Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1944-1953.doi: 10.12307/2023.077
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influencing factors and mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in tendinopathy
Lu Jialin1,2, Gao Yao1, Li Han2, Zhang Ziyu2, Wang Yiming2, Xu Rui2,3, Wang Zhonghan4, Jin Hui1
- 1Department of Pain, 4Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China; 2Bethune Medical Department, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China; 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Received:2022-01-05Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-04-28Published:2022-07-30 -
Contact:Jin Hui, MD, Attending physician, Department of Pain, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China Wang Zhonghan, Resident physician, MD, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Lu Jialin, Master candidate, Department of Pain, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China; Bethune Medical Department, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the Interdisciplinary Research Funding Program for Doctoral candidates of Jilin University, No. 419100200861 (to WZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Jialin, Gao Yao, Li Han, Zhang Ziyu, Wang Yiming, Xu Rui, Wang Zhonghan, Jin Hui. Influencing factors and mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in tendinopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1944-1953.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
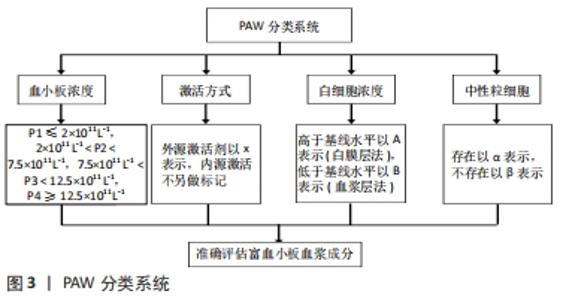
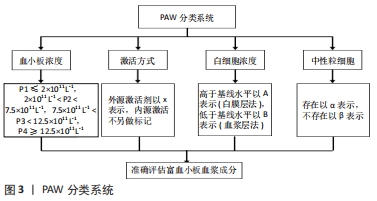
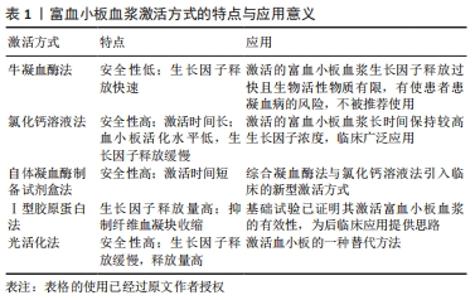
2.1 影响富血小板血浆对肌腱病疗效的相关因素 2.1.1 富血小板血浆制备方式与成分 富血小板血浆成分的差异可能是使其对肌腱病疗效存在争议的主要原因之一。富血小板血浆的最终成分受2个相互关联的因素影响:第一,患者全血中血小板、白细胞和细胞因子的浓度具有较大差异[15];第二,不同富血小板血浆制备系统在设备材料、离心所用全血体积、抗凝方法、离心过程中的转速、次数、时间及离心后各组分的分离方法等方面均有一定差异。因此,不同制备系统生产的富血小板血浆制剂成分具有较大的差异[16-17]。例如,Cascade、Magellan、Biomet GPSⅢ3种不同系统制备的富血小板血浆在血小板捕获效率、白细胞浓度、血小板衍生生长因子AB、血小板衍生生长因子BB和血管内皮生长因子浓度方面存在显著差异,但在血小板和红细胞浓度、转化生长因子β1与纤维蛋白浓度方面的差异并不显著[18]。 目前,富血小板血浆的血小板、白细胞及相关因子浓度没有统一的标准,而且大部分实验中往往只提及富血小板血浆制备套装品牌,未详细介绍提取富血小板血浆的具体参数[19]。因此,有研究者呼吁规范富血小板血浆的制备方案和成分报告,并且分析富血小板血浆的分类系统已经存在[16,20]。DELONG等[17]创建的PAW(platelet,activation,white blood cells)系统被认为是较为合理的富血小板血浆分类系统,通过评价富血小板血浆的绝对血小板计数、激活方式、白细胞与中性粒细胞浓度,相对准确地比较具有不同成分浓度富血小板血浆对肌腱病的治疗效果。具体而言,血小板浓度分为4个水平,P1指小于或等于基线水平(2×1011 L-1),P2指(2-7.5)×1011 L-1,P3指(7.5-12.5)×1011 L-1,P4指大于12.5×1011 L-1;用外源激活剂以x表示,使内源激活不另做标记;白细胞浓度被确定为高于(A)或低于/等于(B)基线水平,白细胞浓度的基线水平为(4-10)×1012 L-1,标有A的富血小板血浆采用白膜层法制备,而采用血浆层法制备的富血小板血浆则属于B;中性粒细胞归入白细胞计数子类别,存在以α表示,不存在以β表示,见图3。该系统有利于对富血小板血浆最佳成分的进一步探究。 "
富血小板血浆的制备方式可以分为血浆分离置换法与密度梯度离心法,前者利用多功能医用血成分自动分离设备采集并浓缩血小板得到富血小板血浆,其余成分则回输至患者体内,最终制剂中血小板浓度与纯度较高,且基本不含红细胞与白细胞,为缺白细胞富血小板血浆制剂。相对于密度梯度离心法而言,血浆分离置换法可以实现富血小板血浆的快速制备,且富血小板血浆各成分浓度(血小板浓度、白细胞浓度)较为稳定,但相对昂贵的设备系统和较高的操作技术门槛限制了血浆分离置换法在临床上的广泛应用,目前大多数相关基础实验及临床研究仍使用传统的密度梯度离心法制备富血小板血浆。密度梯度离心法制备富血小板血浆操作简单、使用方便、成本低廉,首先是抽取患者静脉血,将血液加入含有抗凝剂(EDTA、枸橼酸钠或枸橼酸葡萄糖)的试管中,随后将装有血液的试管配平并放入离心机内离心5-10 min,血液一般分为3层,使用移液器收集中间层黄色血清[21-22]。主流的密度梯度离心法包括血浆层法和白膜层法。血浆层法在制备过程中先以低速离心去除红细胞和白细胞,再以高速离心从剩余的血浆层收集富血小板血浆,最终制剂中基本不含红细胞和白细胞,血小板含量也较低,仅为基线水平的1.5-3倍(P2),为缺白细胞富血小板血浆制剂。白膜层法以高速离心从全血中获取白膜层,最终制剂中血小板含量通常较高,为基线水平的3-8倍(P3、P4),白细胞含量也较高,为富白细胞富血小板血浆制剂[23]。更进一步的,通过该方法生产的富白细胞富血小板血浆过滤出白细胞可以制备高血小板浓度的缺白细胞富血小板血浆[24-25]。现有多种商用富血小板血浆制备系统,根据血小板浓度可以分为低产系统(P2)和高产系统(P3、P4):低产系统包括Arthrex ACP(P2)、Cascade PPR therapy(P2)、PRGF(P2)、RegenKit-BCT(P2),高产系统包扩Biomet GPS (P3)、Harvest SmartPRep 2 APC+(P3)、Arterio Cyte Medtronic Magellan(P3)[26]。但目前的临床试验普遍缺乏对富血小板血浆制备方案和制剂成分的详细记录,无法重现实验或比较不同成分富血小板血浆疗效的差异[3]。例如,一项评估富血小板血浆在肌骨领域应用情况的荟萃分析显示,在纳入的105项临床研究中,只有11项研究(10%)提供了全面的富血小板血浆制备方案报告,17项研究(16%)提供了富血小板血浆制剂的成分报告[16]。 在肌腱病治疗中,富血小板血浆的最佳血小板浓度尚不清楚。目前认为,低血小板浓度富血小板血浆(P1)对肌腱病的治疗效果有限。由血浆层法生产的中等血小板浓度富血小板血浆(P2)在肌腱病治疗中的有效性,已被大量试验证明[27-29]。SáNCHEZ等[30]将血小板浓度为基线3倍(P2)并外源激活的富血小板血浆注射到行跟腱修复后的病变跟腱中,发现富血小板血浆可以显著提升患者跟腱修复质量并减少恢复时间。由白膜层法产生的较高血小板浓度富血小板血浆(P3)可以有效诱导腱细胞的迁移与增殖,并促进新生血管形成[31-32]。过高血小板浓度的富血小板血浆制剂(P4)则可能导致局部细胞凋亡、生长因子受体数量下调与脱敏,从而抑制对肌腱病治疗效果[33]。同时必须考虑白细胞(中性粒细胞)的存在和浓度对肌腱病疗效的影响。基于血浆层法制备的富血小板血浆,白细胞数量与基线相比减少了22倍,几乎消除了这种细胞成分;基于白膜层法制备的富血小板血浆可将白细胞富集至基线水平的3-5倍[34]。此外,不同制备系统生产的富血小板血浆具有不同比例的中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞和单核细胞[34]。白细胞的作用存在争议,一部分研究者认为富血小板血浆中的白细胞具有一定的积极作用,白细胞具有抗菌作用,并可以调控局部免疫环境,有助于预防或控制受损肌腱的感染[18];此外,白细胞通过释放生长因子或刺激血小板释放生长因子进一步提高富血小板血浆中生长因子的浓度[35]。另一部分研究者则认为白细胞不是富血小板血浆的理想成分,白细胞释放的胶原酶如基质金属蛋白酶8、基质金属蛋白酶6等对肌腱基质沉积具有不利影响[36-37]。白细胞释放的弹性蛋白酶与部分炎症因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等,会导致血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β1等生长因子失活,阻碍肌腱组织恢复[38]。最近的研究认为,富血小板血浆中的白细胞是否利于肌腱愈合取决于肌腱病的严重程度:肌腱病早期应用富白细胞富血小板血浆相比缺白细胞富血小板血浆能进一步改善肌腱病变,肌腱病中晚期应用缺白细胞富血小板血浆则更具积极效应。YAN 等[39]通过腱内注射胶原酶制备了兔跟腱病模型,并在注射后第4周分别应用缺白细胞富血小板血浆、富白细胞富血小板血浆和生理盐水治疗病变跟腱,发现缺白细胞富血小板血浆组模型兔的病变跟腱与其他两组相比组织学评分更高、胶原纤维结构和排列状态更优、促分解代谢的炎症因子更少。在此基础上,JIANG等[40]在胶原酶注射后第1周分别应用缺白细胞富血小板血浆、富白细胞富血小板血浆和生理盐水治疗病变跟腱,发现经富白细胞富血小板血浆治疗的病变跟腱具有更成熟的胶原纤维和更良好的机械性能。 2.1.2 富血小板血浆的激活方式 制备的富血小板血浆可以维持抗凝状态达8 h以上,然而富血小板血浆必须经激活才能释放血小板颗粒内容物以发挥治疗作用[41]。富血小板血浆经激活后将形成一个富集生长因子的纤维血凝块,可以释放多种高浓度的生长因子,在促进肌腱细胞增殖和迁移、肌腱基质形成等方面具有积极的作用。富血小板血浆激活剂的选择以及激活时间的长短将通过影响生长因子释放速率造成整体效果的差异,见表1[20]。 "
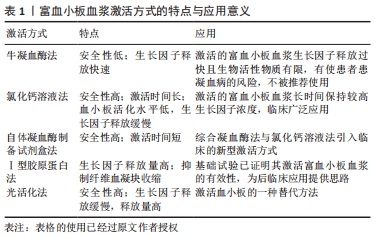

富血小板血浆的主流激活方式分2种:①第1种是使用牛凝血酶,但因牛凝血酶使血小板过快释放生长因子且对人有不良反应,并不推荐使用。MARX[42]的研究表明,牛凝血酶使血小板内约70%的生长因子在10 min内释放,近100%的生长因子在1 h内释放,这无疑会影响富血小板血浆对肌腱病的疗效。据报道,应用牛凝血酶作为激活剂有使患者患凝血病的风险,这是由牛抗因子V抗体与人因子V的交叉反应导致[14]。②第2种是使用氯化钙溶液。氯化钙溶液是一种安全但激活时间较长的激活剂。制备并使用氯化钙溶液激活富血小板血浆不会有任何使患者暴露于病毒或朊病毒的风险。有实验报告氯化钙能促进致密纤维蛋白基质形成,随后完整的血小板被困在其中,血小板的活化程度在该系统达到最小水平,结果是在7 d内缓慢释放生长因子[3]。在实际操作中,使用氯化钙溶液活化血小板至少需要20 min[43]。 近年来,自体凝血酶制备试剂盒作为一种安全、快速的激活方法被引入临床。活性自体凝血酶的制备过程为:在含有负电荷粒子(如玻璃纤维)的注射器中,注入10%氯化钙与少量富血小板血浆或血液,培养该混合物10-15 min,随即过滤去除细胞和纤维蛋白,留下呈凝血酶活性阳性的溶液。制备的自体凝血酶溶液在注射过程中通过双注射器与富血小板血浆混合,激活血小板[44]。 内源性Ⅰ型胶原蛋白也被认为具有激活富血小板血浆内血小板释放生长因子的作用,有研究者认为Ⅰ型胶原蛋白是一种比牛凝血酶更加安全有效的激活方式[17]。一项体外实验比较了Ⅰ型胶原蛋白与牛凝血酶对人富血小板血浆激活效果的差异,发现Ⅰ型胶原蛋白组与牛凝血酶组相比,1-10 d血小板衍生生长因子AB和血管内皮生长因子的释放量相似,但1-5 d转化生长因子β1的释放量更多,而且显著抑制了纤维血凝块的收缩,证明了Ⅰ型胶原蛋白激活富血小板血浆的有效性[45]。 光活化被认为是激活血小板的一种替代方法。最近的一篇论文将经光活化后的富血小板血浆与静息状态和经氯化钙活化的富血小板血浆进行了对比,发现经600-1 200 nm多色光源(近红外区域范围)诱导10 min活化的富血小板血浆,血小板ATP分泌量和钙释放量明显增加,并且实现了生长因子在28 d内的持续释放;与经氯化钙活化的富血小板血浆相比,该激活方法的血小板衍生生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β1等生长因子释放时间更长、释放量也更高[46]。 2.1.3 富血小板血浆的给药方式与施用次数 在肌腱病治疗过程中,如何将富血小板血浆高效、安全地富集在病变部位是影响治疗效果的关键因素之一。富血小板血浆分别注射到肌腱骨膜连接处、肌腱体、肌肉肌腱连接处会产生不同的治疗效果,说明不同的给药位置将决定治疗效果[29]。超声引导治疗是一种有效的治疗方法,此技术得益于微创、低麻醉风险的优势及材料和成像设备的不断进步,在肌骨领域疾病的治疗中得到越来越广泛的应用[47]。超声引导的富血小板血浆注射技术允许医生控制进针深度,从而将富血小板血浆精准地输送到肌腱病变部位[48]。部分研究者使用了一种Peppering technique注射法(Pep法),这种多点注射药物的方法可以消除范围较广的炎症,并引起治疗区域局部出血和化学递质释放,激发病变肌腱的自我修复机制[49]。一些研究者将富血小板血浆注射至健康的腱外周组织,以进一步刺激病变肌腱处细胞合成并释放细胞因子[48]。近年来,为实现富血小板血浆在局部的长时间作用,多种富血小板血浆载药缓释系统被成功开发,包括可注射水凝胶微球[50-51]、可注射水凝胶制剂等[52-53]。CHOI等[54]使用微流控技术制备了可生物降解的富血小板血浆负载聚乙二醇微球系统,该系统极大降低了聚乙二醇的降解速度,实现富血小板血浆内生长因子的缓释,在一定程度上解决单针注射使富血小板血浆内生长因子释放过快的问题。 富血小板血浆最佳施用次数也是争论的焦点。研究表明,单次注射和多次注射在肌腱病治疗中有不同的效果[55]。例如,一项纳入70项研究涉及2 530例患者的评估富血小板血浆对髌腱病疗效的荟萃分析显示,单次注射富血小板血浆在短期内有更好的疗效,而多次注射在长期随访中体现出更显著的益处[56]。据此,应根据肌腱病患者的治疗耐受度和症状严重程度个性化定制富血小板血浆施用方案。对于症状严重、持续时间长或其他治疗方案失败的肌腱病患者,建议将多次富血小板血浆注射与康复训练结合治疗[57]。单次注射富血小板血浆适合症状较轻的肌腱病患者在短期内缓解病痛,但不是最佳的长期治疗方案[56]。 2.2 富血小板血浆治疗的肌腱病机制 了解富血小板血浆治疗肌腱病的机制需从肌腱病的病理特征和肌腱恢复过程入手,目前大量基础研究证实了富血小板血浆可以通过调节炎症与促进组织重建两方面功能发挥对肌腱病的治疗作用,见表2。 "


2.2.1 调节炎症与缓解疼痛 肌腱愈合过程的第一阶段为早期炎症反应。在此阶段,由巨噬细胞和其他炎症细胞释放的炎症因子,如多种白细胞介素(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6等)及环氧合酶(环氧合酶1、环氧合酶2等)含量均显著增加。受高浓度环氧合酶1、环氧合酶2影响,大量前列腺素E2受大量前列腺素E2合酶介导产生并富集在病变肌腱处,引起血管扩张与疼痛[58-60],因此,前列腺素E2被认为是肌腱病中导致炎症和症状的关键因子。ZHANG等[61]发现富血小板血浆中的肝细胞生长因子可拮抗白细胞介素1β,抑制髌腱细胞环氧合酶1、环氧合酶2、前列腺素E2合酶基因表达以及前列腺素E2的产生,从而调节局部炎症反应并减轻疼痛。另有研究发现,富血小板血浆中的肝细胞生长因子可以通过增加IκBα的表达抑制病变肌腱的炎症反应[62]。IκBα是核因子κB的抑制剂,后者是一种参与肌腱病免疫应答的炎症调节因子,被证明在肌腱炎症部位的腱细胞内表达上调[63]。转化生长因子β1与血小板衍生生长因子是富集于富血小板血浆的多功能蛋白质,具有调控多种细胞募集、生长、分裂分化及调节炎症反应等功能[64]。有实验证明,转化生长因子β1与血小板衍生生长因子BB可通过抑制核因子κB的产生调节病变肌腱局部炎症反应[65-66]。富血小板血浆还可以减少病变处肌腱细胞产生促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8及其配体,调节肌腱细胞炎症反应和血管生成状态[67]。 病变肌腱组织内浸润的炎症细胞以巨噬细胞为主,巨噬细胞对早期肌腱组织修复至关重要,而巨噬细胞主要分为M1、M2两种表型:M1型巨噬细胞通过产生白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素12、单核细胞趋化蛋白1、肿瘤坏死因子α等细胞因子促进肌腱炎症反应;M2型巨噬细胞则产生白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、精氨酸酶1等细胞因子抑制肌腱炎症反应并促进腱细胞增殖[68-70]。缺白细胞富血小板血浆不仅可以在病变肌腱愈合初期诱导M1型巨噬细胞富集,还具有促使M1型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞转化的作用,从而缓解肌腱组织内的炎症反应,促进肌腱重塑。NISHIO等[71]的一项随机对照实验发现,接受富白细胞富血小板血浆或缺白细胞富血小板血浆注射治疗的髌腱损伤模型小鼠术后4,7 d腱内M1型巨噬细胞数与对照组相比均显著增加,然而只有缺白细胞富血小板血浆组小鼠术后7,14 d腱内M1型巨噬细胞数/M2型巨噬细胞数明显下降,证明了缺白细胞富血小板血浆抗炎与加快病变肌腱恢复的功能。 富血小板血浆与地塞米松或环丙沙星联用,可以分别降低药物诱导肌腱细胞衰老或凋亡的不良反应,更安全地发挥其抗炎与抗感染药效。地塞米松与环丙沙星对人肌腱细胞有不同的不良反应:地塞米松主要诱导细胞衰老,环丙沙星诱导细胞凋亡。但是与浓度为10%的富血小板血浆(P2)共处理后,地塞米松组衰老细胞数显著减少,环丙沙星组死亡细胞数显著减少,两组正常细胞数均显著增加[72]。 2.2.2 组织重建 促进干细胞迁移、分化与细胞增殖:富血小板血浆能诱导肌腱干细胞、脂肪干细胞等多种干细胞向损伤部位迁移。血小板分泌多种细胞因子,如血小板衍生生长因子B、成纤维细胞生长因子β和趋化因子CXCL-5等,为干细胞迁移提供初始信号[73]。KAJIKAWA等[74]发现注射富血小板血浆后肌腱中来自循环系统的细胞(巨噬细胞、间充质干细胞等)增多,并通过促进增殖、分化等细胞行为在肌腱病治疗过程中发挥重要作用。 富血小板血浆中的血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子具有促进人肌腱细胞增殖的作用[27]。DE MOS 等[75]进行的体外研究发现,富血小板凝块释放剂对人肌腱细胞的增殖和基质代谢都具有积极作用,利于肌腱修复。ZHANG等[76]报道富血小板凝块释放剂更强的促肌腱干细胞增殖作用。大量研究表明富血小板血浆具有诱导肌腱干细胞分化为腱细胞的能力,富血小板血浆能在体外诱导兔肌腱干细胞向腱细胞分化,且新生细胞呈α-SMA阳性,表明细胞具有较高的生物学活性[77-78]。部分研究亦报道富血小板血浆中血小板衍生生长因子具有促进脂肪干细胞向腱细胞分化的作用[79]。需注意,富血小板血浆不会诱导肌腱干细胞表达非腱细胞相关基因(过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体、Sox-9、Runx-2),提示其只具有诱导肌腱干细胞单向成腱细胞分化的作用,不能逆转病变晚期肌腱中正在进行的非腱细胞分化,这可能是临床上肌腱病后期应用富血小板血浆疗效不佳的原因之一[77,80]。 促进血管增生:新生血管形成是肌腱愈合初期的重要过程,充足的血供能为受损腱组织提供营养物质、氧气和细胞因子,募集并促进腱细胞和成纤维细胞迁移、增殖和蛋白合成。部分研究者认为富血小板血浆促进病变肌腱血管形成并提升血管通透性、诱导干细胞与成纤维细胞募集与增殖,为肌腱的损伤修复提供一个适宜的微环境[81]。血小板中的α颗粒内储存了大量促血管生成蛋白,包括血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子、干细胞生长因子、白细胞介素8、CXCL-12、基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9[82],这些促血管生成蛋白共同作用可以促进管壁细胞的募集、增殖并提高管壁的通透性[83]。例如,血管内皮生长因子是一种强大的血管生成刺激剂,在新生血管形成过程中起重要调控作用,而人富血小板血浆中的血管内皮生长因子浓度大约是其在循环系统血浆中浓度的6倍[84]。此外,血小板致密颗粒内储存的小分子物质,如组胺、去甲肾上腺素、多巴胺和血清素等,可以增加血管通透性、允许血浆蛋白外渗到损伤部位,也参与了肌腱的修复过程[78]。富血小板血浆促进血管形成作用也被大量动物实验证明。经富血小板血浆治疗后,新西兰兔髌腱和跟腱受损部位形成新生血管的能力更强、重建速度更快[85]。另一项研究报道,与自然愈合过程相比,马指浅屈肌腱损伤处单针注射富血小板血浆能够显著促进新生血管的形成[86]。 然而,长期处于高度血管化状态对肌腱组织可能具有一定危害[87]。促血管生成因子和抗血管生成因子失衡将促进异常形态血管的形成,导致缺氧和细胞外基质紊乱[88]。血管内皮生长因子作为富血小板血浆中主要的促血管生成蛋白,同时具有刺激基质金属蛋白酶产生和基质金属蛋白酶抑制酶降解的效应,致使细胞外基质的降解。DALLAUDIèRE等[89]利用贝伐珠单抗(Bevacizumab)作为抗血管内皮生长因子制剂注射于胶原蛋白酶形成的大鼠跟腱病模型,结果显示与生理盐水组相比,第6天贝伐珠单抗组的跟腱厚度减小、胶原纤维束一致性提高,第13天两组无明显差异。在此基础上,研究者组合贝伐珠单抗与富血小板血浆联合治疗肌腱病,发现联合治疗组相比单独富血小板血浆组愈合效应更良,并将其归因于血管生成抑制剂在肌腱病早期通过减少新生血管及其分泌的基质蛋白水解酶和前列腺素生成,而在愈合过程后期富血小板血浆制剂为腱组织提供多种且丰富的活性细胞因子,代偿因新生血管减少而降低浓度的部分生长因子,促进干细胞与成纤维细胞募集以及胶原蛋白合成[90]。此外,病变腱组织内血管形成与骨软骨化过程高度耦合,可能对肌腱修复产生不利影响。COCKS等[91]分析29例人类肌腱异位骨化样本发现病变肌腱异位骨化与血管增生在一定意义上具有时间和空间一致性。最近的研究显示,敲除Mohawk基因(Mkx-/-)肌腱异位骨化模型小鼠肌腱组织内促血管生成相关基因表达上调,组织学分析证明腱内血管新生;抑制新生血管形成的小分子药物BIBF1120作用于Mkx-/-模型小鼠以及创伤性肌腱异位骨化模型小鼠均能显著抑制肌腱成骨和血管新生[92]。尽管血管新生是肌腱病病理机制的关键步骤之一,但关于通过抑制新生血管形成治疗肌腱病的研究只占少数,需要进一步确定临床是否针对抑制肌腱血管增生展开一系列治疗手段。 促进肌腱细胞和肌腱干细胞的蛋白合成:胶原纤维是肌腱结构与功能的基本单位,在肌腱基质内密集平行分布[1] 。Ⅰ型胶原蛋白成层排列构成肌腱胶原纤维束的主体结构,弹性蛋白、蛋白多糖、糖蛋白等多种基质分子亦参与纤维束的组建[93]。肌腱基质分子结构与传递应力、稳定关节和缓解冲击功能相适应,起到保护相连肌肉和骨骼免受高强度应力损伤的作用[77]。Ⅲ型胶原蛋白在正常肌腱中含量较少,一般大量存在于损伤后的瘢痕组织,含量高达20%-30%[94-96]。肌腱内Ⅲ型胶原蛋白相对于Ⅰ型胶原蛋白含量增加会抑制胶原纤维的生长,导致粘连和瘢痕组织形成,同时会降低肌腱传递应力能力,增加二次断裂风险[97-98]。富血小板血浆可以使肌腱细胞和肌腱干细胞合成的胶原蛋白总量增加,并特异性增强Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的表达[99]。在此基础上,有研究表明富血小板血浆可增加肌腱组织内Ⅰ型胶原蛋白/Ⅲ型胶原蛋白值[100]。但需注意,富血小板血浆中的白细胞可能会抑制腱细胞合成胶原蛋白,并可通过增加Ⅲ型胶原蛋白/Ⅰ型胶原蛋白值形成大量瘢痕组织,影响病变肌腱功能恢复[101]。 富血小板血浆疗法可以改善肌腱内胶原纤维排列的各向异性,有助于提升肌腱的拉伸能力、弹性模量等力学性能。BOSCH等[4]发现受损马指浅屈肌腱经富血小板血浆治疗后,腱内胶原纤维结构改善,机械荷载和弹性模量增加,代谢活性增强,体现富血小板血浆加快肌腱愈合、改善肌腱力学性能的作用。跟腱、髌腱炎症大鼠模型,经腱内富血小板血浆注射治疗后肌腱纤维组织排列一致性增加,关节活动度提升,提示富血小板血浆对肌腱炎症良好的治疗效果,有助于加快肌腱愈合并改善其力学性能[102]。 富血小板血浆疗法亦可促进肌腱基质内软骨寡聚基质蛋白、核心蛋白聚糖和生腱蛋白C的表达[75-76,100,103]。软骨寡聚基质蛋白作为一种参与肌腱愈合的糖蛋白在正常肌腱中含量丰富,但在受损肌腱的纤维性瘢痕组织中匮乏;核心蛋白聚糖是肌腱基质内的一种蛋白多糖,在正常肌腱中含量丰富,可以与Ⅰ型胶原原纤维结合参与组成胶原纤维;生腱蛋白C亦是一种在肌腱愈合过程中起重要作用的糖蛋白。经富血小板血浆治疗后,此类非胶原基质标志物含量的增加也表明富血小板血浆利于肌腱基质愈合,可以促进病变肌腱恢复。 2.3 富血小板血浆联合疗法辅助肌腱病治疗 富血小板血浆虽然有诸多优点,但肌腱病治疗的影响因素是多重的,应用单一富血小板血浆治疗存在一定局限性:富血小板血浆中生长因子释放过快,难以恢复肌腱力学强度、局部生物活性物质有限等,使得单一富血小板血浆治疗并不能取得满意的效果,富血小板血浆联合治疗对于肌腱病更有现实意义。与组织工程学疗法、临床疗法联用可以在一定程度上提升富血小板血浆对肌腱病的治疗效果,取得更好的预后。该段综述了富血小板血浆联合疗法辅助肌腱病的治疗,包括胶原支架、干细胞等组织工程学疗法,临床上应用的手术、物理康复疗法等,以求进一步增强富血小板血浆对肌腱病的治疗效果,拓展富血小板血浆在肌腱病治疗中的应用范围。 2.3.1 富血小板血浆联合组织工程学重建损伤肌腱 干细胞:富血小板血浆联合干细胞对肌腱病有良好的治疗效果。组织工程修复受损肌腱的方法为将具有修复功能的干细胞单独或与生物支架一起经手术递送到肌腱受损部位,通过干细胞增殖分化修复受损的肌腱组织[104]。有研究报道,与接受常规治疗的动物相比,接受细胞组织工程治疗的肌腱病模型动物2年内肌腱病复发率更低,提示细胞组织工程在肌腱病治疗领域的良好效果[105]。为了解决病变肌腱处细胞密度低、愈合困难等问题,骨髓基质干细胞、脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞等多种干细胞被用作肌腱修复部位的外细胞源与富血小板血浆联用。骨髓基质干细胞是一种源于骨髓的克隆源性非造血基质干细胞,具有多向分化潜能[106-107]。肌腱生理愈合过程中出现在修复部位的腱外源成纤维细胞可能正是源自骨髓基质干细胞[108]。富血小板血浆联合骨髓基质干细胞治疗肌腱病可以发挥富血小板血浆的生物学效应,促进骨髓基质干细胞增殖[109];而且有实验报道,富血小板血浆中超生理浓度的转化生长因子β1和胰岛素样生长因子1在联合治疗过程中具有促进腱细胞增殖与胶原合成、提高病变肌腱的组织学评分、改善肌腱生物力学性能等功能[109-111]。MORIZAKI等[112]通过一项随机对照实验显示,富血小板血浆联合骨髓基质干细胞治疗犬受损肌腱的效果优于单独使用富血小板血浆或骨髓基质干细胞,联合治疗促进骨髓基质干细胞与腱细胞的增殖并显著提升了肌腱的力学性能。与其他来源间充质干细胞相比,脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞拥有更高的生物活性、细胞迁移能力和成腱分化能力,这些特性使脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞成为与富血小板血浆联合治疗肌腱病的理想干细胞种类[113]。一项随机对照实验发现,与单独使用一种疗法相比,脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞联合富血小板血浆疗法可以有效阻止损伤肌腱组织的进一步撕裂,同时起到促进肌腱愈合与调节炎症反应的作用[114]。然而并非所有种类的干细胞与富血小板血浆联用都具有良好的治疗效果,外周血来源间充质干细胞与富血小板血浆的联合治疗与单独使用外周血来源间充质干细胞治疗相比没有提供额外的益处[115]。 组织工程支架:组织工程的支架技术是修复肌腱损伤的主要方法之一,构建的肌腱支架可以作为载体负载细胞及因子、药物,且具有一定机械强度与形状,能够承担部分病变肌腱所受应力。此外,支架可以通过微创手术植入病变肌腱,手术难度低、创伤小,预后较好。理想的肌腱支架应具有良好的生物相容性同时不引起免疫排斥反应,利于肌腱细胞和肌腱干细胞等附着和生长,能促进肌腱干细胞分化,与天然肌腱结构的机械性能相近并随着基质的更新而降解。许多生物学材料因具有作为肌腱支架的潜力而被研究,这些材料可分为自体材料和异种材料两类。在材料支架中,以胶原凝胶为主材料制备的支架显示出良好的性能。与骨髓基质干细胞复合的胶原凝胶支架与肌腱细胞共培养后,可显著提升肌腱细胞活性,植入损伤肌腱后亦能促进肌腱修复,增加肌腱强度与韧性[116]。此外,基于纳米技术制造的Ⅰ型胶原纤维支架可以模仿天然肌腱基质结构,促进支架内间充质干细胞成腱细胞分化并提高腱细胞活性,从而利于肌腱修复[117]。异种支架材料,如猪小肠黏膜下层支架、组织来源胶原纤维支架,能构建大尺寸的移植组织从而修复大面积的肌腱损伤。与对照组相比,美国食品药品监督管理局批准的猪小肠黏膜下层支架设备在体内实验中能显著促进肌腱愈合过程并增强肌腱力学强度[118-119]。但在临床试验中,其对肌腱病患者的疗效并不令人满意,其原因尚不明确[114]。组织来源胶原纤维支架能调节病变部位炎症,促进支架内间充质干细胞表达成腱细胞相关基因,减少肌腱愈合时间,提高肌腱力学性质[120-122]。这些支架结构与天然的细胞外环境非常相似,在肌腱愈合的多个阶段具有招募、聚集与黏附细胞,形成血凝块和生成瘢痕组织等重要功能[123]。同时,支架能在损伤肌腱附近进一步激活血小板,保留血小板衍生生长因子、血管内皮生长因子等生长因子,并增强生长因子的促肌腱愈合作用,进一步缩短肌腱恢复时间、增加肌腱力学强度[45]。Vergenix-STR软组织修复产品由可生物降解的重组胶原-氯化钙支架组成,与富血小板血浆混合构成的凝胶植入受损肌腱后促进血小板释放多种细胞因子并调节炎症信号;随后肌腱细胞与成纤维细胞在此附着、增殖并分泌细胞外基质,减少病变肌腱恢复时间;最终,重组胶原支架被自然降解,并被肌腱细胞分泌的细胞外基质取代[44]。有临床试验显示,经Vergenix-STR软组织修复产品与富血小板血浆联合治疗的外侧上髁炎患者的临床评分与握力显著提高,68%患者的肌腱超声表象明显改善[124]。 2.3.2 富血小板血浆与临床治疗手段联合重建损伤肌腱 手术:与传统手术治疗相比,富血小板血浆作为辅剂与手术联合治疗能加快肌腱恢复、提高肌腱强度、减轻患者疼痛。肌腱损伤的外科修复现正朝微创手术的方向发展,以求更少的疼痛和更快的恢复速度。如何减少手术的并发症,高质量恢复肌腱是研究的重点所在。富血小板血浆提供了一个高度复杂的信号因子库,对确保细胞活化和组织再生至关重要,可作为辅剂与手术联合治疗优化对肌腱病治疗效果。在评估富血小板血浆作为辅剂与跟腱修复术联用治疗跟腱断裂效果的临床试验中,SANCHEZ等[30,124]发现与接受传统手术的对照组相比,在缝合时联合富血小板血浆治疗组患者的踝关节活动度、实现缓慢奔跑所用时间、恢复正常训练所用时间均显著优于对照组。ZOU等[125]在此基础上设计的前瞻性随机对照试验亦探究了富血小板血浆与跟腱修复术联合治疗跟腱断裂的临床效果,发现与只接受手术治疗的患者相比,接受联合治疗的患者中短期内主观评分(SF-36评分、Leppilahti评分)和客观功能测试结果(踝关节活动度、等速小腿肌肉力量)均有显著提升。 康复疗法:偏心运动康复训练作为肌腱病的一线治疗方法已有广泛报道[56]。偏心运动产生的拉力可以改善肌腱组织的胶原纤维排列,适当的机械刺激也能诱导受损肌腱组织血管与胶原纤维增殖,改善肌腱的机械性能。一项病例系列调查显示,与只接受偏心运动康复训练的患者相比,接受单针注射富血小板血浆与偏心运动康复训练联合治疗的慢性髌腱病患者在12个月随访中的临床评分(VISA-P评分、IKDC评分)、疼痛症状和膝关节活动度均有明显改善[126]。但DE VOSR等[127]设计的一项临床试验显示,与只接受偏心运动康复疗法的患者相比,接受富血小板血浆联合偏心运动治疗的慢性跟腱病患者疼痛和关节活动度等指标没有显著改善。研究者认为该试验存在一定局限性:富血小板血浆中血小板和被激活生长因子浓度未知,且富血小板血浆受跟腱所处高应力状态影响可能快速扩散离开肌腱。争议还可能源于不同的治疗部位与肌腱病的严重程度。该联合治疗的具体机制需要进一步研究阐明。 富血小板血浆与光疗法联用可以通过调节局部炎症反应促进肌腱修复。光疗法治疗肌腱病的机制是光生物调节:接受光照的组织通过吸收光子能量,产生光化学或光热效应,诱导调节局部细胞生物学反应。接受光治疗的肌腱组织中炎症因子表达受到抑制、肌腱干细胞成腱能力增加、胶原合成增加且纤维分布更均匀,有效改善了病变肌腱的组织质量。光疗法设备主要包括LED和低功率激光。LED光学器件具有大光斑、高性能和高安全性的特性[128-133],一项富血小板血浆联合LED光照的实验显示,腱细胞经4 J/cm2 LED与富血小板血浆(与全血体积比为5%)联合处理后,细胞存活率与细胞迁移率均提高[131-135]。BARBOSA等[134]采用富血小板血浆与低强度激光联合治疗大鼠跟腱断裂,结果显示0.2 mL单针富血小板血浆(P3)注射联合波长为660,880 nm低强度激光(所用方案功率密度0.35 W/cm2;能量密度7.0 J/cm2)的新型疗法能够加速肌腱愈合过程,缩短肌腱再生时间。 "

| [1] NOURISSAT G, BERENBAUM F, DUPREZ D. Tendon injury: from biology to tendon repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:223-233. [2] KANNUS P, NATRI A. Etiology and pathophysiology of tendon ruptures in sports. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1997;7:107-112. [3] ABATE M, DI GREGORIO P, SCHIAVONE C. Platelet Rich Plasma in Tendinopathies: How to Explain the Failure. Int J Immunopath Ph. 2012; 25:325-334. [4] BOSCH G, VAN SCHIE HTA, DE GROOT MW, et al. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Quality of Repair of Mechanically Induced Core Lesions in Equine Superficial Digital Flexor Tendons: A Placebo-Controlled Experimental Study. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:211-217. [5] COOK JL, PURDAM CR. Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43:409-416. [6] BUTLER DL, JUNCOSA N, DRESSLER MR. Functional efficacy of tendon repair processes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2004;6:303-329. [7] FILARDO G, DI MATTEO B, KON E, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: results and indications. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26:1984-1999. [8] NOURISSAT G, BERENBAUM F, DUPREZ D. Tendon injury: from biology to tendon repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:223-233. [9] BROCKMEYER M, DIEHL N, SCHMITT C, et al. Results of Surgical Treatment of Chronic Patellar Tendinosis (Jumper’s Knee): A Systematic Review of the Literature. Arthroscopy. 2015;31:2424-2429 e3. [10] ENGEBRETSEN L, STEFFEN K, ALSOUSOU J, et al. IOC consensus paper on the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44:1072-1081. [11] BASDELIOGLU K, MERIC G, SARGIN S, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on fracture healing in long-bone pseudoarthrosis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30:1481-1486. [12] LYU FJ, CUI HW, PAN HH, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9:14. [13] LITWINIUK M, KREJNER A, SPEYRER MS, et al. Hyaluronic Acid in Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration. Wounds. 2016;28:78-88. [14] ALSOUSOU J, ALI A, WILLETT K, et al. The role of platelet-rich plasma in tissue regeneration. Platelets. 2013;24:173-182. [15] MAZZOCCA AD, MCCARTHY MB, CHOWANIEC DM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma differs according to preparation method and human variability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:308-316. [16] CHAHLA J, CINQUE ME, PIUZZI NS, et al. A Call for Standardization in Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Protocols and Composition Reporting: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Orthopaedic Literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:1769-1779. [17] DELONG JM, RUSSELL RP, MAZZOCCA AD. Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:998-1009. [18] CASTILLO TN, POULIOT MA, KIM HJ, et al. Comparison of growth factor and platelet concentration from commercial platelet-rich plasma separation systems. Am J Sports Med 2011;39:266-271. [19] SAY F, TURKELI E, BULBUL M. Is platelet-rich plasma injection an effective choice in cases of non-union? Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81:340-345. [20] CHEN X, JONES IA, PARK C. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon and Ligament Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46:2020-2032. [21] RODRIGUES SV, ACHARYA AB, THAKUR SL. Platelet-rich plasma. A review. N Y State Dent J. 2012;78:26-30. [22] MORIMOTO N, KAKUDO N, OGURA T, et al. Easy-to-Use Preservation and Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Combination Wound Therapy With a Gelatin Sheet and Freeze-Dried Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Case Report. Eplasty. 2016;16:e22. [23] LE ADK, ENWEZE L, DEBAUN MR, et al. Current Clinical Recommendations for Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11:624-634. [24] FITZPATRICK J, BULSARA M, ZHENG MH. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Am J Sport Med. 2017;45:226-233. [25] DHURAT R, SUKESH M. Principles and Methods of Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review and Author’s Perspective. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2014;7:189-197. [26] KEVY SV, JACOBSON MS. Comparison of methods for point of care preparation of autologous platelet gel. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2004; 36:28-35. [27] ANITUA E, ANDIA I, SANCHEZ M, et al. Autologous preparations rich in growth factors promote proliferation and induce VEGF and HGF production by human tendon cells in culture. J Orthop Res. 2005;23: 281-286. [28] SANCHEZ M, ANITUA E, AZOFRA J, et al. Ligamentization of tendon grafts treated with an endogenous preparation rich in growth factors: gross morphology and histology. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:470-480. [29] ANITUA E, SANCHEZ M, ZALDUENDO MM, et al. Fibroblastic response to treatment with different preparations rich in growth factors. Cell Prolif. 2009;42:162-170. [30] SANCHEZ M, ANITUA E, AZOFRA J, et al. Comparison of surgically repaired Achilles tendon tears using platelet-rich fibrin matrices. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:245-251. [31] GIUSTI I, D’ASCENZO S, MANCO A, et al. Platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma affects tenocyte behavior in vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:630870. [32] GIUSTI I, RUGHETTI A, D’ASCENZO S, et al. Identification of an optimal concentration of platelet gel for promoting angiogenesis in human endothelial cells. Transfusion. 2009;49:771-778. [33] GRUBER R, VARGA F, FISCHER MB, et al. Platelets stimulate proliferation of bone cells: involvement of platelet-derived growth factor, microparticles and membranes. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13:529-535. [34] FITZPATRICK J, BULSARA MK, MCCRORY PR, et al. Analysis of Platelet-Rich Plasma Extraction: Variations in Platelet and Blood Components Between 4 Common Commercial Kits. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5: 2325967116675272. [35] ZIMMERMANN R, JAKUBIETZ R, JAKUBIETZ M, et al. Different preparation methods to obtain platelet components as a source of growth factors for local application. Transfusion. 2001;41:1217-1224. [36] NWOMEH BC, LIANG HX, DIEGELMANN RF, et al. Dynamics of the matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1 and MMP-8 in acute open human dermal wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 1998;6:127-134. [37] NWOMEH BC, LIANG HX, COHEN IK, et al. MMP-8 is the predominant collagenase in healing wounds and nonhealing ulcers. J Surg Res. 1999; 81:189-195. [38] SUNDMAN EA, COLE BJ, FORTIER LA. Growth factor and catabolic cytokine concentrations are influenced by the cellular composition of platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:2135-2140. [39] YAN R, GU Y, RAN J, et al. Intratendon Delivery of Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing Compared With Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Rabbit Achilles Tendinopathy Model. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45:1909-1920. [40] JIANG G, WU Y, MENG J, et al. Comparison of Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma and Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma on Achilles Tendinopathy at an Early Stage in a Rabbit Model. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48:1189-1199. [41] LANDESBERG R, MOSES M, KARPATKIN M. Risks of using platelet rich plasma gel. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;56:1116-1117. [42] MARX RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62:489-496. [43] MAN D, PLOSKER H, WINLAND-BROWN JE. The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (platelet gel) and autologous platelet-poor plasma (fibrin glue) in cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:229-237; discussion 38-39. [44] HARRISON S, VAVKEN P, KEVY S, et al. Platelet activation by collagen provides sustained release of anabolic cytokines. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39:729-734. [45] FUFA D, SHEALY B, JACOBSON M, et al. Activation of platelet-rich plasma using soluble type I collagen. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66:684-690. [46] IRMAK G, DEMIRTAS TT, GUMUSDERELIOGLU M. Sustained release of growth factors from photoactivated platelet rich plasma (PRP). Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;148:67-76. [47] BARILE A, LA MARRA A, ARRIGONI F, et al. Anaesthetics, steroids and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in ultrasound-guided musculoskeletal procedures. Brit J Radiol. 2016;89:20150355. [48] DE VOS RJ, VAN VELDHOVEN PL, MOEN MH, et al. Autologous growth factor injections in chronic tendinopathy: a systematic review. Br Med Bull. 2010;95:63-77. [49] EDWARDS SG, CALANDRUCCIO JH. Autologous blood injections for refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Am. 2003;28:272-278. [50] NAGAE M, IKEDA T, MIKAMI Y, et al. Intervertebral disc regeneration using platelet-rich plasma and biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:147-158. [51] SAITO M, TAKAHASHI KA, ARAI Y, et al. Intraarticular administration of platelet-rich plasma with biodegradable gelatin hydrogel microspheres prevents osteoarthritis progression in the rabbit knee. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:201-207. [52] LU HT, CHANG WT, TSAI ML, et al. Development of Injectable Fucoidan and Biological Macromolecules Hybrid Hydrogels for Intra-Articular Delivery of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Mar Drugs 2019;17:236. [53] YAMADA Y, UEDA M, NAIKI T, et al. Autogenous injectable bone for regeneration with mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma: tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Tissue Eng. 2004;10:955-964. [54] CHOI MH, BLANCO A, STEALEY S, et al. Micro-Clotting of Platelet-Rich Plasma Upon Loading in Hydrogel Microspheres Leads to Prolonged Protein Release and Slower Microsphere Degradation. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(8):1712. [55] ZAYNI R, THAUNAT M, FAYARD JM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for chronic patellar tendinopathy: comparison of a single versus two consecutive injections. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2015; 5:92-98. [56] ANDRIOLO L, ALTAMURA SA, REALE D, et al. Nonsurgical Treatments of Patellar Tendinopathy: Multiple Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma Are a Suitable Option: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sport Med. 2019;47:1001-1018. [57] KON E, FILARDO G, DELCOGLIANO M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: new clinical application: a pilot study for treatment of jumper’s knee. Injury. 2009;40:598-603. [58] WILLIAMS TJ. Prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin I2 and the vascular changes of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1979;65:517-524. [59] FERREIRA SH, NAKAMURA M, DE ABREU CASTRO MS. The hyperalgesic effects of prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins. 1978;16: 31-37. [60] SMITH WL. The eicosanoids and their biochemical mechanisms of action. Biochem J. 1989;259:315-324. [61] ZHANG J, MIDDLETON KK, FU FH, et al. HGF mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of PRP on injured tendons. PLoS One. 2013;8: e67303. [62] BENDINELLI P, MATTEUCCI E, DOGLIOTTI G, et al. Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: mechanisms of NF-kappaB inhibition via HGF. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225:757-766. [63] DE OLIVEIRA RR, MARTINS CS, ROCHA YR, et al. Experimental diabetes induces structural, inflammatory and vascular changes of Achilles tendons. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74942. [64] PARK SJ, 고재승, 김현만. Effect of TGF-β1 on Osteoclast Differentiation. Int J Oral Biol. 2005;30:135-141. [65] GALLIERA E, CORSI MM, BANFI G. Platelet rich plasma therapy: inflammatory molecules involved in tissue healing. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2012;26:35S-42S. [66] MONTASERI A, BUSCH F, MOBASHERI A, et al. IGF-1 and PDGF-bb suppress IL-1beta-induced cartilage degradation through down-regulation of NF-kappaB signaling: involvement of Src/PI-3K/AKT pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28663. [67] ANDIA I, RUBIO-AZPEITIA E, MAFFULLI N. Platelet-rich plasma modulates the secretion of inflammatory/angiogenic proteins by inflamed tenocytes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473:1624-1634. [68] ARNOLD L, HENRY A, PORON F, et al. Inflammatory monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into antiinflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1057-1069. [69] RAMACHANDRAN P, PELLICORO A, VERNON MA, et al. Differential Ly-6C expression identifies the recruited macrophage phenotype, which orchestrates the regression of murine liver fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E3186-195. [70] RUFFELL D, MOURKIOTI F, GAMBARDELLA A, et al. A CREB-C/EBPbeta cascade induces M2 macrophage-specific gene expression and promotes muscle injury repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106: 17475-17480. [71] NISHIO H, SAITA Y, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. Platelet-rich plasma promotes recruitment of macrophages in the process of tendon healing. Regen Ther. 2020;14:262-270. [72] BABOLDASHTI NZ, POULSEN RC, FRANKLIN SL, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Protects Tenocytes From Adverse Side Effects of Dexamethasone and Ciprofloxacin. Am J Sport Med. 2011;39:1929-1935. [73] NEDEAU AE, BAUER RJ, GALLAGHER K, et al. A CXCL5- and bFGF-dependent effect of PDGF-B-activated fibroblasts in promoting trafficking and differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314:2176-2186. [74] KAJIKAWA Y, MORIHARA T, SAKAMOTO H, et al. Platelet-rich plasma enhances the initial mobilization of circulation-derived cells for tendon healing. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215:837-845. [75] DE MOS M, VAN DER WINDT AE, JAHR H, et al. Can platelet-rich plasma enhance tendon repair? A cell culture study. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36:1171-1178. [76] ZHANG J, WANG JH. Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes differentiation of tendon stem cells into active tenocytes. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38:2477-2486. [77] RILEY G. Tendinopathy--from basic science to treatment. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4:82-89. [78] KIM MH, CURRY FR, SIMON SI. Dynamics of neutrophil extravasation and vascular permeability are uncoupled during aseptic cutaneous wounding. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;296:C848-856. [79] CHENG X, TSAO C, SYLVIA VL, et al. Platelet-derived growth-factor-releasing aligned collagen-nanoparticle fibers promote the proliferation and tenogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:1360-1369. [80] FLAD HD, BRANDT E. Platelet-derived chemokines: pathophysiology and therapeutic aspects. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:2363-2386. [81] FENWICK SA, HAZLEMAN BL, RILEY GP. The vasculature and its role in the damaged and healing tendon. Arthritis Res. 2002;4:252-260. [82] NURDEN AT, NURDEN P, SANCHEZ M, et al. Platelets and wound healing. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3532-3548. [83] ANDIA I, SANCHEZ M, MAFFULLI N. Tendon healing and platelet-rich plasma therapies. Expert Opin Biol Th. 2010;10:1415-1426. [84] EPPLEY BL, WOODELL JE, HIGGINS J. Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: implications for wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114:1502-1508. [85] LYRAS D, KAZAKOS K, VERETTAS D, et al. Immunohistochemical study of angiogenesis after local administration of platelet-rich plasma in a patellar tendon defect. Int Orthop. 2010;34:143-148. [86] BOSCH G, MOLEMAN M, BARNEVELD A, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the neovascularization of surgically created equine superficial digital flexor tendon lesions. Scand J Med Sci Spor. 2011; 21:554-561. [87] HALL K, RAN S. Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by the local environment. Front Biosci. 2010;15:195-212. [88] TEMPFER H, TRAWEGER A. Tendon Vasculature in Health and Disease. Front Physiol. 2015;6:330. [89] DALLAUDIÈRE B, LEMPICKI M, PESQUER L, et al. Acceleration of tendon healing using US guided intratendinous injection of bevacizumab: First pre-clinical study on a murine model. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:e823-e828. [90] DALLAUDIERE B, ZURLINDEN O, PEROZZIELLO A, et al. Combined intra-tendinous injection of Platelet Rich Plasma and bevacizumab accelerates and improves healing compared to Platelet Rich Plasma in tendinosis: Comprehensive assessment on a rat model. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4:351-356. [91] COCKS M, MOHAN A, MEYERS CA, et al. Vascular patterning in human heterotopic ossification. Hum Pathol. 2017;63:165-170. [92] LIN J, YANG Y, ZHOU W, et al.Single cell analysis reveals inhibition of angiogenesis attenuates the progression of heterotopic ossification inMkx−/−mice. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):4. [93] MIENALTOWSKI MJ, BIRK DE. Structure, physiology, and biochemistry of collagens. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;802:5-29. [94] MASUDA K, ISHII S, ITO K, et al. Biochemical analysis of collagen in adhesive tissues formed after digital flexor tendon injuries. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7:665-671. [95] WILLIAMS IF, HEATON A, MCCULLAGH KG. Cell morphology and collagen types in equine tendon scar. Res Vet Sci. 1980;28:302-310. [96] YOSHIDA M, FUNASAKI H, SAITO M, et al. Pathologic gene expression in adhesive subacromial bursae of human shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003:57-64. [97] BIRK DE, MAYNE R. Localization of collagen types I, III and V during tendon development. Changes in collagen types I and III are correlated with changes in fibril diameter. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997;72:352-361. [98] MAFFULLI N, EWEN SW, WATERSTON SW, et al. Tenocytes from ruptured and tendinopathic achilles tendons produce greater quantities of type III collagen than tenocytes from normal achilles tendons. An in vitro model of human tendon healing. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28:499-505. [99] SCHNABEL LV, MOHAMMED HO, MILLER BJ, et al. Platelet rich plasma (PRP) enhances anabolic gene expression patterns in flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthop Res. 2007;25:230-240. [100] JO CH, KIM JE, YOON KS, et al. Platelet-rich plasma stimulates cell proliferation and enhances matrix gene expression and synthesis in tenocytes from human rotator cuff tendons with degenerative tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:1035-1045. [101] ZHOU Y, WANG JH. PRP Treatment Efficacy for Tendinopathy: A Review of Basic Science Studies. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9103792. [102] DALLAUDIERE B, LEMPICKI M, PESQUER L, et al. Efficacy of intra-tendinous injection of platelet-rich plasma in treating tendinosis: comprehensive assessment of a rat model. Eur Radiol. 2013;23:2830-2837. [103] CHEN L, LIU JP, TANG KL, et al. Tendon derived stem cells promote platelet-rich plasma healing in collagenase-induced rat achilles tendinopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:2153-2168. [104] DOCHEVA D, MULLER SA, MAJEWSKI M, et al. Biologics for tendon repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84:222-239. [105] GODWIN EE, YOUNG NJ, DUDHIA J, et al. Implantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells demonstrates improved outcome in horses with overstrain injury of the superficial digital flexor tendon. Equine Vet J. 2012;44:25-32. [106] CHAMBERLAIN G, FOX J, ASHTON B, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25:2739-2749. [107] WANG QW, CHEN ZL, PIAO YJ. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into tenocytes by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 12 gene transfer J Biosci Bioeng. 2005;100:418-422. [108] CAPLAN AI. The mesengenic process. Clin Plast Surg. 1994;21:429-435. [109] MISHRA A, TUMMALA P, KING A, et al. Buffered platelet-rich plasma enhances mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15:431-435. [110] HOU Y, MAO Z, WEI X, et al. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 and vascular endothelial growth factor 165 gene transfer on Achilles tendon healing. Matrix Biol. 2009;28:324-335. [111] SCHNABEL LV, LYNCH ME, VAN DER MEULEN MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and insulin-like growth factor-I gene-enhanced mesenchymal stem cells improve structural aspects of healing in equine flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:1392-1398. [112] MORIZAKI Y, ZHAO C, AN KN, et al. The effects of platelet-rich plasma on bone marrow stromal cell transplants for tendon healing in vitro. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35:1833-1841. [113] BURK J, RIBITSCH I, GITTEL C, et al. Growth and differentiation characteristics of equine mesenchymal stromal cells derived from different sources. Vet J. 2013;195:98-106. [114] CARVALHO ADE M, BADIAL PR, ALVAREZ LE, et al. Equine tendonitis therapy using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet concentrates: a randomized controlled trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4:85. [115] MARTINELLO T, BRONZINI I, PERAZZI A, et al. Effects of in vivo applications of peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (PB-MSCs) and platlet-rich plasma (PRP) on experimentally injured deep digital flexor tendons of sheep. J Orthop Res. 2013;31:306-314. [116] YOUNG RG, BUTLER DL, WEBER W, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells in a collagen matrix for Achilles tendon repair. J Orthop Res. 1998; 16:406-413. [117] KISHORE V, BULLOCK W, SUN X, et al. Tenogenic differentiation of human MSCs induced by the topography of electrochemically aligned collagen threads. Biomaterials. 2012;33:2137-2144. [118] ZHENG MH, CHEN J, KIRILAK Y, et al. Porcine small intestine submucosa (SIS) is not an acellular collagenous matrix and contains porcine DNA: possible implications in human implantation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;73:61-67. [119] ZALAVRAS CG, GARDOCKI R, HUANG E, et al. Reconstruction of large rotator cuff tendon defects with porcine small intestinal submucosa in an animal model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:224-231. [120] WALTON JR, BOWMAN NK, KHATIB Y, et al. Restore orthobiologic implant: not recommended for augmentation of rotator cuff repairs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:786-791. [121] VALENTIN JE, BADYLAK JS, MCCABE GP, et al. Extracellular matrix bioscaffolds for orthopaedic applications. A comparative histologic study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:2673-2686. [122] OMAE H, STEINMANN SP, ZHAO C, et al. Biomechanical effect of rotator cuff augmentation with an acellular dermal matrix graft: a cadaver study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27:789-792. [123] FARKASH U, AVISAR E, VOLK I, et al. First clinical experience with a new injectable recombinant human collagen scaffold combined with autologous platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of lateral epicondylar tendinopathy (tennis elbow). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28:503-509. [124] GAWEDA K, TARCZYNSKA M, KRZYZANOWSKI W. Treatment of Achilles tendinopathy with platelet-rich plasma. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31:577-583. [125] ZOU J, MO X, SHI Z, et al. A Prospective Study of Platelet-Rich Plasma as Biological Augmentation for Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture Repair. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9364170. [126] KAUX JF, BRUYERE O, CROISIER JL, et al. One-year follow-up of platelet-rich plasma infiltration to treat chronic proximal patellar tendinopathies. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81:251-256. [127] DE VOS RJ, WEIR A, VAN SCHIE HTM, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy A Randomized Controlled Trial. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2010;303:144-149. [128] XAVIER M, DE SOUZA RA, PIRES VA, et al. Low-level light-emitting diode therapy increases mRNA expressions of IL-10 and type I and III collagens on Achilles tendinitis in rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2014;29:85-90. [129] XAVIER M, DAVID DR, DE SOUZA RA, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of low-level light emitting diode therapy on Achilles tendinitis in rats. Lasers Surg Med. 2010;42:553-558. [130] SALATE AC, BARBOSA G, GASPAR P, et al. Effect of In-Ga-Al-P diode laser irradiation on angiogenesis in partial ruptures of Achilles tendon in rats. Photomed Laser Surg. 2005;23:470-475. [131] CASALECHI HL, LEAL-JUNIOR EC, XAVIER M, et al. Low-level laser therapy in experimental model of collagenase-induced tendinitis in rats: effects in acute and chronic inflammatory phases. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:989-995. [132] CHEN CH, TSAI JL, WANG YH, et al. Low-level laser irradiation promotes cell proliferation and mRNA expression of type I collagen and decorin in porcine Achilles tendon fibroblasts in vitro. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:646-650. [133] OLIVEIRA FS, PINFILDI CE, PARIZOTO NA, et al. Effect of low level laser therapy (830 nm) with different therapy regimes on the process of tissue repair in partial lesion calcaneous tendon. Lasers Surg Med. 2009;41:271-276. [134] BARBOSA D, DE SOUZA RA, DE CARVALHO WRG, et al. Low-level laser therapy combined with platelet-rich plasma on the healing calcaneal tendon: a histological study in a rat model. Laser Med Sci. 2013;28:1489-1494. [135] ALZYOUD JAM, AL NAJJAR SA, TALAT S, et al. Effect of light-emitting diodes, platelet-rich plasma, and their combination on the activity of sheep tenocytes. Laser Med Sci. 2019;34:759-766. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Zheng Hongrui, Zhang Wenjie, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Shen Yajun, Fan Lei. Femoral neck system combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1390-1395. |
| [3] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [4] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [9] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [10] | Jiang Yifang, Cai Qimin, Chu Zhengyi, Qin Min, Shen Yurong, Gu Yuanping. Simulation analysis of stress distribution of NRT FILES in curved root canals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1038-1042. |
| [11] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [12] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [13] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [14] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [15] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||