microenvironment: Sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett. 2015;368(1):7-13. [35] HU S, MA J, SU C, et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:567-581. [36] YE D, GONG M, DENG Y, et al. Roles and clinical application of exosomal circRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):161. [37] JAKKULWAR S, VAGHA S, CHAUDHARY M. Tumour Budding in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2024;16(9): e69624. [38] HUANG CY, CHOU ST, HSU YM, et al. MEG3-Mediated Oral Squamous-Cell-Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal miR-421 Activates Angiogenesis by Targeting HS2ST1 in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(14):7576. [39] YAN W, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Exosomal miR-130b-3p Promotes Progression and Tubular Formation Through Targeting PTEN in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:616306. [40] PAUTA M, RIBERA J, MELGAR-LESMES P, et al. Overexpression of angiopoietin-2 in rats and patients with liver fibrosis. Therapeutic consequences of its inhibition. Liver Int. 2015;35(4):1383-1392. [41] LI C, SUN CJ, FAN JC, et al. Angiopoietin-2 expression is correlated with angiogenesis and overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30(2):571. [42] POMELLA S, MELAIU O, DRI M, et al. Effects of Angiogenic Factors on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Their Impact on the Onset and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview. Cells. 2024;13(15):1294. [43] LIU J, YAN Z, YANG F, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Enhancing Angiogenesis through Delivering Angiopoietin-2. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):305-317. [44] RUGGERI BA, CAMP F, MIKNYOCZKI S. Animal models of disease: pre-clinical animal models of cancer and their applications and utility in drug discovery. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;87(1):150-161. |
| [1] | Min Changqin, Huang Ying. Construction of pH/near-infrared laser stimuli-responsive drug delivery system and its application in treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [2] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [4] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [5] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [6] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [7] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [8] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [9] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [10] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [11] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [12] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| [13] | Pan Chun, Fan Zhencheng, Hong Runyang, Shi Yujie, Chen Hao. Effect and mechanism of polystyrene microplastics on prostate in male mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7353-7361. |
| [14] |
Zhou Rulin, Hu Yuanzheng, Wang Zongqing, Zhou Guoping, Zhang Baochao, Xu Qian, Bai Fanghui.
Exploration of biomarkers for moyamoya disease and analysis of traditional Chinese medicine targets#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6927-6938.
|
| [15] | Zeng Yu, Xie Chengwei, Hong Yuanqi, Su Shenghui, Dong Xieping. In vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive glass [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5941-5949. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||