Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1950-1955.doi: 10.12307/2024.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wnt signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration
Fan Zhihong1, Zhang Xian2, Li Chao1
- 1Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-09Accepted:2023-03-06Online:2024-04-28Published:2023-08-23 -
Contact:Zhang Xian, Chief TCM physician, Master’s supervisor, Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Fan Zhihong, Master candidate, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Wuxi Science and Technology Innovation and Entrepreneurship Fund Project, No. Y2022009 (to ZX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Zhihong, Zhang Xian, Li Chao. Wnt signaling pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1950-1955.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
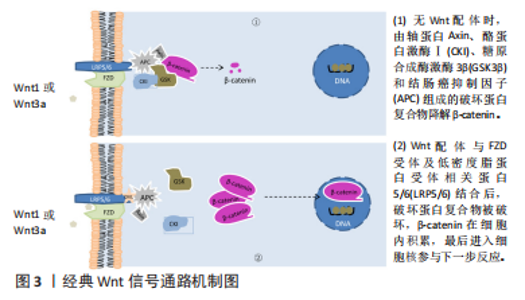
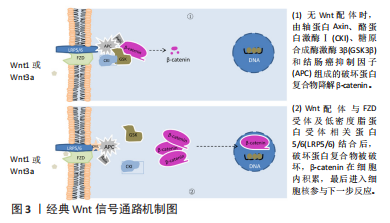
2.1 Wnt信号通路 2.1.1 经典Wnt信号通路 此通路是由β-catenin介导的信号级联反应,参与经典Wnt通路的Wnt配体主要为Wnt1和Wnt3a[7]。在没有Wnt配体的情况下,细胞质内的β-catenin与一个多聚体破坏性蛋白复合物结合,不断被磷酸化,最后泛素化而被降解。该复合物主要由轴蛋白Axin、酪蛋白激酶Ⅰ(Casein kinase I,CKI)、糖原合成酶激酶3β(glycogen synthase kinase 3β,GSK3β)、结肠癌抑制因子(Adenomatous polyposis coli,APC)组成。Axin和结肠癌抑制因子识别并折叠β-catenin,导致β-catenin相应的磷酸盐位点暴露,从而使酪蛋白激酶Ⅰ磷酸化β-catenin的Ser45,之后糖原合成酶激酶3β负责将β-catenin的Ser33、Ser37和Thr41磷酸化[8]。磷酸化后的β-catenin进入泛素介导的蛋白水解途径,泛素化而被降解[9]。因此,在没有Wnt配体时,细胞内的β-catenin含量很低;当有Wnt配体参与时,破坏性蛋白复合物遭到破坏,从而抑制β-catenin的降解,使其在细胞质中不断蓄积。Wnt配体与细胞膜上的跨膜蛋白Frizzled(Fzd)受体及低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6(Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6,LRP5/6)相结合,形成配体-受体复合物,使糖原合成酶激酶3β将低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6在细胞质内的区域进行磷酸化,从而将轴蛋白Axin、结肠癌抑制因子在Fzd受体及低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6的细胞质区域募集。质膜的吸收抑制功能破坏破坏性复合物的形成[10],从而抑制β-catenin降解,使得β-catenin在胞质中不断积累,最后转移进入细胞核内,与转录因子结合,共同驱动相应基因表达,见图3。"

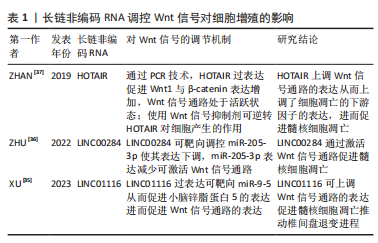
2.1.2 非经典Wnt信号通路 此通路是指不依赖β-catenin的信号传导通路,主要包括Wnt/平面细胞极性(planar cell polarity,PCP)信号通路以及Wnt/Ca2+信号通路,而参与非经典Wnt信号通路的Wnt配体主要为Wnt4、Wnt5a及Wnt11[11-12]。在Wnt/PCP信号通路中,Wnt配体与Fzd受体结合,使得DVL蛋白募集并激活Rac、Rho小GTP酶和JunN-末端激酶,导致肌动蛋白聚合和细胞骨架修饰[13]。而在Wnt/ Ca2+信号通路中,Wnt配体与Fzd结合激活磷脂酶C,将磷脂酰肌醇(4,5)-二磷酸盐水解为肌醇-3,4,5-三磷酸肌醇和二酰基甘油,而肌醇-3,4,5-三磷酸肌醇可以促进内质网释放Ca2+,使细胞内Ca2+水平升高。Ca2+的释放激活Ca2+/钙调素依赖性激酶Ⅱ(Calmodulin-dependent kinase II,CaMKII)和钙调磷酸酶(Calcineurin,CaN),Ca2+/钙调素依赖性激酶Ⅱ可抑制经典Wnt信号的转录活性,而钙调磷酸酶可激活T细胞的核因子使其转移入细胞核调控靶基因的表达[8]。 相对于非经典Wnt信号通路,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在各个领域如肿瘤、骨质疏松研究深入且广泛,相关研究成果也较非经典通路多。因此文章主要从Wnt/β-catenin信号通路来进行论述。 2.2 Wnt信号通路与椎间盘的形成 椎间盘的形成与脊索和体节密切相关。在小鼠中,脊索可形成髓核,而脊索两侧为近轴中胚层,中胚层可形成体节,体节可进一步发育形成纤维环和椎骨[14]。脊索源自脊索祖细胞,而脊索祖细胞对维持脊索后伸展至关重要。而有研究表明,在脊索后伸展的过程中观察到脊索祖细胞中存在大量Wnt信号,且特异性消除β-catenin基因使得Wnt信号的遗传衰减导致脊索后部中断,其结果表明,脊索祖细胞维持脊索后伸展需要维持Wnt信号[15]。一些研究者从Wnt/β-catenin报告小鼠中解剖椎间盘,发现在胚胎18.5 d,Wnt/β-catenin信号在终板、椎板生长板和纤维环中较强,但在髓核中无法检测出来;在出生后第10天,髓核中Wnt/β-catenin信号开始出现,在终板、椎板生长板和纤维环中减弱;出生后第5周,髓核中Wnt/β-catenin信号进一步增强,此时仅在纤维环中观察到微弱的信号[16]。这些研究表明,Wnt信号通路参与了椎间盘的形成,并在这个过程中起着重要作用。 2.3 Wnt信号通路与椎间盘退变的机制 2.3.1 细胞增殖及衰老 细胞通过分裂的方式进行细胞增殖,从而取代衰老及死亡的细胞,使生命体得以延续,而从细胞开始做分裂准备到分裂完成称之为一个细胞周期,细胞增殖便需要经历细胞周期。Wnt信号通路参与细胞增殖,为探究Wnt信号通路在椎间盘退变中抑制细胞增殖的具体原因,早在2010年研究人员就发现使用20 mmol/L浓度的Wnt信号传导激活剂LiCl持续激活 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可导致髓核细胞数量减少[17],细胞周期停滞,细胞增殖速度显著降低;通过细胞周期分析发现,髓核细胞及纤维环细胞的细胞周期主要停滞在G2/M期。由此可知,Wnt信号通路主要通过使细胞周期停滞而达到抑制细胞增殖促进椎间盘退变的作用。而后的研究中以Wnt信号通路为基础机制,探讨某种物质是否通过调控Wnt信号通路对椎间盘细胞增殖起作用,如可调节水和小分子物质进出细胞膜的水通道蛋白3(aquaporin 3,AQP3)[18]。 已有研究表明,水通道蛋白3在人腰椎间盘退变组织中表达降低[19],其表达增加可促进细胞增殖。XIE等[20]发现水通道蛋白3过表达可促进人髓核细胞的增殖;而使用LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,水通道蛋白3过表达促进人髓核细胞的增殖作用被减弱,由此得出Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活可逆转水通道蛋白3对人髓核细胞增殖的影响。再如CCN家族的成员CNN2,有研究表明CCN2不仅能促进软骨骨化过程中细胞的增殖和分化,还参与椎间盘退变,并受Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调节[21];通过进一步探究发现CCN2在退变的椎间盘中表达减少,而Wnt信号通路表达增加可抑制CCN2表达,推测阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可通过激活CCN2来保护髓核细胞进而刺激细胞增殖。位于染色体22q12.2的非编码RNA牛磺酸上调基因(taurine up-regulated gene 1,TUG1)在胃癌、直肠癌及胰腺癌等恶性肿瘤中高表达,为这些肿瘤的癌基因[22]。一项研究表明,在腰椎间盘突出症患者的髓核组织中牛磺酸上调基因和Wnt/β-catenin的表达高于正常髓核组织[23],使用Wnt/β-catenin激活剂处理髓核细胞后表现出细胞增殖减少;当用牛磺酸上调基因-siRNA转染髓核细胞时,受肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的人髓核细胞凋亡明显减少,Wnt/β-catenin途径受到极大抑制,而细胞增殖明显增强,从而得出结论,沉默牛磺酸上调基因可通过阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路来促进人髓核细胞增殖。 衰老是由紫外线损伤、化疗药物、辐射等外部因素或端粒磨损、氧化应激、细胞增殖等内在因素诱发的一种持续性DNA损伤反应引起的,而已有研究证实在肺泡上皮Ⅱ型(Alveolar epithelial type II,ATII)细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达增强,诱导了肺泡上皮Ⅱ型细胞衰老[24]。 而在Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与椎间盘细胞衰老的研究中,有研究报道用LiCl处理髓核及纤维环细胞24 h后,通过检测衰老相关蛋白β-gal发现,β-gal在髓核及纤维环细胞中比例增加2.4倍,证实了Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达增强促进髓核及纤维环细胞衰老[17]。亦有研究显示,使用Wnt/β-catenin激活剂LiCl处理并激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后,观察到体外培养的软骨终板细胞活性降低,细胞衰老趋势加剧,但使用Wnt/β-catenin抑制剂后,细胞衰老趋势被遏制,其结果表明,Wnt/β-catenin参与了年龄和应激诱导的软骨终板细胞衰老[25]。 氧化应激是导致细胞衰老的主要原因之一,为探寻由氧化应激诱导的细胞衰老中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路参与的具体机制,有研究发现NADPH氧化酶4(NADPH oxidase 4,NOX4)是引起氧化应激的主要原因,且在退变的椎间盘中表达上调,而过表达的NADPH氧化酶4可激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进椎间盘细胞衰老;同时还发现zest同系物2(enhancer of zeste homolog 2,EZH2)增强子在衰老细胞中表达降低,而zest同系物2增强子表达下调可促进细胞衰老;进一步研究NADPH氧化酶4、zest同系物2增强子及Wnt信号通路三者间的关系,发现NADPH氧化酶4促进Wnt信号表达导致zest同系物2增强子表达下调进而导致髓核细胞衰老,而zest同系物2增强子表达上调可下调NADPH氧化酶4表达进而降低Wnt信号表达从而抑制髓核细胞衰老[26]。WANG等 [27]的研究表明H2O2可抑制髓核细胞增殖,促进髓核细胞衰老,而长链非编码RNA H19(long non-coding RNA H19,LncRNA H19)在髓核细胞中的过表达有类似H2O2的作用,通过进一步研究发现,H19可与经典Wnt信号通路的关键核因子淋巴细胞增强结合因子(Lymphoid-enhancer-binding factor1,LEF1)竞争miR-22的结合,减弱miR-22对髓核细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号转导的抑制,从而促进了H2O2诱导的髓核细胞衰老。 2.3.2 细胞凋亡 也称为程序性细胞死亡,包括外源性凋亡途径和内源性凋亡途径,而与凋亡相关的信号转导途径种类多样,其中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与细胞凋亡关系密切,且在几种小鼠模型和哺乳动物细胞系中也证实抑制过度表达的Wnt/β-catenin可以促进细胞凋亡和抑制增殖[28]。ZHU等[29]研究发现Wnt/β-catenin信号转导和一种叫做骨膜素(periositin,POSTN)的细胞外基质蛋白在严重退变的椎间盘中高表达,且使用rPOSTN处理髓核细胞后可导致髓核细胞凋亡,但在用Wnt/β-catenin信号抑制剂Iso处理后髓核细胞的凋亡得到抑制;由此可知,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以逆转骨膜素诱导的髓核细胞凋亡。 病毒癌基因v-SKI的细胞内同源物(SKI)参与多种生命过程,有报道表示其可促进成纤维细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡[30]。有研究表明SKI的表达与人类椎间盘退变严重程度呈正相关,且在白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞变形模型中表达显著增加;敲低SKI可逆转白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞凋亡和细胞外基质的降解,而使用Wnt/β-catenin激活剂LiCl却可以再次逆转敲低SKI对髓核细胞的保护作用,进一步促进髓核细胞凋亡[31]。除导致髓核细胞凋亡外,亦有研究显示使用LiCl处理后的软骨终板细胞比未使用LiCl处理的细胞凋亡率显著上升[25]。转录因子p300与年龄相关性疾病密切相关,HAO等[32]的研究表明在收集的椎间盘退变患者的临床组织样本中p300表达下调,而使P300过表达可促进髓核细胞的增殖和抑制细胞的凋亡;通过进一步研究发现过表达的p300可以促进 FOXO3的表达增加从而促使FOXO3与Sirt1启动子结合,FOXO3与Sirt1启动子结合后可增加Sirt1的表达,Sirt1过表达可破坏Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,使Wnt/β-catenin信号通路失活,进而促进髓核细胞增殖和抑制髓核细胞凋亡,延缓椎间盘退变进程。也有研究发现静水压调节牛髓核细胞代谢,但在人髓核细胞中的作用机制不明[33];通过进一步的研究观察,高静水压力(3 040 kPa)可以抑制人髓核细胞的活力并促进髓核细胞凋亡,但使用Wnt/β-catenin途径抑制剂XAV-939却可以逆转高静水压诱导的髓核细胞凋亡和细胞活力的降低。以上研究表明,Wnt/β-catenin通路与椎间盘细胞凋亡关系密切,抑制Wnt信号通路可以减少椎间盘细胞凋亡。 长链非编码RNA在局部组织中呈特异性表达,且功能复杂,其可通过竞争miRNA或通过mRNA吸附直接靶向基因表达介导髓核细胞中的一些列细胞信号通路,参与髓核细胞的增殖或凋亡,从而在椎间盘退变中发挥作用[34]。在诸多细胞信号通路中,Wnt信号通路是长链非编码RNA的靶向目标。有一项研究表明,长链非编码RNA -LINC01116在退行性髓核细胞中表达增高,而沉默该RNA的表达可促进髓核细胞的增殖并抑制细胞凋亡[35];通过进一步的研究发现,LINC01116可以竞争性结合miR-9-5来促进小脑锌脂蛋白5的表达,而小脑锌脂蛋白5可有效促进Wnt信号通路相关因子的表达水平,从而抑制髓核细胞增殖和促进髓核细胞凋亡推动椎间盘退变进程。 长链非编码RNA LINC00284在多种癌症中过表达可促进癌细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡,而有研究发现LINC00284在椎间盘退变组织和白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞中也表达上调,但LINC00284的敲低却可以导致白细胞介素1β诱导的髓核细胞增殖增加、凋亡减少[36];深入研究发现,LINC00284可以靶向miR-205-3p并下调miR-205-3p的表达,从而激活Wnt/β-catenin信号传导抑制髓核细胞增殖和促进髓核细胞凋亡。除以上长链非编码RNA外,TUG1及HOTAIR同样可以靶向下游Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进椎间盘细胞的凋亡[23,37]。这些研究表明,长链非编码RNA在椎间盘退变中扮演着重要角色,其可作为靶向目标从而抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的表达,达到延缓椎间盘退变进程的作用,见表1。"

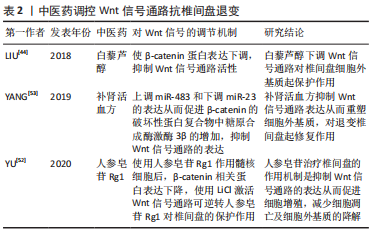
miRNA参与并影响细胞活性,并可以调节基因和蛋白质功能,是一系列小的非编码RNA。研究表明miRNA中的miR-185过表达可靶向抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中的关键调节因子Galectin-3的表达[38],同时Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的表达亦下调,而抑制miR-185可导致Galectin-3、促进自噬因子、促凋亡因子表达增加引起椎间盘细胞凋亡增加;深入研究分析发现miR-185过表达通过下调Galectin-3的表达而抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路进而促进椎间盘细胞生存并抑制细胞凋亡,延缓椎间盘退变进程。综上所述,Wnt信号通路过度激活可导致椎间盘细胞凋亡,而抑制其表达可以缓解椎间盘退变。但有部分研究却结果相反,提示Wnt/β-catenin信号通路被抑制反而促进了细胞凋亡。 有研究证实,miRNA中的miR-532在椎间盘退变患者的血液中表达水平升高,推测miR-532参与椎间盘退变,并与椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡有关[39];通过进一步研究发现用miR-532模拟物转染椎间盘细胞可诱导髓核细胞凋亡,同时细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的共激活因子Bcl-9表达降低,而敲除Bcl-9会直接诱导椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡;此外,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可进一步增强miR-532诱导的细胞凋亡,而使用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激动剂可逆转这一过程;通过进一步分析表明miR-532可靶向Bcl-9下调Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡。这两项研究结果中Wnt信号通路起到的作用截然相反,这说明miRNA与Wnt信号通路之间的作用关系还有待进一步的研究发现。但大部分的研究结果均表明,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达增加促进了椎间盘细胞凋亡。 2.3.3 细胞外基质变化 细胞外基质对维持椎间盘稳态起着重要作用,是组成椎间盘的一部分,其主要为胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖和糖胺聚糖,也包含非胶原成分,如弹性蛋白、脂质、参与分解代谢的酶以及特异性抑制剂等。Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白是椎间盘中含量最多的胶原蛋白[40],为支撑椎间盘形态、抵抗压缩力起着重要作用。椎间盘中蛋白聚糖分子分为与透明质酸结合的聚集蛋白聚糖和不与透明质酸结合的非聚集蛋白聚糖,其中聚集蛋白聚糖主要发生在纤维环中,而非聚集性蛋白聚糖主要发生在髓核中[41]。糖胺聚糖在髓核中含量最大,其在椎间盘的形成和功能中起着重要作用。在椎间盘退变中,细胞外机制降解是其主要特征之一,而降解细胞外基质分子最常见的蛋白酶为基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase,MMPs)。MMP家族的许多成员在退化的椎间盘组织和细胞中高度表达,可导致细胞外基质中胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的降解,从而促进椎间盘发生退变[42]。 在细胞外基质的代谢中,Wnt信号通路也参与其中。既往研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α可诱导髓核细胞变性,增加Wnt/β-catenin信号及MMP-13的表达,抑制Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖的合成,而使用DKK-1特异性阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后可逆转肿瘤坏死因子α对Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖合成的抑制,保护椎间盘组织的正常代谢[43]。此外,亦有研究证明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以激活髓核细胞中的MMPs,促进MMPs mRNA和蛋白的表达,从而增加细胞外基质的降解[17]。而近期的研究也发现,在退变的髓核细胞中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达较正常髓核细胞升高,而进一步检测细胞外基质发现退变组的细胞外基质含量较正常组降低[44]。使用LiCl处理体外培养的软骨终板细胞后,检测出Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达明显增加,同时细胞外基质降解增加,通过RT-qPCR分析检测发现分解代谢酶和MMP-13表达增加[25]。还有研究发现,高静水压和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂SKL2001可促进Wnt信号通路的表达[45],降低髓核细胞蛋白多糖合成和细胞外基质水平,而使用花青素和Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制剂XAV-939处理后可减弱高静水压诱导的髓核细胞细胞外基质的降解,进而对椎间盘起保护作用,延缓其退变。这些研究均显示细胞外基质合成确实与Wnt信号通路相关,其过表达可导致细胞外基质合成降低从而导致细胞外基质含量减少。 探寻Wnt/β-catenin信号通路上游调节因子发现,环状RNA也参与椎间盘退变。WANG等[46]发现环状RNA SEMA4B在椎间盘退变中表达下调,但过表达的SEMA4B能与SFRP1或GSK3β竞争miR-431,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,从而减少细胞外基质的降解。与环状RNA SEMA4B作用相反,在椎间盘退变患者的髓核组织中环状RNA ITCH表达升高,其可结合miR-17-5p,从而减弱miR-17-5p对退行性髓核细胞中SOX4的抑制作用来促进细胞外基质降解;敲低环状RNA ITCH后,细胞外基质降解得到抑制,但使用LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后可逆转这一过程而促进细胞外基质的降解[47]。除环状RNA外,一些长链非编码RNA也可以通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进髓核细胞凋亡,还可以促进细胞外基质的降解影响椎间盘退变进程[35-36]。 Wnt信号通路可抑制细胞周期而影响细胞增殖,通过促进衰老相关因子的表达加速细胞衰老,同时又参与氧化应激,而氧化应激不仅可引起细胞衰老,亦是引起椎间盘退变的因素之一;此外,Wnt信号通路可促进细胞凋亡,但在上述的一项研究中 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路被下调后反而促进髓核细胞凋亡,与上述诸多研究所示抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后髓核细胞凋亡被抑制相矛盾,或许是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与其他通路相串扰的结果;细胞外基质维持细胞的稳态,Wnt信号通路通过促进其合成、抑制其分解而影响椎间盘细胞而加速椎间盘退变进程。综合以上研究,Wnt信号通路主要通过抑制细胞增殖、促进细胞衰老及凋亡、影响细胞外基质而参与椎间盘退变。 2.4 Wnt信号通路与椎间盘的修复 Wnt信号通路参与椎间盘的退变,但也与椎间盘的修复有着联系。WINKLER等[48]发现,Shh信号由NP细胞分泌,并对椎间盘细胞增殖和细胞外基质合成至关重要,而经典Wnt信号通路是其重要激活因子,但Shh信号和Wnt信号却随着年龄增加不断减少;他们通过在一岁龄小鼠的椎间盘中增加Wnt信号从而重新激活Shh信号传导,并发现细胞周期相关的Ccnd1表达增加,表明成年髓核细胞在激活Wnt和Shh信号后具有进入细胞周期的潜力。尽管该研究只是部分逆转椎间盘老化,但为通过控制椎间盘早期生长发育相关分子机制刺激椎间盘再生进而修复椎间盘提供依据。干细胞为近期研究热点,而Wnt信号参与胚胎时期椎间盘的发育,亦参与细胞分化。 COLOMBIER等[49]发现使用糖原合成酶激酶3的选择性小分子抑制剂激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可以诱导人多功能干细胞向中胚层祖细胞分化,在产生足够的中胚层祖细胞后使用高活性的Wnt信号和脊索相关转录因子NOTO转染使其有向脊索分化的趋势,而脊索细胞有助于作为椎间盘修复的再生细胞。同样是研究人多功能干细胞分化成脊索样及髓核样细胞,有研究早期激活Wnt信号通路和阻断骨形态发生蛋白4信号通路,使干细胞能向中胚层祖细胞分化,有助于进一步向脊索分化[50];当培养至第5天时细胞便出现脊索细胞的一些特征基因,进一步培养到15 d后,通过激活TGF-β信号通路,细胞开始表达髓核细胞的一些特征标记;随后将这些髓核样细胞进行抑制,发现其减弱了退变椎间盘的损伤,减少了椎间盘的纤维化,促进了椎间盘的修复。还有研究发现,源自软骨终板细胞的干细胞可以修复椎间盘损伤[51],而使用来自其自身的外泌体可以促进软骨终板细胞来源的干细胞向椎间盘细胞迁移和转化修复椎间盘;通过进一步的实验研究发现,干细胞的外泌体可通过自分泌机制激活Wnt信号通路,Wnt信号通路激活可以进一步刺激转录因子GATA4表达,高表达的GATA4通过TGF-β信号传导促进软骨终板细胞来源的干细胞向椎间盘迁移和转化。 除以上研究外,中医药作为中国瑰宝也在调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路延缓椎间盘退变进程中发挥着重要作用。YU等[52]使用人参皂苷Rg1(Ginsenoside Rg1,G-Rg1)作用于退变的椎间盘组织后,发现随着剂量增加椎间盘细胞的凋亡被抑制,同时细胞增殖和细胞外基质合成得到增加,且Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达也被下调,说明人参皂苷Rg1对于椎间盘具有保护作用,可抑制椎间盘退变的进一步发生;但使用LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路后,人参皂苷Rg1对椎间盘的保护作用被逆转,椎间盘髓核细胞的增殖和细胞外基质的合成被抑制,凋亡增加。补肾活血方由6种中草药组成,被广泛运用于治疗椎间盘退变。 YANG等[53]通过给大鼠喂养补肾活血方获得相关血清,并将血清作用于培养的髓核细胞,发现10%的补肾活血方血清可促进髓核细胞的增殖,同时Wnt信号相关因子糖原合成酶激酶3β蛋白水平增加,而使用LiCl激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可逆转这些的作用,说明补肾活血方可调控Wnt信号通路对椎间盘细胞起正向作用;进一步研究发现,补肾活血方血清作用后可增加细胞外基质合成相关因子,降低细胞外基质降解相关的MMP-3,从而保护椎间盘延缓其退变并重塑细胞外基质,其具体机制可能是通过上调miR-483和下调miR-23的表达,进而抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的表达。中药提取物白藜芦醇亦可限制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路修复细胞外基质而抗椎间盘退变[44]。上述具体研究成果见表2。"
| [1] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al. Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: the antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978. [2] DISEASE GBD, INJURY I, PREVALENCE C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858. [3] BINCH ALA, FITZGERALD JC, GROWNEY EA, et al. Cell-based strategies for IVD repair: clinical progress and translational obstacles. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):158-175. [4] OICHI T, TANIGUCHI Y, OSHIMA Y, et al. Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR Spine. 2020;3(1):e1076. [5] YANG F, LIU W, HUANG Y, et al. Regulated cell death: implications for intervertebral disc degeneration and therapy. J Orthop Translat. 2022;37: 163-172. [6] LORZADEH S, KOHAN L, GHAVAMI S, et al. Autophagy and the Wnt signaling pathway: a focus on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021;1868(3):118926. [7] MACDONALD BT, TAMAI K, HE X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling:components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17(1):9-26. [8] GAJOS-MICHNIEWICZ A, CZYZ M. WNT Signaling in Melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4852. [9] ZHAO H, MING T, TANG S, et al. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):144. [10] ROUTLEDGE D, SCHOLPP S. Mechanisms of intercellular Wnt transport. Development. 2019;146(10):dev176073. [11] FAN J, WEI Q, LIAO J, et al. Noncanonical Wnt signaling plays an important role in modulating canonical Wnt-regulated stemness, proliferation and terminal differentiation of hepatic progenitors. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):27105-27119. [12] CLARK CE, NOURSE CC, COOPER HM. The tangled web of non-canonical Wnt signalling in neural migration. Neurosignals. 2012;20(3):202-220. [13] FRENQUELLI M, TONON G. WNT signaling in hematological malignancies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:615190. [14] MCCANN MR, SéGUIN CA. Notochord cells in intervertebral disc development and degeneration. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(1):3. [15] UKITA K, HIRAHARA S, OSHIMA N, et al. Wnt signaling maintains the notochord fate for progenitor cells and supports the posterior extension of the notochord. Mech Dev. 2009;126(10):791-803. [16] KONDO N, YUASA T, SHIMONO K, et al. Intervertebral disc development is regulated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(8): E513-E518. [17] HIYAMA A, SAKAI D, RISBUD MV, et al. Enhancement of intervertebral disc cell senescence by WNT/β-catenin signaling-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(10):3036-3047. [18] MARLAR S, JENSEN HH, LOGIN FH, et al. Aquaporin-3 in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2106. [19] LI SB, YANG KS, ZHANG YT. Expression of aquaporins 1 and 3 in degenerative tissue of the lumbar intervertebral disc. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4):8225-8233. [20] XIE H, JING Y, XIA J, et al. Aquaporin 3 protects against lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016; 37(3):859-864. [21] HIYAMA A, MORITA K, SAKAI D, et al. CCN family member 2/connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) is regulated by Wnt-β-catenin signaling in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):217. [22] XIE D, ZHANG H, HU X, et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA Taurine Up-Regulated 1 inhibited doxorubicin resistance of bladder urothelial carcinoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(51):88689-88696. [23] CHEN J, JIA YS, LIU GZ, et al. Role of LncRNA TUG1 in intervertebral disc degeneration and nucleus pulposus cells via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491(3):668-674. [24] LEHMANN M, HU Q, HU Y, et al. Chronic WNT/β-catenin signaling induces cellular senescence in lung epithelial cells. Cell Signal. 2020;70:109588. [25] DING L, JIANG Z, WU J, et al. β‑catenin signalling inhibits cartilage endplate chondrocyte homeostasis in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):567-572. [26] LIU C, LIU L, YANG M, et al. A positive feedback loop between EZH2 and NOX4 regulates nucleus pulposus cell senescence in age-related intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Div. 2020;15:2. [27] WANG X, ZOU M, LI J, et al. LncRNA H19 targets miR-22 to modulate H2O2 - induced deregulation in nucleus pulposus cell senescence, proliferation, and ECM synthesis through Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(6):4990-5002. [28] TREJO-SOLIS C, ESCAMILLA-RAMIREZ A, JIMENEZ-FARFAN D, et al. Crosstalk of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the induction of apoptosis on cancer cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(9):871. [29] ZHU D, WANG Z, ZHANG G, et al. Periostin promotes nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2022;36(7):e22369. [30] PENG Y, XIONG RP, ZHANG ZH, et al. Ski promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in fibroblasts under high-glucose conditions via the FoxO1 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(2):e12971. [31] WU Z L, CHEN Y J, ZHANG G Z, et al. SKI knockdown suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and ameliorates disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2022;27(1-2):133-148. [32] HAO Y, REN Z, YU L, et al. p300 arrests intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the FOXO3/Sirt1/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Aging Cell. 2022;21(8):e13677. [33] SHI Z, HE J, HE J, et al. High hydrostatic pressure (30 atm) enhances the apoptosis and inhibits the proteoglycan synthesis and extracellular matrix level of human nucleus pulposus cells via promoting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):3070-3081. [34] RAN R, LIAO HY, WANG ZQ, et al. Mechanisms and functions of long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;235:153959. [35] XU S, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. LINC01116 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through miR-9-5p-mediated ZIC5 and the Wnt pathway and affects the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(7):979-992. [36] ZHU M, YAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. lncRNA LINC00284 promotes nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and ECM synthesis via regulation of the miR‑205‑3p/Wnt/β‑catenin axis. Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(5):179. [37] ZHAN S, WANG K, SONG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates intervertebral disc degenerative changes via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):201. [38] YUN Z, WANG Y, FENG W, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-185 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration through inactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and downregulation of Galectin-3. Mol Pain. 2020;16:1744806920902559. [39] SUN Z, JIAN Y, FU H, et al. MiR-532 downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling via targeting Bcl-9 and induced human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;138(4):263-270. [40] ROUGHLEY PJ. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(23): 2691-2699. [41] SIVAN SS, HAYES AJ, WACHTEL E, et al. Biochemical composition and turnover of the extracellular matrix of the normal and degenerate intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2014;23 Suppl 3:S344-S353. [42] SONG Q, ZHANG F, WANG K, et al. MiR-874-3p plays a protective role in intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing MMP2 and MMP3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;895:173891. [43] YE S, WANG J, YANG S, et al. Specific inhibitory protein Dkk-1 blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway improve protectives effect on the extracellular matrix. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011;31(5):657. [44] LIU H, SHEN J, ZHOU H, et al. Resveratrol regulate the extracellular matrix expression via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in nucleus pulposus cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(4):476-483. [45] XU Y, HE J, HE J. Cyanidin attenuates the high hydrostatic pressure-induced degradation of cellular matrix of nucleus pulposus cell via blocking the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Tissue Cell. 2022;76:101798. [46] WANG X, WANG B, ZOU M, et al. CircSEMA4B targets miR-431 modulating IL-1β-induced degradative changes in nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration via Wnt pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(11):3754-3768. [47] ZHANG F, LIN F, XU Z, et al. Circular RNA ITCH promotes extracellular matrix degradation via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(10):14185-14197. [48] WINKLER T, MAHONEY EJ, SINNER D, et al. Wnt signaling activates Shh signaling in early postnatal intervertebral discs, and re-activates Shh signaling in old discs in the mouse. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e98444. [49] COLOMBIER P, HALGAND B, CHéDEVILLE C, et al. NOTO transcription factor directs human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesendoderm progenitors to a notochordal fate. Cells. 2020;9(2):509. [50] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, CHEN P, et al. Directed differentiation of notochord-like and nucleus pulposus-like cells using human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2020;30(8):2791-2806.e5. [51] LUO L, GONG J, ZHANG H, et al. Cartilage endplate stem cells transdifferentiate into nucleus pulposus cells via autocrine exosomes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:648201. [52] YU L, HAO Y, PENG C, et al. Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the intervertebral disc degeneration rats and the degenerative pulposus cells and its mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;123:109738. [53] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue-Fang modulates nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and extracellular matrix remodeling in intervertebral disk degeneration through miR-483 regulation of Wnt pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19318-19329. [54] PIZZUTE T, HE F, ZHANG XB, et al. Impact of Wnt signals on human intervertebral disc cell regeneration. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(12):3196-1207. |
| [1] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [4] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [5] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [6] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [7] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [8] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [9] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [11] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [12] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [13] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [14] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [15] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

