Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1931-1936.doi: 10.12307/2024.052
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulation of Toll-like receptors on function of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Wang Xin, Huang Jinyong, Wubulikasimu · Mijiti, Xie Zengru
- Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-03-06Accepted:2023-04-28Online:2024-04-28Published:2023-08-23 -
Contact:Xie Zengru, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Xin, Doctoral candidate, Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82260409 (to XZR); Key Project of Department of Science and Technology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2021D01D19 (to XZR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xin, Huang Jinyong, Wubulikasimu · Mijiti, Xie Zengru. Regulation of Toll-like receptors on function of osteoblasts and osteoclasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1931-1936.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
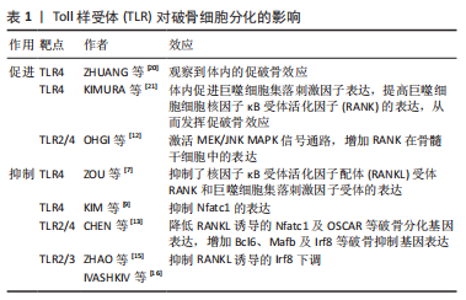
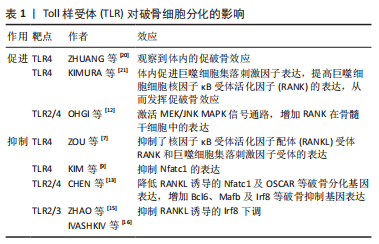
2.1 TLR在骨组织细胞中的表达及激活途径 TLR是模式识别受体家族的成员,是一类具有保守结构的跨膜蛋白。迄今为止,已鉴定出10个人类TLR(TLR1-10)和12个小鼠TLR(TLR1-9和11-13),其中TLR1、TLR2、TLR4、TLR5和TLR6主要存在于质膜表面,而TLR3、TLR7、TLR8和TLR9则位于细胞内膜上。有研究发现小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞前体表达TLR1-TLR9,但在成熟分化的破骨细胞中主要表达TLR2 和TLR4,表明这2个TLR在破骨细胞生成过程中起主要作用[1]。间充质干细胞及成骨细胞中TLR的表达水平因细胞来源、种属、分化程度不同有所差异。人脐血衍生的非限制性体干细胞表达低水平的TLR1,3,5,9和高水平的TLR4和TLR6[2]。据报道,TLR2,3,4,6在成骨细胞中组成性表达。与外周血单核细胞相比,间充质干细胞的TLR2/4的表达量较低。随着间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,TLR2/4的表达显著提高。TLR2/4分布于细胞质膜表面,激活后均通过经典途径(也称为髓样分化蛋白88 依赖途径)激活下游信号通路,而TLR4还可通过替代途径[也称为髓样分化蛋白88 非依赖途径或(TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β,TRIF)依赖性途径]传递信号[3]。经典途径激活后,髓样分化蛋白88 募集 IRAK4,随后募集 IRAK1 和 IRAK2,活化的IRAK1诱导TRAF6的激活。IRAK1/TRAF6复合物募集转化生长因子β激活激酶1,随后激活磷酸肌醇3-激酶、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen actived protein kinase,MAPKs)和关键的促炎转录因子核因子κB 通路引发效应。替代途径发生于经典途径激活后。当TLR受体内化激活后,TRIF相关接头分子募集TRIF,TRIF反过来又招募受体相互作用蛋白1、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3和肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6,以多泛素化激活转化生长因子β激活激酶1。TRIF还促进TANK结合激酶1的肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3 依赖性激活,通过诱导干扰素调节因子3的磷酸化和二聚化发挥效应[4]。 不同TLR识别对应的分子模式,即配体。如TLR2的配体为脂蛋白,TLR4的配体为脂多糖,各项研究中往往通过添加对应的配体来诱导特定TLRs的激活。TLR配体刺激可对TLR本身的表达造成影响,例如脂多糖刺激后巨噬细胞和T细胞中的TLR2 mRNA表达增加,而脂多糖刺激对成骨系细胞TLR表达的影响尚存争议。有研究发现脂多糖增加了MC3T3-E1细胞中TLR4的表达[5],也有研究提及长期暴露于脂多糖环境会降低间充质干细胞中TLR2/4的表达量,以及短时间内脂多糖刺激导致成骨细胞TLR2表达增加,TLR4表达不变[6]。 2.2 TLR对破骨细胞的影响 2.2.1 TLR对破骨分化的抑制 多种TLR受体的激活抑制了核因子κB受体活化因子配体( receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand,RANKL)和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子诱导的小鼠骨髓破骨前体细胞前体和人外周血单核细胞的破骨分化,且此效应与γ-干扰素、白细胞介素4和粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等具有破骨抑制效应的细胞因子无关。TLR4受体的激活抑制了核因子κB受体活化因子(receptor activator of nuclear factor κB,RANK)和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体的表达。用脂多糖刺激骨髓来源巨噬细胞,发现RANK及巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体的表达每24 h就降低25%-30%。当脂多糖早期与破骨细胞前体共培养时,会抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化。当RANKL刺激一段时间之后,脂多糖的存在促进了RANKL引发的骨髓来源巨噬细胞中的破骨细胞生成。由于此效应不能被骨保护素阻断,故与环境中的RANKL无关[7]。LIU等[8]的研究进一步阐释了上述现象,发现早期使用RANKL或脂多糖处理可能使骨髓来源巨噬细胞产生某种定型机制,即经过RANKL处理36 h的骨髓来源巨噬细胞即使在仅存脂多糖的情况下也可继续向破骨细胞分化。同样,用脂多糖处理24 h的RANKL永久失去了响应RANKL向破骨细胞分化的能力。这一效应是由于脂多糖显著抑制了破骨细胞分化通路中主要转录调节因子Nfatc1的表达[9-11]。 牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖曾被认为是TLR2受体的特异性配体,但目前认为,牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖的受体同时包括TLR2和TLR4[12]。与脂多糖刺激的结果类似,牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖呈剂量依赖性降低RANKL诱导的破骨基因表达,且尽管牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖和RANKL都能促进MAPK、蛋白激酶B和核因子κB等破骨形成相关信号通路的激活,但通路的激活并不一定导致破骨细胞分化。牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖处理的骨髓来源巨噬细胞消除了RANKL诱导的破骨相关基因Nfatc1及OSCAR的上调。RANKL诱导的Ca2+震荡对于钙调神经磷酸酶介导的Nfatc1激活很重要,牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖消除了RANKL引发的钙离子震荡。此外,牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖通过抑制Blimp1基因和增加Bcl6、Mafb及Irf8等破骨抑制基因的表达来抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成,此效应依赖于髓样分化蛋白88对Blimp1的调控[13-14]。 Irf8是破骨细胞生成的关键负调节因子,TLR2/3的激活会抑制RANKL诱导的Irf8下调[15-17]。Irf8与Nfatc1结合并抑制其DNA结合能力和转录活性,进而抑制Nfatc1靶向破骨相关基因的表达[18-19]。见表1。"
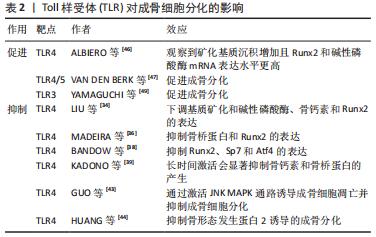
2.2.2 TLR对破骨分化的促进 在生理情况下,注射脂多糖等TLR4配体会显著增加破骨细胞数量,导致骨质流失。而TLR4-/-小鼠消除了脂多糖诱导的骨溶解现象,更进一步证明了LTR4激活在体内的促破骨效应[20,22]。脂多糖及其诱导的促炎细胞因子可刺激小鼠体内巨噬细胞集落刺激因子表达增加,进而提高巨噬细胞表面RANK的表达以促进破骨分化[21,23]。在骨髓细胞分化为骨髓来源巨噬细胞期间,TLR2/4配体通过髓样分化蛋白88依赖途径激活MEK/JNK MAPK信号通路,增加RANK在骨髓干细胞中的表达,从而促进骨髓干细胞向破骨细胞的转变[12]。此外,骨髓细胞中TLR4的失活增强了破骨细胞生成,加速了骨组织修复过程[24]。见表1。 2.2.3 TLR促进巨噬细胞及破骨前体细胞分泌促破骨细胞因子 脂多糖刺激可促进巨噬细胞及破骨前体细胞分泌白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等破骨相关炎症因子,增加炎症因子在全身的表达,这一效应可能需要TLR2/4的协同激活通过髓样分化蛋白88途径实现[21]。而在生理条件下,脂多糖是唯一能导致β-干扰素大量产生的刺激物[25]。 脂多糖刺激可促进磷酸肌醇3-激酶表达增加,进而导致β-干扰素依赖性增加。β-干扰素可通过干扰RANKL诱导的c-Fos表达来抑制破骨分化,c-fos是破骨细胞形成的关键转录因子[26]。β-干扰素通过激活STAT蛋白抑制RANKL刺激后c-fos的诱导,从而消除Nfatc1活性并最终抑制破骨细胞分化。但在经过RANKL预分化处理的破骨细胞中未观察到c-fos表达的降低,这可能是脂多糖对不同分化阶段破骨细胞作用差异的原因。β-干扰素还能够在没有RANKL的情况下刺激诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达,进而导致一氧化氮产生增加。一氧化氮在骨丢失中的作用存在争议,一方面可能通过促进局部过氧亚硝酸盐等炎症化合物的合成,激活核因子κB信号通路促进破骨细胞的分化和生存[27]。另一方面,一氧化氮也被发现存在多种机制抑制核因子κB的激活[28]。人成骨细胞中的TLR4活化同样增加诱导型一氧化氮合酶活性和一氧化氮的产生,而一氧化氮可抑制成骨细胞功能并导致细胞凋亡[27,29]。 2.2.4 TLR对破骨细胞生存、迁移的影响 有研究提及,对TLR2/4的刺激可以直接提高成熟破骨细胞的存活率[30]。TLR4的激活可增强低剂量RANKL引发的破骨前体细胞的破骨分化,并促进成熟破骨细胞在体外的存活[31]。脂多糖可能通过诱导炎性细胞因子的产生促进破骨细胞存活,但也有研究提及,脂多糖促进前破骨细胞的存活与融合的效应独立于RANKL,白细胞介素1或肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子的影响[32]。不过上述观点都认为髓样分化蛋白88途径参与了破骨细胞的存活。此外,有研究提及脂多糖通过激活JNK/ERK MAPK信号通路维持破骨细胞的分化能力和活性[33]。 2.3 TLR对成骨细胞的影响 2.3.1 TLR对成骨分化的抑制 TLR4可通过抑制碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和Runx2的表达来抑制成骨细胞分化[34-35]。缺乏髓样分化蛋白88会影响成骨细胞标志物,包括Runt相关转录因子2和骨桥蛋白,说明TLR4对成骨细胞分化的抑制作用可能依赖于髓样分化蛋白88途径[36-37]。TLR4抑制Runt相关转录因子2、Sp7和Atf4等成骨分化相关基因的表达还可能与ERK MAPK通路的激活有关[21,38]。此外,脂多糖对成骨的影响可能与脂多糖的作用时间相关。脂多糖的短期刺激增加了MC3T3-E1细胞和胎鼠颅盖骨原代成骨细胞中的骨桥蛋白 mRNA表达,而脂多糖的持续作用会显著抑制骨钙素和骨桥蛋白的产生,从而抑制成熟成骨细胞的形成[39-41]。此外,脂多糖还可通过激活JNK MAPK通路诱导成骨细胞凋亡并抑制成骨细胞分化[42-43]。也有研究提及,在炎症环境下,脂多糖可通过TLR4/髓样分化蛋白88/核因子κB依赖途径抑制骨形成蛋白2诱导的成骨分化[44]。 2.3.2 TLR对成骨分化的促进 高剂量长时间的脂多糖刺激可促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化。暴露于脂多糖的间充质干细胞表达了更高的Runt相关转录因子2和碱性磷酸酶mRNA,并且矿化沉积增加,证明脂多糖促进了间充质干细胞的成骨分化[45-46]。有研究指出人脐血衍生的非限制性体干细胞中TLR4/5的激活增加了促炎细胞因子的表达及成骨分化,TLR3的激活抑制了脐带间充质干细胞的成骨分化[47]。但也有研究提及TLR3的激活促进了间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞和成骨细胞的分化能力,而脂多糖抑制了这一过程。脂多糖的成骨抑制效应可能与核因子κB信号通路的激活相关[48-49]。见表2。"
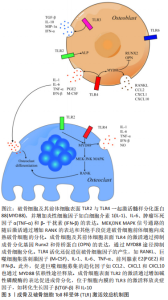
2.3.3 TLR促进成骨细胞及其前体细胞分泌促破骨细胞因子 目前认为,成骨系细胞表面的TLR响应微生物引起的刺激,分泌炎性细胞因子如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、前列腺素E2和肿瘤坏死因子α[50]。TLR4对炎性细胞因子分泌的调节可能与刺激时间相关。例如TLR4-/-小鼠与普通小鼠相比,骨损伤后早期白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、转化生长因子β1、转化生长因子β3、血小板衍生生长因子和RANKL的表达水平较高,晚期白细胞介素1细的表达水平较高,而血管内皮生长因子、RANK、RANKL和骨保护素的表达水平较低[51]。 脂多糖可通过髓样分化蛋白88途径刺激成骨细胞和间充质干细胞中RANKL表达,以及激活蛋白激酶C和MEK/ERK等破骨相关信号通路。除此之外,TLR4的激活还可通过髓样分化蛋白88依赖途径增加CC类趋化因子配体2、炎症趋化因子(C-X-C基序)配体1和炎症趋化因子(C-X-C基序)配体10等趋化因子的表达,通过募集其他免疫细胞,在骨组织的局部免疫反应中起到重要的调节作用[30]。有研究发现,脂多糖刺激了TRIF-/-成骨细胞中白细胞介素6的产生,但不刺激TRIF-/-巨噬细胞中白细胞介素6的产生。也有研究认为白细胞介素6的分泌依赖于TLR2的激活,进而引起核因子κB通路的激活[40]。白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α可通过直接增强RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化以及间接增强成骨细胞/基质细胞中RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的表达来促进破骨形成[52]。 脂多糖可促进巨噬细胞、肥大细胞、间充质干细胞和成骨细胞表达前列腺素E2,活化的TLR4增强环氧合酶2和膜结合型前列腺素E2合酶1的表达可能是机制之一[53]。部分炎性细胞因子也可诱导成骨细胞和基质细胞中表达前列腺素E2。白细胞介素1与前列腺素E2的产生可在骨髓细胞中强烈诱导RANKL的表达,以此刺激破骨细胞生成。TLR4的激活还可通过p38 MAPK信号通路显著增加原代鼠颅盖骨成骨细胞和成骨细胞样细胞MC3T3-E1中的基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA表达,进而促进软骨基质的降解[21]。 TLR3的激活增加间充质干细胞表达抗炎因子,如转化生长因子β和白细胞介素10,促炎因子例如白细胞介素1β、γ-干扰素和白细胞介素6主要由TLR4激活产生。也有研究提及TLR3/4的激活均增加了脐带间充质干细胞中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素10和γ-干扰素的表达,其中TLR4的激活导致转化生长因子β、单核细胞趋化蛋白3和血管内皮生长因子表达的增加,趋化因子配体3和α-扰素仅在TLR3激活的情况下增加[54]。而TLR4/5的刺激会导致白细胞介素6及白细胞介素8产生增加。TLR4/TLR9的激活增加了成骨细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α与巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的表达,而不增加RANKL的表达。两种受体的激活对骨保护素的表达没有显著影响[55-56]。见图3。"
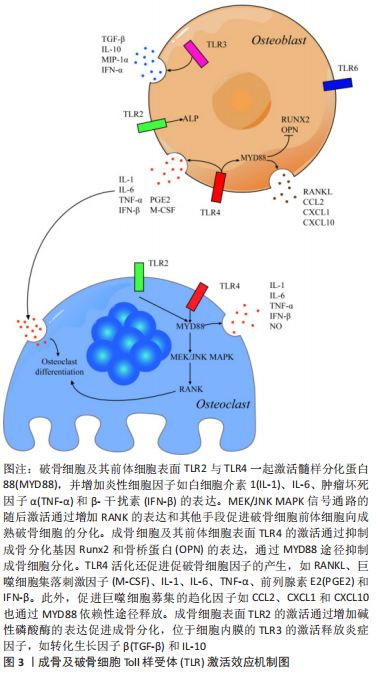

2.3.4 TLR对成骨细胞生存、迁移的影响 有研究提及,TLR2/4的激活促进了成骨细胞的迁移,并不会对间充质干细胞的增殖和细胞活性造成显著影响[57]。但也有一些研究认为,TLR2的激活降低了间充质干细胞的基础运动,增加了间充质干细胞的增殖速率[58]。脂多糖也具有较弱的促进间充质干细胞迁移运动的能力。TLR4的激活可能通过核因子κB信号通路导致成骨细胞活性降低,并促进其凋亡[59]。间充质干细胞中TLR4表达的缺失完全消除了脂多糖对间充质干细胞增殖、成骨分化和细胞因子产生的影响[60]。脂多糖对间充质干细胞的影响还跟剂量有关,适当剂量的脂多糖对间充质干细胞的凋亡具有某种保护作用,同时还在体外增强间充质干细胞的增殖[61]。而TLR3的激活能够显著促进人类间充质干细胞的迁移[58]。值得注意的是,目前TLR2/4的激活在成骨细胞细胞分化和迁移中的必要性仍存在质疑[62]。 2.4 TLR介导细胞间的相互作用 虽成骨与破骨细胞除了维持正常的骨代谢平衡外,二者之间也存在复杂的相互作用。TLR4的激活虽不能直接诱导骨髓来源巨噬细胞转变为破骨细胞,但可刺激骨髓来源巨噬细胞与成骨细胞共培养体系中破骨细胞的生成[63]。在体外,脂多糖主要通过TLR4间接作用于成骨细胞,而不是直接作用于破骨细胞前体。共培养实验表明,脂多糖主要作用于成骨细胞以诱导体内破骨细胞生成,且需要在分离的骨髓来源巨噬细胞和成骨细胞中都具有TLR4活性[21]。除了细胞间的相互作用外,生理状态下细胞表面的多种TLR可能共同发挥作用。例如TLR2的信号传导促进了成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶的表达和矿化,而激活的TLR4下调了由TLR2诱导的成骨标志,进一步证明骨骼系统与免疫系统共同构建了由受体和细胞因子共同参与的复杂调控网络[64]。 除了通常意义的骨细胞外,构成关节等运动系统结构的其他组织细胞,也可能通过TLR进行复杂的相互作用。例如经TLR2/4配体刺激的类风湿关节炎患者的滑膜成纤维细胞可通过共培养促进单核细胞高表达抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、RANK、组织蛋白酶K、降钙素受体和基质金属蛋白酶9,证明其促进了单核细胞向破骨细胞的分化[65]。而在骨关节炎慢性期,TLR4积极促进基质金属蛋白酶介导的软骨破坏。除了破骨细胞造成的骨质降解外,TLR2/4的激活还刺激骨关节炎患者关节软骨细胞中白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子的产生,诱导骨关节炎患者关节软骨细胞表达一氧化氮和基质金属蛋白酶,促进关节软骨的降解和关节肿胀的发生[66-67]。而进一步的研究认为关节软骨的降解似乎更加依赖于TLR2的激活通过髓样分化蛋白88依赖的途径实现,TLR4的作用有限[68]。 而在感染环境下,例如金黄色葡萄球菌可通过成骨细胞表面的TLR2增强RANKL表达,通过调节 RANKL/骨保护素比例刺激破骨细胞形成和骨吸收[69]。且随着感染次数增加,活化的TLR2在T细胞及巨噬细胞等多种免疫细胞中介导不同的炎性细胞因子分泌[30]。TLR受体也可与其他模式识别受体,如NOD样受体相互作用。例如TL2与TLR4可与NOD受体协同增强白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子的产生[70]。"

| [1] TAKAMI M, KIM N, RHO J, et al. Stimulation by toll-like receptors inhibits osteoclast differentiation. J Immunol. 2002;169(3):1516-1523. [2] SALLUSTIO F, CURCI C, STASI A, et al. Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Actuating Stem/Progenitor Cell Repair Mechanisms: Different Functions in Different Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:6795845. [3] TAKEDA K, KAISHO T, AKIRA S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003; 21:335-376. [4] SATO S, SUGIYAMA M, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and TANK-binding kinase 1, and activates two distinct transcription factors, NF-kappa B and IFN-regulatory factor-3, in the Toll-like receptor signaling. J Immunol. 2003;171(8):4304-4310. [5] TANG Y, SUN F, LI X, et al. Porphyromonas endodontalis lipopolysaccharides induce RANKL by mouse osteoblast in a way different from that of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J Endod. 2011;37(12):1653-1658. [6] MASOOMIKARIMI M, SALEHI M. Modulation of the Immune System Promotes Tissue Regeneration. Mol Biotechnol. 2022;64(6):599-610. [7] ZOU W, BAR-SHAVIT Z. Dual modulation of osteoclast differentiation by lipopolysaccharide. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(7):1211-1218. [8] LIU J, WANG S, ZHANG P, et al. Molecular mechanism of the bifunctional role of lipopolysaccharide in osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem, 2009;284(18): 12512-12523. [9] KIM JH, KIM N. Regulation of NFATc1 in Osteoclast Differentiation. J Bone Metab.2014;21(4): 233-241. [10] YIM M. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Metab. 2020;27(4):227-235. [11] BOLAMPERTI S, VILLA I, RUBINACCI A. Bone remodeling: an operational process ensuring survival and bone mechanical competence. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):48. [12] OHGI K, KAJIYA H, GOTO TK, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 activation primes and upregulates osteoclastogenesis via lox-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):132. [13] CHEN Z, SU L, XU Q, et al. IL-1R/TLR2 through MyD88 Divergently Modulates Osteoclastogenesis through Regulation of Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells c1 (NFATc1) and B Lymphocyte-induced Maturation Protein-1 (Blimp1). J Biol Chem. 2015;290(50):30163-30174. [14] TEIXEIRA HS, ZHAO J, KAZMIERSKI E, et al. TLR3-Dependent Activation of TLR2 Endogenous Ligands via the MyD88 Signaling Pathway Augments the Innate Immune Response. Cells. 2020;9(8):1910. [15] ZHAO J, KONG HJ, LI H, et al. IRF-8/Interferon (IFN) Consensus Sequence-binding Protein Is Involved in Toll-like Receptor (TLR) Signaling and Contributes to the Cross-talk between TLR and IFN-γ Signaling Pathways. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(15):10073-10080. [16] IVASHKIV LB, ZHAO B, PARK-MIN KH, et al. Feedback inhibition of osteoclastogenesis during inflammation by IL-10, M-CSF receptor shedding, and induction of IRF8. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1237:88-94. [17] PARK-MIN KH. Mechanisms involved in normal and pathological osteoclastogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(14):2519-2528. [18] BOYCE BF, XIU Y, LI J, et al. NF-κB-Mediated Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2015;30(1):35-44. [19] HONG G, CHEN Z, HAN X, et al. A novel RANKL-targeted flavonoid glycoside prevents osteoporosis through inhibiting NFATc1 and reactive oxygen species. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(5):e392. [20] ZHUANG L, JUNG JY, WANG EW, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lipopolysaccharide Induces Osteoclastogenesis Through a Toll-Like Receptor 4 Mediated Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(5):841-847. [21] KIMURA K, KITAURA H, FUJII T, et al. Anti-c-Fms antibody inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclastogenesis in vivo. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;64(2):219-227. [22] ALONSO-PÉREZ A, FRANCO-TREPAT E, GUILLÁN-FRESCO M, et al. Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 on Osteoblast Metabolism and Function. Front Physiol. 2018;9:504. [23] NARA Y, KITAURA H, OGAWA S, et al. Anti-c-fms Antibody Prevents Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption in Co-Culture of Osteoblasts and Osteoclast Precursors In Vitro and in Ovariectomized Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6120. [24] WANG D, GILBERT JR, TAYLOR GM, et al. TLR4 Inactivation in Myeloid Cells Accelerates Bone Healing of a Calvarial Defect Model in Mice. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(2):296e-306e. [25] GOTTSCHALK RA, DORRINGTON MG, DUTTA B, et al. IFN-mediated negative feedback supports bacteria class-specific macrophage inflammatory responses. Elife. 2019;8:e46836. [26] TSUBAKI M, KATO C, ISONO A, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α induces osteoclast formation by activation of the MEK/ERK/c-Fos pathway and inhibition of the p38MAPK/IRF-3/IFN-β pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2010; 111(6):1661-1672. [27] LEE SK, HUANG H, LEE SW, et al. Involvement of iNOS-dependent NO production in the stimulation of osteoclast survival by TNF-alpha. Exp Cell Res. 2004;298(2):359-368. [28] REYNAERT NL, CKLESS K, KORN SH, et al. Nitric oxide represses inhibitory kappaB kinase through S-nitrosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(24):8945-8950. [29] CHOI SH, KIM SJ. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and osteoclastic differentiation by Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014;10(Suppl 3):S494-S500. [30] NIU Q, GAO J, WANG L, et al. Regulation of differentiation and generation of osteoclasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 1034050. [31] OMI M, MISHINA Y. Role of osteoclasts in oral homeostasis and jawbone diseases. Oral Sci Int. 2020;18(1):14-27. [32] SUDA K, WOO J, TAKAMI M, et al. Lipopolysaccharide supports survival and fusion of preosteoclasts independent of TNF-α, IL-1, and RANKL. J Cell Physiol. 2002;190(1):101-108. [33] CHANG Y, HU CC, WU YY, et al. Ibudilast Mitigates Delayed Bone Healing Caused by Lipopolysaccharide by Altering Osteoblast and Osteoclast Activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1169. [34] LIU YH, HUANG D, LI ZJ, et al. Toll-like receptor-4-dependence of the lipopolysaccharide-mediated inhibition of osteoblast differentiation. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027191. [35] 张倩璐, 江婷, 赵国军. 脂多糖抑制成骨细胞分化作用研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2019,35(21):2743-2746. [36] MADEIRA MFM, QUEIROZ-JUNIOR CM, CISALPINO D, et al. MyD88 is essential for alveolar bone loss induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide in mice. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2013;28(6):415-424. [37] CAI X, LI Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Enhanced dual function of osteoclast precursors following calvarial Porphyromonas gingivalis infection. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(3):410-425. [38] BANDOW K, MAEDA A, KAKIMOTO K, et al. Molecular mechanisms of the inhibitory effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on osteoblast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;402(4):755-761. [39] KADONO H, KIDO J, KATAOKA M, et al. Inhibition of osteoblastic cell differentiation by lipopolysaccharide extract from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1999;67(6):2841-2846. [40] KWON Y, PARK C, LEE J, et al. Regulation of Bone Cell Differentiation and Activation by Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(11):5805. [41] 王瑞, 杨谛, 于雅琼, 等. 牙髓卟啉单胞菌内毒素对成骨细胞分化的抑制作用[J]. 上海口腔医学,2021,30(4):350-354. [42] MA J, WANG Z, ZHAO J, et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Inhibition of Osteoblast Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:2045-2052. [43] GUO C, YUAN L, WANG J, et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Induces the Apoptosis and Inhibits Osteoblast Differentiation Through JNK Pathway in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Inflammation. 2014;37(2):621-631. [44] HUANG RL, YUAN Y, ZOU GM, et al. LPS-stimulated inflammatory environment inhibits BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation through crosstalk between TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and BMP/Smad signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(3):277-289. [45] ANDRUKHOV O. Toll-Like Receptors and Dental Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Front Oral Health. 2021;2:648901. [46] ALBIERO ML, AMORIM BR, MARTINS L, et al. Exposure of periodontal ligament progenitor cells to lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli changes osteoblast differentiation pattern. J Appl Oral Sci. 2015;23(2): 145-152. [47] VAN DEN BERK LC, JANSEN BJ, SIEBERS-VERMEULEN KG, et al. Toll-like receptor triggering in cord blood mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(9B):3415-3426. [48] ZENG J, GUO J, SUN Z, et al. Osteoblastic and anti-osteoclastic activities of strontium-substituted silicocarnotite ceramics: In vitro and in vivo studies. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):435-446. [49] YAMAGUCHI M, WEITZMANN MN. The intact strontium ranelate complex stimulates osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by antagonizing NF-κB activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;359(1-2):399-407. [50] ANDRUKHOV O. Toll-Like Receptors and Dental Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Front Oral Health. 2021;2:648901. [51] WANG D, TAYLOR GM, GILBERT JR, et al. Enhanced Calvarial Bone Healing in CD11c-TLR4-/- and MyD88-/- Mice. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(4): 933e-940e. [52] TERKAWI MA, MATSUMAE G, SHIMIZU T, et al. Interplay between Inflammation and Pathological Bone Resorption: Insights into Recent Mechanisms and Pathways in Related Diseases for Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1786. [53] SUZUKI Y, KIKUCHI T, GOTO H, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis Fimbriae Induce Osteoclastogenesis via Toll-like Receptors in RAW264 Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):15293. [54] LEITE FR, DE AQUINO SG, GUIMARÃES MR, et al. Relevance of the myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) on RANKL, OPG, and nod expressions induced by TLR and IL-1R signaling in bone marrow stromal cells. Inflammation. 2015;38(1):1-8. [55] MEKHEMAR M, TÖLLE J, HASSAN Y, et al. Thymoquinone-Mediated Modulation of Toll-like Receptors and Pluripotency Factors in Gingival Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells. Cells. 2022;11(9):1452. [56] SOUZA P, LERNER UH. Finding a Toll on the Route: The Fate of Osteoclast Progenitors After Toll-Like Receptor Activation. Front Immunol. 2019;10: 1663. [57] LI MJ, LI F, XU J, et al. rhHMGB1 drives osteoblast migration in a TLR2/TLR4- and NF-κB-dependent manner. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(1):e300. [58] EVARISTO-MENDONÇA F, SARDELLA-SILVA G, KASAI-BRUNSWICK TH, et al. Preconditioning of Rat Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Toll-Like Receptor Agonists. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7692973. [59] 徐頔, 刘永光. LPS介导TLR4/NF-κB信号转导对小鼠成骨细胞活性和凋亡的影响[J]. 西南国防医药,2018,28(12):1153-1156. [60] HE X, WANG H, JIN T, et al. TLR4 Activation Promotes Bone Marrow MSC Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation via Wnt3a and Wnt5a Signaling. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e149876. [61] WANG Z, ZHANG F, WANG L, et al. Lipopolysaccharides can protect mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and enhance proliferation of MSCs via Toll-like receptor(TLR)-4 and PI3K/Akt. Cell Biol Int. 2009;33(6):665-674. [62] MI L, ZHANG N, WAN J, et al. Remote ischemic post‑conditioning alleviates ischemia/reperfusion‑induced intestinal injury via the ERK signaling pathway‑mediated RAGE/HMGB axis. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(5):773. [63] LIU J, WANG S, ZHANG P, et al. Molecular mechanism of the bifunctional role of lipopolysaccharide in osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(18): 12512-12523. [64] MARSH S, CONSTANTIN-TEODOSIU T, CHAPMAN V, et al. In vitro Exposure to Inflammatory Mediators Affects the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Progenitors. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:908507. [65] EPSLEY S, TADROS S, FARID A, et al. The Effect of Inflammation on Bone. Front Physiol. 2020;11:511799. [66] CUI Y, WANG Y, ZHAO D, et al. Loganin prevents BV-2 microglia cells from Aβ(1-42) -induced inflammation via regulating TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(12):1632-1642. [67] XU X, LI N, WU Y, et al. Zhuifeng tougu capsules inhibit the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and alleviate knee osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo experiments. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:951860. [68] GOMES DSI, LIMA C, SILVA J, et al. Is there an Inflammation Role for MYD88 in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Inflammation. 2021;44(3):1014-1022. [69] KASSEM A, LINDHOLM C, LERNER UH. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Stimulation of Osteoblasts Mediates Staphylococcus Aureus Induced Bone Resorption and Osteoclastogenesis through Enhanced RANKL. PLoS One. 2016;11(6): e156708. [70] HE Y, WU Z, CHEN S, et al. Activation of the pattern recognition receptor NOD1 in periodontitis impairs the osteogenic capacity of human periodontal ligament stem cells via p38/MAPK signalling. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(12):e13330. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Huang Haoran, Fan Yinuo, Wei-Yang Wenxiang, Jiang Mengyu, Fang Hanjun, Wang Haibin, Chen Zhenqiu, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi. Urolithin A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1149-1154. |
| [6] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [7] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [8] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [9] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [10] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [12] | Zhu Zhiqi, Yuan Sijie, Zhang Zilin, Ji Shijie, Meng Mingsong, Yan Anming, Han Jing. Mechanism underlying the effect of Liuwei Dihuang Pill on osteolysis and osteogenesis induced by titanium particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 392-397. |
| [13] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [14] | Chai Shuang, Ma Jiangtao, Yang Yanbing, Su Xiaochuan, Xie Yan, Teng Junyan, Qin Na. The role and mechanism of estrogen receptor in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by Gushukang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2574-2578. |
| [15] | Xie Heng, Gu Ye, Gu Yingchu, Wu Zerui, Fang Tao, Wang Qiufei, Peng Yuqin, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Ferroptosis in bone diseases: therapeutic targets of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2613-2618. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||