Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (13): 2124-2132.doi: 10.12307/2023.260
Advantage of supramalleolar osteotomy for asymmetric ankle arthritis: a system evaluation
Shang Wei, Fu Panfeng, Kang Zhe, Zhu Shaobo
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-11Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-05-08Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:Zhu Shaobo, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Shang Wei, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shang Wei, Fu Panfeng, Kang Zhe, Zhu Shaobo. Advantage of supramalleolar osteotomy for asymmetric ankle arthritis: a system evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2124-2132.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
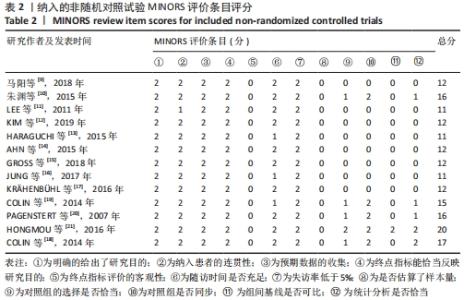
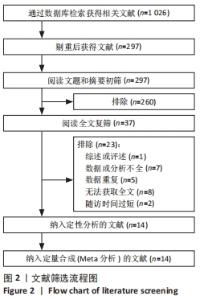
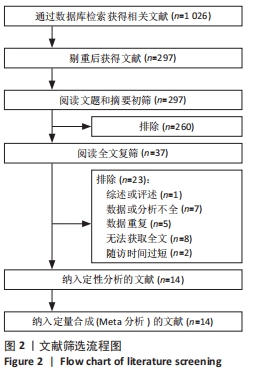
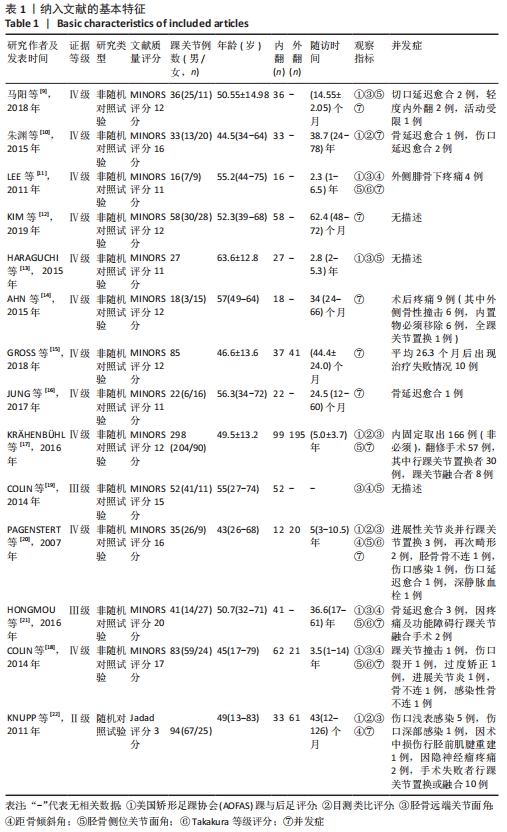
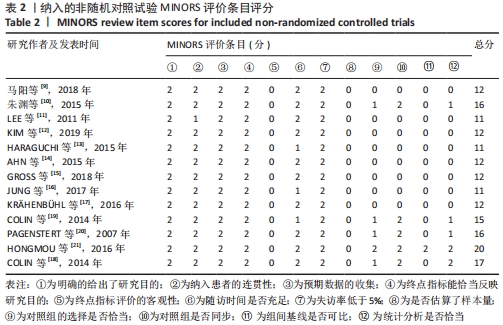
2.3 文献质量评价 系统评价纳入1个随机对照试验,13个非随机对照试验。随机对照试验采用改良的 Jadad 量表评分进行质量评价,其评分为3分,为低质量研究。13个非随机对照试验采用MINORS评价条目进行评分。13个试验均有明确的研究目的,收集了预期设定的数据,终点指标能恰当地反映研究目的,并且失访率均< 5%,1个试验未详细描述数据的连贯性,该条目得1分;13个试验结果均未对客观终点指标的评价采用单盲法或主管重点指标未采用评价者双盲法,该项目得0分,只有1个试验该条目描述了盲法,但不清晰,故得1分;3个试验无法判断是否含随访时间< 1年的病例,故得1分,只有1个试验测出了95%CI,但未计算预期的样本量,得1分,其余试验该条目得0分;4个试验对照组选择不是很恰当,得1分,2个试验对照组选择恰当,得2分,其余7个试验未行对照研究,得0分;6个试验的对照组与实验组均同步;1个试验组间的基线标准有相似性,得2分,另1个试验组间的基线标准相似性相对较小,故得1分,其余试验该条目得0分;6个有对照组的试验中3项试验统计分析恰当,得2分,另3个试验的统计分析相对不充分,得1分。13个非随机对照试验的平均得分为13.59分,因此,纳入的13个非随机对照试验综合质量评价为“中等质量”研究。纳入非随机对照试验的文献质量评价见表2。"
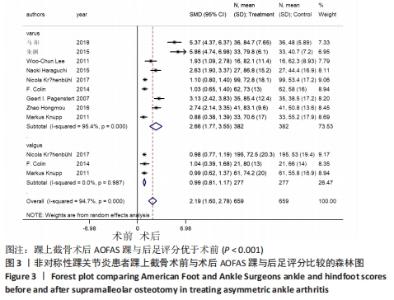
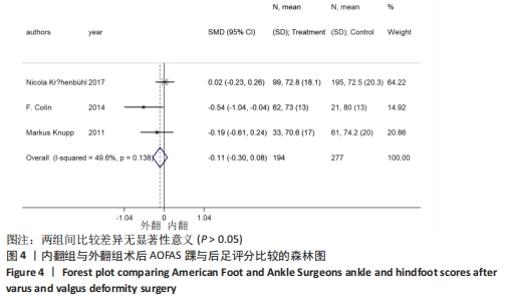
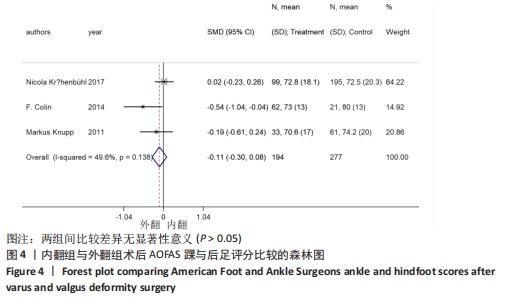
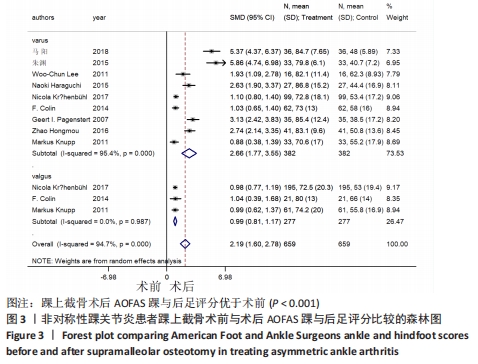
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 AOFAS踝与后足评分 9个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的AOFAS踝与后足评分[9-11,13,17-18,20-22],合计样本量659例,其中9个研究报告了内翻组,3个研究同时报告了内、外翻组[17-18,22]。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2 =94.7%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前AOFAS踝与后足评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=2.19,95%CI (1.60,2.78),P < 0.001],见图3。按畸形类型行亚组分析,9个内翻组踝上截骨术后与术前AOFAS踝与后足评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=2.66,95%CI(1.77,3.55),P < 0.001],3个外翻组踝上截骨术后与术前AOFAS踝与后足评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.99,95%CI(0.81,1.17),P < 0.001]。另外,将3个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后AOFAS踝与后足评分研究行统计学分析,各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.138,I2=49.6%),采用固定效应模型行统计分析(图3b),结果显示:两组术后无明显差异[SMD=-0.11,95%CI(-0.30,0.08),P=0.266],见图4。术后AOFAS踝与后足评分无论是在总体上及内、外翻组均优于术前,内、外翻组间无明显差异。"
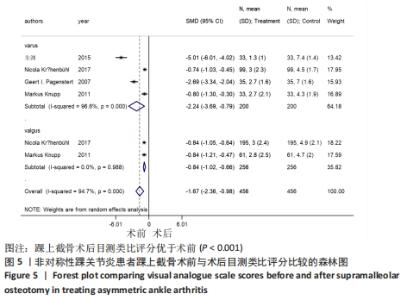
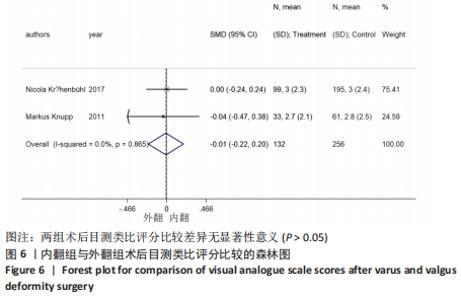
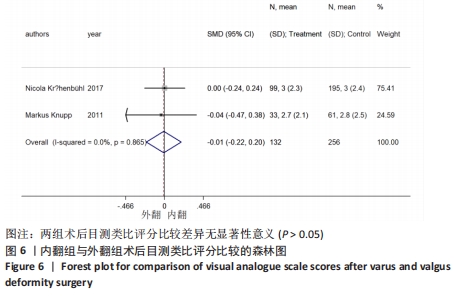
2.4.2 目测类比评分 4个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的目测类比评分[10,17,20,22],合计样本量456例,其中4个研究报告了内翻组,2个研究同时报告了内、外翻组[20,22]。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2=94.7%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前目测类比评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-1.67,95%CI(-2.36,-0.98),P < 0.001],见图5。行亚组分析,内翻组踝上截骨术前和术后的目测类比评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-2.24,95%CI(-3.69,-0.79),P=0.002],外翻组踝上截骨术前和术后的目测类比评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.84,95%CI(-1.02,-0.66),P < 0.001]。另外,将2个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后目测类比评分的研究行统计学分析,各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.865,I2 =0%),采用固定效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:两组术后目测类比评分比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.01,95%CI(-0.22,0.20),P=0.923],见图6。踝上截骨术后的目测类比评分无论是在总体上及内、外翻组均优于术前,内、外翻组间无明显差异。"

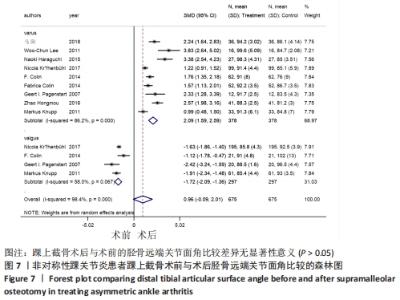
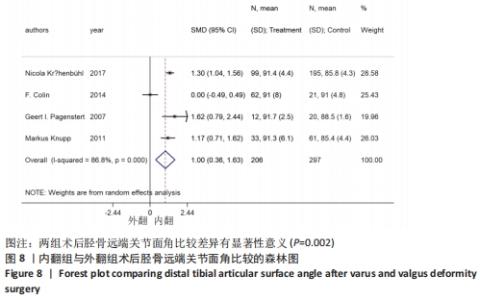
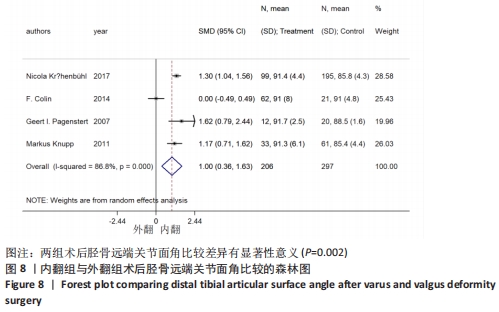
2.4.3 胫骨远端关节面角 9个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的胫骨远端关节面角[9,11,13,17-19,21-22],合计样本量675例,其中9个研究报告了内翻组,4个研究同时报告了内、外翻组[17-18,20,22]。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2=98.4%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前的胫骨远端关节面角比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.96,95%CI(-0.09,2.01),P=0.073],见图7。行亚组分析,内翻组踝上截骨术后与术前的胫骨远端关节面角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=2.09,95%CI(1.59,2.59),P=0.002],外翻组踝上截骨术后与术前的胫骨远端关节面角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-1.72,95%CI(-2.09,-1.36),P < 0.001]。另外,将2个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后胫骨远端关节面角的研究行统计学分析,各研究间无明显异质性(P < 0.001,I2=86.8%),采用随机效应模型进行统计分析,结果显示:两组术后胫骨远端关节面角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=1.00,95%CI(0.36,1.63),P=0.002],见图8。总体上术后胫骨远端关节面角与术前无明显差异(P=0.073),但亚组分析内、外翻组时,内、外翻组术后均优于术前,出现该情况的原因是胫骨远端关节面角内、外翻畸形分别小于、大于正常值的范围,故总体出现偏差,内、外翻组间术后胫骨远端关节面角虽有明显差异但差异值较小(0.36°-1.63°),实际临床意义可能不明显。"

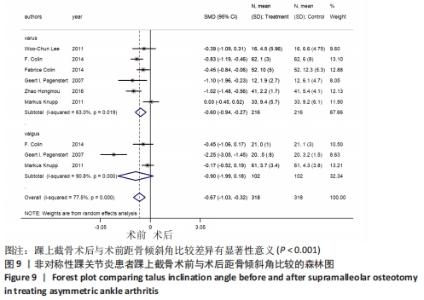
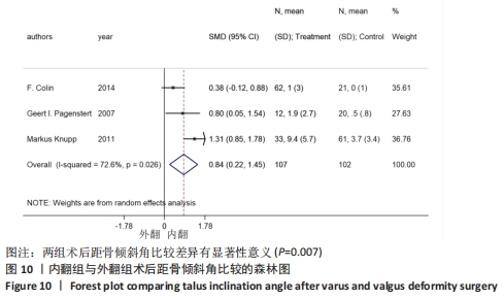
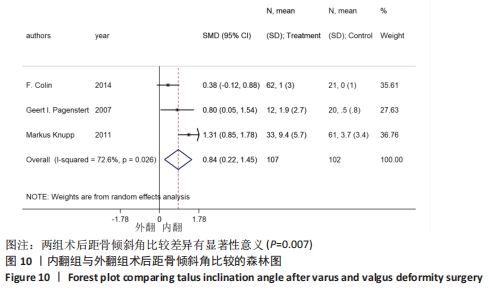
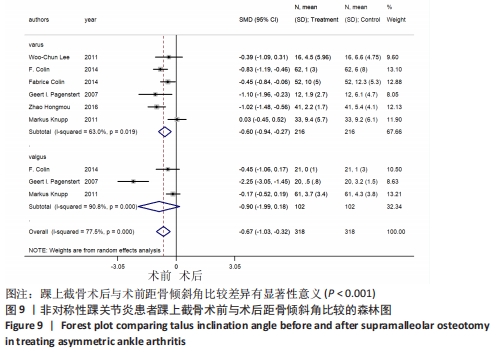
2.4.4 距骨倾斜角 6个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的距骨倾斜角[11,18-22],合计样本量318例,其中6个研究报告了内翻组,3个研究同时报告了内、外翻组。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2=77.5%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前距骨倾斜角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.67,95%CI (-1.03,-0.32),P < 0.001],见图9。行亚组分析,内翻组踝上截骨术后与术前距骨倾斜角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.60,95%CI(-0.94,-0.27),P < 0.001],外翻组踝上截骨术后与术前距骨倾斜角比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.90,95%CI(-1.99,0.18),P=0.104]。另外,将3个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后距骨倾斜角的研究行统计学分析,各研究间有明显异质性(P=0.026,I2=72.6%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:两组术后距骨倾斜角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.84,95%CI(0.22,1.45),P=0.007],见图10。总体上与内翻组术后距骨倾斜角均与术前有明显差异,而外翻组术后与术前无明显差异,这提示内翻组术后距骨倾斜角有所改善,而外翻组术后无明显改变。"
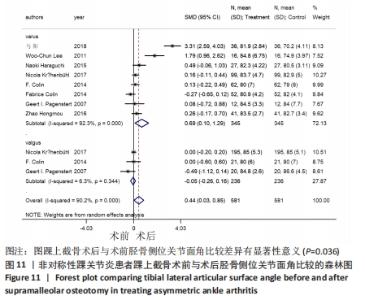
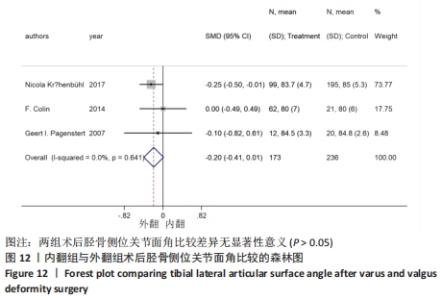
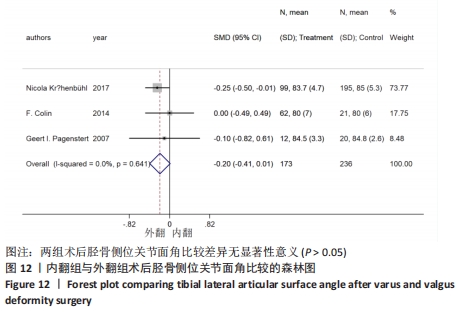
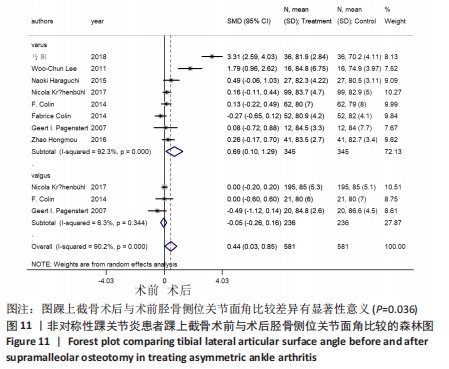
2.4.5 胫骨侧位关节面角 8个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的胫骨侧位关节面角[9,11,13,17-21],合计样本量581例,其中8个研究报告了内翻组,3个研究同时报告了内、外翻组[17-18,20]。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2=90.2%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前胫骨侧位关节面角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.44,95%CI(0.03,0.85),P=0.036],见图11。行亚组分析,内翻组术后与术前胫骨侧位关节面角比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.69,95%CI(0.10,1.29),P=0.022],外翻组术后与术前胫骨侧位关节面角比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.05,95%CI(-0.26,0.16),P=0.63]。另外,将3个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后胫骨侧位关节面角的研究行统计学分析,各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.641,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行统计分析,结果显示:两组术后胫骨侧位关节面角比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.20,95%CI(-0.41,0.01),P=0.065],见图12。总体上与内翻组术后胫骨侧位关节面角均优于术前,外翻组术后与术前无明显差异,这是因为外翻组的胫骨侧位关节面角基本在正常值范围,而术后内、外翻组间胫骨侧位关节面角无明显差异,也说明内翻畸形术后胫骨侧位关节面角改善较明显。"
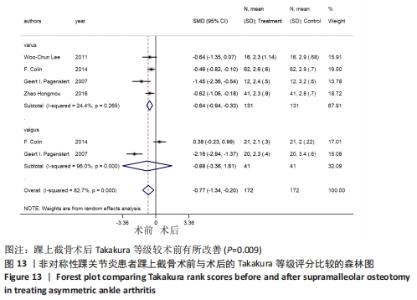
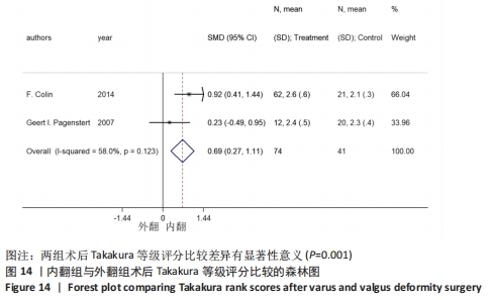
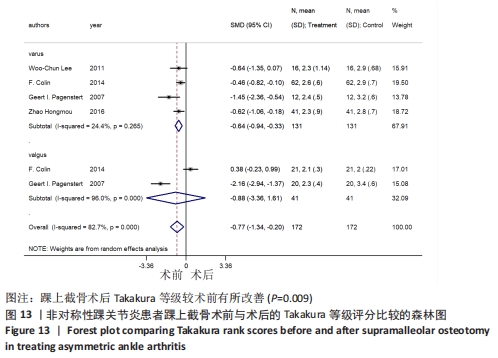
2.4.6 Takakura等级评分 4个研究报告了踝上截骨术前和术后的Takakura等级评分[11,18,20-21],合计样本量172例,其中4个研究报告了内翻组,2个研究同时报告了内、外翻组。总体异质性检验显示存在异质性(P < 0.001,I2=82.7%),采用随机效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:踝上截骨术后与术前Takakura等级评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.77,95%CI (-1.34,-0.20),P=0.009],见图13。行亚组分析,内翻组术后与术前Takakura等级评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=-0.64,95%CI(-0.94,-0.33),P < 0.001],外翻组术后与术前Takakura等级评分比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=-0.88,95%CI(-3.36,1.61),P=0.49]。另外,将2个同时报告内翻与外翻组术后Takakura等级评分的研究行统计学分析,各研究间无明显异质性(P=0.123,I2=58%),采用固定效应模型行统计分析,结果显示:两组术后Takakura等级评分比较差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.69,95%CI(0.27,1.11),P=0.001],见图14。总体上及内翻组术后Takakura等级评分均较术前改善,外翻组术后与术前无明显差异,内、外翻组间术后有明显差异,这可能是因为外翻畸形的研究数量较少,统计效能不足,这提示踝上截骨在影像学上能缓解关节炎的进展,至于能否逆转关节炎,还需更多的研究证明。"
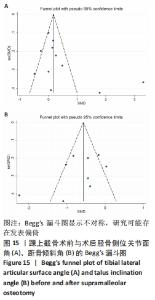
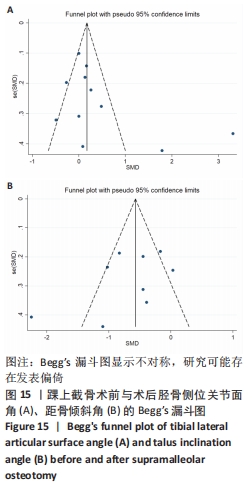
2.4.7 并发症 由于统计指标差异较大,未能行Meta分析,仅综述所统计的并发症。 2.5 异质性及敏感度分析 在进行总体分析时,异质性较高,逐个剔除单项研究后再次进行Meta分析结果显示,异质性仍然较高。异质性来源可能包括以下几个方面:①各研究组间不同术者手术技术操作的熟练程度不一致;②各研究组使用的测量工具不同;③AOFAS踝与后足评分、目测类比评分等为主观指标,量化上可能有一定的差异;④研究间在患者性别、年龄、基础疾病等方面构成比上存在差异。但这些指标的森林图术后较术前相比基本保持一致的趋势,只是量的差异,故整体的研究结果是可靠的。 2.6 单纯踝上截骨及联合腓骨截骨术后的疗效 由于纳入文献中仅有1个此类研究报告,故未能进行Meta分析。 2.7 发表偏倚 对各结局指标分析绘制Begg’s漏斗图识别发表偏倚,部分漏斗图不对称,说明此次研究可能存在发表偏倚。以踝上截骨术前与术后的胫骨侧位关节面角、踝上截骨术前与术后的距骨倾斜角为例显示漏斗图,见图15。"
| [1] KIM YS, PARK EH, KOH YG, et al. Supramalleolar Osteotomy with Bone Marrow Stimulation for Varus Ankle Osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2014;7: 1558-1566. [2] 王玉光,陆芸.踝关节骨关节炎治疗方法的临床回顾[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(1):77-80. [3] MAFFULLI N, LONGO UG, LOCHER J, et al. Outcome of Ankle Arthrodesis and Ankle Prosthesis: A Review of the Current Status. Br Med Bull. 2017;124(1):91-112. [4] HARAGUCHI N, OTA K, TSUNODA N, et al. Weight-Bearing-Line Analysis in Supramalleolar Osteotomy for Varus-Type Osteoarthritis of the Ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(4):333-339. [5] HINTERMANN B, RUIZ R, BARG A. Novel Double Osteotomy Technique of Distal Tibia for Correction of Asymmetric Varus Osteoarthritic Ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 2017; 38(9):970-981. [6] LEE W, AHN J, CHO J, et al. Realignment Surgery for Severe Talar Tilt Secondary to Paralytic Cavovarus. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 11:1552-1559. [7] STUFKENS SA, VAN BERGEN CJ, BLANKEVOORT L, et al. The Role of the Fibula in Varus and Valgus Deformity of the Tibia: A Biomechanical Study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(9):1232-1239. [8] SLIM K, NINI E, FORESTIER D, et al. Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies (Minors): Development and Validation of a New Instrument. ANZ J Surg. 2003;9:712-716. [9] 马阳,丁俊杰,拓晓瑜.截骨术在不对称踝关节关节炎治疗中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(5):569-571. [10] 朱渊,徐向阳,刘津浩,等.截骨治疗踝关节创伤后畸形愈合[J].足踝外科电子杂志,2015,2(2):11-14. [11] LEE W, MOON J, LEE K, et al. Indications for Supramalleolar Osteotomy in Patients with Ankle Osteoarthritis and Varus Deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;13: 1243-1248. [12] KIM YS, KIM YB, KOH YG. Prognostic Factors Affecting Correction Angle Changes After Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using an Opening Wedge Plate for Varus Ankle Osteoarthritis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(3):417-422. [13] HARAGUCHI N, OTA K, TSUNODA N, et al. Weight-Bearing-Line Analysis in Supramalleolar Osteotomy for Varus-Type Osteoarthritis of the Ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;4:333-339. [14] AHN T, YI Y, CHO J, et al. A Cohort Study of Patients Undergoing Distal Tibial Osteotomy without Fibular Osteotomy for Medial Ankle Arthritis with Mortise Widening. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;5:381-388. [15] GROSS CE, BARFIELD W, SCHWEIZER C, et al. The Utility of the Ankle SPECT/CT Scan to Predict Functional and Clinical Outcomes in Supramalleolar Osteotomy Patients. J Orthop Res. 2018;7:2015-2021. [16] JUNG H, LEE D, LEE S, et al. Second-Look Arthroscopic Evaluation and Clinical Outcome After Supramalleolar Osteotomy for Medial Compartment Ankle Osteoarthritis. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;12: 1311-1317. [17] KRÄHENBÜHL N, ZWICKY L, BOLLIGER L, et al. Mid- to Long-Term Results of Supramalleolar Osteotomy. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;2:124-132. [18] COLIN F, GAUDOT F, ODRI G, et al. Supramalleolar Osteotomy: Techniques, Indications and Outcomes in a Series of 83 Cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;4: 413-418. [19] COLIN F, BOLLIGER L, HORN LANG T, et al. Effect of Supramalleolar Osteotomy and Total Ankle Replacement on Talar Position in the Varus Osteoarthritic Ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;5:445-452. [20] PAGENSTERT GI, HINTERMANN B, BARG A, et al. Realignment Surgery as Alternative Treatment of Varus and Valgus Ankle Osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 462:156-168 [21] HONGMOU Z, XIAOJUN L, YI L, et al. Supramalleolar Osteotomy with or without Fibular Osteotomy for Varus Ankle Arthritis. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;9:1001-1007. [22] KNUPP M, STUFKENS SAS, BOLLIGER L, et al. Classification and Treatment of Supramalleolar Deformities. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;11:1023-1031. [23] LACORDA JB, JUNG HG, IM JM. Supramalleolar Distal Tibiofibular Osteotomy for Medial Ankle Osteoarthritis: Current Concepts. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(3):271-278. [24] KRÄHENBÜHL N, SUSDORF R, BARG A, et al. Supramalleolar osteotomy in post-traumatic valgus ankle osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2020;44(3):535-543. [25] EGLOFF C, PAUL J, PAGENSTERT G, et al. Changes of Density Distribution of the Subchondral Bone Plate After Supramalleolar Osteotomy for Valgus Ankle Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2014;10:1356-1361. [26] ZHAO H, LIANG X, LI Y, et al. Supramalleolar Osteotomy with Distraction Arthroplasty in Treatment of Varus Ankle Osteoarthritis with Large Talar Tilt Angle: A Case Report and Literature Review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;5:1125-1128. [27] DEFORTH M, KRÄHENBÜHL N, ZWICKY L, et al. Supramalleolar Osteotomy for Tibial Component Malposition in Total Ankle Replacement. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;9:952-956. [28] KNUPP M, STUFKENS SA, VAN BERGEN CJ, et al. Effect of Supramalleolar Varus and Valgus Deformities on the Tibiotalar Joint: A Cadaveric Study. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;6: 609-615. [29] ALAJLAN A, VALDERRABANO V. Joint Preserving Surgery for Valgus Ankle Osteoarthritis. Foot Ankle Clin. 2022;27(1): 57-72. [30] CHOI GW, LEE SH, NHA KW, et al. Effect of Combined Fibular Osteotomy on the Pressure of the Tibiotalar and Talofibular Joints in Supramalleolar Osteotomy of the Ankle: A Cadaveric Study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;1:59-64. [31] ZHAO H, LIANG X, LI Y, et al. The Role of Fibular for Supramalleolar Osteotomy in Treatment of Varus Ankle Arthritis: A Biomechanical and Clinical Study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):127. [32] HARNROONGROJ T, CHUCKPAIWONG B. Benefit of Adding Fibular Osteotomy to Open-Wedge, Valgus, Distal Tibial Osteotomy for Correcting Varus Ankle Arthritis: An In Vitro Study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;2:234-237. |
| [1] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [2] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [3] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [4] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [5] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| [6] | Feng Liang, Gong Shuhui, Huo Hongfeng. Effect of short-foot training on foot and ankle function in patients with flat feet: Meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 799-804. |
| [7] | Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812. |
| [8] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [9] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [10] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [11] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| [12] | Huang Huida, Huang Yongming, Zhou Junde, Liu Wenbo, Lin Yuewei, Su Haitao. Comparison of two techniques in locating tibial prosthesis during total knee arthroplasty of varus knee [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2038-2043. |
| [13] | Hu Fei, Wang Jie. Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 76-82. |
| [14] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [15] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||