Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 609-614.doi: 10.12307/2023.897
Previous Articles Next Articles
Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis
Liu Luxing1, Di Mingyuan2, Yang Qiang3
- 1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; 2Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 3Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China
-
Received:2022-12-05Accepted:2023-01-13Online:2024-02-08Published:2023-07-14 -
Contact:Yang Qiang, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China -
About author:Liu Luxing, Master candidate, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82072435 (to YQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
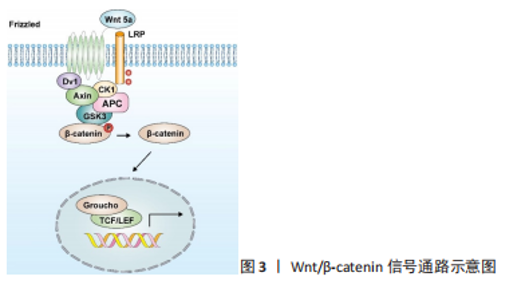
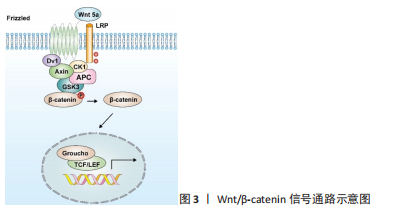
2.1 wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在调节软骨代谢和疾病中起着至关重要的作用,在生理条件下调节软骨细胞增殖和功能[5]。在Wnt信号通路中起着重要作用的蛋白有Wnt蛋白、β-catenin、Axin、Frz、Gsk3及APC等[6],见图3。BERGWITZ等[7]研究发现Wnt-5a和Wnt-5b可以通过不同方式来调控软骨细胞的增殖,其中Wnt-5a对关节软骨细胞的增长和维持起着关键的作用。此外,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路也是一种独特的调控关节炎发生发展的信号通路,已有研究证实Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在各种骨关节炎的发病中呈过度激活状态[8]。然而近年来还有研究表明,对该通路的过度刺激和抑制均可促进骨关节炎的发生发展[9]。故而中药有效成分对该通路的抑制或激活作用仍需进一步探究。"

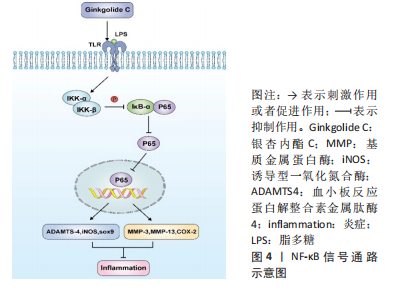
ZHENG等[10]研究发现补骨脂素不仅在体外可以激活大鼠软骨细胞的细胞功能,而且软骨细胞在经补骨脂素处理后,细胞中Wnt-4, Frizzled-2,β-catenin和cyclin D1相关基因和蛋白表达水平显著上调,GSK-3β的基因和蛋白表达水平下调;此外,补骨脂素能够诱导β-catenin核易位,并且Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的抑制剂Dickkopf-1(DKK-1)部分抑制了β-catenin和cyclin D1的表达。由此可以证明补骨脂素可能通过激活Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路促进软骨细胞增殖。 DING等[11]通过大鼠前交叉韧带断裂的方法建立动物模型,并向其关节腔内注射大黄素,发现大黄素能够降低白细胞介素1β诱导的大鼠软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase,MMP)3、MMP-13、血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶(recombinant a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin,ADAMTS)4和ADAMTS-5的mRNA和蛋白表达水平,而在形态学和组织学分析中也证实了大黄素可以改善骨关节炎的进展。这预示着大黄素是一种有前景的能够防治骨关节炎的药物。 ZHONG等[12]利用白细胞介素1β诱导骨关节炎患者来源的软骨细胞,通过细胞活力测定、糖胺聚糖分泌、免疫荧光、Western blotting、qRT-PCR等方法验证了青蒿素能够抑制白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和MMP-13的表达,显示出强大的抗炎作用;同时采用关节前交叉韧带横断和内侧半月板切除的方法构建大鼠骨关节炎模型,并通过大体观察、形态学染色、免疫组化和酶联免疫吸附法发现青蒿素具有预防软骨细胞凋亡和软骨退变的作用;进一步验证了青蒿素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨关节炎进展和软骨降解,提示青蒿素可能作为Wnt/β-catenin拮抗剂减轻炎症和防止软骨降解。 野黄芩苷是从植物灯盏花中分离得到的一种具有抗炎作用的黄酮类化合物葡醛酸苷。LIU等[13]通过DMM法建立动物模型,研究中发现野黄芩苷具有抑制炎症和保护软骨退化的作用,其可以下调MMP-1、MMP-13、ADAMTS-5、Wnt3a、Frizzled7的mRNA和蛋白表达,促进Ⅱ型胶原和Aggrecan的表达,同时抑制β-catenin的迁移和p38的磷酸化进入细胞核,这可能与介导Wnt/β-catenin和MAPK信号通路有关。此外,黄芪皂苷[14]、当归多糖[15]、川芎嗪[16]、薯蓣皂苷[17]、淫羊藿苷[18-19]、虎杖苷等也被证实在防治骨关节炎方面通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的相关基因或蛋白发挥作用[20]。 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路作为经典的信号通路之一,在骨关节炎的发生发展中发挥着重要作用。研究发现通过调节该通路中相关分子水平,能够抑制某些炎症因子的表达水平如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、MMP-13、ADAMTS等。而 Gsk3作为Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中重要的蛋白之一,在骨关节炎修复过程中Gsk3的表达被抑制在多个研究中得到了证实。除此之外,Ⅱ型胶原和Aggrecan作为软骨中重要的组成成分,某些中药有效成分如薯蓣皂苷能够促进Ⅱ型胶原和Aggrecan的表达,进而保护软骨细胞,延缓关节软骨退变。由此可见,中药有效成分调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路降低炎症反应的同时延缓了软骨细胞的退变,从而有效减缓了病情进展。 2.2 NF-κB信号通路 核因子κB(nuclear factor κB,NF-κB)是一种重要的转录因子,它能够调控细胞增殖和凋亡相关基因的表达,同时可以对炎症和免疫反应做出应答[21]。NF-κB 由 Rel 家族5个成员的同源和异源二聚体组成,包括NF-κB1 (p105/p50)、NF-κB2 (p100/p52)、Rela (p65)、RelB和c-Rel。在细胞未受刺激时,NF-κB通过与IκB相互作用保留在细胞质中。然而在细胞受到刺激后,IκB发生磷酸化并降解,使NF-κB复合物转移到细胞核,与NF-κB 反应物结合激活多种免疫调节蛋白、促炎细胞因子、趋化因子、黏附分子和生长因子的表达[22],见图4。由于NF-κB是一种多功能的转录因子,可以参与多种生物过程,因此全面了解NF-κB通路在骨关节炎病理中的作用将有助于制定靶向治疗的策略[23]。"

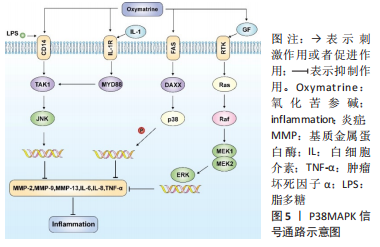
JI等[24]研究发现异甘草素不仅显著降低COX-2和MMP-13 的mRNA和蛋白表达水平,而且对于促凋亡Bax、cleaved-caspase-3和cleavedcaspase-9蛋白表达以及NF-κB p65磷酸化也具有明显的抑制作用,然而抗凋亡Bcl-2的表达却展现出明显的促进作用;随后在小鼠骨关节炎模型中证实了异甘草素增加透明软骨的厚度和软骨基质中蛋白多糖的产生,这说明异甘草素的抗炎抗凋亡作用可能与下调NF-κB信号通路有关。 JIANG等[25]研究发现双氢青蒿素可以抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的MMP-3、MMP-9、ADAMTS5、CCl-2、CCl-5和CXCL1的表达,并通过抑制NF-κB信号通路促进软骨细胞自噬,抑制软骨细胞的分解代谢和炎症因子水平。 RAN等[26]在研究中发现五味子乙素能够降低白细胞介素1β诱导的MMP3、MMP13、白细胞介素6和诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)的上调,同时改善了Ⅱ型胶原、aggrecan和sox9的表达水平。在大鼠骨关节炎模型中发现五味子乙素对于软骨退变具有明显的抑制作用,经Western blot验证其主要通过抑制NF-κB信号通路延缓骨关节炎的进展水平。 WANG等[27]采用Hulth法建立膝关节炎模型,并通过联合白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导构建膝关节炎软骨细胞模型;同时制备羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖纳米颗粒(HA/cNPs),用于姜黄素的递送,经测试HA/cNP对姜黄素的最佳载药量为38.44%,且具有良好的缓释作用;最终证实HA/cNP经过处理后抑制了NF-κB信号通路,抑制MMP-1和MMP-13的表达,增加了Ⅱ型胶原的表达,从而发挥抗炎抗凋亡的作用。除此之外,连翘苷元[28]、杜仲多糖[29]、前胡素[30]、桑辛素[31]、牛膝总皂苷[32]、白芍总苷[33]、马钱子苷[34]、银杏内酯C等有效成分在防治骨关节炎的研究中发现与NF-κB信号通路也有着密切的联系[35]。 在骨关节炎相关机制的研究中,NF-κB信号通路是研究较为成熟且研究较多的通路之一。NF-κB信号通路主要参与细胞的炎症免疫等反应,在骨关节炎的发生发展过程中发现NF-κB信号通路出现功能失衡的情况。骨关节炎的发生与炎症因子的表达有着密不可分的关系,关节腔内细胞,滑膜组织分泌的炎性递质如MMP-13能够加速软骨细胞的基质降解和滑膜炎症。此外,还有一些中药有效成分能够明显抑制p65的表达,减少IκBα降解和磷酸化,通过介导NF-κB信号通路抑制炎性因子的释放,使骨关节炎的进展水平得到改善。 2.3 p38 MAPK信号通路 p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路是参与炎症反应调控的重要信号通路,它参与调控关节软骨细胞增殖、分化、凋亡,炎性因子以及疼痛递质的产生,在骨关节炎发展中起着重要作用。p38 MAPK可分为p38α、p38β、p38δ和p38γ等4种亚型[36]。在骨关节炎病理过程中,p38MAPK信号通路可被炎性因子、生长因子等多种细胞外应激因子激活,然后将信号传递给转录因子,调节靶基因的表达,见图5。此外,该通路还能调节软骨细胞的增殖分化和基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)的合成,以及调节炎症因子的分泌和疼痛递质的产生。因此,p38MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎软骨破坏中起着至关重要的作用[37]。"

王象鹏等[38]研究发现槲皮素在骨性关节炎疾病防治中具有降低软骨炎性因子表达的作用,可通过抑制 p38 MAPK通路相关因子表达而向好发展,所有结果显示槲皮素具有降低骨关节炎炎性因子表达、保护骨关节炎患者关节软骨的作用。赵宝祥[39]在研究中证实威灵仙总皂苷可以通过抑制白细胞介素1β/MAPKs信号通路的活化,上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2、下调促凋亡因子Bax、Caspase-3、Caspase-9,减少软骨细胞的凋亡,延缓软骨组织退变从而发挥治疗作用。苏友新等[40]研究发现柚皮苷能够促进软骨细胞的增殖,保护软骨细胞的功能,其机制可能与柚皮苷降低诱导退变软骨细胞中 caveolin-1、p-p38与p-ATF-2的表达,抑制“caveolin-p38MAPK”通路的活动,进而减少通路下游白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA的表达有关。JIANG等[41]研究发现氧化苦参碱可以抑制脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞炎性退变,同时在体条件下抑制骨关节炎软骨退变,并且通过实验进一步证实氧化苦参碱可以共同调节MAPK和NF-κB信号通路发挥抑制软骨退变的作用。然而还有学者证实了人参皂苷Rb1[42]、栀子苷等成分通过抑制P38 MAPK信号转导通路治疗骨关节炎[43],进一步阐述了该通路在骨关节炎发生发展中的重要作用。 在骨关节炎疾病发生发展中P38 MAPK信号通路发挥着举足轻重的作用,其不仅可以调控滑膜组织的炎症反应还影响着软骨细胞的凋亡。Bcl-2和Bax是与细胞凋亡相关的两种重要基因,有些中药有效成分通过调控Bcl-2和Bax,抑制了软骨细胞的凋亡,从而发挥了保护软骨细胞、减轻关节软骨退变的作用。此外,P38 MAPK信号通路被激活后可以促基质进金属蛋白酶的合成以及白细胞介素1、NO等致炎因子的释放,故而抑制P38 MAPK信号通路,能够抑制相关炎症因子的表达,达到抗炎保护软骨作用。 2.4 PI3K/Akt信号通路 3-磷酸肌醇激酶(phosphoinositide 3 kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,PKB/Akt)信号转导通路是经典信号通路之一,广泛存在于多种细胞中,在调节细胞生存、增殖、分化、凋亡和代谢等方面发挥重要作用[44]。PI3K是一种由一个催化亚基和一个调节亚基组成的异源二聚体蛋白,共有3种同工酶Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ型,其中Ⅰ型被认为与关节软骨损伤的发生发展关系密切。PI3K下游靶蛋白AKT位于细胞中,是一种丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,也被称为PKB,共有3 种亚型 AKT1、AKT2、AKT3,其中AKT1与 AKT2参与骨细胞合成和代谢的平衡调节[45],见图6。"
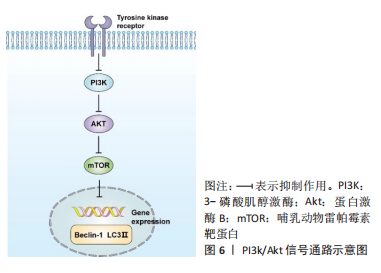

商连斌等[46]采用前交叉韧带及内侧副韧带离断术进行动物造模,造模成功后给予续断总皂苷灌胃处理,2周后取术侧膝关节软骨组织,通过苏木精-伊红染色以及Western blot法评估续断总皂苷的作用,结果证实续断总皂苷对大鼠软骨具有一定的保护作用,其主要通过抑制PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路的过度活化而发挥作用的。姚旭等[47]体外培养人软骨细胞 C28/I2,经过白细胞介素1β处理后复制炎症模型,用芍药苷治疗后采用Western blot和免疫荧光等方法观察,结果发现经过芍药苷处理后p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白表达明显下降,肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6浓度减少,说明芍药苷通过抑制细胞内PI3K/AKT信号通路减少炎症因子的生成来治疗骨关节炎。TANG等[48]采取切断前交叉韧带和内侧半月板的方法建立动物骨关节炎模型,随后予以大鼠腹腔注射淫羊藿苷,4周后取大鼠膝关节组织进行分析评估,结果表明淫羊藿苷可以显著抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞的凋亡率以及PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路,且骨关节炎软骨组织严重的病理状态也得到了明显的缓解。此外,白杨素[49]、杨梅素[50]、蛇床子素[51]、青藤碱[52]、青蒿素[53]、金丝桃苷等中药有效成分也均被证实通过作用PI3K/Akt信号通路发挥抗骨关节炎作用[54],有望被运用在未来的临床治疗中。 PI3k/Akt信号通路与骨关节炎的发病过程有着密切联系。此外,有研究证明该通路在细胞自噬过程中也发挥着关键作用。通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路不仅能够促进骨关节炎软骨细胞自噬,还能缓解相关炎症反应。LC3Ⅱ与 Beclin-1是两种重要的自噬相关蛋白。如芍药苷和淫羊藿苷等中药有效成分通过抑制PI3k/Akt信号通路过度活化,控制了该通路对于细胞自噬作用的抑制,从而促进了软骨细胞自噬作用,最终达到修复软骨细胞、恢复关节内环境的目的。 2.5 JAK2/STAT3信号通路 酪氨酸蛋白激酶(Janus kinase,JAK)2/信号转导子和转录激活子(signal transduction and activator of transcription,STAT)3信号通路是近年来发现的重要的细胞内信号转导通路家族,它主要参与炎症反应、氧化应激、细胞损伤、凋亡、介导机体免疫功能等过程[55],见图7。已有研究证实JAK2/STAT3通路在骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖与凋亡的过程中发挥着重要调控作用。"


YANG等[56]报道该通路在类风湿性关节炎发生发展中也起着关键作用。李旭升等[57]采用Glasson法建立动物模型,术后每天腹腔注射姜黄素,4周后取材,随后采用Western blot评估p-JAK2、p-STAT3和Bax蛋白的表达情况,同时检测琥珀酸脱氢酶(SDH)、细胞色素C氧化酶(COX)改变以及免疫组织化学法观察标本的变化;结果发现姜黄素组软骨组织退变程度明显优于对照组,且p-JAK2、p-STAT3蛋白表达升高,Bax蛋白表达降低,琥珀酸脱氢酶和COX蛋白表达水平均升高,由此说明姜黄素可激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路,增加软骨细胞线粒体抗氧化应激能力,缓解关节软骨的退变,降低了骨关节炎发展的水平。 刘军等[58]通过切断小鼠膝关节内侧半月板和内侧副韧带建立动物模型,术后予以薯蓣皂苷腹腔注射,4周后取材,并提取软骨细胞进行培养,随后评估P-JAK2、p-STAT3、Bax等相关蛋白表达情况以及线粒体中超氧化物歧化酶的含量及活性,分析薯蓣皂苷的作用机制;最终证实薯蓣皂苷通过激活JAK2/STAT3通路,减轻软骨细胞炎症反应、线粒体氧化应激损伤和细胞凋亡,从而发挥预防及治疗的作用。高伟静等[59]通过无菌分离人膝骨关节炎软骨细胞,利用黄芪多糖干预48 h后,采用MTT、Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法、PI染色法以及Western blot评估黄芪多糖的作用机制,最终得出结论黄芪多糖具有促进人膝骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖并抑制其凋亡的作用,其机制可能与激活JAK2/STAT3 通路有关。 胡炯等[60]研究发现染料木素可以增加骨关节炎关节软骨的胶原和蛋白多糖含量,使软骨组织接近正常软骨。此外染料木素还显著下调肿瘤坏死因子α、MMP-13、Bax蛋白表达,而p-JAK2、p-STAT3 及 Bcl-2 蛋白表达水平明显上升,由此可以说明染料木素可激活 JAK2/STAT3 信号通路,抑制炎症反应和软骨细胞凋亡,明显缓解关节软骨的退变,降低骨关节炎进展水平。 近年来对于骨关节炎相关的信号通路研究较为成熟。JAK2/STAT3信号通路是细胞信号转导重要途径之一,主要参与了细胞的增殖分化、炎症和免疫等反应。研究发现JAK2/STAT3信号通路的活化可以促进炎症因子的释放,从而加重骨关节的炎症反应。此外,JAK2/STAT3信号通路和细胞凋亡存在着重要的联系,如黄芪多糖能够促进Bcl-2表达的同时抑制Bax的相关表达,抑制了软骨细胞凋亡,起到了保护软骨细胞、防治骨关节炎的作用。 2.6 其他通路 随着骨关节炎研究的逐渐深入,越来越多的信号通路被研究者们所发现。 除了上述介绍的信号通路外,Notch和TLR/MyD88信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中也发挥着重要的作用。Notch信号通路在新生血管生成方面发挥着至关重要的作用。谢平金等[61]研究发现在早期膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜、软骨及软骨下骨中,川芎嗪和过表达miR-20b-5p可能通过抑制血管内皮生长因子/Notch1信号通路介导的血管新生在一定程度上改善多方面的组织学表现,抑制早期膝骨关节炎的进展。 Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)是重要的固有免疫模式识别受体,通过识别损伤相关分子模式及病原相关分子模式,启动髓样分化因子88(myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88,MyD88)依赖途径后激活NF-κB信号通路,引发炎性递质及细胞因子的分泌,触发固有免疫应答,在膝骨关节炎滑膜炎的发生中发挥作用[62]。郑洁等[63]采用Hulth方法建立兔膝骨关节炎模型,术后予以青藤碱关节腔内注射干预10次,利用PCR和Western blot 检测分析发现青藤碱中、高剂量组TLR2、TLR4、MyD88 的mRNA和蛋白表达均显著下调,证实青藤碱通过下调TLR/MyD88 通路中相关分子的表达抑制兔膝骨性关节炎软骨免疫反应,延缓骨关节炎症。"

| [1] ZHAO X, MENG F, HU S, et al. The Synovium Attenuates Cartilage Degeneration in KOA through Activation of the Smad2/3-Runx1 Cascade and Chondrogenesis-related miRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:832-845. [2] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017; 19(9):53. [3] 刘朝晖,马剑雄,张顺,等.膝骨关节炎的现状及治疗方法的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(8):688-693. [4] GUNARATNE R, PRATT DN, BANDA J, et al. Patient Dissatisfaction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(12):3854-3860. [5] HE Z, LIU M, ZHANG Q, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated in the progress of mandibular condylar cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone loss induced by overloaded functional orthopedic force (OFOF). Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e10847. [6] 王华敏,宓轶群,刚嘉鸿.信号通路在膝骨关节炎实验研究中的进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(2):267-272. [7] BERGWITZ C, WENDLANDT T, KISPERT A, et al. Wnts differentially regulate colony growth and differentiation of chondrogenic rat calvaria cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1538(2-3):129-140. [8] YUASA T, OTANI T, KOIKE T, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling stimulates matrix catabolic genes and activity in articular chondrocytes: its possible role in joint degeneration. Lab Invest. 2008;88(3):264-274. [9] SHANG X, BÖKER KO, TAHERI S, et al. The Interaction between microRNAs and the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):9887. [10] ZHENG W, LIN P, MA Y, et al. Psoralen promotes the expression of cyclin D1 in chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(5): 1377-1384. [11] DING QH, YE CY, CHEN EM, et al. Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:222-230. [12] ZHONG G, LIANG R, YAO J, et al. Artemisinin Ameliorates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(6):2575-2590. [13] LIU F, LI L, LU W, et al. Scutellarin ameliorates cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin and MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:105954. [14] 颜春鲁,李盛华,安方玉,等.富硒黄芪皂苷对大鼠退变软骨细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控机制研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2018, 34(10):1210-1213. [15] 徐翀,申利民,苑文杰.当归多糖通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞氧化应激损伤与炎症反应[J].陕西中医,2022,43(6):700-703,770. [16] 肖强,郭子龙,杨晓宏.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨川芎嗪延缓膝骨关节炎软骨退变的机制[J].中医药导报,2022,28(2):37-42,52. [17] LU J, ZHANG T, SUN H, et al. Protective effects of dioscin against cartilage destruction in a monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-indcued osteoarthritis rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1029-1038. [18] 马玮玮,李瑛.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的淫羊藿苷治疗膝骨关节炎机制研究现状[J].湖北中医杂志,2022,44(6):63-66. [19] 刘摇摇,刘湘宁,田银平,等.淫羊藿苷对骨骼系统药理作用机制的研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(12):1516-1520. [20] HU L, LUO D, ZHANG H, et al. Polydatin inhibits IL-1β-mediated chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates cartilage degradation: Involvement of the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. Tissue Cell. 2022;78:101865. [21] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275. [22] 郑晓慧,董博,袁普卫,等.NF-κB信号通路在骨性关节炎软骨破坏中的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(7):540-544. [23] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734. [24] JI B, GUO W, MA H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses IL-1β induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells by inhibiting NF-κB and exerts chondroprotective effects on a mouse model of anterior cruciate ligament transection. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1709-1718. [25] JIANG LB, MENG DH, LEE SM, et al. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits catabolism in rat chondrocytes by activating autophagy via inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38979. [26] RAN J, MA C, XU K, et al. Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:1195-1204. [27] WANG J, WANG X, CAO Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for the delivery of curcuminoid in knee osteoarthritis and an in vitro evaluation in chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(5): 2604-2614. [28] 胡芯源,曹珊,陈文明,等.连翘苷元通过抑制TLR4介导的NF-κB信号通路减轻大鼠骨关节炎软组织损伤和基质降解[J].免疫学杂志,2021, 37(2):115-121. [29] 李宁博,骆晓飞,尹夏,等.杜仲多糖通过抑制NF-κB通路减轻IL-1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(7):661-668. [30] HE L, PAN Y, YU J, et al. Decursin alleviates the aggravation of osteoarthritis via inhibiting PI3K-Akt and NF-kB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107657. [31] JIA Y, HE W, ZHANG H, et al. Morusin Ameliorates IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Inflammation and Osteoarthritis via NF-κB Signal Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:1227-1240. [32] 黄竞杰,杨俊兴,陈浩雄.牛膝总皂苷治疗膝骨关节炎的药理研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(4):592-595. [33] 张燕丽,田园,付起凤,等.白芍的化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中医药学报,2021,49(2):104-109. [34] WAN H, LI C, YANG Y, et al. Loganin attenuates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation, cartilage degeneration, and rat synovial inflammation by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB. J Int Med Res. 2022;50(8): 3000605221104764. [35] MA T, JIA L, ZHAO J, et al. Ginkgolide C slows the progression of osteoarthritis by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and blocking the NF-κB pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1027553. [36] 王迷娜,刘璐,赵洛鹏,等.膝骨关节炎炎性因子及信号通路的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(4):388-392. [37] HAN F, JIANG H, QU W, et al. KLF11 protects chondrocytes via inhibiting p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(12):6505-6516. [38] 王象鹏,谢文鹏,毕亦飞,等.基于p38 MAPK信号通路分析槲皮素保护骨性关节炎关节软骨的机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(7): 169-177. [39] 赵宝祥.基于IL-1β/MAPKs通路探讨威灵仙总皂苷对骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2016. [40] 苏友新,闫虎,陈宝军,等.壮骨健膝方含药血清中药物成分骨碎补柚皮苷对IL-1β诱导兔退变软骨细胞“caveolin-p38MAPK”信号通路的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2014,34(12):1492-1498. [41] JIANG Y, SANG W, WANG C, et al. Oxymatrine exerts protective effects on osteoarthritis via modulating chondrocyte homoeostasis and suppressing osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(8):3941-3954. [42] HOSSAIN MA, ALAM MJ, KIM B, et al. Ginsenoside-Rb1 prevents bone cartilage destruction through down-regulation of p-Akt, p-P38, and p-P65 signaling in rabbit. Phytomedicine. 2022;100:154039. [43] CHEN Y, SHOU K, GONG C, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8384576. [44] WANG X, PAN J, LIU D, et al. Nicorandil alleviates apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy through PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8): 5349-5359. [45] 邓欢,吕艺蓁,刘宣,等.PI3K/AKT信号通路调控骨关节疾病软骨细胞自噬及损伤的机制[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(2):309-314. [46] 商连斌,金连峰,王哲,等.续断总皂苷对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织中PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路影响的实验研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2021,48(5): 188-191,后插2. [47] 姚旭,王清华,茹艺,等.芍药苷抑制PI3K/AKT信号促进细胞自噬治疗骨关节炎[J].吉林中医药,2020,40(8):1076-1079. [48] TANG Y, LI Y, XIN D, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by regulating autophagy of chondrocytes by mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):2984-2999. [49] 杨阳,何宇,史于传,等.白杨素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制LPS诱导的软骨细胞自噬[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(5):662-668. [50] 杨鑫,李源力,蒋萍,等.杨梅素通过PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路对骨性关节炎发展的影响[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2020,41(1): 48-57. [51] 段志远,于强,周驰,等.蛇床子素对膝骨关节炎大鼠的作用及对PI3K/Akt/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2021,27(1):111-114.. [52] 郑洁,袁普卫,赵莉平,等.青藤碱通过PI3K/AKt-mTOR信号通路调节膝OA兔软骨自噬水平机制研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(8): 30-33. [53] LI J, JIANG M, YU Z, et al. Artemisinin relieves osteoarthritis by activating mitochondrial autophagy through reducing TNFSF11 expression and inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in cartilage. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022; 27(1):62. [54] SUN K, LUO J, JING X, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine. 2021;80:153387. [55] PARK SK, DAHMER MK, QUASNEY MW. MAPK and JAK-STAT signaling pathways are involved in the oxidative stress-induced decrease in expression of surfactant protein genes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(2):334-346. [56] YANG Y, LIU Y, YU H, et al. Sesquiterpenes from Kadsura coccinea attenuate rheumatoid arthritis-related inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signal pathways. Phytochemistry. 2022;194:113018. [57] 李旭升,陈慧,甄平,等.JAK2/STAT3信号通路介导姜黄素在骨性关节炎软骨细胞代谢中的影响[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(12):1104-1109. [58] 刘军,何晓乐,甄平,等.JAK2/STAT3信号通路介导薯蓣皂苷元对骨性关节炎软骨细胞代谢的影响[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2016,45(5): 452-459. [59] 高伟静,林朋朝.黄芪多糖通过JAK2/STAT3通路调控人膝骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖与凋亡[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(2):67-71,91. [60] 胡炯,王伟东,王昌兴,等.染料木素调控JAK2/STAT3信号通路改善骨性关节炎大鼠软骨代谢的作用研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2018,23(4):383-388. [61] 谢平金,罗臻,卢启贵,等.川芎嗪和过表达miR-20b-5p干预早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠滑膜,软骨和软骨下骨血管新生的组织学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):237-245. [62] 韩宪富,李宁,谢兴文,等.TLR4/MyD88信号通路在膝骨关节炎滑膜炎中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(11):1690-1694. [63] 郑洁,赵莉平,胡亚莉,等.青藤碱对兔膝骨关节炎模型软骨Toll样受体2、4及髓样分化因子88表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2018,25(9):49-51. |
| [1] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [2] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [3] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [4] | Maisituremu·Heilili, Zhang Wanxia, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 505-509. |
| [5] | Qiao Hujun, Wang Guoxiang. Evaluation of rat osteoarthritis chondrocyte models induced by interleukin-1beta [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 516-521. |
| [6] | Liu Yuhan, Fan Yujiang, Wang Qiguang. Comparison of protocols for constructing animal models of early traumatic knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 542-549. |
| [7] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| [8] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [9] | Yan Binghan, Li Zhichao, Su Hui, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang, Tan Guoqing. Mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [10] | Chen Junyan, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. Cartilage targeting function in the drug delivery system by intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 458-463. |
| [11] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [12] | Yin Linwei, Huang Xiarong, Qu Mengjian, Yang Lu, Wang Jinling, Jia Feiyang, Liao Yang, Zhou Jun. Effects of treadmill exercise on osteoporosis and wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway in aged rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 231-236. |
| [13] | Xie Peng, Zhang Jiang, Deng Xiaolei, Wei Bo, Hou Decai. A systematic review of mouse model construction for sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 263-266. |
| [14] | Meng Zhicheng, Qiao Weiping, Zhao Yang, Liu Hongfei, Li Kaijie, Ma Bo. Effects of immune cells and related cytokines in the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| [15] | Ying Chunmiao, Pan Xiaolong, Liu Feixiang, Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 121-130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||