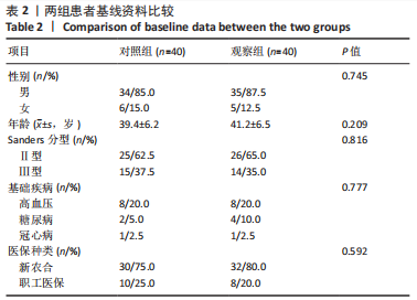
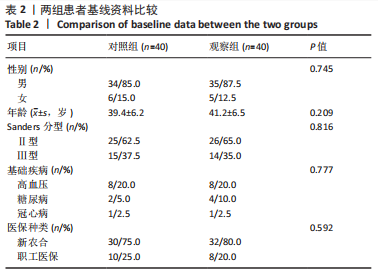
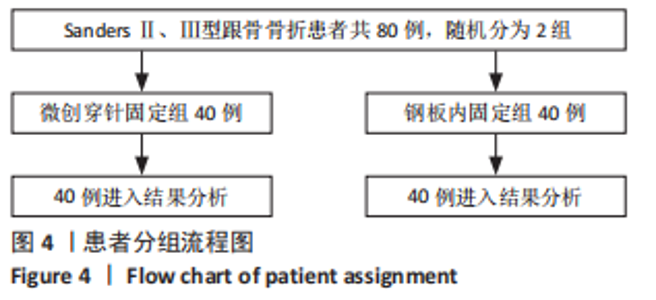
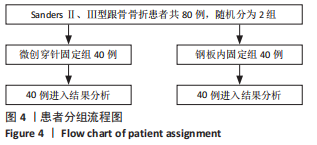
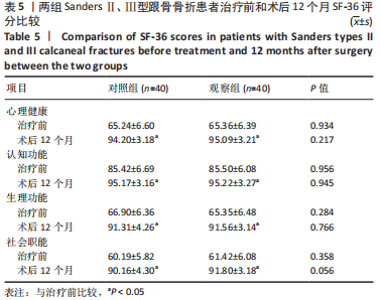
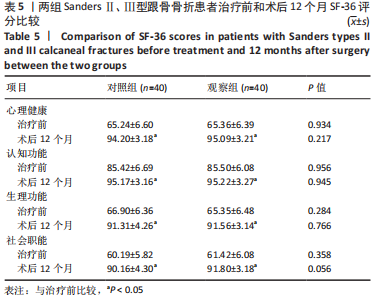
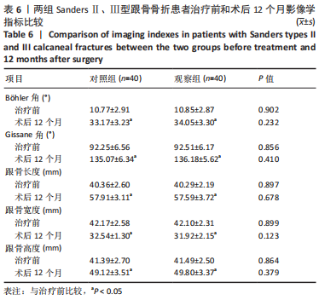
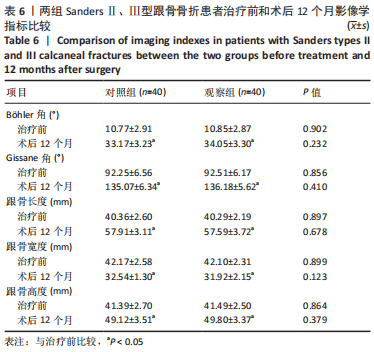
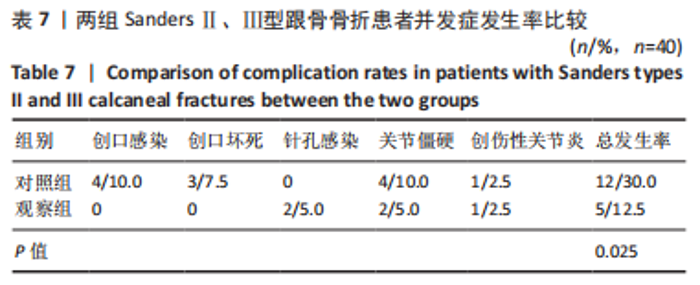
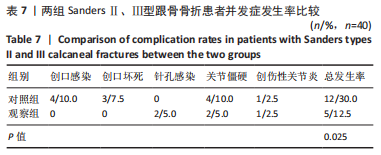
[1] VAN HOEVE S, POEZE M. Outcome of Minimally Invasive Open and Percutaneous Techniques for Repair of Calcaneal Fractures: A Systematic Review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;55(6):1256-1263.
[2] 张昊,焦建宝,于青,等.微创内固定术与切开复位治疗跟骨骨折疗效及安全性对比研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2018,27(10):1073-1076.
[3] 罗换新.促愈活血方辅助急诊外侧入路手术治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折效果及可能机制[J].安徽医药,2022,26(6):1202-1205.
[4] 武勇.跟骨骨折的治疗进展[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(12):1077-1079.
[5] 段晓东,王保云,蔡长马.跗骨窦切口空心钉与外侧L形切口钢板内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2021,36(6):639-641.
[6] 吴毛,胡钢,严松鹤,等.手法复位结合经跗骨窦入路微创治疗跟骨骨折20例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2021,29(12):54-56,60.
[7] 朱仕文,杨明辉,武勇.跟骨关节内骨折的诊断与治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(5):472-474.
[8] TILLE E, MYSLIWIETZ J, BEYER F, et al. Intraarticular use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rate after primary total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):341.
[9] VOSOUGHI AR, ROUSTAEI N, MAHDAVIAZAD H. American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society ankle-hindfoot scale: A cross-cultural adaptation and validation study from Iran. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;24(3):219-223.
[10] RUSHING CJ, SPINNER SM, HARDIGAN P. The Visual Analogue Scale for Pain: A Comparison of Scores Reported to Residents Versus an Attending Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020;13(3):207-210.
[11] KOH DTS, CHEN JY, YEW AKS, et al. Functional outcome and quality of life in patients with hip fracture after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(2):2309499019852338.
[12] DE BOER AS, VAN LIESHOUT EMM, VELLEKOOP L, et al. The Influence of Radiograph Obliquity on Böhler’s and Gissane’s Angles in Calcanei. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2020b;59(1):44-47.
[13] 王彦志.撬拨及手法复位结合跗骨窦切口微型钢板辅助空心钉轴向固定治疗SandersⅢ型跟骨骨折疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2020,29(34):3782-3785,3789.
[14] 叶聪,黎惠金,张雄辉,等.80例SandersⅡ~Ⅲ型跟骨骨折患者预后分析[J].中外医疗,2019,38(16):71-73.
[15] KAYALI C, OZAN F, ALTAY T, et al. Efficacy of calcium phosphate cementing in the surgical treatment of Sanders Type II and III calcaneal fractures using screw fixation with sinus tarsi approach. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021;55(3):265-270.
[16] 王宝鹏,常西海,李光磊,等.两种切口内固定治疗SandersⅡ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(10):897-901.
[17] YAO LF, WANG HQ, ZHANG F, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of calcaneal fractures via the sinus tarsi approach based on a 3D printing technique. Math Biosci Eng. 2019;16(3):1597-1610.
[18] 沈杰,姜雪峰,黄国伟,等.跗骨窦入路微创钢板内固定治疗SandersⅡ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J].中国微创外科杂志,2020,26(6):540-544.
[19] 洪伟武,苏海涛,彭嘉杰,等.经跗骨窦切口与传统L形切口治疗跟骨骨折:系统评价与Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18):2939-2944.
[20] 温明韬,梁学振,李嘉程,等.两种方式固定Sanders Ⅱ型跟骨骨折后的力学稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):838-842.
[21] 何平,尹国栋,罗剑,等.小切口撬拨复位克氏针内固定术与切开复位钢板内固定术治疗SandersⅡ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的疗效对比[J].实用医学杂志,2020,36(15):2088-2093.
[22] 刘延子,陈树涛,王长水,等.3D打印辅助治疗复杂跟骨骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2021,27(2):183-186.
[23] 沈美华,施凯兵,张红,等.3D打印技术在Sanders Ⅲ、Ⅳ型跟骨骨折手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(14):1259-1263.
[24] 刘艺祥,许晓光,谢强.正骨手法联合经皮撬拨复位克氏针内固定治疗SandersⅡ型跟骨骨折疗效观察[J].福建中医药,2021,52(1):17-19.
[25] 戴锋,俞鹏飞,姜宏.跗骨窦小切口撬拨复位克氏针内固定治疗Sanders Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(12):1080-1083.
[26] 张博禹,张俊国,谢文勇,等.跟骨骨折术后距下关节炎与足部功能预后的危险因素分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(12):958-963. |