Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (35): 5634-5641.doi: 10.12307/2023.823
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proteomic study of Jintiange capsule in the treatment of retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis rats
Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng
- Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-10-08Accepted:2022-11-16Online:2023-12-18Published:2023-06-02 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoyun, MD, Associate chief physician, Master's supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Chi, MD candidate, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Jintiange Scientific Research and Training Fund for Middle-aged and Young People, No. Project 61 (to ZXY); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi, Nos. 2021GXNSFAA220089 (to CF) and 2020GXNSFBA159053 (to ZXY); The Development and Promotion Project of Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology in Guangxi, No. GZSY22-36 (to ZXY); 2021 School-level Youth Innovation Research Team Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021TD001 (to ZXY); Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education, No. YCBZ2021075 (to ZC); Huang Yourong Guipai TCM Master Training Project, No. GZYKJF [2022]6 (to ZXY [project participant])

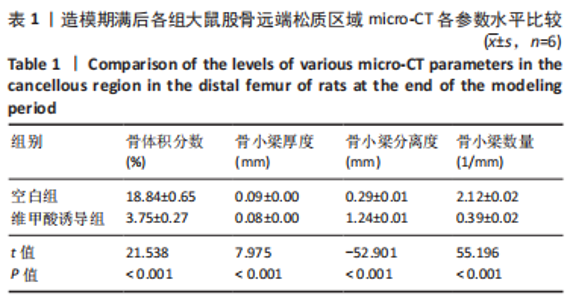
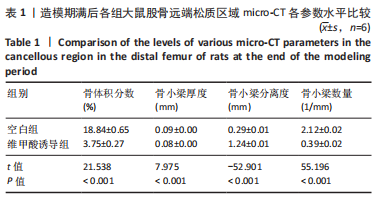
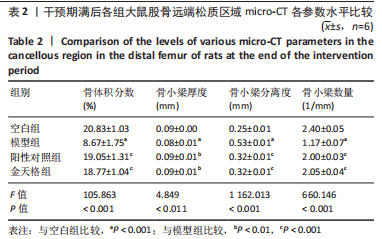
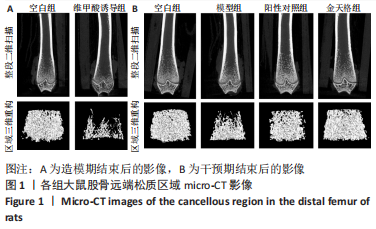
2.3 金天格胶囊对骨质疏松症大鼠骨小梁结构的影响 干预期满后,股骨micro-CT扫描结果表明,各组的骨体积分数(P < 0.001)、骨小梁厚度(P=0.011)、骨小梁分离度(P < 0.001)和骨小梁数量(P < 0.001)均存在显著差异,见图1B、表2。进一步两两比较显示,与空白组相比,模型组骨体积分数、骨小梁厚度和骨小梁数量显著降低(P < 0.001,P=0.011,P < 0.001),骨小梁分离度显著增高(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,阳性对照组骨体积分数、骨小梁厚度和骨小梁数量显著增高(P < 0.001,P=0.002,P < 0.001),骨小梁分离度显著降低(P < 0.001);与模型组相比,金天格组骨体积积分数、骨小梁厚度和骨小梁数量显著增高(P < 0.001,P=0.009,P < 0.001),骨小梁分离度显著降低(P < 0.001);与阳性对照组相比,金天格组骨体积分数、骨小梁厚度、骨小梁分离度和骨小梁数量均无明显变化(P > 0.05)。说明采用金天格胶囊和阿仑膦酸钠片均能够改善骨质疏松症大鼠的骨量流失,增加骨小梁厚度和数目,减少骨小梁间隙,两种药物作用效果无差异。"

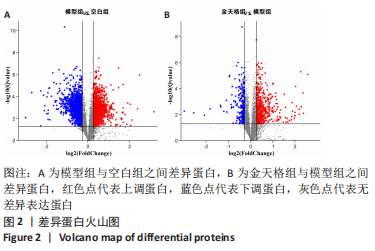
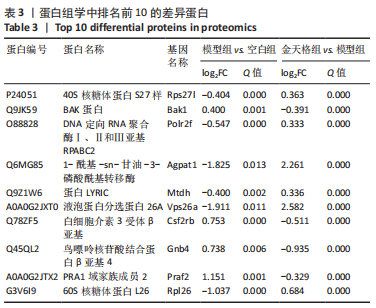
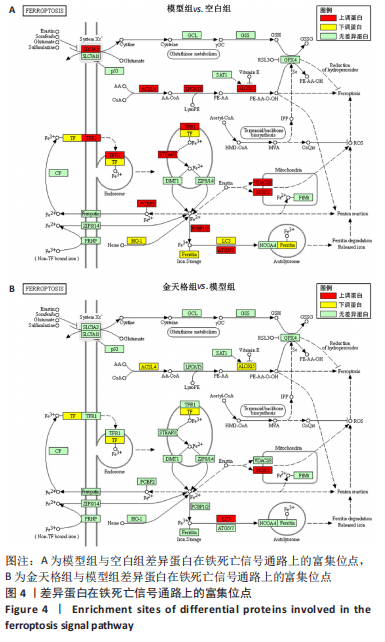
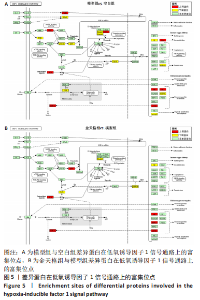
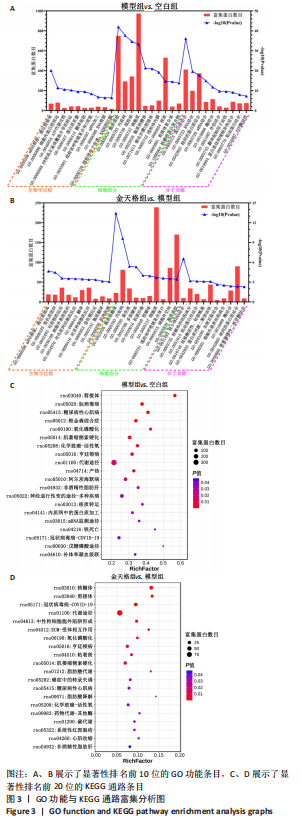
2.5 GO功能与KEGG通路富集结果 将模型组与空白组之间差异蛋白以及金天格组与模型组之间差异蛋白分别导入DAVID数据库。富集结果表明(图3),模型组与空白组之间差异蛋白涉及ATP代谢过程、骨化、缺氧反应、细胞铁离子稳态、成骨细胞分化的调节等382条生物学进程;线粒体、吞噬囊泡、胞质核糖体、黏着斑等204条细胞组分;ATP酶活性、谷胱甘肽转移酶活性、氧转运蛋白活性、L-乳酸脱氢酶活性等153条分子功能(图3A);铁死亡、脂肪酸代谢、低氧诱导因子1信号通路、氧化磷酸化等82条信号通路(图3C)。金天格组与模型组之间差异蛋白涉及骨化、过氧化氢生物合成、缺氧反应、酰基辅酶A脱氢酶催化脂肪酸β氧化等91条生物学进程;线粒体、外泌体、胞质囊泡、核糖体等57条细胞组分;谷胱甘肽转移酶活性、ATP酶活性、转录辅因子活性等32条分子功能(图3B);低氧诱导因子1信号通路、脂肪酸代谢、氧化磷酸化、细胞外基质受体相互作用等24条信号通路(图3D)。其中,关于铁死亡信号通路,模型组的长链脂酰辅酶A合成酶1、花生四烯酸-15-脂加氧酶、溶血卵磷脂酰基转移酶3、转铁蛋白受体、前列腺六次跨膜蛋白3表达比空白组高,转铁蛋白、铁蛋白重链1、铁蛋白轻链1表达比空白组低(图4A);而金天格组的长链脂酰辅酶A合成酶1、花生四烯酸-15-脂加氧酶、转铁蛋白表达比模型组低(图4B)。"
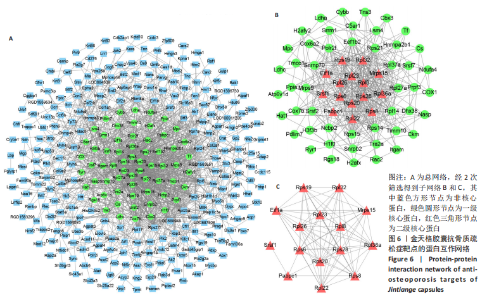
2.6 金天格胶囊抗骨质疏松症的核心靶点 将此次研究中骨质疏松症的2 749个疾病靶点与金天格胶囊的773个药效靶点取交集,得到金天格胶囊抗骨质疏松症的治疗靶点共453个。上述治疗靶点经Uniprot数据库校对、STRING数据库分析后,得到由328个蛋白、1 161条互作关系构成的总网络(图6A);经第1次筛选后得到由64个蛋白、361条互作关系构成的一级子网络(图6B);经第2次筛选后得到由15个蛋白、80条互作关系构成的二级子网络(图6C)。其中,蛋白互作网络中有转铁蛋白、核糖体蛋白S14、核糖体蛋白S21等49个一级核心蛋白,核糖体蛋白S6、核糖体蛋白S20、核糖体蛋白S28等15个核心程度更高的二级核心蛋白,它们可能是金天格胶囊发挥抗骨质疏松症作用的重要靶点。"

| [1] CUI Z, MENG X, FENG H, et al. Estimation and projection about the standardized prevalence of osteoporosis in (mainland China. Arch Osteoporos. 2019;15(1):2. [2] 曹志红,丁曼旎,赵彦风.虎产品中医药用史的阶段特征——基于《中华医典》数据库的分析[J]. 自然辩证法通讯,2021,43(7):71-77. [3] 王鸥,夏维波,成志峰,等.金天格胶囊治疗原发性骨质疏松症的有效性及安全性:随机、双盲双模拟、阳性药平行对照、多中心临床试验[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(2):142-151. [4] 《中成药治疗优势病种临床应用指南》标准化项目组.中成药治疗骨质疏松症临床应用指南(2021年)[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2022,42(4):393-404. [5] YANG Z, YUAN ZZ, MA XL. Network Pharmacology-Based Strategy and Molecular Docking to Explore the (Potential Mechanism of Jintiange Capsule for Treating Osteoporosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5338182. [6] 胡张洁.血清蛋白质组学筛选绝经后骨质疏松生物标志物[D].福州:福建医科大学,2021. [7] YANG L, HOU A, ZHANG X, et al. TMT-based proteomics analysis to screen potential biomarkers of Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix for osteoporosis in rats. Biomed Chromatogr. 2022;36(4):e5339. [8] 张建花,沈燚,何玉琼,等.二仙汤抗骨质疏松有效组分对维甲酸致骨丢失大鼠的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2018,39(2):165-170. [9] WEN B, ZHOU R, FENG Q, et al. IQuant: an automated pipeline for quantitative proteomics based upon isobaric tags. Proteomics. 2014; 14(20):2280-2285. [10] SAVITSKI MM, WILHELM M, HAHNE H, et al. A Scalable Approach for Protein False Discovery Rate Estimation in Large Proteomic Data Sets. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14(9):2394-2404. [11] CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194-1202. [12] SHERMAN BT, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation (of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(W1):W216-W221. [13] KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, TANABE M, et al. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45(D1):D353-D361. [14] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, NASTOU KC, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D605-D612. [15] TANG Y, LI M, WANG J, et al. CytoNCA: a cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 2015;127:67-72. [16] 高世勇,李婉秋,王帅,等.基于网络药理学的小陷胸汤治疗大肠癌的机制研究[J].中草药,2022,53(3):773-782. [17] 韩昶晓,田向东,朱光宇,等.金天格胶囊对经皮球囊椎体后凸成形术后患者骨密度、骨代谢及生活质量的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(1):110-113. [18] 林若慧,陈赛楠,叶云金,等.基于TMT蛋白质组学分析骨疏康胶囊治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5141-5147. [19] GASCHLER MM, STOCKWELL BR. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;482(3):419-425. [20] KAGAN VE, MAO G, QU F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13(1):81-90. [21] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13(1):91-98. [22] CHEN P, SONG M, WANG Y, et al. Identification of key genes of human bone marrow stromal cells adipogenesis at an early stage. PeerJ. 2020; 8:e9484. [23] KLEIN RF, ALLARD J, AVNUR Z, et al. Regulation of bone mass in mice by the lipoxygenase gene Alox15. Science. 2004;303(5655):229-232. [24] JIANG Z, WANG H, QI G, et al. Iron overload-induced ferroptosis of osteoblasts inhibits osteogenesis and promotes osteoporosis: An in vitro and in vivo study. IUBMB Life. 2022;74(11):1052-1069. [25] WANG Y, LIU Y, LIU J, et al. NEDD4L-mediated LTF protein degradation limits ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):581-587. [26] SHANG N, WU J. Egg White Ovotransferrin Attenuates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Resorption. Nutrients. 2019;11(9):2254. [27] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(5):280-296. [28] 贾鹏,邓廉夫.低氧诱导因子-α信号通路与骨形成[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(6):676-680. [29] NI S, YUAN Y, QIAN Z, et al. Hypoxia inhibits RANKL-induced ferritinophagy and protects osteoclasts from (ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;169:271-282. [30] WEI J, YANG Y, LU M, et al. Recent Advances in the Discovery of HIF-1α-p300/CBP Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(4):296-309. [31] SEMENZA GL. Pharmacologic Targeting of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;59(1):379-403. [32] BEI J, ZHU S, DU M, et al. Integrative analysis of multiomics data identified acetylation as key variable of (excessive energy metabolism in hyperthyroidism-induced osteoporosis rats. J Proteomics. 2022;252: 104451. |
| [1] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [3] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| [4] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [5] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [6] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [7] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [8] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [9] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [10] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [12] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [13] | Zhang Shudong, Huang Yilin, Yao Qi. Punicalagin treats postmenopausal osteoporosis by promoting osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4101-4105. |
| [14] | Liu Jing, Liang Fangyuan, Li Jia, Wang Hua. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea based on proteomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4129-4136. |
| [15] | Tao Jingwei, Zhou Jingya, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong, Fan Xiao. Effect and mechanism of tetramethylpyrazine regulating ferroptosis in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4158-4163. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 1457
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 304
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||