Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (18): 2884-2891.doi: 10.12307/2023.346
Previous Articles Next Articles
Safety of interbody fusion with one-hole split endoscope for L4/5 spondylolisthesis evaluated by three-dimensional CT
Liu Changzhen1, Sun Ning1, Zhu Kai1, Liu Xin1, Dou Yongfeng1, Wang Jianye1, Bi Jingwei1, Zhu Tengyue2, Sun Zhaozhong1
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, The Sixth Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
-
Received:2022-05-05Accepted:2022-06-17Online:2023-06-28Published:2022-09-17 -
Contact:Sun Zhaozhong, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Changzhen, Master candidate, Department of Spine Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Program, No. 2017YFC0114002 (to SZZ); Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. 2R2017LH021 (to SZZ); “Clinical + X” Project of Binzhou Medical College, No. BY2021LCX17 (to SZZ); Science and Technology Project of Binzhou Medical College, No. BY2018KJ03 (to LX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Changzhen, Sun Ning, Zhu Kai, Liu Xin, Dou Yongfeng, Wang Jianye, Bi Jingwei, Zhu Tengyue, Sun Zhaozhong. Safety of interbody fusion with one-hole split endoscope for L4/5 spondylolisthesis evaluated by three-dimensional CT[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2884-2891.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] AKKAWI I, ZMERLY H. Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: A Narrative Review. Acta Biomed. 2022;92(6):e2021313. [2] HEO DH, SON SK, EUM JH, et al. Fully endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion using a percutaneous unilateral biportal endoscopic technique: technical note and preliminary clinical results. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;43(2):E8. [3] KORECKIJ TD, FISCHGRUND JS.Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(7):236-241. [4] BERNARD F, MAZERAND E, GALLET C, et al. History of degenerative spondylolisthesis: From anatomical description to surgical management. Neurochirurgie. 2019;65(2-3):75-82. [5] 李玉乔,孙天威,马彬,等.腰椎滑脱亚型间影像学参数与生活质量评分的对照分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):943-948. [6] CHAN AK, SHARMA V, ROBINSON LC, et al. Summary of Guidelines for the Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2019;30(3):353-364. [7] AUSTEVOLL IM, HERMANSEN E, FAGERLAND MW, et al. Decompression with or without Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385(6):526-538. [8] ZHANG J, LIU TF, SHAN H, et al. Decompression Using Minimally Invasive Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: A Review. Pain Ther. 2021;10(2):941-959. [9] LENZ M, OIKONOMIDIS S, HARTWIG R, et al. Clinical outcome after lumbar spinal fusion surgery in degenerative spondylolisthesis: a 3-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(5):721-727. [10] WANG PT, ZHANG JN, LIU TJ, et al. Comparison of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and isthmic lumbar spondylolisthesis: effect of pedicle screw placement on proximal facet invasion in surgical treatment. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):6. [11] KIM CW, PHILLIPS F. The History of Endoscopic Posterior Lumbar Surgery. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(suppl 3):S6-S10. [12] AKBARY K, KIM JS. Recent Technical Advancements of Endoscopic Spine Surgery with Disparate or Disruptive Technologies and Patents. World Neurosurg. 2021; 145:693-701. [13] HUSSAIN I, APUZZO MLJ, WANG MY. Foundations in Spinal Endoscopy. World Neurosurg. 2022;160:125-131. [14] SIMPSON AK, LIGHTSEY HM 4TH, XIONG GX, et al. Spinal endoscopy: evidence, techniques, global trends, and future projections. Spine J. 2022;22(1):64-74. [15] HUSSAIN I, HOFSTETTER CP, WANG MY. Innovations in Spinal Endoscopy. World Neurosurg. 2022;160:138-148. [16] CHUNG AS, MCKNIGHT B, WANG JC. Scientific View on Endoscopic Spine Surgery: Can Spinal Endoscopy Become a Mainstream Surgical Tool? World Neurosurg. 2021;145:708-711. [17] QIN R, WU T, LIU H, et al. Minimally invasive versus traditional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21851. [18] KANALA RR, YERRAGUNTA T, YERRAMNENI VK, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Technical tips, learning curve, short-term clinical outcome, and brief review. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2021; 12(4):387-392. [19] QIN R, WU T, LIU H, et al. Minimally invasive versus traditional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21851. [20] SCHNAKE KJ. TPLIF (decompression and TLIF) in degenerative spondylolisthesis L4/5. Eur Spine J. 2016;25 Suppl 2:272-273. [21] WU AM, CHEN CH, SHEN ZH, et al. The Outcomes of Minimally Invasive versus Open Posterior Approach Spinal Fusion in Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: The Current Evidence from Prospective Comparative Studies. Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:8423638. [22] TIEBER F, LEWANDROWSKI KU. Technology advancements in spinal endoscopy for staged management of painful spine conditions. J Spine Surg. 2020;6(Suppl 1): S19-S28. [23] LEWANDROWSKI KU, SORIANO-SÁNCHEZ JA, ZHANG X, et al. Surgeon training and clinical implementation of spinal endoscopy in routine practice: results of a global survey. J Spine Surg. 2020;6(Suppl 1):S237-S248. [24] KOSLOSKY E, GENDELBERG D. Classification in Brief: The Meyerding Classification System of Spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(5):1125-1130. [25] CHAN AK, MUMMANENI PV, BURKE JF, et al. Does reduction of the Meyerding grade correlate with outcomes in patients undergoing decompression and fusion for grade I degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis? J Neurosurg Spine. 2021;1-8. [26] TAKAMI M, TAIJI R, OKADA M, et al. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion after reduction using the percutaneous pedicle screw system in the lateral position for Meyerding grade II spondylolisthesis: a preliminary report of a new lumbar reconstruction strategy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):17. [27] CHAREST-MORIN R, ZHANG H, SHEWCHUK JR, et al. Dynamic morphometric changes in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: A pilot study of upright magnetic resonance imaging. J Clin Neurosci. 2021;91:152-158. [28] 杨进,孔清泉,吴浩,等.重度腰椎滑脱手术的L5神经根牵张损伤机制[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(17):1573-1578. [29] O’ROURKE MR, GROBLER LJ. L4-L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis: indications and technique for operative management. Iowa Orthop J. 1998;18:76-86. [30] GILCHRIST RV, SLIPMAN CW, BHAGIA SM. Anatomy of the intervertebral foramen. Pain Physician. 2002;5(4):372-378. [31] ZHENG Z, WANG Y, WANG T, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Facet Joint Orientation and Its Effect on the Lumbar. J Healthc Eng. 2022; 2022:2486745. [32] NAEEM K, NATHANI KR, BARAKZAI MD, et al. Modifications in lumbar facet joint are associated with spondylolisthesis in the degenerative spine diseases: a comparative analysis. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021;163(3):863-871. [33] GARCÍA-RAMOS CL, VALENZUELA-GONZÁLEZ J, BAEZA-ÁLVAREZ VB, et al. Degenerative spondylolisthesis I: general principles. Espondilolistesis degenerativa lumbar I: principios generales. Acta Ortop Mex. 2020;34(5):324-328. [34] MATSUO Y, KAITO T, IWASAKI M, et al. 3D morphometric analysis of laminae and facet joints in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(5):756-760. [35] 镐英杰,李志磊,于磊,等. Quadrant通道下微创经椎间孔螺钉置入椎间融合:早期腰椎滑脱纠正[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(17):2699-2703. [36] LIU Z, DUAN Y, RONG X, et al. Variation of facet joint orientation and tropism in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis and disc herniation at L4-L5: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;161:41-47. [37] PICHAISAK W, CHOTIYARNWONG C, CHOTIYARNWONG P. Facet joint orientation and tropism in lumbar degenerative disc disease and spondylolisthesis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98(4):373-379. [38] ZHANG KH, ZHANG WH, XU BS, et al. CT-based Morphometric Analysis of Approach of Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):212-220. [39] ZHAO X, ZHAO J, GUAN J, et al. Measurement of the nerve root of the lower lumbar region using digital images. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(8):e9848. [40] KANG YN, HO YW, CHU W, et al. Effects and Safety of Lumbar Fusion Techniques in Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Global Spine J. 2022;12(3):493-502. [41] FENTON-WHITE HA. Trailblazing: the historical development of the posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF). Spine J. 2021;21(9):1528-1541. |
| [1] | Wang Jianye, Liu Xin, Tian Lin, Sun Ning, Li Yuefei, Bi Jingwei, Liu Changzhen, Sun Zhaozhong . Measuring the position relation between nerve tissue and bony structure in lumbar spinal canal decompression area by constructing a three-dimensional model of the lumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 539-546. |
| [2] | Li Jinglian, Zhang Hongfei, Yan Jiapeng, Zhou Jiabin, Yu Hao. Lag screw path for fixation of sacroiliac joint dislocation through S1 pedicle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2337-2341. |
| [3] | Gu Yueguang, Shen Jianhuan, Ni Jieli, Guo Shuyu, Yan Zhongyi, Zhang Yang. Effect of osteogenesis in patients with alveolar cleft after bone grafting investigated by volume analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1501-1504. |
| [4] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [5] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [6] | Wei Yangyang, Chen Jiacheng, Sun Jun, Wang Qiuan, Yuan Feng. Comparison of lumbar-pelvic sagittal parameters after single-level and double-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5300-5306. |
| [7] | Zhou Junde, Fan Zhirong, Su Haitao, Peng Jiajie, Zhou Lin, Hong Weiwu, Huang Huida. Comparison of three-dimensional printing-assisted pedicle screw placement and traditional surgery for lumbar spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4898-4904. |
| [8] | Liu Yang, Xu Baoshan, Xu Haiwei, Li Ning, Jiang Hongfeng, Wang Tao, Liu Yue. Imaging changes in spinal-pelvic sagittal alignment in sitting and standing positions in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3857-3861. |
| [9] | Wen Wangqiang, Xu Haoxiang, Zhang Zepei, Miao Jun. Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3883-3889. |
| [10] | Zhang Junwei, Cui Yutao, Li Zuhao, Wang Zhonghan, Liu He, Luo Wenbin. Application of bioprinting in reconstruction of musculoskeletal interface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2585-2591. |
| [11] |
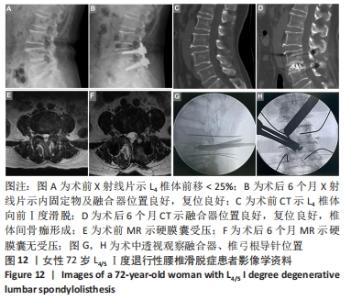
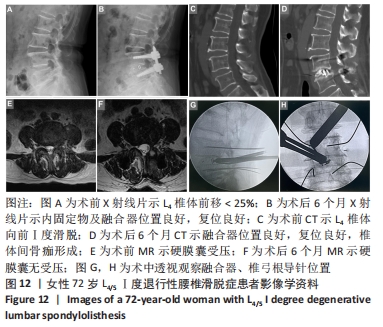
Rong Feilong, Yin Ruofeng, Feng Mengmeng, Zhang Boyin, Liu Yi, Zhao Baolin.
Correlation between degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis and muscle volume around the vertebral body: CT and MRI data analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3840-3845.
|
| [12] |
Ma Junfeng, Wang Wei, Wang Zikuo, Jiang Zehua, Long Mingxing, Yuan Jianjun, Zhu Rusen, Hu Wei, Zhang Xueli.
Correlation between facet joint effusion in magnetic resonance imaging and lumbar stability after interspinous and degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3845-3851.
|
| [13] | Ni Wei-feng, Xu Jian-guang, Xue Feng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of in situ and reductive interbody fusion of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1563-1570. |
| [14] | Chen Tao, Jia Shi-qing, Chen Wu, Li Pin-quan. Interbody fusion and internal fixation for lumbar spondylolisthesis: Changes of spnio-pelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 576-581. |
| [15] | Li Xiao-lin, Ren Bo-xu, Xu Zi-sheng. Finite element model of rabbit tibial fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(4): 620-624. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||