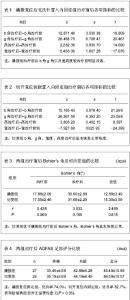
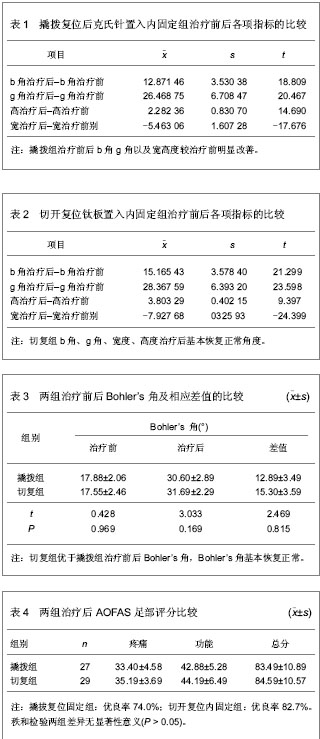
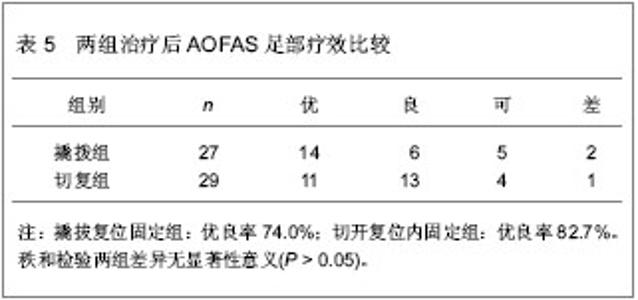
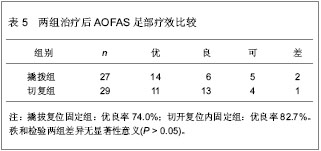
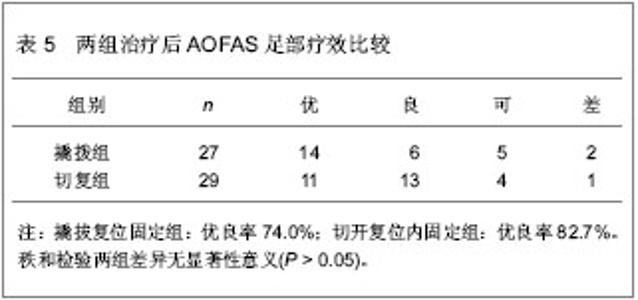
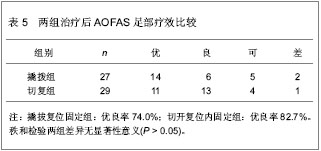
| [1] Barei DP,Bellabarba C,Sangeorzan BJ,et al.Fractures of the calcaneus.Orthop Clin North Am.2002;33(1):263-285.[2] 俞光荣,燕晓宇.跟骨骨折治疗方法的选择[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(2):134-141. [3] 郑移兵,齐越峰.跟骨骨折治疗研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2012, 25(11): 962-966.[4] 田士松,陈爱桂.切开复位内固定治疗移位关节内跟骨骨折[J].河北医药,2008,30(9):1453.[5] Strømsøe K,Mørk E,Hem ES.Open reduction and internal fixation in 46 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Injury.1998;29(4):313-316.[6] Melcher G,Degonda F,Leutenegger A,et al.Ten-year follow-up after operative treatment for intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus.J Trauma.1995;38(5):713-716.[7] 梁军,胡滨成.跟骨的形态结构特点及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000,16(2):118-120.[8] Sarrafian SK.Biomechanics of the subtalar joint complex.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1993;(290):17-26.[9] Rammelt S,Barthel S,Biewener A,et al.Calcaneus fractures. Open reduction and internal fixation.Zentralbl Chir.2003; 126(8): 517-528.[10] Gavlik JM,Rammelt S,Zwipp H.Percutaneous, arthroscopically-assisted osteosynthesis of calcaneus fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2002;122(8):424-428.[11] Stehlík J,Stulík J.Combined method of treating dislocated fractures of the calcaneus.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2002;69(4):209-218.[12] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-02-10.https://www.cnki.net[13] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2013-02-10.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[14] 李灿杨,吴征杰,潘志雄.撬拨复位闭合穿针和切开复位钢板固治疗跟骨骨折的临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(2): 18-20.[15] 韩杰,何燕飞,雷翔宇.经皮撬拨复位内固定治疗跟骨骨折[J].河南科技大学学报(医学版),2010,28(2):116-117.[16] 韩立新,李旭芬,李凤新.跟骨压缩性骨折切开复位与撬拨复位治疗比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(6):701-703.[17] Paley D,Hall H.Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A critical analysis of results and prognostic factors.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1993;75(3):342-354.[18] Loucks C,Bohler's angle: correlation with outcome in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures.J Orthop Trauma.1999;13(8):554-558.[19] Ramanujam CL,Wade J,Selbst B,et al.Recurrent acute compartment syndrome of the foot following a calcaneal fracture repair.Clin Podiatr Med Surg.2010;27(3):469-474.[20] Harvey EJ,Grujic L,Early JS,et al.Morbidity associated with ORIF of intra-articular calcaneus fractures using a lateral approach.Foot Ankle Int.2001;22(11):868-873.[21] Atesok K,Finkelstein J,Khoury A,et al.The use of intraoperative three-dimensional imaging (ISO-C-3D) in fixation of intraarticular fractures.Injury.2007; 38(10): 1163-1169.[22] Folk JW,Starr AJ,Early JS.Early wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures: analysis of 190 fractures.J Orthop Trauma.1999;13(5):369-372.[23] Richter M,Geerling J,Zech S,et al.Intraoperative three-dimensional imaging with a motorized mobile C-arm (SIREMOBIL ISO-C-3D) in foot and ankle trauma care: a preliminary report.J Orthop Trauma.2005;19(4):259-266.[24] Sanders R.Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2000;82(2):225-250.[25] 郭宗信.跟骨骨折内固定手术并发症分析[J].交通医学,2006, 20(5):556-557.[26] 魏金亮,邱波,汪喆,等.跟骨关节内骨折切开复位与撬拨复位治疗比较[J].临床外科杂志,2011,19(9):632-634.[27] Potenza V,Caterini R,Farsetti P,et al.Primary subtalar arthrodesis for the treatment of comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures.Injury.2010;41(7):702-706.[28] Rammelt S,Zwipp H.Calcaneus fractures: facts, controversies and recent developments.Injury.2004;35(5):443-461.[29] 白正发,贺西京.撬拨复位治疗跟骨骨折中的手法技巧[J].中国社区医师,2007,19(6):75.[30] 吴铁男,郭豪,郭宏钰,等.金针撬拨法治疗跟骨骨折100例[J].中国骨伤,2000,13(1):45.[31] 彭光军,王荣华,衡德峰,等.跟骨骨折不同内固定方法治疗的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(20):1686-1688. |