Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (20): 3246-3251.doi: 10.12307/2024.339
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis
Ge Ruiyang1, Ni Can2, Yang Kun1, Yan Fuhua2
- 1Hospital/School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Periodontology, Nanjing Stomatological Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-12Accepted:2023-06-05Online:2024-07-18Published:2023-09-11 -
Contact:Yan Fuhua, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Periodontology, Nanjing Stomatological Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China Yang Kun, Associate professor, Hospital/School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Ge Ruiyang, Master candidate, Hospital/School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82001051 (to NC); Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline (Laboratory) Cultivation Unit, No. JSDW202246 (to YFH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ge Ruiyang, Ni Can, Yang Kun, Yan Fuhua. The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3246-3251.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 巨噬细胞与牙周炎 巨噬细胞作为固有免疫重要组成部分广泛存在于人体各组织中,参与构成机体防御病原微生物入侵和感染的第一道防线,在吞噬、抗原提呈、代谢等生理过程中发挥重要作用[5]。牙周炎患者牙龈组织中巨噬细胞数量较健康牙龈组织明显增加[6-7]。巨噬细胞是参与牙周组织破坏的炎症因子的主要来源,在牙周致病菌及其毒性产物刺激下可分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、基质金属蛋白酶、前列腺素E2等[6]。LAM等[8]通过口腔接种牙龈卟啉单胞菌(Porphyromonas gingivalis,P.gingivalis)构建小鼠牙周炎模型,发现牙周炎状态下牙龈组织中出现大量巨噬细胞浸润,而用氯膦酸二钠脂质体对小鼠体内巨噬细胞进行清除后牙龈组织中的巨噬细胞浸润显著减少,明显减缓了牙槽骨破坏。文献报道称,巨噬细胞来源的炎症因子在牙龈组织及龈沟液中的累积与牙周炎病变程度和进展相关,而抑制这些促炎因子的释放则与骨吸收和炎症细胞浸润状态的改善有关[9-10]。 2.1.1 巨噬细胞极化及相关分型 巨噬细胞具有可塑性和多能性,可在不同微环境中表现为不同亚型并发挥独特功能[11-12],影响多种疾病的发生发展和骨代谢。根据活化途径和功能可大致将巨噬细胞分为经典激活型(M1)和替代激活型(M2)两大类。 M1型,即“促炎型”巨噬细胞,可由脂多糖、干扰素γ、肿瘤坏死因子α等激活,合成并分泌大量促炎因子和抗菌物质,包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、诱导型一氧化氮合酶及趋化因子等,具有较强抗原提呈、杀菌及促炎作用,但也常导致邻近组织损伤[13-15]。 M2型,又称为“抑炎型”巨噬细胞,主要由白细胞介素4、白细胞介素13等因子诱导形成,可分泌白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β、精氨酸酶1等,又可分为M2a、M2b、M2c、M2d四种亚型,在血管生成、抗炎及促进组织修复和伤口愈合中起重要作用[13,15-17]。 2.1.2 巨噬细胞极化与牙周炎的关系 NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3炎性小体在多种炎性疾病的发生发展中发挥重要作用[18]。HAN等[19]在小鼠牙周炎模型中观察到,牙周炎小鼠牙龈组织中M1型巨噬细胞浸润较健康对照组明显上升,且血清瘦素水平与M1型巨噬细胞数量呈正相关,体外实验发现瘦素可通过激活NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3炎性小体来促进巨噬细胞M1极化,从而加重牙周炎所致骨破坏。LAM等[8]研究发现,牙周炎小鼠牙龈组织中浸润的巨噬细胞以M1型(CD86+)居多,且占据明显主导地位。一项针对灵长类动物的研究发现,牙周炎时M1型巨噬细胞相关基因的表达显著升高,而M2型巨噬细胞相关基因表达变化幅度则相对较小[20]。VINIEGRA等[21]在丝线结扎诱导的小鼠牙周炎模型中发现,CD86、肿瘤坏死因子α等M1型巨噬细胞的标志物在炎症破坏期表达增多且主要集中在结扎丝线部位,而M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206、转化生长因子β等则在骨重建期间表达增多,在用氯膦酸二钠脂质体清除巨噬细胞后骨破坏和再生均减少。YU等[22]对小鼠牙周炎模型中巨噬细胞的分型及数量分析发现,牙周炎时M1和M2型巨噬细胞数量均增长,但M1/M2的比例显著上调。 综上所述,在牙周炎牙周破坏期病损区域的巨噬细胞以M1型为主,且骨组织破坏与其密切相关;而消除炎症刺激后,在受损组织的再生与修复阶段,巨噬细胞类型则以M2型为主。因此,巨噬细胞从M2型向M1型的转换可能是牙周炎组织破坏的重要机制。 2.1.3 巨噬细胞极化影响牙周炎的可能机制 (1)巨噬细胞极化与免疫微环境:M1型巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子,参与牙周组织破坏。研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子可诱导成骨细胞凋亡,并抑制成骨细胞前体细胞和间充质干细胞的成骨分化[23-29];同时,肿瘤坏死因子α还能促进成牙骨质细胞凋亡,抑制成牙骨质细胞的分化及矿化过程[30-31]。另一方面,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子参与了破骨过程。核因子κB受体活化因子/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素轴是调节破骨细胞功能的重要通路。研究发现,成骨/基质细胞在炎症递质作用下可产生核因子κB受体活化因子配体,而核因子κB受体活化因子配体可与破骨细胞前体细胞表面的核因子κB受体活化因子结合,继而通过一系列信号级联反应,促进破骨细胞的分化、活化和成熟;同时,这些细胞也可分泌骨保护素,骨保护素作为核因子κB受体活化因子配体的诱饵受体,可与核因子κB受体活化因子配体特异性结合,从而阻断核因子κB受体活化因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体的结合,抑制其向破骨细胞分化[32- 33]。在炎症条件下,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子可以刺激成骨/基质细胞中核因子κB受体活化因子配体的分泌,同时下调骨保护素的分泌,间接促进破骨细胞的形成和成熟[1,34-35]。此外,这些炎症因子也可以与核因子κB受体活化因子配体协同作用,直接作用于破骨细胞前体细胞、促进破骨细胞生成,并诱导骨细胞凋亡,促进骨破坏[25,35]。因此,M1型巨噬细胞所分泌的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子可以通过下调成骨活动、上调破骨活动,将骨稳态推向破骨方向,导致净骨量的减少。 M2型巨噬细胞分泌的白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β等具有抗炎及修复作用,可拮抗肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎症因子的作用[1],促进牙周组织再生与修复;并且,它们可下调成骨/基质细胞所分泌的核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素比例,并能直接作用于Th17细胞和破骨细胞前体细胞、减少破骨细胞生成,抑制破骨活动[1,34,36]。其中,白细胞介素10对成骨/基质细胞中核因子κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素表达的调节作用在人牙周膜细胞中已得到验证[37],且作为经典抗炎因子,白细胞介素10还可抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等的合成与分泌,从而抑制炎症反应、改善炎症微环境[38]。这些发现提示白细胞介素10可抑制骨吸收、参与牙周炎骨代谢过程,而这也被系列实验所证实。LI等[39]通过向实验性牙周炎大鼠颚侧牙龈注射白细胞介素10质粒-脂质体进行局部基因转染,发现在大鼠牙周组织中成功表达的白细胞介素10可抑制骨吸收,并降低组织中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和核因子κB受体活化因子配体等的表达。牙周炎患者唾液和龈沟液中白细胞介素10浓度和量均较正常人群明显降低[40-41]。抑制M1型巨噬细胞中核因子κB的激活可减轻其协同刺激分子的表达和炎症反应[42]。M2型巨噬细胞分泌的白细胞介素10则可通过抑制核因子κB的激活,减轻炎症反应。CHEN等[43]还发现,通过外泌体直接将白细胞介素10 mRNA递送给细胞来上调骨髓间充质干细胞等白细胞介素10的表达,进而调节细胞分化和骨代谢。此外,M2型巨噬细胞还可通过分泌转化生长因子β来诱导Runx2介导的成骨细胞分化,并通过Smad通路依赖或非依赖方式抑制成骨细胞的凋亡[44]。对不同类型巨噬细胞所分泌的不同细胞因子及其作用,见表1。"

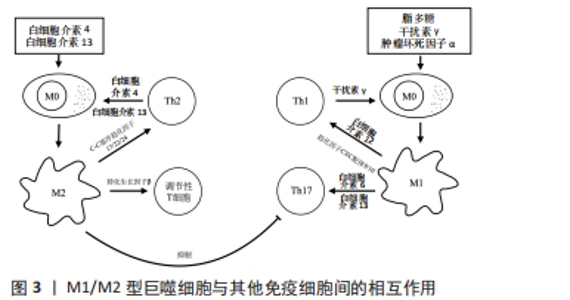
(2)巨噬细胞极化与其他免疫细胞:患牙周炎时,牙周致病菌除激活固有免疫外还会激活T细胞,特别是CD4+T细胞[45]。CD4+T细胞分为5 个亚群,即辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞2、辅助性T细胞17、滤泡辅助T细胞和调节性T细胞,其中辅助性T细胞1、17在牙周炎组织中数量更多,与组织破坏密切相关[46-47];而辅助性T细胞2和调节性T细胞在健康牙周组织更多,与组织修复和免疫抑制相关[45]。 作为专职抗原提呈细胞,M1型巨噬细胞高表达协同刺激分子CD40和主要组织相容性复合物Ⅱ类分子,为T细胞活化提供第一信号。辅助性T细胞1由白细胞介素12诱导分化而成,可分泌白细胞介素2、肿瘤坏死因子α、干扰素γ和淋巴毒素等炎症因子。当巨噬细胞表面CD40与辅助性T细胞1细胞表面CD40L结合后,既可以促进CD4+T细胞的选择性扩增[48];还可活化核因子κB,在免疫系统的发育以及动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病、类风湿性关节炎和癌症等多种疾病的免疫调控中发挥重要作用,并诱导基质金属蛋白酶、诱导型一氧化氮合酶和环氧合酶2等多种促炎因子的转录[49-50]。辅助性T细胞1细胞所分泌的干扰素γ可以驱动巨噬细胞M1极化,而M1型巨噬细胞又可通过分泌白细胞介素12、趋化因子CXC配体9、趋化因子CXC配体10等进一步促进辅助性T细胞向辅助性T细胞1分化以及辅助性T细胞1的募集,从而放大炎症过程。M1型巨噬细胞分泌的白细胞介素6和白细胞介素23还可促进辅助性T细胞17的形成。辅助性T细胞17可分泌白细胞介素17、白细胞介素21、白细胞介素22和粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等。其中白细胞介素17具有强大的促炎作用,是引起炎症性骨破坏的重要炎症因子之一[2,51]。白细胞介素17可诱导前列腺素E2、基质金属蛋白酶和核因子κB受体活化因子配体的产生,促进骨组织的破坏,也可以通过促进趋化因子CXC配体9、趋化因子CXC配体10、C-C基序趋化因子2、C-C基序趋化因子7、趋化因子CXC配体1、趋化因子CXC配体2、趋化因子CXC配体5和趋化因子CXC配体8等趋化因子的表达来募集T细胞、中性粒细胞和单核细胞,并通过基质金属蛋白酶和前列腺素E2加强这一过程。粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子则可以提高所募集免疫细胞的存活率和活力[51]。此外,自然杀伤细胞和M1型巨噬细胞间也存在类似的相互促进关系。根据所分泌细胞因子的不同,可将自然杀伤细胞分为自然杀伤1和自然杀伤2两个亚群,其中自然杀伤1可以通过分泌干扰素γ促进巨噬细胞M1极化,M1型巨噬细胞又可通过分泌白细胞介素12促进自然杀伤1细胞的分化[52]。因此,M1巨噬细胞除自身直接作用外,还可通过与辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞17、自然杀伤细胞等的相互作用放大炎症反应,促进更多炎症因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体等的分泌,加重牙周组织的破坏。 M2型巨噬细胞可通过与辅助性T细胞2、调节性T细胞等的相互作用调控炎症及骨代谢。辅助性T细胞2可通过分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素13使巨噬细胞向M2方向极化,而M2型巨噬细胞分泌的C-C基序趋化因子17、C-C基序趋化因子22和C-C基序趋化因子24等趋化因子,又可与辅助性T细胞2以及调节性T细胞表面的相应受体C-C基序趋化因子受体4和C-C基序趋化因子受体3结合,从而促进这些细胞的募集,放大辅助性T细胞2和M2型巨噬细胞间的相互作用[52]。辅助性T细胞2细胞所分泌的白细胞介素10、白细胞介素13、白细胞介素4等因子可以改善炎症状态并抑制破骨细胞生成。此外,M2型巨噬细胞分泌的转化生长因子β可诱导调节性T细胞形成并抑制辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞2及CD8+T细胞功能,以下调适应性免疫。调节性T细胞是具有免疫抑制功能的T细胞亚群,在建立和维持自身免疫耐受以及各种免疫反应的负调控中发挥重要作用[53],可分为CD4+CD25+Tr细胞、Tr1和辅助性T细胞3,在牙周炎过程中同样担任重要角色。在使用牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖诱导的牙周炎模型和孕期牙周炎小鼠中,均观察到调节性T细胞减少和辅助性T细胞17的增多,提示辅助性T细胞17/调节性T细胞比例失衡在牙周炎过程中起重要作用[54-55],而使用药物或材料促进调节性T细胞的富集和增殖,则可显著改善牙周炎所致的骨组织破坏[56-57]。TIEMESSEN等[42]的研究发现,CD4+CD25+Tr细胞可分泌白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4和白细胞介素13等抑制炎症反应,并通过这些细胞因子以及细胞间直接接触抑制巨噬细胞功能。调节性T细胞还能下调辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞2、辅助性T细胞17、效应T细胞、自然杀伤细胞、抗原提呈细胞、B细胞等免疫细胞的功能,从而抑制过度炎症反应,改善炎症微环境。然而,转化生长因子β也可通过诱导辅助性T细胞17和CD4+T细胞而促进适应性免疫[44],这提示免疫反应是一个双向动态变化过程,其对骨代谢的最终影响取决于免疫天平的偏向。M1/M2型巨噬细胞与其他免疫细胞间的相互作用,见图3。"
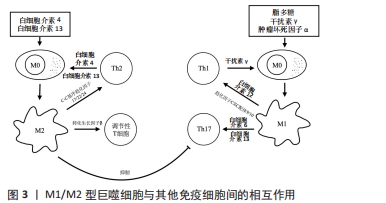

(3)巨噬细胞极化与铁死亡:生理过程所需的大部分铁来自巨噬细胞回收红细胞中的铁[58],是人体必需的微量元素之一,在氧气输送、细胞能量产生等多种生理过程中发挥重要作用[59]。铁在血液循环中以转铁蛋白的形式存在,通过转铁蛋白受体1和二价金属转运蛋白1进入细胞内,与铁蛋白结合并储存于细胞内,或经由铁转运蛋白直接释放回循环中[60]。健康状态下铁蛋白和游离铁处于平衡状态,但在一些病理条件中则可能出现铁过载现象,细胞内铁积聚,并通过芬顿反应产生大量活性氧,导致脂质过氧化和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4耗竭,最终细胞死亡,即铁死亡[61]。M1型巨噬细胞通过高表达铁蛋白、低表达铁转运蛋白大量储存铁,限制铁释放,达到抑菌目的;而M2型巨噬细胞则通过释放铁来促进组织修复[5,62]。M1型巨噬细胞以糖酵解为主,在抗感染、促炎方面发挥重要作用;M2型巨噬细胞则以有氧氧化为主,这一途径能为组织重建提供持续稳定的能量。研究发现,铁过载时,糖酵解增强且肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、C-C基序趋化因子2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶等M1标记物水平升高[63-64],提示铁死亡可促进巨噬细胞的M1极化。而M1型巨噬细胞也可通过释放多种炎症因子来调控铁代谢,如白细胞介素6可通过促进铁调素的产生来降低铁转运蛋白表达[65],白细胞介素1β可通过p38-MAPK通路来促进铁转运蛋白的表达[66]。综上所述,巨噬细胞可通过呼吸爆发活动产生大量活性氧,其分泌的炎症因子可调控铁代谢,且M1型巨噬细胞有大量储铁的特点,提示巨噬细胞与铁死亡之间联系紧密。牙周炎作为一种复杂的慢性炎症性疾病,其生发展过程中存在一定程度的铁代谢紊乱[67],铁死亡存在于牙周炎过程中[68-69]。大量活性氧和抗氧化剂的耗竭是铁死亡的特定诱因之一,而牙周炎的“keystone”病菌牙龈卟啉单胞菌的脂多糖可引起线粒体功能障碍、大量活性氧的产生以及氧化应激[70],导致谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的消耗。有研究发现,牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖可上调人牙龈成纤维细胞中活性氧及转铁蛋白受体1的表达,同时下调谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4,使细胞内活性氧和铁积聚,导致人牙龈成纤维细胞铁死亡,而在使用铁死亡抑制剂Ferrostatin-1后,牙周炎所致的组织损伤和骨破坏都得到了改善[68,71]。巨噬细胞在该过程中的角色值得进一步探究,通过靶向调节巨噬细胞来调节铁死亡或许是未来牙周炎防治的新方向之一。 2.2 巨噬细胞与牙周治疗 牙周炎由细菌感染和失调的宿主免疫反应之间复杂的相互作用所引发,目前以牙周基础治疗(龈上洁治术和龈下刮治及根面平整术)为主,辅以牙周手术及药物治疗等,虽可有效清除局部菌斑刺激,但通常只能控制或延缓疾病进展,难以获得理想的牙周组织再生,而牙周炎治疗的目的除清除感染外,更要促进牙周炎过程中受损牙周组织的修复和再生。目前的牙周再生技术以使用屏障膜为核心的引导组织再生为主,但其疗效可预期性差,存在较大个体差异[72],并且有着相对较严格的适应证等诸多局限。因此,寻求更有效的牙周治疗方法迫在眉睫。基于牙周炎的发病机制,调节宿主免疫炎症反应可能有望在减少牙周组织破坏的同时改善局部免疫微环境,获得更多牙周组织再生。 2.2.1 外源性材料 目前已有诸多研究发现一些具有免疫调节性能的外源性生物材料可通过调控巨噬细胞极化来促进牙周组织的再生和修复,抑制牙周炎的发生发展。钼是人体所必需的微量元素之一,被细胞摄取后以钼辅因子的形式参与多种生物过程[73],其中就包括线粒体代谢[74]。HE等[75]在犬牙周缺损模型中使用含有钼的3D打印生物活性玻璃陶瓷支架,发现M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD206及精氨酸酶1远高于仅使用生物活性玻璃陶瓷支架的对照组,对照组M1型巨噬细胞标志物诱导型一氧化氮合酶、C-C基序趋化因子受体7在术后均高于实验组,且实验组在术后8 周可观察到大量新生骨组织,提示含有钼的3D打印生物活性玻璃陶瓷支架通过促进巨噬细胞M2极化来增强牙槽骨再生;将含有钼的3D打印生物活性玻璃陶瓷粉末加入至未分化的RAW264.7细胞中孵育,发现线粒体中钼含量明显上升,提示线粒体对钼的摄取具有特异性,同时还观察到线粒体数量和功能均有所升高,进一步研究发现该材料在增强氧化磷酸化的同时减弱糖酵解来促进巨噬细胞代谢转变,从而调控其向M2型极化。课题组前期研究发现,金纳米颗粒以粒径依赖的方式发挥抗炎和成骨作用,其中45 nm金纳米颗粒在降低M1型巨噬细胞标志物CD86表达的同时可增加精氨酸酶1的表达,促进巨噬细胞的M2型极化和骨形态发生蛋白2的表达,从而改善免疫微环境,抑制牙周炎进展,促进牙周组织再生;此外,还发现45 nm金纳米颗粒能够上调人牙周膜前体细胞自噬相关基因LC3和Beclin-1的表达,且促成骨作用可被自噬抑制剂所逆转[76-77]。自噬是由溶酶体介导的一种细胞分解代谢途径,在巨噬细胞极化过程中发挥重要作用[78-79]。但现有研究发现,使用不同物质诱导自噬激活可能会导致巨噬细胞极化走向截然相反的道路,在牙周炎条件下,不同粒径的金纳米颗粒和自噬在巨噬细胞极化过程中是否发挥作用、发挥何种作用仍需进一步探索。ZHUANG等[80]在小鼠牙龈卟啉单胞菌诱导和结扎诱导的牙周炎模型中使用含C-C基序趋化因子2的材料诱导巨噬细胞向M2型极化,发现可显著减少破骨细胞数量,抑制牙槽骨吸收。此外,含有镁离子的硫酸钙/β-磷酸三钙复合陶瓷[81]、聚多巴胺介导的氧化石墨烯和羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒支架[82]、槲皮素负载二氧化铈纳米复合物和骨细胞外基质凝胶等材料也均可通过调节巨噬细胞极化来促进牙周再生或改善牙周炎局部微环境[83-84],其主要机制包括通过调节长链非编码RNA PVT1/miR-21-5p/smad2分子轴[81]、巨噬细胞糖酵解或RhoA/ROCK途径等使巨噬细胞极化向M2倾斜[82],继而下调促炎细胞因子表达、上调抗炎细胞因子的释放,达到抗炎和促成骨双重作用,具有优良的牙周炎治疗潜力。 2.2.2 内源性物质 髓样细胞触发受体是表达于多数固有免疫细胞的免疫球蛋白超家族跨膜受体,可分为髓样细胞触发受体1、髓样细胞触发受体2及髓样细胞触发受体样转录物1、髓样细胞触发受体样转录物2、髓样细胞触发受体样转录物3,其中髓样细胞触发受体1被认为可以触发和放大炎症反应[85-86]。WU等[87]通过提取牙周炎患者牙龈组织RNA进行高通量测序发现,牙周炎患者牙龈组织中髓样细胞触发受体1表达显著上升,并与肿瘤坏死因子α、诱导型一氧化氮合酶等M1型巨噬细胞相关基因的表达呈正相关。通过丝线结扎构建髓样细胞触发受体1基因敲除小鼠牙周炎模型发现,髓样细胞触发受体1基因敲除组M1型巨噬细胞标志物CD86表达降低,牙槽骨吸收程度显著低于对照组。进一步研究发现,髓样细胞触发受体1通过上调STAT3/低氧诱导因子1α信号通路来促进巨噬细胞M1极化。因此,髓样细胞触发受体1或许是未来牙周炎治疗的靶点之一,通过靶向抑制髓样细胞触发受体1来抑制巨噬细胞M1极化以达到控制炎症,促进骨组织再生的目的。 胞外囊泡是细胞释放到胞外的膜衍生囊泡,可分为外泌体、凋亡小体和微泡3种亚型,所携带的多种物质在细胞间信息交流过程中发挥重要作用[88-89]。巨噬细胞可以通过分泌胞外囊泡来影响成骨过程。KANG等[90]发现使用M1型巨噬细胞分泌的胞外囊泡可显著降低骨再生,而M0和M2型巨噬细胞分泌的胞外囊泡则可促进成骨。LIU等[91]也发现,M2型巨噬细胞分泌的胞外囊泡可通过BMP2/Smad5通路促进间充质干细胞成骨。同时,来自其他细胞的胞外囊泡也可影响巨噬细胞极化。研究发现,铁死亡心肌细胞源性外泌体通过Wnt/β-cantenin通路与巨噬细胞相互作用,诱导其 M1极化[92]。 MicroRNA(miRNA)是一种内源性表达的短RNA,是胞外囊泡所携带的“货物”之一,因其可调节大多数RNA [93],几乎影响着所有生长发育和疾病发生发展过程[94]。研究发现,M2型巨噬细胞胞外囊泡中含有大量miR-5106,并通过抑制盐诱导激酶2和盐诱导激酶3基因表达来促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨[95]。巨噬细胞极化同样受miRNA的调控。miR-9、miR-127、miR-155和miR-126b可通过抑制BCL-6或增强巨噬细胞对干扰素γ反应来促进其M1极化,从而促进炎症反应;miR-124、miR-223、miR-34a、miR-132、miR-146a、miR-125a-5P和let-7c则可减少肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等促炎因子的释放,抑制巨噬细胞的M1极化并促进M2极化[96]。因此,通过胞外囊泡和表观遗传学调控牙周组织局部巨噬细胞极化在未来牙周炎骨免疫治疗方面或许有着巨大潜力。 综上,调节巨噬细胞表型及细胞因子分泌有助于降低牙周炎炎症水平、改善牙周微环境,从而减少组织破坏或促进牙周组织再生。目前已有许多研究着力于开发药物或生物材料来调节巨噬细胞功能,从而达到免疫调控治疗牙周炎的目的,但由于巨噬细胞的作用贯穿牙周炎发生发展过程,在抗感染、骨破坏和骨修复过程中均扮演重要角色,且极化本身是一个复杂的动态过程,受诸多因素的影响,所以仍需探索更多可能的机制来明确材料或药物与巨噬细胞间的交互作用。当下普遍认为,牙周炎与包括糖尿病、心血管疾病、阿尔茨海默病等诸多系统性疾病联系紧密,通过调控宿主免疫炎症的手段治疗牙周炎也许可以为某些系统性疾病的治疗提供帮助,寻找更加安全稳定的药物或材料拥有巨大前景。"

| [1] COCHRAN DL. Inflammation and Bone Loss in Periodontal Disease. J Periodontol. 2008;79(8s):1569-1576. [2] IKEUCHI T, MOUTSOPOULOS NM. Osteoimmunology in periodontitis; a paradigm for Th17/IL-17 inflammatory bone loss. Bone. 2022;163:116500. [3] KAYAL RA. The Role of Osteoimmunology in Periodontal Disease. BioMed Res Int. 2013;2013:639368. [4] GRAVES DT, LI J, COCHRAN DL. Inflammation and uncoupling as mechanisms of periodontal bone loss. J Dent Res. 2011;90(2):143-153. [5] BISWAS SUBHRA K, MANTOVANI A. Orchestration of Metabolism by Macrophages. Cell Metab. 2012;15(4):432-437. [6] HAJISHENGALLIS G, KOROSTOFF JM. Revisiting the Page & Schroeder model: the good, the bad and the unknowns in the periodontal host response 40 years later. Periodontol 2000. 2017;75(1):116-151. [7] LAPPIN DF, KJELDSEN M, SANDER L, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2000;35(6):369-373. [8] LAM RS, O’BRIEN-SIMPSON NM, LENZO JC, et al. Macrophage depletion abates Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone resorption in mice. J Immunol. 2014;193(5):2349-2362. [9] SIMA C, GLOGAUER M. Macrophage subsets and osteoimmunology: tuning of the immunological recognition and effector systems that maintain alveolar bone. Periodontolgy 2000. 2013;63(1):80-101. [10] FAGEEH HI, FAGEEH HN, PATIL S. Monocyte Differentiation into Destructive Macrophages on In Vitro Administration of Gingival Crevicular Fluid from Periodontitis Patients. J Pers Med. 2021;11(6):555. [11] MICHALSKI MN, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages and skeletal health. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:43-54. [12] SINDER BP, PETTIT AR, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages: Their Emerging Roles in Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12):2140-2149. [13] MANTOVANI A, SICA A, SOZZANI S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(12):677-686. [14] MURRAY PETER J, ALLEN JUDITH E, BISWAS SUBHRA K, et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(2): 339-340. [15] IVASHKIV LB. Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization and function. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(5):216-223. [16] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604. [17] VARIN A, GORDON S. Alternative activation of macrophages: immune function and cellular biology. Immunobiology. 2009;214(7):630-641. [18] YIN L, LI X, HOU J. Macrophages in periodontitis: A dynamic shift between tissue destruction and repai. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2022;58:336-347. [19] HAN Y, HUANG Y, GAO P, et al. Leptin Aggravates Periodontitis by Promoting M1 Polarization via NLRP3. J Dent Res. 2022;101(6):675-685. [20] GONZALEZ OA, NOVAK MJ, KIRAKODU S, et al. Differential Gene Expression Profiles Reflecting Macrophage Polarization in Aging and Periodontitis Gingival Tissues. Immunol Invest. 2015;44(7):643-664. [21] VINIEGRA A, GOLDBERG H, ÇIL Ç, et al. Resolving Macrophages Counter Osteolysis by Anabolic Actions on Bone Cells. J Dent Res. 2018;97(10):1160-1169. [22] YU T, ZHAO L, HUANG X, et al. Enhanced Activity of the Macrophage M1/M2 Phenotypes and Phenotypic Switch to M1 in Periodontal Infection. J Periodontol. 2016;87(9):1092-1102. [23] JEONG BC. ATF3 mediates the inhibitory action of TNF-alpha on osteoblast differentiation through the JNK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(3):696-701. [24] ZHENG L, WANG W, NI J, et al. Role of autophagy in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis of osteoblast cells. J Investig Med. 2017;65(6):1014-1020. [25] OSTA B, BENEDETTI G, MIOSSEC P. Classical and Paradoxical Effects of TNF-α on Bone Homeostasis. Front Immunol. 2014;5:48. [26] PAVALKO FM, GERARD RL, PONIK SM, et al. Fluid shear stress inhibits TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts: a role for fluid shear stress-induced activation of PI3-kinase and inhibition of caspase-3. J Cell Physiol. 2003;194(2):194-205. [27] WANG N, ZHOU Z, WU T, et al. TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation upregulates microRNA-150-3p and inhibits osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting beta-catenin. Open Biol. 2016;6(3):150258. [28] GUO C, YANG X G, WANG F, et al. IL-1alpha induces apoptosis and inhibits the osteoblast differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells through the JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(1):319-327. [29] KANESHIRO S, EBINA K, SHI K, et al. IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(4):378-392. [30] WANG YL, HE H, LIU ZJ, et al. Effects of TNF-alpha on Cementoblast Differentiation, Mineralization, and Apoptosis. J Dent Res. 2015;94(9):1225-1232. [31] WANG X, SUN H, LIAO H, et al. MicroRNA-155-3p Mediates TNF-alpha-Inhibited Cementoblast Differentiation. J Dent Res. 2017;96(12):1430-1437. [32] ZUPAN J, JERAS M, MARC J. Osteoimmunology and the influence of pro-inflammatory cytokines on osteoclasts. Biochem Med(Zagreb). 2013;23(1):43-63. [33] COCHRAN DL. Inflammation and bone loss in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2008;79(8 Suppl):1569-1576. [34] LERNER UH. inflammation-induced bone remodeling in periodontal disease and the influence of post-menopausal osteporosis. J Dental Res. 2006;85(7):596-607. [35] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(4):292-304. [36] SUN X, GAO J, MENG X, et al. Polarized Macrophages in Periodontitis: Characteristics, Function, and Molecular Signaling. Front Immunol. 2021;12:763334. [37] ZHANG L, DING Y, RAO GZ, et al. Effects of IL-10 and glucose on expression of OPG and RANKL in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016;49(4): 4324. [38] ZHANG Q, CHEN B, YAN F, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits bone resorption: a potential therapeutic strategy in periodontitis and other bone loss diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:284836. [39] LI Y, MA S, GUO J, et al. Effect of local hIL-10 gene therapy on experimental periodontitis in ovariectomized rats. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica. 2017;75(4):268-279. [40] ZHANG Q, CHEN B, ZHU D, et al. Biomarker levels in gingival crevicular fluid of subjects with different periodontal conditions: A cross-sectional study. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;72:92-98. [41] ÖNGÖZ DEDE F, BALLI U, BOZKURT DOĞAN Ş, et al. Interleukin-32 levels in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva of patients with chronic periodontitis after periodontal treatment. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(3):397-407. [42] TIEMESSEN MM, JAGGER AL, EVANS HG, et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(49):19446-19451. [43] CHEN X, WAN Z, YANG L, et al. Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via IL-10 mRNA. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20(1):110. [44] TRAVIS MA, SHEPPARD D. TGF-beta activation and function in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:51-82. [45] YUAN Y, ZHANG H, GU Q, et al. Analysis of Th-cell subsets in local and systemic environments from experimental periodontitis rats. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2023;38(2): 83-92. [46] ZHU X, ZHU J. CD4 T Helper Cell Subsets and Related Human Immunological Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):8011. [47] BI CS, SUN L J, QU HL, et al. The relationship between T-helper cell polarization and the RANKL/OPG ratio in gingival tissues from chronic periodontitis patients. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2019;5(4):377-388. [48] LAMAN JD, CLAASSEN E, NOELLEB RJ. Functions of CD40 and Its Ligand, gp39 (CD40L). Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):371-420. [49] TAK PP, FIRESTEIN GS. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(1):7-11. [50] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):56. [51] VELDHOEN M. Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity. Nat Immunol. 2017;18(6):612-621. [52] BISWAS SK, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(10):889-896. [53] THOMAS R, QIAO S, YANG X. Th17/Treg Imbalance: Implications in Lung Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4865. [54] ZHENG Y, DONG C, YANG J, et al. Exosomal microRNA-155-5p from PDLSCs regulated Th17/Treg balance by targeting sirtuin-1 in chronic periodontitis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):20662-20674. [55] HAYS A, DUAN X, ZHU J, et al. Down-regulated Treg cells in exacerbated periodontal disease during pregnancy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;69:299-306. [56] CAFFERATA EA, TERRAZA-AGUIRRE C, BARRERA R, et al. Interleukin-35 inhibits alveolar bone resorption by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance during periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47(6):676-688. [57] LIU Z, CHEN XZ, ZHANG Z, et al. Nanofibrous Spongy Microspheres to Distinctly Release miRNA and Growth Factors to Enrich Regulatory T Cells and Rescue Periodontal Bone Loss. ACS Nano. 2018;12(10):9785-9799. [58] YANG Y, WANG Y, GUO L, et al. Interaction between macrophages and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):355. [59] PLAYS M, MÜLLER S, RODRIGUEZ R. Chemistry and Biology of Ferritin. Metallomics. 2021;13(5):mfab021. [60] VOGT AS, ARSIWALA T, MOHSEN M, et al. On Iron Metabolism and Its Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4591. [61] BOGDAN AR, MIYAZAWA M, HASHIMOTO K, et al. Regulators of Iron Homeostasis: New Players in Metabolism, Cell Death, and Disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016; 41(3):274-286. [62] MA J, ZHANG H, CHEN Y, et al. The Role of Macrophage Iron Overload and Ferroptosis in Atherosclerosis. Biomolecules. 2022;12(11):1702. [63] HU X, CAI X, MA R, et al. Iron-load exacerbates the severity of atherosclerosis via inducing inflammation and enhancing the glycolysis in macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18792-18800. [64] HANDA P, THOMAS S, MORGAN-STEVENSON V, et al. Iron alters macrophage polarization status and leads to steatohepatitis and fibrogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;105(5):1015-1026. [65] REN F, YANG Y, WU K, et al. The Effects of Dandelion Polysaccharides on Iron Metabolism by Regulating Hepcidin via JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:7184760. [66] PERSICHINI T, MAIO N, DI PATTI MC, et al. Interleukin-1beta induces ceruloplasmin and ferroportin-1 gene expression via MAP kinases and C/EBPbeta, AP-1, and NF-kappaB activation. Neurosci Lett. 2010;484(2):133-138. [67] GROENINK J, WALGREEN-WETERINGS E, NAZMI K, et al. Salivary lactoferrin and low-Mr mucin MG2 in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans- associated periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1999;26(5):269-275. [68] QIAO S, LI B, CAI Q, et al. Involvement of ferroptosis in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-stimulated periodontitis in vitro and in vivo. Oral Dis. 2022. doi: 10.1111/odi.14292. [69] ZHANG S, JIN H, DA J, et al. Role of ferroptosis-related genes in periodontitis based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0271202. [70] MAO H, ZHAO Y, LI H, et al. Ferroptosis as an emerging target in inflammatory diseases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020;155:20-28. [71] XING L, DONG W, CHEN Y, et al. Fibroblast ferroptosis is involved in periodontitis-induced tissue damage and bone loss. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;114:109607. [72] LIU Y, GUO L, LI X, et al. Challenges and Tissue Engineering Strategies of Periodontal-Guided Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022;28(8):405-419. [73] HUANG XY, HU DW, ZHAO FJ. Molybdenum: More than an essential element. J Exp Bot. 2022;73(6):1766-1774. [74] SCHWARZ G. Molybdenum cofactor and human disease. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2016;31:179-187. [75] HE XT, LI X, ZHANG M, et al. Role of molybdenum in material immunomodulation and periodontal wound healing: Targeting immunometabolism and mitochondrial function for macrophage modulation. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121439. [76] NI C, ZHOU J, KONG N, et al. Gold nanoparticles modulate the crosstalk between macrophages and periodontal ligament cells for periodontitis treatment. Biomaterials. 2019;206:115-132. [77] ZHANG Y, KONG N, ZHANG Y, et al. Size-dependent Effects of Gold Nanoparticles on Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Progenitor Cells. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1214-1224. [78] OELSCHLAEGEL D, WEISS SADAN T, SALPETER S, et al. Cathepsin Inhibition Modulates Metabolism and Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(9):2579. [79] CHEN P, CESCON M, BONALDO P. Autophagy-mediated regulation of macrophages and its applications for cancer. Autophagy. 2014;10(2):192-200. [80] ZHUANG Z, YOSHIZAWA-SMITH S, GLOWACKI A, et al. Induction of M2 Macrophages Prevents Bone Loss in Murine Periodontitis Models. J Dent Res. 2019;98(2):200-208. [81] ZHOU J, SUN S, HE Y, et al. Role of magnesium-doped calcium sulfate and beta-tricalcium phosphate composite ceramics in macrophage polarization and osteo-induction. Odontology. 2022;110(4):735-746. [82] LI Y, YANG L, HOU Y, et al. Polydopamine-mediated graphene oxide and nanohydroxyapatite-incorporated conductive scaffold with an immunomodulatory ability accelerates periodontal bone regeneration in diabetes. Bioact Mater. 2022; 18:213-227. [83] WANG Y, LI C, WAN Y, et al. Quercetin-Loaded Ceria Nanocomposite Potentiate Dual-Directional Immunoregulation via Macrophage Polarization against Periodontal Inflammation. Small. 2021;17(41):e2101505. [84] WU RX, HE XT, ZHU JH, et al. Modulating macrophage responses to promote tissue regeneration by changing the formulation of bone extracellular matrix from filler particles to gel bioscaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:330-340. [85] DECZKOWSKA A, WEINER A, AMIT I. The Physiology, Pathology, and Potential Therapeutic Applications of the TREM2 Signaling Pathway. Cell. 2020;181(6):1207-1217. [86] TAMMARO A, DERIVE M, GIBOT S, et al. TREM-1 and its potential ligands in non-infectious diseases: from biology to clinical perspectives. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;177: 81-95. [87] WU D, WENG Y, FENG Y, et al. Trem1 Induces Periodontal Inflammation via Regulating M1 Polarization. J Dent Res. 2022;101(4):437-447. [88] CHENG L, HILL AF. Therapeutically harnessing extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022;21(5):379-399. [89] MARAR C, STARICH B, WIRTZ D. Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5):560-570. [90] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627. [91] LIU A, JIN S, FU C, et al. Macrophage-derived small extracellular vesicles promote biomimetic mineralized collagen-mediated endogenous bone regeneration. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):33. [92] SUN S, WU Y, MAIMAITIJIANG A, et al. Ferroptotic cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes promote cardiac macrophage M1 polarization during myocardial infarction. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13717. [93] KILIKEVICIUS A, MEISTER G, COREY DR. Reexamining assumptions about miRNA-guided gene silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(2):617-634. [94] BARTEL DP. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell. 2018;173(1):20-51. [95] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. M2 Macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020;18(1): 66. [96] ESSANDOH K, LI Y, HUO J, et al. MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response. Shock. 2016;46(2):122-131. |
| [1] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [2] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [3] | Chen Zhiling, Huang Xuecheng, Pan Min, Huang Ying, Wu Yuntian. Evaluation of the relationship between neck and shoulder pain and scalene muscles based on shear wave elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1265-1270. |
| [4] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [5] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [6] | Yan Binghan, Li Zhichao, Su Hui, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang, Tan Guoqing. Mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [7] | Liu Wendong, Xia Hongle, Liu Lin, Shen Runbin, Guo Wei, Wang Xuyang, Li Guoliang. Three-dimensional digital model-assisted minimally invasive needle penetration and steel plate internal fixation in treatment of Sanders types II and III calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2819-2824. |
| [8] | Jiang Jie, Liu Juan, Yu Yanyan, Yang Yue, Wang Qianhui. Mechanism by which moxibustion pretreatment attenuates oxidative stress injury in a rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2488-2493. |
| [9] | Yao Siqi, Li Wenzheng, Wang Hong. Transforming growth factor beta/Smad signaling pathway and targeted therapy of keloid scars [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2619-2624. |
| [10] | Zhai Haoyan, Zhao Yuan, Fan Dengying, Liu Chunyan. The role of reactive oxygen species in periodontitis and periodontal tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2254-2260. |
| [11] | Tong Tong, Liu Chunyan, Liu Bing, Zhao Fei. Long non-coding RNA and periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2267-2273. |
| [12] | Zhao Hexiang, Chen Ziyan, Wang Jing, Ge Zhenlin. Biomechanical characteristics of orthodontic tooth movement before and after increasing alveolar bone mass with periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2133-2139. |
| [13] | Dong Hongfei, Huang Xi, Li Xianhui, Zhang Yanbiao, Wang Xuyang, Wang Bing, Sun Hongyu. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in promoting acute skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2047-2053. |
| [14] | Pan Jianke, Yang Meiping, Han Yanhong, Zhao Di, Huang Hetao, Cao Houran, Liu Jun, Luo Minghui, Li Xiang, Chen Hongyun, Yang Weiyi. Stepwise treatment strategy for spontaneous osteonecrosis of the medial femoral condyle of the knee joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1907-1913. |
| [15] | Sun Jinyi, Wang Qinying, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Chen Helin, Zeng Xiao, Shu Jiayu, Li Wenjie, Luo Yuncai, Dong Qiang. The role of silent information regulator in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1737-1742. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||