Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (24): 3883-3889.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2753
Previous Articles Next Articles
Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration
Wen Wangqiang1, 2, Xu Haoxiang1, 2, Zhang Zepei2, Miao Jun2
- 1Clinical College of Orthopedics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300203, China; 2Second Department of Spine, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China
-
Received:2019-12-03Revised:2019-12-10Accepted:2020-01-16Online:2020-08-28Published:2020-08-15 -
Contact:Miao Jun, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Second Department of Spine, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China -
About author:Wen Wangqiang, Master candidate, Clinical College of Orthopedics, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300203, China; Second Department of Spine, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81472140, 81572199
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Wangqiang, Xu Haoxiang, Zhang Zepei, Miao Jun. Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3883-3889.
share this article
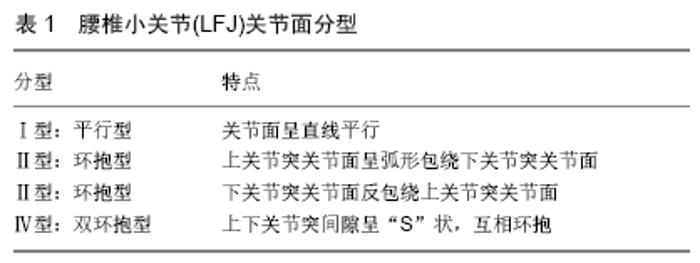
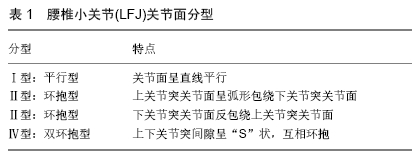
2.1 LFJ的解剖结构 LFJ由2个相邻椎骨的上椎骨的下小平面与下椎骨的上小平面相对合及包绕在外部的关节囊共同构成,位于腰椎左右后外侧方,连接相邻腰椎的椎弓,作为真正的滑膜关节,每个小关节都包含一个能够容纳1.0-1.5 mL液体的独特关节空间、滑膜、透明软骨表面和纤维囊[12],是腰椎运动节段不可缺少的一部分。 2.1.1 LFJ关节面 LFJ关节面是复杂的三维结构,在多平面生物力学中起着脊柱椎骨稳定器的作用。国内学者孟庆兰[13]研究发现,不同节段腰椎上关节面的方向也有所不同,总的趋势是从胸椎过渡到腰椎,小平面的方向从冠状变为矢状。这与戴力扬[14]的研究结果相似。同时同节段关节突关节面的空间朝向略有不同,但基本上与水平面构成90°角。关于关节面的分型目前为大多数学者接受的观点主要是根据上下关节突关节面的形态和空间位置关系,将其分为4种类型,见表1。Ⅰ型:平行型,即关节面呈直线平行;Ⅱ型:环抱型,上关节突关节面呈弧形包绕下关节突关节面;Ⅲ型:反环抱型,下关节突关节面反包绕上关节突关节面;Ⅳ型:双环抱型,上下关节突间隙呈“S”状,互相环抱。关节面的复杂解剖形态为适应脊柱的不同类型负荷提供了解剖学基础[15]。 "

2.1.2 LFJ关节腔 LFJ存在一宽约0.5 mm的潜在弧形间隙, 能够容纳1.0-1.5 mL关节液使得关节能够平滑的活动。上下关节突表面覆盖关节软骨,以环状放射从中间向周围逐渐变薄,中心部位厚度最厚可达1 mm[16],并且关节腔整体形态呈现前窄后宽,从上至下依次增大。 2.1.3 LFJ关节囊 LFJ关节囊主要包绕于关节突的后外侧,LFJ的纤维囊厚度大约1 mm,主要由或多或少横向排列的胶原纤维组成,这种复杂的纤维结构及其在载荷作用下的演化在决定LFJ关节囊在机械性能方面起着至关重要的作用[17]。关节囊的后部较厚,并由多裂肌产生的纤维支撑。而关节囊前侧则被黄韧带所代替,与前壁融为一体,向内延伸至椎板,向外扩展至上关节突前面,以加强前壁。关节囊背侧较薄,主要由关节突关节副韧带、棘间韧带及后外侧多裂肌肌束加强。而在上壁和下壁,关节囊与软骨边缘的距离更远,形成囊下凹,这为小关节上下及前后移动提供了解剖学基础。国外学者YAMASHITA等[18]通过对5具人类尸体LFJ囊的宏观和微观研究发现纤维囊的外层是致密的规则结缔组织,由平行的胶原纤维束组成。纤维囊的内层由弹性纤维束组成,类似于黄韧带。在关节的上部和中部,纤维从内侧到外侧延伸,穿过关节间隙。而在关节的下部,纤维相对较长,并在上内至下外侧方向延伸,覆盖下关节凹处,并且比关节上层和中层厚。黄磊涛等[19]通过组织学研究发现退化后的小关节细胞形态异常,且排列显得杂乱无章。研究发现LFJ囊的解剖和组织学特征在其外层和内层之间的差异及的复杂性影响和决定了LFJ的生物力学和神经生理学。 2.1.4 LFJ的神经支配 LFJ分布有丰富的神经末梢,用以感受和传递疼痛信息,这些神经主要受脊神经后内侧支支配[20]。脊神经自椎间孔发出,分为脑膜支、交通支、腹支和背支。背支分为内侧支和外侧支,在下横突上缘形成30°角,背支的内侧和外侧支供应周围的皮肤和肌肉,内侧支在下椎骨的上关节突的外侧边缘处向后,内侧和尾侧延伸,然后内侧分支进入纤维骨管。在离开纤维骨管之后,内侧分支沿着椎板向内侧和尾侧下降,从而支配小关节线内侧的结构;内侧支在离开纤维骨管的过程中还产生小的关节分支,提供LFJ的外侧和下侧。离开纤维骨管后,内侧分支产生小分支,支配小关节的内侧和上方。因此,每个小关节至少接受来自在同一水平和上方水平内侧支的双重神经支配。SHUANG等[21]通过解剖了12具成年尸体的腰椎,也得出了相同的结论。例如,L4/5小关节的下极受L4内侧支的支配,上极受L3内侧支的支配,而L3内侧支通常分别在L5和L4的横突上被阻断。因此当腰椎关节突关节发生神经病变产生疼痛时,只切除本节段的内侧支而忽略上节段的内侧支,完全达不到理想的治疗效果。LFJ的这种神复杂经支配方式为腰腿痛的发病与难以治愈提供了解剖学基础。 2.2 LFJ的退变的危险因素 随着国家经济的发展,人口老龄化的加剧,下腰痛发病率呈现明显上升的趋势,严重地降低人们的生活质量,给家庭、社会和医疗资源带来沉重的负担,现已逐渐引起人们的重视。但是腰痛发病的原因和机制却是各种各样,历年来在这个方面研究的热度未曾减退,在其多发的病因的研究中发现LFJ退变是引起腰痛的原因之一。作者现就对LFJ退变的危险因素进行综述。 2.2.1 年龄 腰椎关节突关节的退变随着年龄的增长而呈现逐渐严重的趋势[22]。CYRON等[23]研究发现在年轻人中,LFJ非常结实,能够支撑几乎2倍的体质量,而老年人中则没有这样的强度。LEWIN[24]通过对LFJ进行的解剖分析回顾后得出结论:45岁之后,正常人群LFJ普遍出现各种形式的高级骨关节退变,例如软骨退变、软骨下骨硬化及骨赘形成等。ENOKIDA等[25]通过使用MRI调查60例无腰椎疾患的受试者的LFJ的T2值,研究发现年龄与LFJ的T2值之间存在很强的正相关(r= 0.717),随着年龄的增长,FJ的T2值显著增加,LFJ的变性更加明显。国内学者李宁华等[26]通过调查西安、石家庄、上海、广州、哈尔滨、成都等6个城市6 218例符合纳入标准的人群进行腰椎骨关节炎的流行病学问卷调查,研究发现腰椎骨关节炎在大部分城市有共同的危险因素如年龄因素(OR=1.031-1.121),并且40岁及以上男女人群腰椎骨关节炎总患病率为29.4%。甚至IRWIN等[27]发现年龄增长是与骶髂关节疼痛风险相关的唯一因素。因此可以肯定的是年龄是小关节退变的一个重要危险因素。 2.2.2 性别 LFJ退变在男女性别之间也有显著性的差异。EUBANKS等[28]通过对647例尸体腰椎标本LFJ进行解剖学研究,结果表明男性LFJ骨性关节炎的发病率和严重程度远高于女性。MORIMOTO等[29]研究发现,随着年龄的增长,女性在L4/5关节突关节方向更容易向矢状和水平方向发展,这种LFJ的形状使椎体更容易滑动,进而导致腰椎滑脱的发生概率明显升高。矛盾的是FUJIWARA等[30]在一项MRI研究中发现腰椎关节突关节退变在患病率上,男性和女性的差异几乎没有显著性意义,其原因有可能是样本量比较少,导致数据不具有代表性。但是被学者们普遍认可的是绝经后女性的小关节骨关节炎的患病率更高,腰背痛比相同年龄的男性更普遍,并且这可能与女性绝经后相对较低的性激素水平引起的生理变化有关[31]。 2.2.3 异常应力 LFJ的退变的原因之一是由于异常应力在小关节反复累加而引发的。 从组织学角度研究发现覆盖在关节表面关节软骨可以使得相邻椎骨之间实现无摩擦运动,同时还承受压缩、拉伸和剪切载荷。与其他双关节(膝、髋、小关节)的关节软骨一样,其特定的机械性能在很大程度上取决于软骨的组成(水含量,蛋白聚糖,胶原纤维的方向),以及关节承受的负荷[32]。WORKMAN等[33]通过研究发现关节表面层和纤维状横向互连在有效减轻冲击负荷中的占据着重要的地位,但当超越生理阈值的应力可导致关节软骨形态及功能异常,进而引起小关节发生退变。OROZCO等[34]通过获取牛的膝关节软骨盘,然后进行生理相关的为期12 d的动态压缩,发现软骨的损伤与周围病变差异有显著性意义,软骨的组成成分蛋白聚糖流失明显,关节退化加剧。PAN等[35]对89例志愿者小关节1.5-2.5 mm的软骨下区域进行计算机断层骨密度测定,并且发现在腰痛患者中上小平面和小平面中心区域的软骨下骨矿物质密度最高,而骨下骨矿物质密度被认为反映了作用在关节上的应力的累积,长期分布。YAMABE等[36]通过对20例无症状志愿者,在生理负荷腰部弯曲,伸展和旋转等运动后前后进行了MRI检查,并发现运动后每个腰椎水平的T2值均显著降低,并得出结论腰椎运动负荷后,每个腰椎水平的小关节水分含量均显著下降。因此快速或冲击负荷会不仅会导致关节内压力显著增加,而且能够减少蛋白聚糖的合成,增加水分的流失,并通过坏死破坏组织,引起软骨下骨的最初破坏,导致骨关节炎。临床上也能得到相应的验证,例如乔聚义[37]通过回顾性分析639例LFJ退变患者的影像学改变后,发现腰椎关节在受到异常压力和炎症干扰时腰痛发生的概率都明显提升。 从LFJ生物力学角度研究,成对的关节突关节和椎间盘共同起到支撑和稳定脊柱的作用,并通过限制所有运动平面的运动来减少脊柱伤害,在整个脊柱的承载运动及稳定中起了十分重要的作用[38]。正常人体负荷情况下,LFJ能够承载机体3%-25%的负荷,其余则由椎间盘及韧带等机构载荷,但如果发生小关节炎,关节受力异常关节负荷最高能够到达47%[39]。同时,在运动情况下,LFJ同椎间盘及韧带之间的负荷分配随着脊柱活动方式或姿势的改变而不同[40],进而导致LFJ受力不平衡。肖进等[41]研究发现,处于直立位时两侧小关节受力约占轴向压缩载荷的15%;前屈运动情况下两侧小关节受力减小,且随着前屈幅度不断增加受力不断的减小;而后伸时则与前屈时的情况相反,随着后伸角度的进一步增加小关节受力也逐渐增大;左右侧弯时,一侧LFJ受力减小,对侧LFJ受力增大;左右旋转时,一侧LFJ受力减少,对侧LFJ受力增大。CHOWDHURY等[42]通过对14例健康人举重活动动态测得小关节的体内运动特点,并发现关节突关节的屈曲、侧弯和上下平移均存在显著的载荷效应。L5-S1关节的侧弯和扭转明显大于L2-L3、L3-L4和L4-L5小关节。BYRNE等[43]通过动态立体放射照相成像来量化健康个体在功能活动期间腰部小关节运动学,并发现负重状态下的体内屈伸运动在尾段(L4/L5和L5/S1)上显示的平移要比在颅骨段(L2/L3和L3/L4)上的平移更大,这表明了异常的活动及超生理负荷下小关节受力不均则会增加小关节退变的风险。并且除了承载部分轴向负荷,两侧小关节还能够抵抗大部分施加于脊柱腰椎的剪切力,其余小部分则主要由椎间盘承受。因此,双侧小关节具有保护椎间盘避免过度反应弯曲及旋转带来的异常应力所引起的不良反应。 从小关节的完整性角度来看可以发现,小关节的完整对于腰椎的承重具有重大意义。ZENG等[44]通过建立了L3-L5的三维非线性有限元模型,在屈曲、伸展、左/右横向弯曲和左/右轴向旋转下,发现单侧小关节切除术使椎间旋转范围增加了11.7%,椎间盘内压力增加了10.7%,而双侧小平面切除术使椎间旋转范围增加了40.7%,椎间盘内压力增加了23.6%。在轴向旋转的情况下,向右旋转时单侧小关节切除术和双侧小关节切除术可使椎间旋转范围分别增加101.3%和354.3%,向左旋转则分别使椎间旋转范围增加1.1%和265.3%。因此,在单侧/双侧小关节全切除术后,人体在运动时应更加的谨慎尤其是一些复杂的运动应当避免。吴超等[45]通过生物力学研究发现,全椎板切除如果合并50%以上小关节破坏将明显降低颈椎的稳定性。QIAN等[46]对3例无脊柱疾病的成年男性应用经皮经孔椎间孔内镜下分级切除L5左上关节突(1/4,2/4,3/4和4/4),腰椎的运动在伸展、侧屈和旋转过程中均存在着明显差异,并得出结论,上关节突1/4切除后,腰椎的生物力学和稳定性发生了部分变化,而超过2/4的切除术则是更加明显。李慧友等[47]通过尸体实验也得出了类似的结果:当切除1/3双侧小关节时,脊柱仍能够维持在一个相对稳定的平衡状态;而切除超过1/2和2/3小关节后脊柱腰椎运动节段的活动范围显著增加,腰椎稳定平衡被打破。徐波等[48]通过对颈椎进行生物力学研究后,建议在双侧小关节切除达到50%后附加植骨融合或采用颈椎内固定器械固定,以保持颈椎稳定性。因此,完整的LFJ才能够保证脊柱受力的稳定性,完整的小关节是脊柱稳定运动的基石,是腰椎稳定平衡的保证。 2.2.4 关节面方向 从LFJ关节面的解剖因素来看,成人关节面变是以矢状方向为主并且近乎弧形。从生物力学方面考虑,偏向矢状面的小关节存在着腰椎结构力学上的薄弱点,从而增加了小关节局部的应力,并且较大的矢状面关节取向可以限制轴向旋转并增加抗扭强度,进而加速了LFJ退行性改变。MORIMOTO等[29]通过大量研究后发现以矢状方向为主的小关节退行性腰椎滑脱及各种退行性病变的发病率都显著升高。同样LIU等[49]通过研究也发现L4-L5的腰椎退行性滑脱患者的关节矢状方向更加明显,L4-L5水平的LFJ的矢状方向和骨关节炎之间存在显著相关性。其他学者通过体外生物力学研究也发现LFJ的冠状位越大,小关节的接触力就越高[50],这就会导致小关节退化加剧,腰椎可能会变得不稳定。国内学者侯宁[51]通过研究发现腰椎关节突关节的退变程度与其矢状化和水平化程度之间均存在相关性,即退变加重,矢状化和水平化程度增加。同时腰椎关节突关节形成矢状化和水平化改变最主要的原因不是先天存在的结构变异,而可能是后天的退变重塑过程。 2.2.5 小关节不对称性 小关节的方向在腰椎生物力学中起重要作用。小关节角度之间的不对称性最早定义为左右关节突关节角度的不对称,其中一个关节的矢状位比另一个关节大5°或7°。据KARACAN等[52]统计,人群中不对称LFJ发生的概率为10%-70.5%。RONG等[53]通过生物力学方法得出结论小关节不对称性可能是颈椎间盘退变或刻面变性发展的解剖学危险因。KO等[54]研究462例患者发现在社区人群中小关节不对称的下腰痛患病率为46.3%,其严重形式在L4-5水平上更为常见(24.7%),并且低位关节的患病风险更高。MOHANTY等[55]回顾性研究了2011至2015年间对脊椎损伤患者进行的124次CT扫描,总共分析了566个未受伤的运动节段,并且得出结论左右关节突关节角在腰椎的不同水平上并不相同,平均从L1-L2逐渐增加到L5-S1,这可以解释较低水平腰椎的运动范围更大。并且在这项研究中,L4-L5和L5-S1的关节突关节不对称患病率较高,这可以解释在这些水平下椎间盘脱出和其他退行性疾病的发生率较高。因此可以得出结论:不对称的关节突关节在脊柱疾病的发生发展中是不可忽略的一部分,不对称角度越大,关节退变越明显。 2.2.6 腰椎节段水平 许多研究都证明腰椎各节段中,小关节退变主要集中在L4/5[24,30,49,54]。FUJIWARA等[30]研究发现,L4-5小关节的退变程度远远高于L3-4。SABNIS等[56]通过研究72例慢性下腰痛患者的影像也得出了相近的结果,他发现椎间盘退变小关节骨关节炎主要发生在较低的腰椎水平(L4-L5分别为68%和47%,L5-S1分别为79%和54%)。MOHANTY等[55]发现L4-L5和L5-S1的关节突关节不对称患病率较高。但目前关于LFJ退变不同节段表现不同程度退变的原因及具体机制仍困扰着许多学者,目前能为大多数人所接受的是因为L4/5腰椎节段承受着多数人体负荷,其体内运动范围过大,反复劳损导致的。 2.2.7 椎间盘退变 椎间盘退变与小关节退变的相互关系一直困扰着学者们。有研究指出脊柱的退变最开始来自于椎间盘退变,椎间盘退变最后的结果之一就是引起小关节退变,两者的严重程度呈正相关[30,57]。椎间盘的长期变性的结果就是有可能造成相邻椎体间距变小,椎间高度丢失以及椎体体内运动范围增大,且椎间盘高度变窄可能会使小关节不对称性在同一水平上进一步加重,最后导小关节异常应力和异常运动,关节退变的相关表现也因此而产生,如骨赘形成、关节面磨损、关节增生肥大等[6]。这一系列改变又会引起侧隐窝或椎间孔管狭窄变形,脊神经根受压,引起腰痛,但是正如文章前面所述正常情况下,LFJ具有保护椎间盘不受剪切力及过屈和旋转的影响,且LFJ承载机体3%-25%负荷,在反复劳损的情况下小关节也有一定概率发生退变[39]。当LFJ退变时,椎间盘来自小关节的保护作用减弱,受到更大的负荷,进而导致椎间盘退变加速,从而引起各种相关疾病[44]。SONG等[58]通过使用CT和MRI参数评估了椎间盘与LFJ退化之间的相关性并且发现大多数小关节骨性关节炎可能出现在椎间盘退变超过Ⅲ级的节段,并且小关节不对称与腰椎间盘退变显著相关。因此有的学者提出两者之间不存在明确的相关性。SWANEPOEL等[59]研究发现约有30%的LFJ退变发生早于椎间盘或者其他附件的退变,因此他认为脊柱的退变有可能不是最早来自于椎间盘。但目前更为人所接受的是椎间盘退变有可能导致小关节退变,且小关节退变也会导致脊柱承载负荷功能明显减弱,腰椎负荷中心前移至椎间盘,椎间盘的退变情况被默默提前了[44]。因此作者也认为脊柱节段中的小关节与椎间盘中的任一个发生退变都会影响另外一个,因此LFJ退变与椎间盘退变互为因果,相辅相成[60]。 "

| [1] GHORMLEY RK. Low back pain with special reference to the articular facets with presentation as operative procedure. JAMA. 1933;101(23):1773-1777. [2] MANCHIKANTI L, SINGH V. Review of chronic low back pain of facet joint origin. Pain Physician. 2002;5(1):83-101. [3] AL-NAJJIM M, SHAH R, RAHUMA M, et al. Lumbar facet joint injection in treating low back pain: Radiofrequency denervation versus SHAM procedure. Systematic review. J Orthop. 2018;15(1):1-8. [4] 白贤明,邢文华.LBP临床诊断和治疗研究进展[J].内蒙古医学杂志, 2018,50(4):29-32. [5] BORENSTEIN D. Does osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine cause chronic low back pain? Curr Pain Head Rep. 2004; 8(6):512-517. [6] TETREAULT L, GOLDSTEIN CL, ARNOLD P, et al. Degenerative cervical myelopathy: a spectrum of related disorders affecting the aging spine. Neurosurgery. 2015;77 Suppl 4:S51-S67. [7] ALONSO F, KIRKPATRICK CM, JEONG W, et al. Lumbar facet tropism: a comprehensive review. World Neurosurg. 2017;102:91-96. [8] 胡勇文.退变性腰椎失稳的研究进展[D].北京:北京中医药大学, 2008. [9] DAI LY. Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop. 2001;25(1):40-42. [10] ZHANG J, SHU Y, ZHU Q, et al. Lumbar facet joint degeneration contributes to degenerative lumbar scoliosisinduced by asymmetric stress in rabbits. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2019;39(8):993-997. [11] ZHENG J, YANG Y, CHENG B, et al. Exploring the pathological role of intervertebral disc and facet joint in thedevelopment of degenerative scoliosis by biomechanical methods. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;70:83-88. [12] GLOVER JR. Arthrography of the joints of the lumbar vertebral arches. Orthop Clin North Am. 1977;8(1):37-42. [13] 孟庆兰.腰椎上关节面方位角变化规律及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(4):283-285. [14] 戴力扬.腰椎关节突关节的临床解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 1991,9(3):179-182. [15] 李瑞.腰椎关节突关节毗邻血管的应用解剖学及影像学研究现状[J].滨州医学院学报,2013,36(3):201-203,211. [16] JAUMARD NV, WELCH WC, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury anddegenerative conditions. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(7): 71010. [17] BAN E, ZHANG S, ZAREI V, et al. Collagen organization in facet capsular ligaments varies with spinal region and with ligament deformation. J Biomech Eng. 2017,139(7): 710091-710099. [18] YAMASHITA T, MINAKI Y, OZAKTAY AC, et al. A morphological study of the fibrous capsule of the human lumbar facet joint. Spine. 1996;21(5):538-543. [19] 黄磊涛,赖琦,李帆,等.人腰椎小关节软骨不同染色方法的差异比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(24):3784-3789. [20] BOGDUK N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(3):286-293. [21] SHUANG F, HOU S, ZHU J, et al. Clinical anatomy and measurement of the medial branch of the spinal dorsal ramus. Medicine. 2015;94(52):e2367. [22] 闫广辉,李志赏,魏巍,等.腰椎间盘和腰椎小关节的退变顺序及其与年龄的相关性分析[J].检验医学与临床,2018,15(6):744-746. [23] CYRON BM, HUTTON WC. The tensile strength of the capsular ligaments of the apophyseal joints. J Anat. 1981; 132(Pt 1):145-150. [24] LEWIN T. Osteoarthritis in lumbar synovial joints: a morphologic study. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1964;35(Supp 73):71-73. [25] ENOKIDA S, TANISHIMA S, TANIDA A, et al. Evaluation of age-related changes in lumbar facet joints using T2 mapping. J Orthop Sci. 2019. [26] 李宁华,薛庆云,张毅,等.中国六城市中老年人群腰椎骨关节炎患病危险因素地区调查:6128名资料分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(47):9508-9512. [27] IRWIN RW, WATSON T, MINICK RP, et al. Age, body mass index, and gender differences in sacroiliac joint pathology. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;86(1):37-44. [28] EUBANKS JD, LEE MJ, CASSINELLI E, et al. Prevalence of lumbar facet arthrosis and its relationship to age, sex, and race: an anatomic study of cadaveric specimens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(19):2058-2062. [29] MORIMOTO M, HIGASHINO K, MANABE H, et al. Age-related changes in axial and sagittal orientation of the facet joints: Comparison with changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):50-56. [30] FUJIWARA A, TAMAI K, YAMATO M, et al. The relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: an MRI study. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(5):396-401. [31] WANG YXJ. Menopause as a potential cause for higher prevalence of low back pain in women than in age-matched men. J Orthop Trans. 2016;8:1-4. [32] MOREL V, MERCAY A, QUINN TM. Prestrain decreases cartilage susceptibility to injury by ramp compression invitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(11):964-970. [33] WORKMAN J, THAMBYAH A, BROOM N. The influence of early degenerative changes on the vulnerability of articularcartilage to impact-induced injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2017;43:40-49. [34] OROZCO GA, TANSKA P, FLOREA C, et al. A novel mechanobiological model can predict how physiologically relevant dynamic loading causes proteoglycan loss in mechanically injured articular cartilage. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1): 15599. [35] PAN C, SIMON P, ESPINOZA ORIAS AA, et al. Lumbar facet joint subchondral bone density in low back pain and asymptomaticsubjects. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(4):571-576. [36] YAMABE D, MURAKAMI H, CHOKAN K, et al. Evaluation of water content in lumbar intervertebral discs and facet joints before and after physiological loading using T2 mapping MRI. Spine. 2017;42(24):E1423-E1428. [37] 乔聚义.下腰椎小关节退变的磁共振成像及CT表现特征分析[J]. 实用医学影像杂志,2016,17(3):265-266. [38] CLAESON AA, BAROCAS VH. Computer simulation of lumbar flexion shows shear of the facet capsular ligament. Spine J. 2017;(1):109-119. [39] YANG KH, KING AI. Mechanism of facet load transmission as a hypothesis for low-back pain. Spine. 1984;9(6):557-565. [40] 都承斐,李俊伟,刘海英,等.随动载荷对腰椎小关节接触力的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2017,32(4):363-368. [41] 肖进,原林,赵卫东,等.身体姿势对腰椎小关节受力的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2003,21(1):87-89. [42] CHOWDHURY SK, BYRNE RM, ZHOU Y, et al. Lumbar facet joint kinematics and load effects during dynamic lifting. Human Factors. 2018,60(8):1130-1145. [43] BYRNE RM, ZHOU Y, ZHENG L, et al. Segmental variations in facet joint translations during in vivo lumbar extension. J Biomech. 2018;70:88-95. [44] ZENG Z, ZHU R, WU Y, et al. Effect of graded facetectomy on lumbar biomechanics. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017(1):1-6. [45] 吴超,王振宇,林国中,等.颈椎单侧半椎板及不同程度小关节切除术后生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2018,17(4):352-356. [46] QIAN J, YU SS, LIU JJ, et al. Biomechanics changes of lumbar spine caused by foraminotomy via percutaneoustransforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2018,98(13):1013-1018. [47] 李慧友,朱青安,李桂兰,等.双侧小关节分级切除对腰椎稳定性影响的三维运动研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(10):692-694. [48] 徐波,金大地,史占军,等.中下颈椎双侧小关节部分切除对颈椎稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1995,5(3): 115-118. [49] LIU Z, DUAN Y, RONG X, et al. Variation of facet joint orientation and tropism in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis and disc herniation at L4-L5: A systematic review andmeta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;161: 41-47. [50] LIU X, HUANG Z, ZHOU R, et al. The effects of orientation of lumbar facet joints on the facet joint contactforces: an in vitro biomechanical study. Spine. 2018;43(4):E216-E220. [51] 侯宁.腰椎关节突关节的矢状化和水平化与其退变之间关系的探究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2019. [52] KARACAN I, AYDIN T, SAHIN Z, et al. Facet angles in lumbar disc herniation: their relation to anthropometricfeatures. Spine. 2004;29(10):1132-1136. [53] RONG X, WANG B, DING C, et al. The biomechanical impact of facet tropism on the intervertebral disc and facetjoints in the cervical spine. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1926-1931. [54] KO S, CHAE S, CHOI W, et al. The prevalence of facet tropism and its correlation with low back pain in selected community-based populations. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2): 176-182. [55] MOHANTY SP, PAI KANHANGAD M, KAMATH S, et al. Morphometric study of the orientation of lumbar zygapophyseal joints in a SouthIndian population. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(3):613399771. [56] SABNIS AB, CHAMOLI U, DIWAN AD. Is L5-S1 motion segment different from the rest? A radiographic kinematic assessment of 72 patients with chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(5):1127-1135. [57] SUN D, LIU P, CHENG J, et al. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration, paraspinal muscle atrophy, and lumbar facet joints degeneration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):167. [58] SONG Q, LIU X, CHEN D, et al. Evaluation of MRI and CT parameters to analyze the correlation between disc andfacet joint degeneration in the lumbar three-joint complex. Medicine. 2019;98(40):e17336. [59] SWANEPOEL MW, ADAMS LM, SMEATHERS JE. Human lumbar apophyseal joint damage and intervertebral disc degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54(3):182-188. [60] 付长林,张斌,刘远,等.腰痛患者腰椎小关节退变与椎间盘退变的MRI比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7401-7405. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [4] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [5] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [6] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [7] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [8] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [9] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [10] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [11] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [12] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [13] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [14] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [15] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||