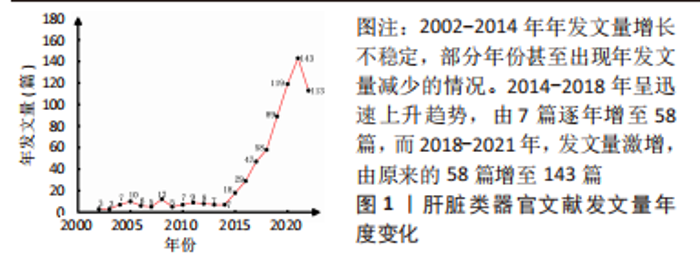
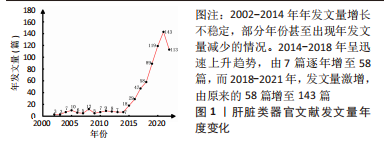
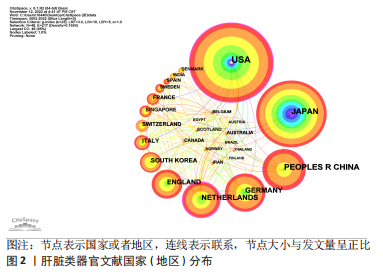
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 1099-1104.doi: 10.12307/2024.134
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids
Xu Canli1, He Wenxing1, Wang Lei1, Wu Fangting1, Wang Jiahui1, Duan Xuelin2, Zhao Tiejian1, 3, Zhao Bin1, 4, Zheng Yang1
- 1Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science, 2College of Zhuang Medicine, 3College of Basic Medicine, 4Finance Office, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-10-08Accepted:2023-04-14Online:2024-03-08Published:2023-07-17 -
Contact:Zheng Yang, Master, Lecturer, Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xu Canli, Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China He Wenxing, Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82204755 (to ZY); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960751 (to ZTJ); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Youth Project), No. 2020GXNSFBA297094 (to ZY); Scientific Research Project of Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022CX004 (to ZB); Scientific Research Project of Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022MS002 (to WL); Scientific Research Project of Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022MS008 (to ZY); Scientific Research Project of Faculty of Chinese Medicine Science of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022QJ001 (to WJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
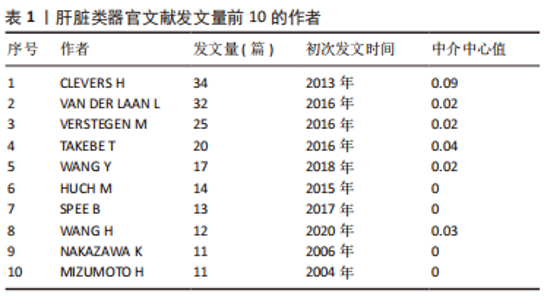
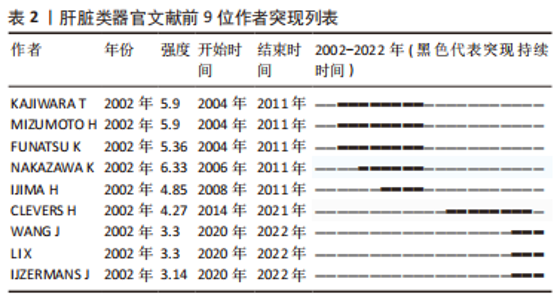
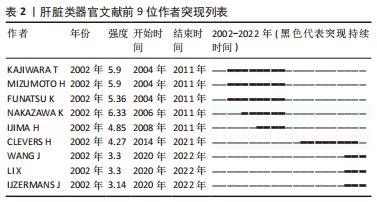
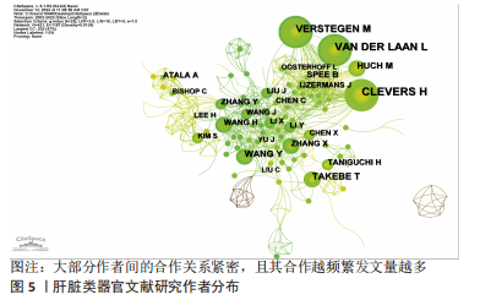
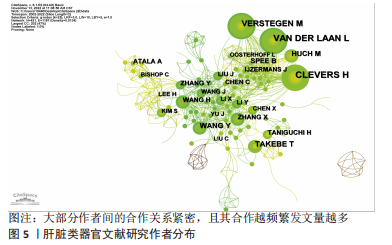
2.4 肝脏类器官研究作者分布与作者突现分析 对数据进行作者共现分析和可视化后得到图5,大部分作者间的合作关系紧密,且其合作越频繁发文量越多。发文量前10的作者见表1,发文量最高的是CLEVERS H(34篇),同时与其他学者合作交流最频繁的也是这位作者。另外,从前9名作者突现表(表2)中发现,尽管NAKAZAWA K持续突现的时间稍短,但是突现度最高,强度达到6.33,这表明NAKAZAWA K在肝脏类器官研究领域发展潜力大、能力强。根据核心作者最低发文量公式N=0.749×ηmax1/2(ηmax即该领域中最高产的作者发文量)[11],ηmax=34,N≈4,筛查出核心作者人数为91人。"
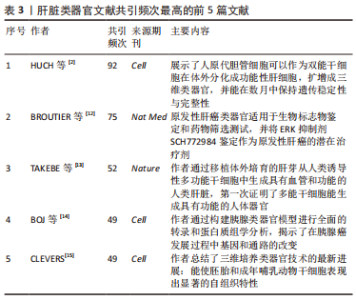
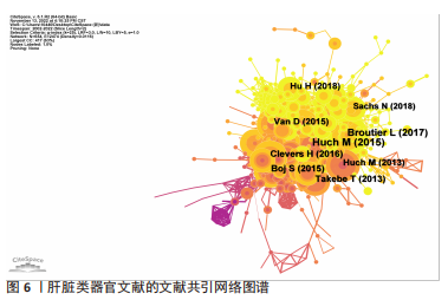
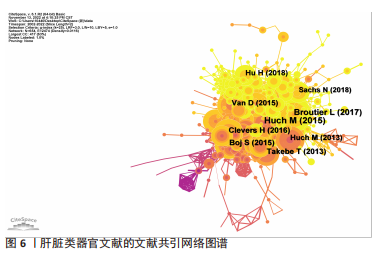
2.5 肝脏类器官文献共引分析 对肝脏类器官文献进行文献共引分析得到网络图谱,见图6。共引频次最高的前5篇文章分别是“Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver”(92次)、“Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening”(75次)、“Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant”(52次)、“Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer”(49次)、“Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids”(49次),详见表3。说明这5篇文章的学术性高,参考性强,被广泛认可。"
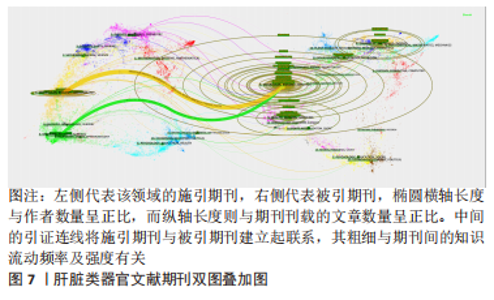
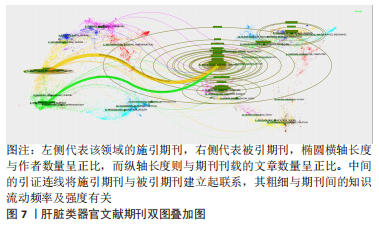
2.6 肝脏类器官文献期刊双图叠加分析 对肝脏类器官文献进行期刊双图叠加分析和可视化,得到图7,左侧代表该领域的施引期刊,右侧代表被引期刊,椭圆横轴长度与作者数量呈正比,而纵轴长度则与期刊刊载的文章数量呈正比,中间的引证连线将施引期刊与被引期刊建立起联系,其粗细与期刊间的知识流动频率及强度有关。图中2条显著的连线由上到下分别表示发表在Molecular(分子学)/Biology(生物学)/Immunology(免疫学)类期刊的文章多引用Molecular/Biology/Genetics(遗传学)类期刊的文献;发表在Medicine(医学)/Medical(内科)/Clinical(临床)类期刊的文章常引用Molecular/Biology/Genetics类期刊的文献。此外,肝脏类器官研究还涉及Mathematics(数学)、Physics(物理学)、Animal(动物)、Science(自然科学)等领域,表明肝脏类器官的研究与其他学科交叉融合,综合性高。"
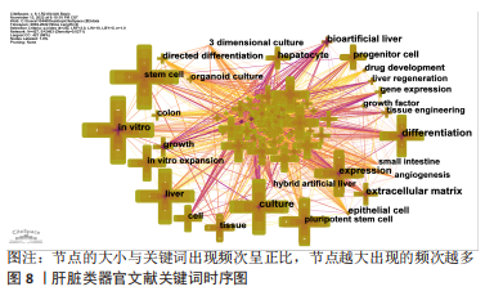
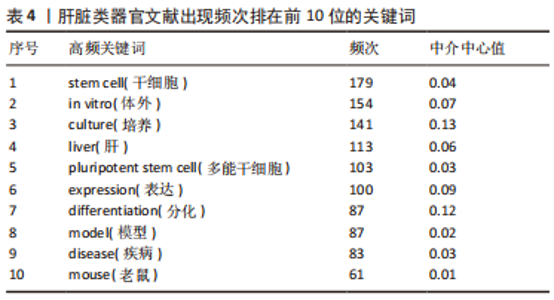
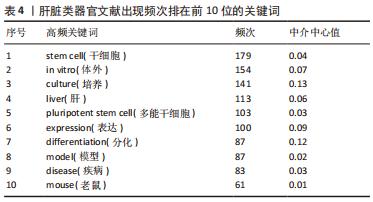
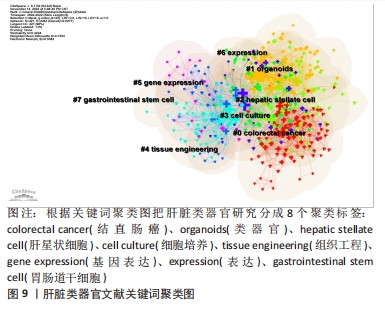
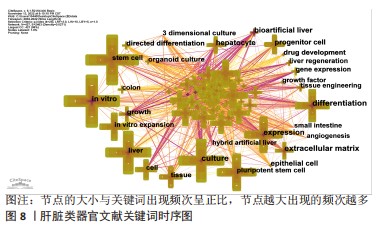
2.7 肝脏类器官文献关键词时序图分析与聚类分析 关键词是一篇文章的精髓,是对文章主旨的高度概括和凝练,其出现频次反映一个研究领域的热点与趋势。对关键词进行分析后,得到关键词时序图,见图8,节点的大小与关键词出现频次呈正比,节点越大出现的频次越多。把出现频次排在前10位的关键词进行统计,见表4。通过聚类分析,得到了Q=0.424 4,S=0.735 4的关键词聚类图,见图9(Q值与S值是衡量聚类结构是否合理的2个重要指标,Q > 0.3说明聚类结构显著,S > 0.5提示聚类结果同质性较高)[16],表明图9的聚类结构具有合理性。聚类标签代表文章的研究主题,是根据文章的标题、摘要、关键词通过特殊的算法得到[10]。根据关键词聚类图把肝脏类器官研究分成8个聚类标签:colorectal cancer(结直肠癌)、organoids(类器官)、hepatic stellate cell(肝星状细胞)、cell culture(细胞培养)、tissue engineering(组织工程)、gene expression(基因表达) 、expression(表达)、gastrointestinal stem cell(胃肠道干细胞)。图中各关键词聚类重叠,表明各关键词联系紧密,主要的研究方向一致。综合表4、图8与图9,总结出肝脏类器官领域的主要研究热点是体外干细胞三维培养、分化及基因表达。"
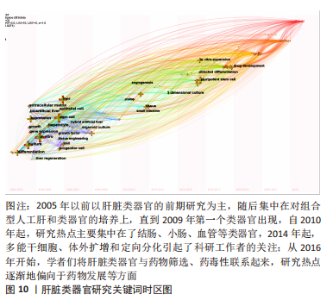
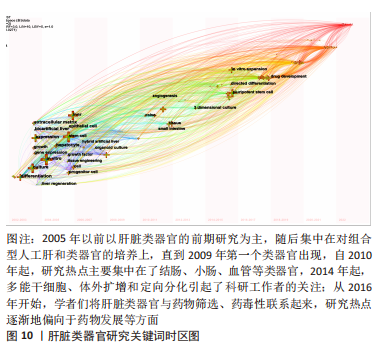
2.9 肝脏类器官研究领域发展趋势 关键词时区图主要是在时间维度上客观地反映肝脏类器官研究重点的演变。结合图10可以清晰地看出肝脏类器官的发展动态和热点趋势:2005年以前的研究主要集中在体外干、祖细胞的培养、增殖与分化及基因表达上,以肝脏类器官的前期研究为主;随着这些研究领域的不断成熟,学者们开始转向了对组合型人工肝和类器官的培养上,直到2009年,第一个类器官出现[17];自2010年起,研究热点主要集中在了结肠、小肠、血管等类器官研究,2012-2013年,3D培养风靡学术界,是当时的研究热点,其中肝脏类器官于2013年被首次成功培育[18];2014年起,多能干细胞、体外扩增和定向分化引起了科研工作者的关注;从2016年开始,学者们将肝脏类器官与药物筛选、药毒性联系起来,研究热点逐渐地偏向于药物发展等方面。根据时区图推测出今后的发展方向和研究专题主要以临床应用如再生医学、精准医学等为主。"

2.10 肝脏类器官研究的发展问题、瓶颈和突破方向 肝脏类器官拥有着众多的优势,但同样也存在着许多的问题和瓶颈:①缺乏血管化结构[19],容易导致类器官缺氧和代谢障碍,最终诱发组织坏死;②难以还原肝癌与免疫系统相互作用关系;③肝脏类器官成本较高、耗时长,这是其限制因素之一;④肝脏类器官的培育方法、质量控制以及药物筛选指标等缺乏全球性的统一标准,这是导致不同国家和机构在肝脏类器官领域出现研究差异的重要原因之一;⑤工程技术问题,现有技术培育的肝脏类器官尺寸较小,未能达到标准肝脏大小,且难以完全模拟肝脏复杂的生理结构和功能,如肿瘤类器官培养过程中缺乏基质细胞,导致肿瘤微环境无法重新建立,最终影响实际应用效果。此外,肿瘤类器官的高昂培育成本导致其无法在临床上广泛应用[20]。同时,在进入临床应用之前,安全问题、伦理关系以及法律责任等问题是肝脏类器官不容忽视的矛盾。因此,推动制定全球性统一标准,结合3D打印、微流体、基因编辑等技术来打破研究瓶颈,并且与动物模型等多种培养方式相结合以提高实验精准性[19]。最后,国家应制定相关法律法规,规范类器官的临床应用,同时加大政策支持,培养高尖人才,促进国内肝脏类器官的快速发展。"

| [1] LUI VC, HUI KP, BABU RO, et al. Human liver organoid derived intra-hepatic bile duct cells support SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5375. [2] HUCH M, GEHART H, VAN BOXTEL R, et al. Long-term culture of genome-stable bipotent stem cells from adult human liver. Cell. 2015; 160(1-2):299-312. [3] AKBARI S, SEVINÇ GG, ERSOY N, et al. Robust, Long-Term Culture of Endoderm-Derived Hepatic Organoids for Disease Modeling. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;13(4):627-641. [4] 林丽,雷妙,林佳漫,等.肝脏类器官的研究进展及应用[J].中国科学:生命科学,2023,53(2):185-195. [5] ASRANI SK, DEVARBHAVI H, EATON J, et al. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol. 2019;70(1):151-171. [6] KIM J, KOO BK, KNOBLICH JA. Human organoids: model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(10):571-584. [7] 任全娥.大数据背景下的文献计量学研究进展与学科融合[J].情报理论与实践,2019,42(1):48-52. [8] 潘颖,孙瑜峥,刘岩.科技文献阅读中语素意识研究的可视化分析[J].情报科学,2019,37(12):123-127. [9] 史艳龙,方德宝,冉启豪,等.基于Web of Science数据库的2000-2019年结直肠癌肝转移文献计量分析[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2020,29(4):400-411. [10] 谭令,龙霖梓,邓秘,等.抗血小板活化的文献计量学及可视化分析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(1):195-208. [11] 陈莹,常静玲,李新龙,等.基于CiteSpace的近20年蚓激酶相关研究的文献计量学分析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022, 24(1):388-397. [12] BROUTIER L, MASTROGIOVANNI G, VERSTEGEN MM, et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat Med. 2017;23(12):1424-1435. [13] TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013; 499(7459):481-484. [14] BOJ SF, HWANG CI, BAKER LA, et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell. 2015;160(1-2):324-338. [15] CLEVERS H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids. Cell. 2016; 165(7):1586-1597. [16] 高振,徐一喆,董竞成.基于文献计量学的中外中医药研究主题及热点比较[J].中医杂志,2022,63(13):1283-1290. [17] SATO T, VRIES RG, SNIPPERT HJ, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459(7244): 262-265. [18] HUCH M, DORRELL C, BOJ SF, et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature. 2013; 494(7436): 247-250. [19] 王溢贤,朱妍静,王红阳,等.肝脏类器官研究进展与应用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1132-1141. [20] CORRÒ C, NOVELLASDEMUNT L, LI VSW. A brief history of organoids. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;319(1):C151-C165. [21] AKBARI S, ARSLAN N, SENTURK S, et al. Next Generation Liver Medicine Using Organoid Models. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:345. [22] 赵梦雨,代荣阳,张钰哲.从免疫浸润角度分析肝癌患者性别和预后生存关系的差异[J].昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020, 45(6):119-127. [23] PRIOR N, INACIO P, HUCH M. Liver organoids: from basic research to therapeutic applications. Gut. 2019;68(12):2228-2237. [24] 丁明宁,薛晓勇,李晓骄阳.肝胆类器官在中药研究中的应用进展[J].中草药,2021,52(18):5789-5795. [25] ZHAO Y, YIN X, QIN H, et al. Two supporting factors greatly improve the efficiency of human iPSC generation. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(5):475-479. [26] LIN Y, FANG ZP, LIU HJ, et al. HGF/R-spondin1 rescues liver dysfunction through the induction of Lgr5+ liver stem cells. Nat Commun. 2017; 8(1):1175. [27] DEKKERS JF, WIEGERINCK CL, DE JONGE HR, et al. A functional CFTR assay using primary cystic fibrosis intestinal organoids. Nat Med. 2013; 19(7):939-945. [28] 王佳慧,郭新华,郑博文,等.基于miR-125b/NLRP3信号通路探讨莪术醇抗肝纤维化的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022,40(11): 95-99. [29] 王挺帅,张荣臻,王明刚,等.基于Kuffer细胞NF-κB信号通路探讨解毒化瘀颗粒拮抗肝功能衰竭的作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志, 2021,36(4):1878-1883. [30] BAI Y, YANG Z, XU X, et al. Direct chemical induction of hepatocyte-like cells with capacity for liver repopulation. Hepatology. 2023;77(5): 1550-1565. |
| [1] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [2] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [3] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [4] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [6] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [7] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [8] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [9] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [10] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [12] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [13] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [14] | Lyu Moran, Xu Wenxin, Wang Di, Li Ming. New trends and developments of functional training research in the field of health care [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 302-307. |
| [15] | Xie Enli, Tao Huimin. Application trends of blood flow restriction training in clinical rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 258-262. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||