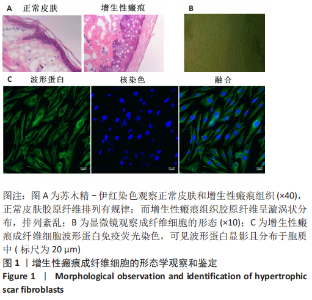
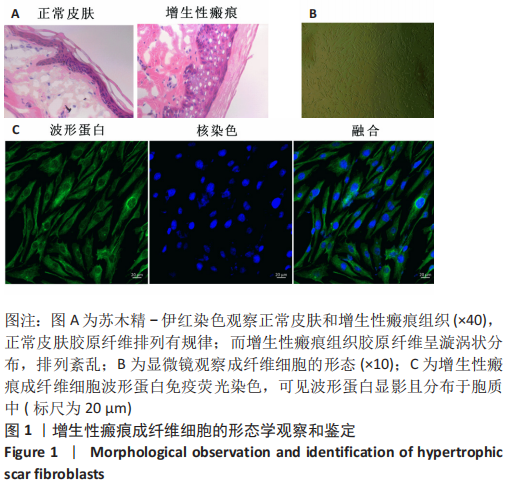
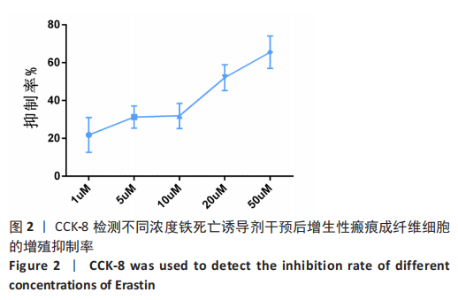
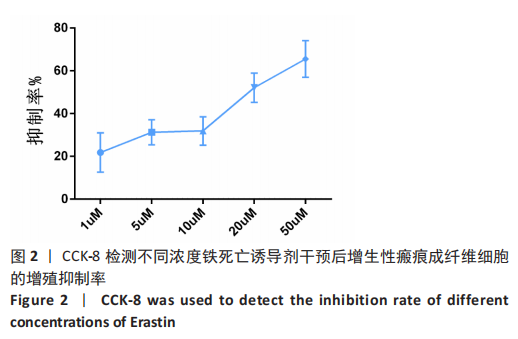
[1] WEI J, WANG Z, ZHONG C, et al. LncRNA MIR503HG promotes hypertrophic scar progression via miR-143-3p-mediated Smad3 expression. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(5):792-800.
[2] ZHANG R, LIU D, XIE Q, et al. Inhibition of miR-9 attenuates fibroblast proliferation in human hyperplastic scar by regulating TGF-β1. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(6):3645-3650.
[3] XUE Y, QI C, DONG Y, et al. Poly (γ-glutamic acid)/chitooligo-saccharide/papain hydrogel prevents hypertrophic scar during skin wound healing. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(11):1724-1734.
[4] CHEN L, WANG DL, WEI ZR, et al. Effects of local transplantation of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the formation of hyperplastic scar on rabbit ears. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016;32(10):582-587.
[5] CHEN W, FU X, SUN X, et al. Analysis of differentially expressed genes in keloids and normal skin with cDNA microarray. J Surg Res. 2003;113(2):208-216.
[6] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[7] HUANG F, YANG R, XIAO Z, et al. Targeting Ferroptosis to Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: A New Continent to Be Explored. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:737971.
[8] WU J, FENG Z, CHEN L, et al. TNF antagonist sensitizes synovial fibroblasts to ferroptotic cell death in collagen-induced arthritis mouse models. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):676.
[9] YE Z, ZHUO Q, HU Q, et al. FBW7-NRA41-SCD1 axis synchronously regulates apoptosis and ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Redox Biol. 2021;38:101807.
[10] SUI X, ZHANG R, LIU S, et al. RSL3 Drives Ferroptosis Through GPX4 Inactivation and ROS Production in Colorectal Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1371.
[11] SEHM T, FAN Z, GHOOCHANI A, et al. Sulfasalazine impacts on ferroptotic cell death and alleviates the tumor microenvironment and glioma-induced brain edema. Oncotarget. 2016;7(24):36021-36033.
[12] WANG J, WANG T, ZHANG Y, et al. CPEB1 enhances erastin-induced ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by suppressing twist1 expression. IUBMB Life. 2021;73(9):1180-1190.
[13] LV Z, WANG F, ZHANG X, et al. Etomidate Attenuates the Ferroptosis in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Rat Model via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Shock. 2021;56(3):440-449.
[14] ZHI Y, WANG H, HUANG B, et al. Panax Notoginseng Saponins suppresses TRPM7 via the PI3K/AKT pathway to inhibit hypertrophic scar formation in vitro. Burns. 2021;47(4):894-905.
[15] OOSTERHOFF TCH, BEEKMAN VK, VAN DER LIST JP, et al. Laser treatment of specific scar characteristics in hypertrophic scars and keloid: A systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(1):48-64.
[16] MENCHACA AD, STYLE CC, OLUTOYE OO. A Review of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid Treatment and Prevention in the Pediatric Population: Where Are We Now? Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2022;11(5):255-279.
[17] ELSAIE ML. Update on management of keloid and hypertrophic scars: A systemic review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(9):2729-2738.
[18] OLIVEIRA GV, METSAVAHT LD, KADUNC BV, et al. Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Position statement of the Brazilian expert group GREMCIQ. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35(11):2128-2142.
[19] CHEN X, LI J, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2054-2081.
[20] QIN Y, QIAO Y, WANG D, et al. Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease: Mechanisms and potential applications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;141:111872.
[21] WU X, LI Y, ZHANG S, et al. Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3052-3059.
[22] 李琦,孙贵才.淫羊藿苷对骨髓间充质干细胞铁死亡及向心肌样细胞分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):1988-1992.
[23] MAJERNÍKOVÁ N, DEN DUNNEN WFA, DOLGA AM. The Potential of Ferroptosis-Targeting Therapies for Alzheimer’s Disease: From Mechanism to Transcriptomic Analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:745046.
[24] XU S, WU B, ZHONG B, et al. Naringenin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating the nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) /System xc-/ glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis to inhibit ferroptosis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):10924-10934.
[25] 周邓婧,宋启斌,李娜.Erastin联合顺铂诱导顺铂耐药鼻咽癌细胞发生铁死亡[J].肿瘤学杂志,2021,27(11):900-904.
[26] JOSHI S, AGARWAL S, PANJLA A, et al. Inhibiting Erastin-Induced Ferroptotic Cell Death by Purine-Based Chelators. Chembiochem. 2022;23(9):e202100654.
[27] XU T, DING W, JI X, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8):4900-4912.
[28] LI Y, ZENG X, LU D, et al. Erastin induces ferroptosis via ferroportin-mediated iron accumulation in endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2021;36(4):951-964.
[29] FANG D, MALDONADO EN. VDAC Regulation: A Mitochondrial Target to Stop Cell Proliferation. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;138:41-69.
[30] YANG Y, LUO M, ZHANG K, et al. Nedd4 ubiquitylates VDAC2/3 to suppress erastin-induced ferroptosis in melanoma. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):433. |