Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (23): 3747-3754.doi: 10.12307/2023.536
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chinese medicine promotes post-stroke brain function remodeling based on visual decoding of functional magnetic resonance imaging
Zhang Jinsheng1, Tian Li2, Li Sanqiang3, Zhang Xixian3
- 1The Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, Henan Province, China; 3Medical School of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-04Accepted:2022-09-02Online:2023-08-18Published:2023-01-16 -
Contact:Zhang Jinsheng, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jinsheng, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Central Plains Science and Technology Outstanding Innovative Talents Project, No. 2020(48); the Key Research, Development and Promotion Project of Henan Province in 2021, No. 212102311134
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jinsheng, Tian Li, Li Sanqiang, Zhang Xixian. Chinese medicine promotes post-stroke brain function remodeling based on visual decoding of functional magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3747-3754.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
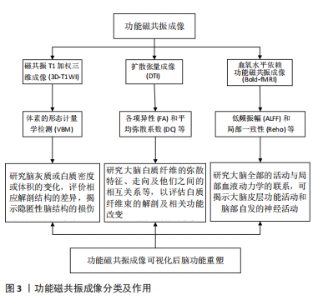
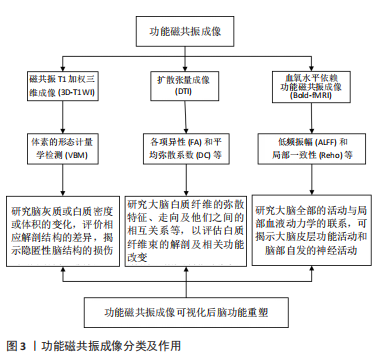
2.1 功能磁共振成像可视化 功能磁共振成像技术可从微观层面上阐明大脑重塑和神经再生的演变过程,对探索脑功能重建有重要价值。不仅可观察脑梗死半暗带区脑组织代偿、功能移位、重塑和通路重现过程,也可视化神经细胞再生和功能重组情况,是实现动态研究脑功能重塑和形态重构的重要手段[1-3]。 神经突触活动可导致局部脑区脑血流和氧耗的变化,磁共振信号可反映局部脑血流量和耗氧量,血氧水平依赖功能磁共振成像(blood oxygenation level dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging,BOLD-fMRI)通过大脑神经细胞氧气和能量消耗的变化,可视化反映脑组织细胞的功能活动和不同神经系统的改变情况。研究发现,脑组织对不同外界刺激均会在相应大脑皮质得到反映,信号刺激会促进神经重塑和功能重建、提高大脑记忆触发基因开关的建立、内环境的改变和各种激素释放和信号通路的连接[4]。 崔阳阳等[5]采用静息态功能磁共振成像(functional magnetic resonance imaging,rs-fMRI)分析躯体症状障碍患者和健康者脑功能自发活动变化,发现躯体障碍患者在右侧楔前叶、左侧海马旁回、右侧脑桥的局部一致性(regional homogeneity,ReHo)值降低显著,表明这些自发活动降低脑区可能是躯体症状障碍的关键靶区。曾繁勇等[6]通过任务态磁共振研究发现脑梗死患者病变侧完成对指康复治疗时,患者双侧大脑半球相关脑区均可激活,尤其在双侧运动前区皮质、健侧后顶叶皮质均表现出皮质兴奋性增高,而随着康复治疗持续,双侧皮质异常的运动网络连接逐渐恢复正常,临床上患者症状逐渐好转,表明该脑区病变轻重对预后脑梗死早期神经康复和功能重建具有重要意义。 目前临床上常用的磁共振成像技术包括结构和功能两方面。其中扩散张量成像(diffusion tensor imaging,DTI)技术主要观察和可视化分析神经纤维的细微结构变化,可揭示颅内病变对病变侧和对侧脑白质纤维的影响[7]。史静等[8]通过旋律语调疗法治疗后发现患者右侧额下回、上后回和扣带回的脑白质纤维各向异性(fractional anisotropy,FA)明显降低,右侧额下回均有髓鞘形成、轴突侧枝萌发和纤维连贯性等微结构重塑现象。CHEN等[9]采用DTI研究缺血性脑血管病患者和健康人脑白质纤维的异同,结果发现脑梗死的梗死侧FA值明显低于健侧,且偏瘫肢体肌力轻重与梗死侧脑白质纤维FA值呈现正相关。 体素的形态计量学(voxel-based morphometry,VBM)是3D-T1结构像常用的分析方法,通过分析每个体素的脑灰质或白质密度或体积的变化,分析双侧大脑半球神经元活动协同性可以揭示大脑隐匿性结构损伤和脑功能活动的差异,实现从不可视到可视化脑功能重塑研究新领域[10-12]。BOLD-fMRI技术多用于检测大脑全部的活动与局部血液动力学的联系,可揭示大脑皮质功能活动和脑部自发的神经活动。局部一致性(rregional homogeneity,ReHo)检测静息状态下脑区功能活跃情况和局部脑区功能活动的差异,ReHo值升高提示该部位神经功能活动兴奋性较强,同一脑区的神经元活动性均表现同时升高。低频振幅(amplitude of low frequency fluctuation,ALFF)反映不同脑组织神经元的自发活动水平,用来评价安静状态下不同脑组织大脑自发局部一致性信号变化。ALFF及ReHo值的变化在一定程度上可反映卒中后患者认知水平的变化,其值增高常提示脑卒中患者认知功能的改善明显,这对判断脑损伤后智能障碍有指导价值[13-16]。TSAI等[17]研究发现与健康人智能相比,脑卒中后智能障碍患者半暗带损伤之楔前区和后扣带回皮质ReHo和ALFF以及默认模式网络(default mode network,DMN)连接强度明显降低,这可能是导致急性脑梗死出现认知障碍的原因之一。目前关于各种磁共振成像分类及作用见图3。"
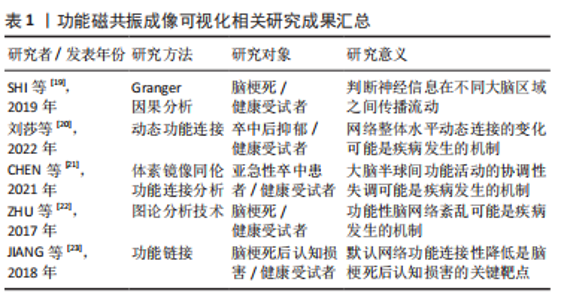
功能磁共振常采以基于种子点的相关分析、独立成分分析、体素镜像同伦功能连接分析、动态功能连接、Granger因果分析等分析方法揭示不相邻脑区功能活动的同步性和相邻脑区之间连接关系。其中,Granger因果分析(Granger causality analysis,GCA)可判断神经信息在不同大脑区域之间传播流动,揭示脑组织不同区域之间内在相互联系[18]。SHI等[19]基于功能磁共振成像数据的多变量格兰杰因果分析研究卒中后抑郁情绪网络发现从腹内侧前额叶皮质(ventromedial prefrontal cortex,VMPFC)、前扣带皮质(anterior cingulate cortex,ACC)及杏仁核(amygdala,AMYG)到丘脑的顺序是正向调节,当交互顺序相反时,调节作用是负向的,其中丘脑可以通过ACC预测岛叶(insular lobe,IC)的负性活动,背外侧前额叶皮质(dorsolateral prefrontal cortex,DLPFC)可以通过颞极(temporal pole,TP)预测ACC的活动。刘莎等[20]通过动态功能连接分析默认网络研究卒中后抑郁患者发病机制,发现卒中后抑郁患者的注意力网络总体时间变异性较健康受试者升高,表明其注意力网络动态功能改变可能是网络整体水平动态连接的变化,而非某功能节点的局部变化。因此,卒中后抑郁症发病病机可能与默认网络功能连接异常有关。CHEN等[21]研究发现,静息状态下脑卒中患者胼胝体、枕中回和顶下回的体素-镜像同伦连接(voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity,VMHC)显著升高,颞下回和中央前回VMHC降低,而动态下脑卒中患者颞下回和中央前回动态VMHC变异性增加,提示卒中后大脑半球间功能活动的协调性失调。 此外,功能磁共振成像不仅可以观察脑梗死恢复过程,也能准确发现脑功能活动的部位和范围,从整体水平上研究残存脑组织的重塑和功能代偿通路,对进一步明确脑卒中后遗症大脑重塑和神经再生有重要价值。ZHU等[22]利用功能磁共振成像的图论分析技术探讨了功能性脑网络的拓扑特性在脑梗死相关脑区的演变过程,发现与健康组相比,脑梗死的功能性脑网络路径最短,整体效率高,脑梗死患者的额前回、额中回和额下回外侧部节点程度增加,额前回、额中回和额上回内侧部节点效率提高明显,表明脑梗死后智能障碍的主要原因是功能性脑网络紊乱。JIANG等[23]研究发现默认网络功能连接性降低是脑梗死后认知损害的关键靶点,尤其在急性脑干梗死患者中,与健康组相比其右侧前额叶皮质和楔前叶的默认网络功能连接性降低显著,且患者血清中高同型半胱氨酸与右侧楔前叶连接负相关。 目前国内外功能磁共振成像可视化相关研究进展见表1。"
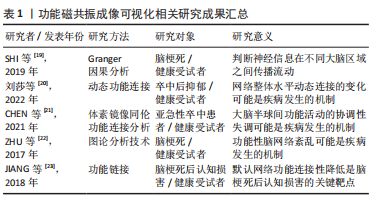

2.2 脑卒中后脑功能重塑机制的可视化研究 功能磁共振成像技术在脑梗死后脑功能的重构及神经重塑取得一定进展,已经证明卒中后脑功能重塑既有健侧脑组织的功能补偿,也有病灶侧脑组织的再生和修复,大脑的这种特性叫做神经可塑性变化,也是脑卒中后脑功能重塑的基础。脑卒中后脑组织不仅存在灰质体积扩大、皮质厚度和皮质表面积增加等结构重组情况,又有脑功能激活增强、功能连接增加等功能重组现象[15,24-25]。李明哲等[26]观察经颅交流电刺激对缺血性脑卒中大鼠rs-fMRI的影响,发现缺血后经颅交流电刺激在促进脑功能重塑的过程中既有健侧的代偿又有患侧的重塑。 功能磁共振成像研究发现卒中后脑损伤可以促进神经自发性功能恢复,但脑重构和神经再生并不是一成不变的,随时间变化脑重构和神经再生既有代偿又有萎缩,尤其在半暗带区可见大量胶质细胞及神经元结构发生变化。MALANDRAKI等[27]通过研究口腔期和咽期脑区激活情况,发现咽期多受后脑岛和扣带回等皮质下脑网络支配,吞咽中枢均接受双侧大脑皮质支配,如果一侧大脑皮质受损只会导致咽功能短时间受损,通过治疗可以加快梗死同侧或梗死对侧皮质功能重组进程,促使吞咽功能恢复正常。刘明等[28]利用DTI技术研究脑白质在中医肝气郁结证患者中的变化,发现肝气郁结证患者两侧大脑顶叶翻转角较健康人升高明显;肝气郁结证患者听右梭状回ALFF值升高明显,左侧岛叶,右侧额上回、额中回、额下回及左侧额上回的ALFF值表达显著降低,提示这些脑区可能是肝气郁结、情志不舒患者的神经病变靶区。 王佩佩等[29]采用VBM动态分析了丘脑梗死患者的灰质改变情况,发现梗死病灶远隔部位存在灰质体积增加和灰质体积减少,受损伤脑区及邻近部位出现明显大脑结构萎缩,其机制可能是顺行性或逆行性轴突变性、脑血流量减低导致神经代谢率减低造成梗死脑区出现萎缩。蒋宇等[30]基于体素的病变症状映射生成视频透视相关病变的统计图发现,左侧小脑后叶的损害与单独小脑损害患者吞咽困难的严重程度有关,小脑病变的患者在口腔和咽部均有吞咽困难,并且呈双侧不对称,在左侧大脑半球有更广泛的分布,并累及小脑深部核团。有学者通过fMRI和ReHo技术研究脑卒中合并抑郁障碍患者的脑功能演变情况,研究发现在额叶、小脑、边缘叶、扣带回及顶叶等脑组织表现ReHo降低趋势,在枕叶和扣带回等脑区表现ReHo增高趋势[31]。林志诚等[32]从ReHo角度研究发现经针刺治疗后脑梗死患者的重要脑功能区ReHo值发生明显变化。有学者通过动态功能连接分析发现在急性期,梗死区域与梗死对侧区之间抑制化信号减弱,亚急性期梗死对侧区对梗死区去抑制化信号增加,梗死区域对梗死对侧区逐渐正常化,慢性期仍显示梗死对侧对梗死区去抑制化信号仍存在[33],因此,通过恢复梗死侧半球网络联系对卒中后康复发挥着重要作用,提示脑网络的动态变化是卒中后大脑康复的微观物质基础。 作者总结了脑卒中后脑功能重塑机制的可视化研究进展,见表2。"
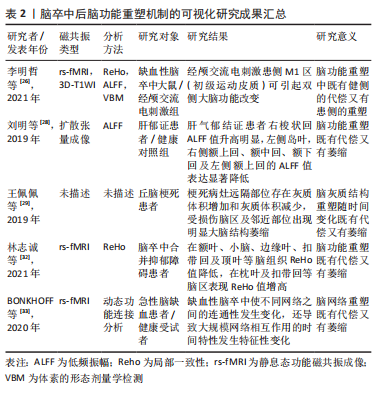
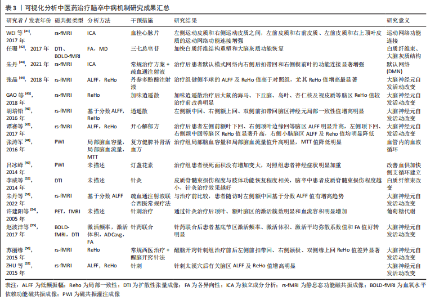
2.3 中医药脑卒中后脑功能重塑机制的可视化探索 2.3.1 中医药治疗脑卒中病机制研究 脑卒中又称为中风,临床多表现为昏厥、口眼歪斜、言语不利和半身不遂等。《黄帝内经·素问》曰:“血之与气,并走于上,则为大厥,厥则暴死”,明确指出气血逆乱、血行不畅、痰瘀互结是导致中风发生主要原因。在《图注八十一难经辨真》“脉者,资使之肾间动气,资生于胃中谷气,贯出于十二经中”的论述,说明脉始于先天之本、肾中之精气,补肾固本促进脉道畅利。又《灵枢·营卫生会篇》:“老者之气血衰,其肌肉枯,气道涩……”,指出了年龄渐增,肾精渐耗,气血亏耗不足,血脉运行不畅,瘀滞脉络,日久脉道不利,瘀血闭塞脑窍,导致肢体失用、言语不利及饮水呛咳等脑卒中病发生。 郭晟等[34]研究发现中老年人血瘀证检出率随年龄增大而增加,但增龄并又不单纯表现“血瘀”之证,也有“肾精虚损”的证候。这也与清·王清任《医林改错》:“元气既虚,必不能达于血管,血管无气,必停留而瘀”的观点相吻合。有学者基于MRA探索了脑卒中证候与血管病变相关性研究,发现脑病动脉硬化程度由重到轻中医证候依次为风痰阻络、痰热腑实、气虚血瘀、阴虚风动和风火上扰[35]。 中医学认为脑卒中多由饮食不节、情志所伤、气虚邪中等导致人体阴阳失调、气血逆乱和脉络阻塞,脑卒中治疗应以活血化瘀、通络祛滞、益气活血和补气扶正为主。现代药理学研究证明:中医药可改善大脑皮质局部血流,增加半暗带组织血氧供应,激活大脑细胞兴奋性,促进调节神经环路重组,加快受损脑功能重塑及恢复。辛铭正等[36]研究发现气络推动无力和血络瘀滞是脑梗死的主要原因,提倡以益气通络、活血通络为主,遵循“络以通为用”的治则。 田金洲等[37]基于文献挖掘技术发现脑卒中后认知障碍主要以肾精亏虚、痰浊阻窍、瘀血阻络、气血亏虚证候为主,中医证候肾虚、痰浊、血瘀与脑梗死部位和影像学改变有正相关性。毕丽丽等[38]通过脑卒中复元合剂治疗脑卒中发现,该药可以明显降低纤维蛋白原、血液黏度及促进神经功能修复。张梅奎[39]通过DWI及波谱成像研究益脑通络胶囊对大脑中动脉栓塞干预作用,发现与模型组相比,益脑通络胶囊组DWI信号强度降低明显,显示益脑通络胶囊具有促进大脑重塑作用。张路遥[40]通过DWI研究了脑卒中患者中医证型与梗死部位相关性,发现病变部位在枕叶、半卵圆中心和小脑等患者多有眩晕症。总的来看,中药在脑卒中早期能加快血液复供、改善梗死区微环境,促进神经干细胞增殖分化而降低脑损伤程度,中药在脑卒中的中晚期能抑制神经胶质细胞增殖分化,延缓和减轻胶质瘢痕形成,加快神经重塑。 2.3.2 可视化分析中医药治疗脑卒中病机制 利用功能磁共振成像研究中医药对卒中后大脑神经元结构和代谢异常治疗作用,对验证多靶点、多途径调控脑卒中后脑功能重塑、提高中医药临床疗效有重要意义。中医药能够“进一步持续”改善溶栓或介入治疗后梗死区或缺血区的微环境,促进卒中后脑梗死区域的神经再生和修复。WEI等[41]研究了血栓心脉片对脑梗死后神经功能的治疗作用,并用功能磁共振成像研究其治疗机制,发现治疗组患者脑区运动网络功能连接恢复明显,尤其对左侧运动皮质和右侧运动皮质之间、左前皮质和右前皮质、左前皮质和右上顶叶皮质的运动网络功能连接变化明显,这些脑区功能连接恢复情况与患者运动功能恢复呈正相关。 有研究采用扩散张量成像技术评价三七总皂苷对脑梗死患者神经功能重组及大脑结构重塑的影响,研究发现三七总皂苷通过提高血液循环、降低血液黏稠度、减轻细胞毒性水肿,改善血供加快白质纤维结构重塑和大脑灰质功能恢复,揭示了三七总皂昔对脑卒中患者有脑功能保护及神经重塑的效果[42]。朱丹等[43]采用rs-fMRI观察疏血通注射液联合常规治疗对急性缺血性脑卒中患者默认模式网络内功能连接的影响,发现治疗后患者DMN内右侧后扣带回和右侧楔前叶的功能连接显著增强,且右侧楔前叶功能连接的改变与NIHSS和BI评分显著相关,提示疏血通注射液联合常规治疗缺血性脑卒中可能通过调节DMN内右侧楔前叶功能连接从而改善神经功能缺损症状。有学者研究观察了丹参多酚酸注射液对脑梗死患者神经功能缺损修复情况及功能磁共振成像对其治疗机制的可视化研究[44],结果显示治疗组健侧半球的低频振幅及ReHo值高于对照组,尤其治疗后健侧区的局部一致性提高显著,神经元功能激活明显改善。 GAO等[45]通过加味逍遥散对抑郁症动物模型研究发现,加味逍遥散治疗后大鼠的海马、下丘脑、岛叶、杏仁核及视皮质等脑区局部一致性数值比治疗前改善明显;亦有学者发现逍遥散治疗抑郁症患者6周后,患者抑郁症情绪低落、饮食不佳等症状减轻明显,通过功能磁共振成像技术研究显示左侧额中回、右侧额上回、双侧前扣带回脑区神经元局部一致性值增高明显[46]。谭赛等[47]通过开心解郁方对血管性抑郁症患者研究发现,治疗8周后治疗组患者左侧前额叶下回、右侧顶叶边缘回等脑区低频振幅值显著升高,左侧顶下回及右侧颖中回等脑区局部一致性值亦有显著升高,右侧小脑脑区ALFF及Reho值均明显降低。 中医药通过多环节改善血供,加快侧支循环的建立,通过调控缺血缺氧微环境中复杂的信号通路和关联靶点减轻神经髓鞘的损伤和再生,提高神经纤维的可塑性,将阴阳失调的机体大环境和组织特定的微环境改善为阴阳调和的环境,促进精气血津液新生,激活神经生长因子新生,提高神经干细胞在脑梗死边缘区的存活率、增殖分化能力,促进脑梗死后结构重建和功能修复。张涛军[48]利用复方健脾补肾活血方对脑缺血梗死区血液循环及和局部脑血流量值的影响,采用PWI技术发现治疗组局部脑血容量和局部脑血流量值升高明显,平均通过时间值降低明显,表明健脾补肾活血方不仅可以改善脑梗死恢复期血管内的血液循环,功能磁共振成像亦可视化地证明了大脑血供的变化。吕冰峰[49]观察灯盏花素对急性期脑梗死患者梗死面积的变化情况,研究显示治疗组患者梗死面积没有增加变大,对照组患者神经症状明显加重,PWI发现异常区域面积扩大,表明活血化瘀方药通过改善血供加快侧支循环建立,减轻脑部梗死区范围,促进脑梗死患者的康复。 文章作者所在课题组通过补肾化瘀生新方对大鼠大脑中动脉缺血再灌注损伤模型研究发现,发现该方对于神经干细胞有激活作用,并促进神经干细胞分化增殖,加快向病变脑区的迁移,有利于脑缺血后神经功能重建和大脑重塑,表明补肾化瘀生新方可促进自体神经干细胞对损伤脑组织的修复和再生[50-51]。有研究利用扩散张量成像和三维重建技术观察脑卒中患者病变侧皮质脊髓束变化,发现皮质脊髓束损伤程度与肢体功能恢复程度相关,验证了DTI技术对评估脑卒中临床疗效的客观性和可靠性[52]。朱丹等[53]运用功能磁共振成像观察疏血通注射液联合西医常规疗法对脑卒中后神经元活动低频振幅的变化,发现与健康组比较,治疗组患者治疗前左侧额中回和左侧顶下小叶基于分数ALFF值明显降低,治疗后左侧额中回基于分数ALFF值有增高趋势,表明疏血通注射液可能是通过调节左侧额中回神经元内在活动实现对脑卒中的治疗作用。 功能磁共振成像也可用于非药物疗法影响和调节卒中后神经可塑性,实现“脑可塑”。许建阳等[54]通过fMRI研究发现通过针灸治疗后顶叶、额叶脑区的激活簇数明显增加,顶叶、额叶脑组织血流容积明显增加,患者的认知能力较治疗前有明显改善。赵波沣等[55]血氧水平依赖功能磁共振成像和扩散张量成技术观察针药联合应用治疗脑梗死的临床类型,结果显示治疗组患者基底节区激活频率、激活体积、激活平均弥散系数值和FA值均有明显变化,患者的总有效率优于常规治疗,针药联合后患者激活频率、激活体积、激活平均弥散系数值和FA值好转明显。苏丽缘[56]采用醒脑开窍针法对吞咽功能障碍患者皮质吞咽中枢的影响,治疗2周后发现醒脑开窍针刺组治疗前后左侧前扣带回、右侧颖极、双侧缘上回ReHo值差异显著,表明针刺能够增强吞咽功能障碍患者吞咽皮质中枢功能。ZHU等[57]通过ALFF及ReHo方法分析针刺对脑卒中后抑郁症患者身体运动、精神和思维的影响,发现针刺太溪穴后有关脑区ALFF及ReHo值增高明显,说明通过针灸太溪穴可以治疗脑卒中后抑郁症,通过观察相关脑区的ALFF及ReHo值变化可以预后病情的演变。因此,借助于功能磁共振成像揭示中医药全方位、多靶点、多途径调节脑卒中后神经结构和功能可塑性,对发现中医药实现“脑可塑”机制有重要价值。 作者总结了可视化分析中医药治疗脑卒中病机制,见表3。"


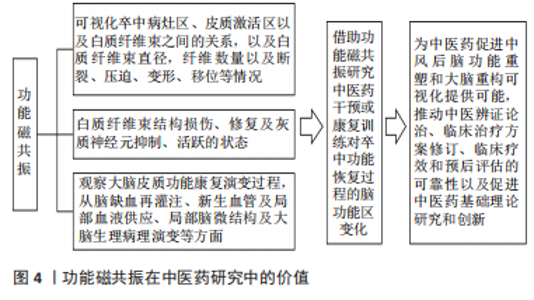
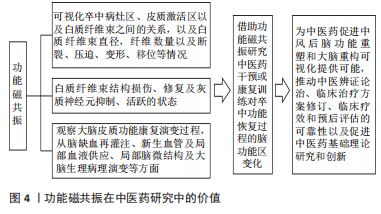
BOLD和DTI技术的结合对比较康复治疗前后大脑皮质功能的演变过程,揭示脑梗死患者神经功能修复的规律有重要价值。借助于DWI分析脑缺血再灌注损伤情况探讨脑卒中后遗症患者脑缺血再灌注损伤况、血管复流和无复流情况:DTI分析患侧和健侧纤维束数量差值作为纤维束损伤程度的指标,观察治疗前后纤维束数量变化以及与肌力的相关性。以ALFF与ReHo分析结果作为感兴趣区,分析感兴趣与全脑之间的功能连接探索反映局部大脑的神经活动特征,有利于探讨抑郁症患者局部神经活动特征及抑郁程度关系。联合应用ReHo值和功能连接(FC)可揭示脑梗死后主观认知,轻度认知障碍患者的关键靶区。rs-fMRI通过观察血液氧合水平变化,发现血流量和容量的活跃脑区,可以间接反映神经元活动异常。LIN等[58]采用VBM对正常老年大脑灰质体积进行量化,发现吞咽效率与年龄呈显著负相关,与左侧小脑后部的灰质体积呈正相关。ZHANG等[59]基于体素为基础的病变-症状映射(VLSM)研究表明,左侧顶下回是缺血性脑卒中吞咽障碍关键脑区。 功能磁共振可在人体活体直观而准确地观察神经功能及结构重塑情况,是目前量化探究神经功能恢复、神经重组机制的重大进步。通过DTI和BOLD-fMRI技术联合应用观察脑梗死患者白质纤维束结构损伤、修复及灰质神经元抑制/活跃的状态,DTI可以测定白质纤维束走行方向和结构完整性,观察卒中病灶区、皮质激活区以及白质纤维束之间的关系,以及白质纤维束直径、纤维数量以及断裂、压迫、变形及移位等情况。血氧水平依赖功能、DTI可比较治疗前后大脑皮质功能康复演变过程,从脑缺血再灌注、新生血管及局部血液供应、局部脑微结构及大脑生理病理演变等方面,为中医药干预和减轻脑缺血损伤程度提供科学依据。有研究发现电休克疗法可以减少脑卒中后抑郁症重症患者右侧舌回5-羟色胺受体,音乐疗法结合头针治疗4周后脑卒中后抑郁症患者血流动力学和神经元兴奋性增强;单侧舌回和视觉皮质区的ALFF值增高明显[60]。综上可知,神经递质异常和感觉运动网络、额顶叶网络、突显网络等梗死区静息态功能网络连接异常变化与患者神经功能改善和生活能力提高正相关,通过右侧楔前叶的功能网络连接可以作为评价缺血性脑卒中治疗效果的潜在指标之一。 陈栩铤等[61]通过高频重复经颅磁刺激对健侧大脑半球舌骨上肌群皮质对应区干预,可促进卒中后吞咽障碍患者吞咽功能相关脑区(大脑顶叶、顶上小叶、BA7区及BA40区激活范围)的激活进而改善卒中后吞咽障碍患者的吞咽功能。项目组通过VBM探讨冰火疗法对卒中后吞咽障碍患者灰质体积与吞咽之间的关系,通过全脑ALFF分析探讨冰火疗法对卒中后吞咽障碍患者局部脑区自发活动强弱与吞咽之间的关系,经冰火疗法治疗后左侧顶下小叶灰质体积显著升高,卒中后吞咽障碍患者14 d后右侧小脑前叶、右侧边缘叶以及右侧额中下回、右侧扣带回中部灰质体积均显著降低,这显示虽经冰火疗法康复治疗仍有部分脑区随时间出现灰质体积萎缩。综上可知,通过功能磁共振成像技术可视化的解读康复训练如何恢复凋亡神经细胞和激活储备神经代偿能力,如何激活相关脑区神经结构重建和神经功能代偿过程,如何促进吞咽中枢功能的恢复和重建提高吞咽肌肉的运动协调性。"

| [1] HIDALGO DE LA CRUZ M, VALSASINA P, SANGALLI F, et al. Dynamic functional connectivity in the main clinical phenotypes of multiple sclerosis. Brain Connect. 2021;11(8):678-690. [2] STEWART JC, DEWANJEE P, TRAN G, et al. Role of corpus callosum integrity in arm function differs based on motor severity after stroke. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;14:641-647. [3] 王东岩,何雷,宋晶,等.静息态功能磁共振技术在针灸脑科学领域中的应用研究进展[J].针灸临床杂志,2019,35(3):77-80. [4] 金悦,林岚,熊敏,等.基于功能磁共振成像的认知储备在脑老化过程中的研究综述[J].医疗卫生装备,2022,43(4):82-87. [5] 崔阳阳,梁怀彬,朱千,等.结合局部一致性和低频振幅探究躯体症状障碍患者大脑自发性活动的改变 [J].波谱学杂志,2022,39(1): 64-71. [6] 曾繁勇,张志强,杨昉,等.急性缺血性卒中患者运动皮质激活及功能重组的功能磁共振成像研究[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2017, 17(12):883-890. [7] 郝清,丁思萱,李冬雪,等.应用扩散张量成像技术对急性缺血性卒中机体功能障碍与锥体束损伤程度的相关性研究[J].磁共振成像,2021,12(1):3-8, 20. [8] 史静,董慧珠,李伟荣,等.弥散张量成像在评价青年脑卒中后失语症预后中的作用[J].中国药物与临床,2019,19(13):2185-2187. [9] CHEN X, ZHANG H, ZOU Y. A functional magnetic resonance imaging study on the effect of acupuncture at GB34 (Yanglingquan) on motor-related network in hemiplegic patients. Brain Res. 2015;1601:64-72. [10] PACHECO-CASTILHO AC, MIRANDA RPC, NORBERTO AMQ, et al. Dysphagia is a strong predictor of death and functional dependence at three months post-stroke. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022;80(5):462-468. [11] 徐涵,吴霜.卒中后吞咽神经功能代偿与重塑的机制研究进展[J].中国康复,2020,35(4):212-216. [12] KANG BX, MA J, SHEN J, et al. Altered brain activity in end-stage knee osteoarthritis revealed by resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Behav. 2022;12(1):e2479. [13] 陈芷涵,王容,李郁欣,等.功能磁共振成像动态脑功能连接网络分析方法及其在脑疾病中的应用[J].中国临床神经科学,2020,28(5): 571-578. [14] CORDANI C, VALSASINA P, PREZIOSA P, et al. Action observation training promotes motor improvement and modulates functional network dynamic connectivity in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2021;27(1): 139-146. [15] YUAN YS, XU HL, LIU ZD, et al. Brain functional remodeling caused by sciatic nerve transposition repair in rats identified by multiple-model resting-state blood oxygenation level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):418-426. [16] 欧芳元,黄俊浩,易小琦,等.静息态fMRI比率低频振幅技术在针刺治疗脑梗死的研究[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志,2019,25(3): 236-241. [17] TSAI YH, YUAN R, HUANG YC, et al. Disruption of brain connectivity in acute stroke patients with early impairment in consciousness. Front Psychol. 2014;4:956. [18] ALLEGRA M, FAVARETTO C, METCALF N, et al. Stroke-related alterations in inter-areal communication. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;32:102812. [19] SHI Y, LIU W, LIU R, et al. Investigation of the emotional network in depression after stroke: a study of multivariate Granger causality analysis of fMRI data. J Affect Disord. 2019;249:35-44. [20] 刘莎,张训,黄癸卯,等.利用静息态功能磁共振成像探讨抑郁症患者注意力网络动态连接的整体变化[J].磁共振成像,2022,13(6): 40-44. [21] CHEN J, SUN D, SHI Y, et al. Altered static and dynamic voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity in subacute stroke patients: a resting-state fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021;15(1):389-400. [22] ZHU Y, BAI L, LIANG P, et al. Disrupted brain connectivity networks in acute ischemic stroke patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017;11(2):444-453. [23] JIANG L, GENG W, CHEN H, et al. Decreased functional connectivity within the default-mode network in acute brainstem ischemic stroke. Eur J Radiol. 2018;105:221-226. [24] ZENDEHROUH E, SENDI MSE, SUI J, et al. Aberrant functional network connectivity transition probability in major depressive disorder. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020;2020:1493-1496. [25] SEILER A, NöTH U, HOK P, et al. Multiparametric quantitative MRI in neurological diseases. Front Neurol. 2021;12:640239. [26] 李明哲,魏雷,张英杰,等.经颅交流电刺激对缺血性脑卒中大鼠rs-fMRI的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(3):260-266. [27] MALANDRAKI GA, SUTTON BP, PERLMAN AL, et al. Age-related differences in laterality of cortical activations in swallowing. Dysphagia. 2010;25(3):238-249. [28] 刘明,熊航,陈云翔,等.肝气郁结证脑白质磁共振扩散张量成像研究[J].医学研究杂志,2019,48(10):44-47. [29] 王佩佩,李琼阁,单艺,等.丘脑梗死患者灰质体积改变与运动功能相关性的随访研究[J].医学影像学杂志,2019,29(3):345-349. [30] 蒋宇,黄小华,刘念.基于体素的形态学分析在缺血性脑卒中的研究进展[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2021,44(2):157-160. [31] 李大年,郑燕婷,刘玉洁,等.肝郁证患者局部脑区神经活动变化静息态功能磁共振成像研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2021,28(12): 88-92. [32] 林志诚,游咏梅,王君,等.脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者下丘脑功能连接和全脑各向异性的磁共振成像研究[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2021,27(5):504-509. [33] BONKHOFF AK, ESPINOZA FA, GAZULA H, et al. Acute ischaemic stroke alters the brain’s preference for distinct dynamic connectivity states. Brain. 2020;143(5):1525-1540. [34] 郭晟,周承志.中医活血化瘀法治疗急慢性心脑血管疾病的异与同[J].中国医药导报,2020,17(19):140-143. [35] 杨洋.基于MRA及血管超声缺血性中风中医证候与脑供血动脉病变的相关性分析研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学,2017. [36] 辛铭正,曹晓岚,孙灵芝.基于络病理论探讨分水岭脑梗死的病理机制及中医药治疗进展[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2021,29(3): 128-131. [37] 田金洲,盛彤,刘峘,等.卒中后患者认知损害的脑影像学改变与中医证候的关系[J].中医杂志,2004,45(2):132-134. [38] 毕丽丽.中风复元合剂治疗分水岭脑梗死临床观察[J].中国中医急症,2016,25(12):2366-2368. [39] 张梅奎.益脑通络胶囊对缺血性中风神经细胞保护作用的实验研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2003. [40] 张路遥.206例急性缺血性脑卒中患者头颅MRI表现与中医病证相关性初探[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2016. [41] WEI D, XIE D, LI H, et al. The positive effects of Xueshuan Xinmai tablets on brain functional connectivity in acute ischemic stroke: a placebo controlled randomized trial. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15244. [42] 任珊.结合功能磁共振评价联合三七总皂苷对中风病患者神经重塑的研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2017. [43] 朱丹,刘永康,厉励,等.基于fMRI技术观察中西医结合治疗对急性缺血性脑卒中默认网络的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2021, 37(6):871-877. [44] 张晶. 丹参多酚酸治疗急性脑梗死静息态功能磁共振的临床研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2018. [45] GAO L, HUANG P, DONG Z, et al. Modified Xiaoyaosan (MXYS) exerts anti-depressive effects by rectifying the brain blood oxygen level-dependent fmri signals and improving hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1098. [46] 胡培铅.抑郁症患者脑功能改变及药物治疗抑郁症的静息态功能磁共振研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2016. [47] 谭赛,方继良,黄世敬,等.开心解郁方治疗血管性抑郁症脑机制fMRI初步研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2017,15(3):261-266,273. [48] 张涛军.健脾补肾活血方结合运动疗法对脑梗死患者缺血区血液循环的影响[D].郑州:河南中医药大学,2016. [49] 吕冰峰.灯盏花素注射液治疗缺血半暗带脑梗死临床观察[J].河南职工医学院学报,2014,26(3):268-269. [50] 张金生.微环境、神经干细胞、脑衰老与补肾化瘀生新[J].中华中医药学刊,2021,39(11):5-8. [51] 张金生,张宝霞,刘雪曼.补肾化瘀生新方优化缺血缺氧微环境对间充质干细胞旁分泌效应及分化率的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2021,39(9):9-16, 259. [52] 李威,张音,蒋亚文.运用DTI分析针灸治疗脑卒中疗效25例[J].内蒙古中医药,2014,33(35):97-98. [53] 朱丹,刘永康,赵宇栋,等.基于比率低频振幅探讨疏血通注射液联合西医常规疗法对急性缺血性脑卒中的疗效及机制研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(5):112-117. [54] 许建阳,王发强,王宏,等.针刺太冲穴对fMRI脑功能成像的研究[C]//第八次全国中西医结合影像学术交流大会全国中西医结合影像学研究进展学习班论文集. 2005:35-37. [55] 赵波沣,胡元明,陈树平.功能磁共振成像对针刺联合中医药治疗脑梗死疗效评价[J].中国医学装备,2017,14(7):72-75. [56] 苏丽缘.针刺对脑卒中后吞咽障碍患者脑功能影响的观察[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2015. [57] ZHU B, WANG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Acupuncture at KI3 in healthy volunteers induces specific cortical functional activity: an fMRI study. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:361. [58] LIN CS, WU CY, WANG DH, et al. Brain signatures associated with swallowing efficiency in older people. Exp Gerontol. 2019;115:1-8. [59] ZHANG J, JIANG H, WU F, et al. Neuroprotective effects of hesperetin in regulating microglia polarization after ischemic stroke by inhibiting TLR4/NF-B pathway. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021:9938874. [60] 倪雯沁,陈月蓉,徐赟赟,等. 基于功能磁共振成像技术探讨针灸治疗焦虑抑郁的中枢机制[J]. 针刺研究,2022,47(8):728-733. [61] 陈栩铤,顾旭东,姚云海,等.单侧高频重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中吞咽障碍及功能性磁共振成像的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(12):1105-1109. [62] PLUTA R, JANUSZEWSKI S, CZUCZWAR SJ. Neuroinflammation in post-ischemic neurodegeneration of the brain: friend, foe, or both? Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4405. [63] TAO T, LIU M, CHEN M, et al. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: challenges and prospective. Pharmacol Ther. 2020; 216:107695. |
| [1] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [2] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [4] | Zhang Yi, Ren Sicong, Huangfu Huimin, Xu Jing, Yang Zhen, Zhou Yanmin. Effects of scaffolds on angiogenic microenvironment and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3391-3397. |
| [5] | Zhang Weiye, Zhan Jiawen, Zhu Liguo, Wang Shangquan, Chen Ming, Wei Xu, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Han Tao, Cai Chuhao, Zhou Shuaiqi, Shao Chenchen. Effect of nucleus pulposus cells-derived exosomes under cyclic mechanical tension on endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 223-229. |
| [6] | Luo Wenhao, Feng Le, Huang Haixia, Liu Min, Wang Pin. Effect of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitor Tideglusib on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under high glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 2968-2974. |
| [7] | Ying Chunmiao, Ma Yucheng, Fan Feiyan, Gao Chen, Wang Shaona, Yang Xing, Zhang Yunke. Action mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine to regulate neural stem cells in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2385-2394. |
| [8] | Zhu Biwen, Wang Dongzhi, Wu Di, Gong Tiancheng, Pan Haopeng, Lu Yuhua, Guo Yibing, Wang Zhiwei, Huang Yan. Biomimetic microenvironment constructed from gelatin methacrylamide/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes the function of insulinoma cell line MIN6 in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1824-1831. |
| [9] | Zhu Zhenghuan, Zou Hongjun, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Cellular microenvironment in nerve repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 114-120. |
| [10] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [11] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| [12] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [14] | Liu Yang, Zhu Zhiqiang, Zhao Xiaowei, Xiang Yujie, Xiao Jian, Cheng Lifen. Hot topics and international frontiers of electromyography in the field of body movements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5707-5715. |
| [15] | She Jian, Zhao Jing, Zhang Jiaming, Xia Haisha, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Zheng Zhong, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of literature on eye tracking in cognitive behaviors of autistic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5724-5732. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||