Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2574-2578.doi: 10.12307/2024.298
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role and mechanism of estrogen receptor in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by Gushukang
Chai Shuang, Ma Jiangtao, Yang Yanbing, Su Xiaochuan, Xie Yan, Teng Junyan, Qin Na
- Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province (Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital), Zhengzhou 450016, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-17Accepted:2023-04-15Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-31 -
Contact:Qin Na, PharmD, Chief pharmacist, Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province (Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital), Zhengzhou 450016, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chai Shuang, MD, Attending physician, Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province/Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Zhengzhou 450016, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (Youth Science Foundation Project), Nos. 202300410555 (to CS) and 222300420198 (to MJT); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82174413 (to QN and CS [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chai Shuang, Ma Jiangtao, Yang Yanbing, Su Xiaochuan, Xie Yan, Teng Junyan, Qin Na. The role and mechanism of estrogen receptor in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by Gushukang[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2574-2578.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
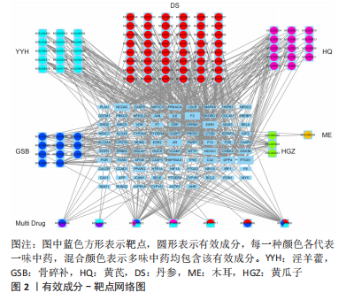
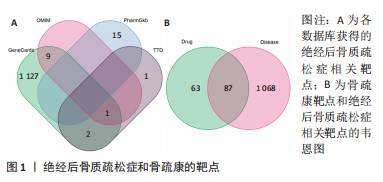
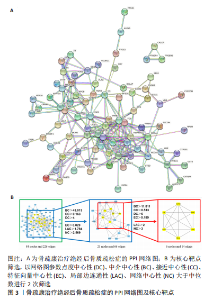
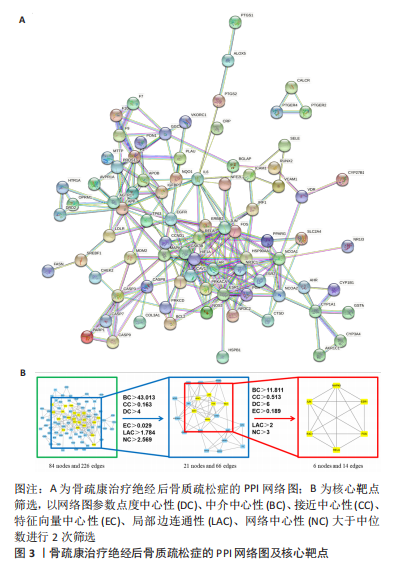
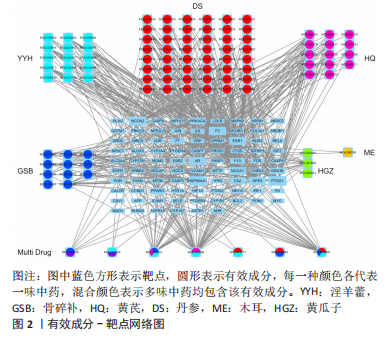
2.2 骨疏康有效成分-靶点网络图 将前一步获得的87个骨疏康治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的靶点及对应的有效成分导入Cytoscape软件(V3.7.1)构建骨疏康有效成分-靶点网络图,如图2所示,网络图共包含186个点,579个边,处于核心的有效成分有MOL000098(quercetin,槲皮素),MOL000422(kaempferol,山柰酚),MOL00006(luteolin,木犀草素),MOL004328(naringenin,柚皮素),MOL00354(isorhamnetin,异鼠李素),分别与51,25,21,14,14个靶点相连。在所有成分中,MOL000449(Stigmasterol)、MOL000359(sitosterol)、山柰酚、槲皮素、MOL001771(poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol)、MOL000569(digallate)、木犀草素为两味及两味以上中药的共有成分,靶点NCOA2,ESR2,AR,F2,ESR1,PTGS1与多种有效成分相连(图中较大的蓝色方形),可能是骨疏康治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的核心靶点。"
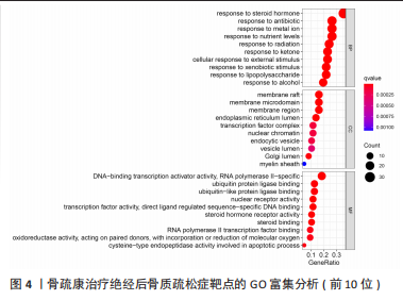
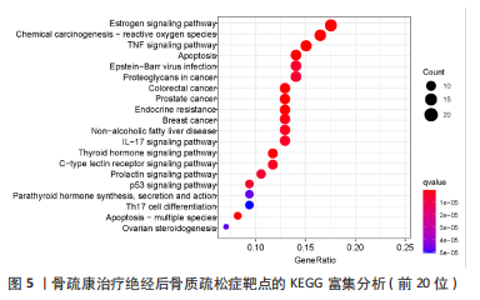
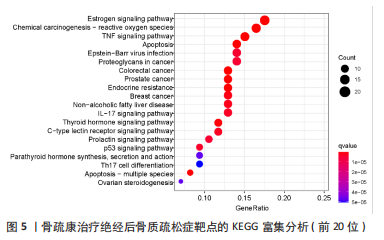
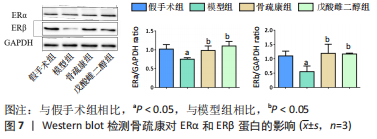
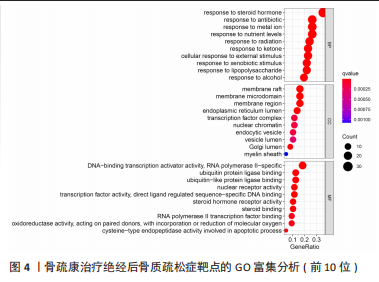
2.4 基因功能和信号通路富集分析结果 对87个靶点进行富集分析,共富集获得GO条目1 797个,其中细胞组分(cellular component,CC)61个,分子功能(molecular function,MF)107个,和生物学过程(biological process,BP)1 629个。图4显示了各条目前10位,BP主要富集在对类固醇激素的反应、对抗生素的反应,CC主要富集在膜筏、膜微区、膜区等;MF主要富集在DNA 结合转录激活因子活性、RNA 聚合酶Ⅱ特异性、泛素蛋白连接酶结合和核受体活性。KEGG富集分析共获得134条信号通路,排除明显不相关的疾病途径,如化学致癌-受体激活、脂质和动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路、流体剪切应力与动脉粥样硬化等,发现骨疏康可能通过雌激素、TNF、凋亡、内分泌抵抗、IL-17、甲状腺激素、甲状旁腺激素的合成、分泌和作用和P53信号通路治疗绝经后骨质疏松症(图5)。"
| [1] GKASTARIS K, GOULIS DG, POTOUPNIS M, et al. Obesity, osteoporosis and bone metabolism. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(3):372-381. [2] SLUPSKI W, JAWIEN P, NOWAK B. Botanicals in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1609. [3] 中华中医药学会.绝经后骨质疏松症(骨痿)中医药诊疗指南(2019年版)[J].中医正骨,2020,32(2):1-13. [4] 侍方,李欣,张蕊.骨疏康胶囊联合鲑鱼降钙素、戊酸雌二醇对绝经后骨质疏松患者的临床疗效[J].中成药,2020,42(12):3188-3192. [5] CHAI S, WAN L, WANG JL, et al. Gushukang inhibits osteocyte apoptosis and enhances BMP-2/Smads signaling pathway in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 2019;64:153063. [6] THOMPSON DD, SIMMONS HA, PIRIE CM, et al. FDA Guidelines and animal models for osteoporosis. Bone. 1995;17(S4):125S-133S. [7] LI XL, WANG L, BI XL, et al. Gushukang exerts osteopreserve effects by regulating vitamin D and calcium metabolism in ovariectomized mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(2):224-234. [8] 杨骏杰,赵永见,王强,等.骨疏康颗粒对去卵巢小鼠体重、血清骨代谢指标和组织形态学的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(9):1212-1216. [9] 郑志坚,舒冰,赵世天,等.骨疏康颗粒对去卵巢小鼠骨质疏松模型骨丢失和破骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(7):3647-3651. [10] GE YW, FENG K, LIU XL, et al. Quercetin inhibits macrophage polarization through the p-38alpha/beta signalling pathway and regulates OPG/RANKL balance in a mouse skull model. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(5):3203-3216. [11] VAKILI S, ZAL F, MOSTAFAVI-POUR Z, et al. Quercetin and vitamin E alleviate ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by modulating autophagy and apoptosis in rat bone cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3495-3509. [12] HUANG YY, WANG ZH, DENG LH, et al. Oral Administration of Quercetin or Its Derivatives Inhibit Bone Loss in Animal Model of Osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6080597. [13] SONG JE, TIAN J, KOOK YJ, et al. A BMSCs-laden quercetin/duck’s feet collagen/hydroxyapatite sponge for enhanced bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(3):784-794. [14] LI X, JIANG Q, WANG T, et al. Comparison of the Antioxidant Effects of Quercitrin and Isoquercitrin: Understanding the Role of the 6’’-OH Group. Molecules. 2016;21(9):1246. [15] CORDOBA A, MANZANARO-MORENO N, COLOM C, et al. Quercitrin Nanocoated Implant Surfaces Reduce Osteoclast Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3319. [16] WONG SK, CHIN KY, IMA-NIRWANA S. Quercetin as an Agent for Protecting the Bone: A Review of the Current Evidence. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6448. [17] YANG L, TAKAI H, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Kaempferol stimulates bone sialoprotein gene transcription and new bone formation. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110(6):1342-1355. [18] LIU H, YI X, TU S, et al. Kaempferol promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and improves osteoporosis by downregulating miR-10a-3p and upregulating CXCL12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;520:111074. [19] XIE B, ZENG Z, LIAO S, et al. Kaempferol Ameliorates the Inhibitory Activity of Dexamethasone in the Osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 Cells by JNK and p38-MAPK Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:739326. [20] ADHIKARY S, CHOUDHARY D, AHMAD N, et al. Dietary flavonoid kaempferol inhibits glucocorticoid-induced bone loss by promoting osteoblast survival. Nutrition. 2018;53:64-76. [21] LIANG G, ZHAO J, DOU Y, et al. Mechanism and Experimental Verification of Luteolin for the Treatment of Osteoporosis Based on Network Pharmacology. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:866641. [22] JING Z, WANG C, YANG Q, et al. Luteolin attenuates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by regulating ERK/Lrp-5/GSK-3beta signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):4472-4490. [23] ORSOLIC N, NEMRAVA J, JELEC Z, et al. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Chrysin and Naringenin in a Drug-Induced Bone Loss Model in Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2872. [24] EASTELL R, O’NEILL TW, HOFBAUER LC, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16069. [25] ABU-AMER Y. NF-kappaB signaling and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(9):2377-2386. [26] CHENG CH, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. Osteoporosis Due to Hormone Imbalance: An Overview of the Effects of Estrogen Deficiency and Glucocorticoid Overuse on Bone Turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1376. [27] SHARMA AR, NAM JS. Kaempferol stimulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway to induce differentiation of osteoblasts. J Nutr Biochem. 2019; 74:108228. [28] WU W, FU J, GU Y, et al. JAK2/STAT3 regulates estrogen-related senescence of bone marrow stem cells. J Endocrinol. 2020;245(1):141-153. [29] WANG Z, BAO HW, XU YJ. Cnidium lactone prevents bone loss in an ovariectomized rat model through the estrogen-alpha/BMP-2/Smad signaling pathway. J Gene Med. 2020;22(8):e3198. [30] LIU Y, WANG X, CHANG H, et al. Mongolian Medicine echinops prevented postmenopausal osteoporosis and induced ER/AKT/ERK pathway in BMSCs. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):275-281. [31] 李晓曦,陈宇恒,唐秀凤,等.基于雌激素作用的淫羊藿女贞子配伍对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的影响研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(9): 1-6. [32] 张则业,杨佳迪,颜倩,等.基于网络药理学结合体内实验研究探讨四物汤的植物雌激素样效应及其分子机制[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(10): 2750-2758. [33] WANG T, WANG Y, ZHUANG X, et al. Interaction of Coumarin Phytoestrogens with ERalpha and ERbeta: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Molecules. 2020;25(5):1165. |
| [1] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [2] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [3] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [4] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [5] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [6] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [7] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Mechanism of beta-sitosterol on hypertrophic scar fibroblasts: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 216-223. |
| [8] | Zhang Jingtao, Hu Minhua, Liu Shitao, Li Shuyuan, Jiang Zexin, Zeng Wenxing, Ma Luyao, Zhou Qishi. Regularity and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compound prescriptions in the treatment of primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2555-2560. |
| [9] | Pan Chengzhen, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Mo Jian, Zhang Chi, Wei Yuanxun, Wei Zongbo. Mechanism by which terpenoid herbal monomers prevent osteoporosis by regulating nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2234-2241. |
| [10] | Gao Zhengang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Jiang Wen. Mechanism of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and its traditional Chinese medicine interventions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2242-2247. |
| [11] | Mo Jian, Ye Sentao, Zhang Xiaoyun. Progress in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with monomer and compound Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1756-1761. |
| [12] | Xu Kangli, An Lanhua, Zhang Jinsheng, Du Xiaoyan, Yin Lele, Zhang Xixian. Research hotspots and frontiers of functional magnetic resonance imaging in treatment of ischemic stroke by traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1789-1796. |
| [13] | Ying Chunmiao, Pan Xiaolong, Liu Feixiang, Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 121-130. |
| [14] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [15] | Liu Hao, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Wang Liping, Yang Kunhai, Hu Yongrong, Qu Bo. Lumbar MRI vertebral bone quality score to evaluate the severity of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 606-611. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||