[1] SCHEPERS T, VAN LIESHOUT EM, VAN GINHOVEN TM, et al. Current concepts in the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: results of a nationwide survey. Int Orthop. 2008;32:711-715.
[2] WALLIN KJ, COZZETTO D, RUSSELL L, et al. Evidence-based rationale for percutaneous fixation technique of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review of clinical outcomes. Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53(6):740-743.
[3] VOSOUGHI AR, SHAYAN Z, SALEHI E, et al. Agreement between Sanders classification of intraarticular calcaneal fractures and assessment during the surgery. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;26(1):94-97.
[4] HARNROONGROJ T, HARNROONGROJ T, SUNTHARAPA T, et al. The new intra-articular calcaneal fracture classification system in term of sustentacular fragment configurations and incorporation of posterior calcaneal facet fractures with fracture components of the calcaneal body. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(5):519-526.
[5] 洪伟武,苏海涛,彭嘉杰,等. 经跗骨窦切口与传统L形切口治疗跟骨骨折:系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(18):2939-2944.
[6] XIA S, FU B, WANG B, et al. Computed Tomography Imaging-Based Preoperative Virtual Simulation for Calcaneal Fractures Reduction. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(2):248-252.
[7] SWORDS MP, PENNY P. Early Fixation of Calcaneus Fractures. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017;22(1):93-104.
[8] 王郑浩, 李开南. 基于CT三维重建技术绘制骨折地图的临床应用进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(2):175-179.
[9] 王郑浩,李开南,汪学军,等. 基于三维CT的关节内桡骨远端骨折地图研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2019,39(22):1373-1380.
[10] 俞光荣, 梅炯, 朱辉,等. 跟骨的解剖分部及其临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2001,19(4):299-301.
[11] 王冰, 李涛, 朱裕成,等. 跟骨前部与载距突关系的解剖学研究及其临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(2):131-135.
[12] SANDERS R, FORTIN P, DIPASQUALE T, et al. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):87-95.
[13] ESSEX- LOPRESTI TLP. The mechanism,reduction technique,and results in fractures of the OS calcis. Br J Surg. 1952;39(157):395-419.
[14] ZWIPP H, TSCHEME H, THERMANN H, et al. Osteosynthesis ofdisplaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. Results in 123 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(290):76-86.
[15] CROSBY LA, FITZGIBBONS T. Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg. 1990;72(6):852-859.
[16] ZHENG G, XIA F, YANG S, et al. Application of medial column classification in treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(19):4400-4409.
[17] JH JIMÉNEZ-ALMONTE, KING JD, LUO TD, et al. Classifications in Brief: Sanders Classification of Intraarticular Fractures of the Calcaneus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(2):467-471.
[18] SCHEPERS T, VAN LIESHOUT EM, GINAI AZ, et al.Calcaneal Fracture Classification: A Comparative Study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009;48(2):156-162.
[19] 刘延子,高武长. 3D打印联合关节镜下机械臂辅助经皮螺钉内固定治疗跟骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2822-2826.
[20] ARMITAGE BM, WIJDICKS CA, TARKIN IS, et al. Mapping of scapular fractures with three-dimensional computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(9):2222-2228.
[21] COLE PA, MEHRLE RK, BHANDARI M, et al. The pilon map: fracture lines and comminution zones in OTA/AO type 43C3 pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(7):e152-156.
[22] MELLEMA JJ, DOORNBERG JN, DYER G, et al. Distribution of Coronoid Fracture Lines by Specific Patterns of Traumatic Elbow Instability. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(10):2041-2046.
[23] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, FAN J, et al. Analyses of fracture line distribution in intra-articular distal radius fractures. Radiol Med. 2019;124(7):613-619.
[24] 于涛, 张英琪, 李兵,等. 旋后外旋型踝关节骨折的后踝骨折线分布研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(12):1015-1018.
[25] 居家宝, 陈建海, 张一翀,等. 骨折地图在创伤骨科中的应用[J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2020,8(3):283-286.
[26] DUGARTE AJ, TKANY L, SCHRODER LK, et al. Comparison of 2 versus 3 dimensional fracture mapping strategies for 3 dimensional computerized tomography reconstructions of scapula neck and body fractures. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):265-271.
[27] 邓朝阳, 杨朝晖. 胫骨平台骨折线的三维模型分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):350-355.
[28] FU Y, LIU R, LIU Y, et al. Intertrochanteric Fracture Visualization and Analysis Using a Map Projection Technique. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;57(3):633-642.
[29] SU Q, ZHANG Y, LIAO S, et al. 3D Computed Tomography Mapping of Thoracolumbar Vertebrae Fractures. Medical Science Monitor. 2019; 25:2802-2810.
[30] NI M, LV ML, SUN W, et al. Fracture mapping of complex intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(4):333.
[31] GUO X, LIANG X, JIN J, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography mapping of 136 tongue-type calcaneal fractures from a single centre. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(24):1787.
[32] GUO X, LIANG X, JIN J, et al. Evaluation of Sanders Type 2 Joint Depression Calcaneal Fractures in 197 Patients from a Single Center Using Three-Dimensional Mapping. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e932748.
[33] 李文祥,施忠民. 基于跟骨骨折影像学分析对跟骨矢状面分区的研究[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2019,40(6):364-368.
[34] CARR JB, HAMILTON JJ, BEAR LS. Experimental intra-articular calcaneal fractures: anatomic basis for a new classification. Foot Ankle. 1989; 10(2):81-87.
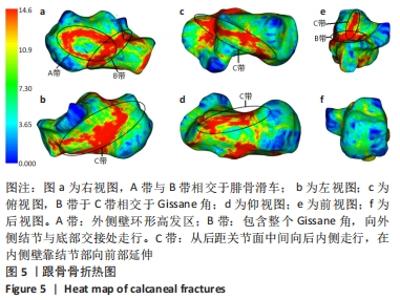
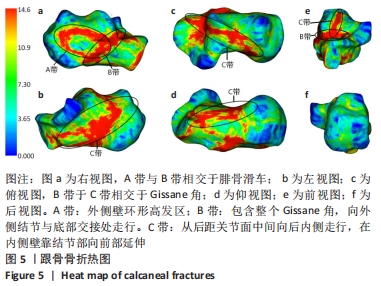
|