Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2582-2588.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3119
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics and effects of cell-scaffold composite for periodontal soft tissue augmentation
Bi Haoran, Luo Yaxin, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun
- Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-15Revised:2020-07-17Accepted:2020-08-15Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Yang Kun, MD, Associate professor, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Bi Haoran, Master candidate, Department of Periodontology, Hospital of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760199 (to YK); the Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Province, No. [2018]1185, and No. [2020]1Y328 (to YK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bi Haoran, Luo Yaxin, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun. Characteristics and effects of cell-scaffold composite for periodontal soft tissue augmentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2582-2588.
share this article
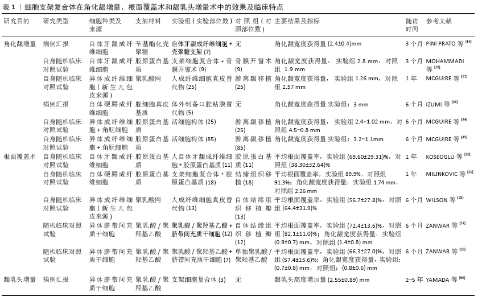
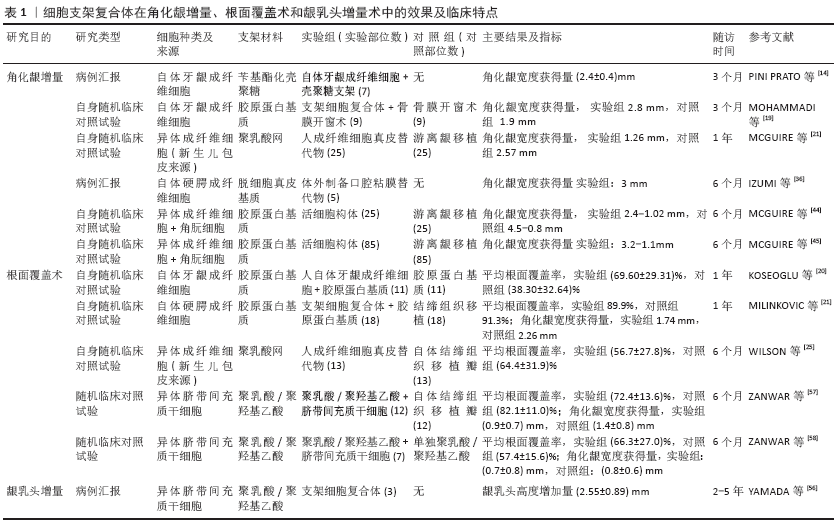
2.1 成纤维细胞复合体 不同部位的成纤维细胞具有功能异质性,最早将自体或同种异体成纤维细胞、角质细胞结合透明质酸移植用于治疗大面积烧伤、糖尿病溃疡等[8]。牙龈上皮的特异性分化主要源自于下方结缔组织的原有分化模式[9],同时牙龈成纤维细胞在细胞外基质中的生态位[10]、发育起源诱导血管生成及重塑细胞外基质作用决定了其在牙周软组织中独特的作用[11-12]。将成纤维细胞结合支架材料在移植部位产生一个代谢活跃的区域,各种材料的支架对邻近细胞在该区域的定植、血管生成和再上皮化产生影响。随着支架消失,成纤维细胞自身分泌的生长因子[13](如:血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子、角质细胞生长因子)和其他蛋白质(包括:纤维连接蛋白、糖胺聚糖和细胞因子等)与遗留下的细胞外基质一同帮助重塑细胞外基质。目前已经研究用于成纤维细胞传递的支架材料,包括胶原蛋白支架、透明质酸、聚乳酸网、脱细胞真皮基质和壳聚糖等材料。 2.1.1 自体成纤维细胞的应用 PINI PRATO等[14]将人自体牙龈成纤维细胞在苄基酯化透明质酸上培养,应用于1例需要角化龈增量的患者,并取得一定效果。2003年该作者再次将相同的技术用于5例患者上,3个月后移植部位角化龈数量平均获得了1.5-2.5 mm,但是移植物需要完全覆盖在受植床上,因此仅适用于无需根面覆盖的软组织增量手术[15]。数项研究发现,成纤维细胞联合胶原支架材料对细胞增殖、分化及迁移起一定积极作用,而且对伤口的早期愈合起到保护作用[16-17]。同时Ⅰ型胶原组成的支架的抗原性低,当与3D打印、涂层及预处理等技术相结合时更能便于细胞黏附和生长[18]。MOHAMMADI等[19]将人自体牙龈成纤维细胞种植于胶原蛋白支架上应用于9例患者进行角化龈增量的自身随机对照试验,分为骨膜开窗术的对照组与加入组织工程结构的试验组,3个月随访,试验组角化龈获得量(2.8 mm)与对照组(1.9 mm)差异显著,且对4例患者行组织活检后发现试验组与对照组的组织学结果均一致:除单核细胞浸润的纤维血管组织外,角化上皮由致密的结缔组织支撑。K?SEO?LU等[20]将自体牙龈成纤维细胞培养于胶原蛋白膜上,与单纯使用胶原蛋白膜作比较得到较好的根面覆盖率。MILINKOVIC等[21]同样采取了自身分口对照的设计,将自体牙龈成纤维细胞移植于脱细胞真皮基质上应用于18例拟行根面覆盖术的患者,同自体结缔组织移植瓣作比较,1年后随访显示,实验部位与对照部位间除角化龈增量上有差异[(2.79±0.17),(3.37±0.22) mm]外,平均根面覆盖率(89.9%,91.3%)、美学评分等均没有差异,表明了该组织工程结构可能替代自体结缔组织移植瓣。 2.1.2 同种异体成纤维细胞的应用 相对于自体细胞来说,异体成纤维细胞无需术前组织活检获取,同时异体人成纤维细胞的植入免疫反应较弱,并且来源容易获得,当建立稳定的细胞系后将促进后续临床试验及应用的商业化[22]。由新生儿包皮来源的成纤维细胞株和可水解三维聚乳酸网组成的人成纤维细胞真皮替代物(HF-DDS),被广泛用于治疗糖尿病足溃疡。与皮肤移植、伤口敷料或应用生长因子比较发现,HF-DDS愈合更快、伤口完全愈合概率更高,不良反应发生率也并不显著。MCGUIRE等[23]首次将HF-DDS应用于包含22例角化龈不足患者的随机对照试验,12个月随访发现游离龈移植术组(2.57 mm)高于HF-DDS组(1.26 mm),软组织收缩率试验组(45.5%)高于对照组(21.8%),该作者推测HF-DDS的较高收缩率、较低的角化龈增量可能与直接将其暴露于口腔环境有关系;在与周围组织的牙龈质地匹配度(90.9%,27.3%)和颜色匹配度(90.9%,22.7%)上,HF-DDS组优于游离龈移植术组。考虑到HF-DDS的厚度平均为250 μm,MCGUIRE等分别对17例患者进行了不同厚度的干预,发现使用三四层的HF-DDS比使用单层HF-DDS的角化龈增量要高,提示HF-DDS的疗效与其层数有关;此外,作者未观察到任何的不良反应。在另一项研究HF-DDS研究中,WILSON等[24]通过自身对照分口设计将HF-DDS与自体结缔组织移植瓣应用于冠向复位瓣术中进行比较,发现实验部位与对照部位之间退缩深度的减少、角化龈增加、探诊深度、临床附着水平无明显差异,平均根面覆盖率也没有差异,分别为56.7%与64.4%。该研究还将5例使用双层移植物与5例单层移植物的患者进行比较,发现双层组覆盖值(2.5 mm)比单层组(1.75 mm)效果更好,再一次证明HF-DDS的治疗效果与材料厚度有关。在成纤维细胞的动物实验中,壳聚糖可作为良好的成纤维细胞及生长因子移植负载支架[25],壳聚糖是天然甲壳素脱乙酰化的衍生物,其生物相容性良好、可塑性强、多孔结构益于细胞附着,有诱导骨形成、抑制牙周微生物的作用[26],并在牙周组织再生的研究中取得良好结果[27]。LOFFI等[28]将犬自体牙龈成纤维细胞负载于壳聚糖体上评价犬角化龈增加量的效果,术后各组角化牙龈平均宽度均增加,单纯壳聚糖对照组和壳聚糖复合体实验组之间没有差异;组织学结果显示,在愈合阶段两组上皮均正常角化,且细胞层数、上皮细胞或炎性细胞浸润均无统计学差异,两组均无不良反应,这与NOVAES等[29]对脱细胞真皮基质植入牙龈成纤维细胞后的组织学评价相一致。在动物实验中,陈欣戬等[30]将碱性成纤维细胞生长因子转染的牙龈成纤维细胞接种于脱细胞真皮基质,然后应用在比格犬中也获得了角化龈增加。 成纤维细胞复合体在软组织增量手术上获得了一定的效果。CARIO等[31]系统回顾发现冠向复位技术+脱细胞真皮基质联合自体牙龈成纤维细胞可能成为根面覆盖术中最佳选择的手术方式之一。但是衡量成纤维细胞复合体在软组织增量中的益处,还需增加适当的干预措施,如单独使用支架或只是单纯伤口敷料作为对照及开展大样本多中心的临床研究。同时不同组织来源的成纤维细胞可减少丝裂原和干扰素γ的产生及抑制异体抗原刺激的T细胞增殖[32],提示了异体成纤维细胞的在将来牙周软组织增量中的良好应用前景。 2.2 角质细胞复合体 按部位及功能的不同口腔上皮分为角化或非角化的复层鳞状上皮,主要由角质细胞(又可称为角质形成细胞)组成,角化龈表面的角质细胞则分为4层:基底层、棘层、颗粒层、角化层,其中角化龈的更新迭代与完整性主要通过角质深层角质干细胞的分化、更新向表面迁移维持。在伤口愈合过程中,角质细胞释放细胞因子和生长因子(如血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子α、表皮生长因子家族的双调蛋白和内皮细胞生长因子样因子)促血管再生、再上皮化、伤口愈合及减轻炎症。口腔黏膜上皮细胞片也被用于眼表重建,用于治疗食管溃疡及膀胱重建[33]。角质细胞培养在1975年以前一直是个困扰,直到将其与小鼠胚胎3T3共培养后发现角质细胞的生长良好,同时为预防3T3细胞系过度生长[34],使用辐射消除其有丝分裂能力而保留代谢活性。 为解决种植体周围软组织不足的问题,UEDA等[35]将自体角质细胞与3T3-J2细胞在含有胎牛血清的细胞培养基中共培养取得角质细胞上皮片,然而在对12例患者的应用中观察到该移植物机械性能不良及难以固定,并且部分移植部位1周仍出现渗出、红斑、出血。随后,IZUMI等[36]把自体角质细胞结合脱细胞真皮基质浸泡在必要的信号分子中得到体外制备口腔黏膜替代物,对5例参试者进行了牙周软组织增量,固定口腔黏膜替代物于骨膜床分别在30,90,180 d随访,试验过程中没有观察到任何受试者出现并发症或不良反应,角化牙龈宽度平均增加3.0-4.0 mm,角化牙龈厚度平均增加1.0-2.0 mm,表明口腔黏膜替代物在口腔内使用是安全的并有能力增加牙周软组织量。 NAKANISHI等[37-38]发现口腔黏膜替代物通过释放多种细胞因子和生长因子促进了血管的初始形成,促进了移植后角质形成细胞从伤口边缘的迁移,提示了口腔黏膜替代物中角质细胞起到原位生物反应器的作用。需要注意的是,口腔黏膜替代物中移植细胞的代谢及活力决定了疗效的好坏,使用无创性方法对细胞活力进行检测是必不可少的,如葡萄糖消耗率的检测[39]、通过观察拉曼光谱指标确定口腔黏膜替代物的热应力或定量血管内皮生长因子[40]、白细胞介素8、人β-防御素1及金属肽酶抑制剂1、2的释放[41],来排除不符合标准的移植物,以提高组织工程结构在制造过程中的质量控制及移植后的作用。未来尚需进一步研究确定口腔黏膜替代物角质细胞表达的特异性细胞因子,以及异体角质细胞构成的口腔黏膜替代物在牙周软组织增量中的应用。 2.3 成纤维细胞-角质细胞复合体 成纤维细胞和角质形成细胞是组织愈合过程中的两种主要细胞类型。角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞通过双旁分泌信号环(称为串扰或动态相互作用)相互沟通来调节上皮间的动态平衡,协调恢复细胞外基质,促进伤口愈合[42],尤其是成纤维细胞释放血管生成因子及刺激内皮细胞的生长确保了移植物的存活[43]。活细胞构体最早用于治疗糖尿病足溃疡,主要由三维牛胶原基质、角质细胞和人类新生儿包皮来源真皮成纤维细胞组成的双层结构,活细胞构体中成纤维细胞负责细胞外基质的稳态,确保角质细胞的生长和分化,反过来角质细胞形成外部上皮层并提供屏障效应。 MCGUIRE等[44]应用活细胞构体于牙周软组织增量手术中,将25例受试者50个位点随机分为:活细胞构体实验组和游离龈移植术对照组,3,6个月后对角化龈增量、质地、颜色进行评价和测量,结果发现游离龈移植术组(4.5-0.8 mm)的角化龈增量大于活细胞构体组(2.4-1.02 mm),但是活细胞构体组较游离龈移植术组的质地、颜色明显改善(P < 0.001),患者更偏向于选择活细胞构体(P=0.041)。MCGUIRE等[45]进一步通过包括96例患者的多中心随机对照试验对活细胞构体的效果与游离龈移植术进行比对,6个月时,游离龈移植术比活细胞构体产生更多的角化牙龈(分别为4.6-1.0 mm、3.2-1.1 mm),但活细胞构体组新生角化龈与相邻牙龈的颜色和质地相匹配。SCHEYER等[46]对上述两项研究的组织学与图像数据分析得出同样结果:与游离龈移植术相比,活细胞构体组的膜龈联合位置更协调、邻近软组织颜色更匹配,且不会形成瘢痕。随后NEVINS[47]也证明了其在安全性和角化组织再生方面的相似结果。因此活细胞构体是一种安全有效的角化龈增量方法。 理想的替代移植物材料应该能够再生至少2 mm角化龈[48],而新增角化龈的美学评价(包括质地、颜色、外形)同样至关重要。所以相较游离龈移植术而言,牙周软组织增量中活细胞构体的临床研究取得了突破性进展。2012年3月,使用相同平台技术生产的活细胞构体衍生物GINTUIT?获得美国食品及药物管理局批准,成为首个口腔软组织增量的上市产品[49]。活细胞构体的主要优点是角质细胞和成纤维细胞之间的旁分泌信号(或称串扰)在伤口愈合过程中起着关键作用。NEVINS[47]经过对活细胞构体在移植部位的DNA持续性分析,7周后没有显示活细胞构体在该部位的存在,证明了活细胞构体作为局部伤口愈合剂引导患者自身细胞发育出与周围牙龈相匹配的新组织,而并非单纯的组织移植。事实上,WOJTOWICZ等[50]观察到活细胞构体调节细胞因子和生长因子的表达,包括骨形态发生蛋白、成纤维细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子1、血小板衍生生长因子和血管内皮生长因子,这与只包括单一细胞类型的组织工程结构都不同,提示上皮再生应同时包括角质细胞和成纤维细胞。值得一提的是,目前的研究多集中于只负载一种细胞类型或单一培养环境的单相支架,从仿生学角度出发,双相和多相或梯度支架可能更好地模拟了下方包括基底膜在内的复杂内部结构[51]。猪胶原蛋白制成的Mucograft?具有独特的三维结构[52],由致密的宏观结构和底层的海绵状微观结构组成,这可能为种子细胞提供一个合适的环境。 2.4 间充质干细胞复合体 目前,间充质干细胞来源获取稳定、自我复制能力强,在组织再生领域应用广泛。已有研究报道了骨髓来源间充质干细胞通过分化为成纤维细胞、成骨细胞和成牙本质细胞促进牙周组织再生的特性[53],而脐带来源间充质干细胞拥有高频率的成纤维细胞集落形成单位且迅速分化为骨结节促进骨形成[54],这为以干细胞为主的组织工程结构临床应用提供了先决条件。 透明质酸普遍存在于结缔组织、皮肤及细胞外基质当中,并具有天然降解性、生物相容性及亲水性,因此被广泛作为细胞移植载体。OKABE等[55]通过动物实验发现,将骨髓间充质干细胞结合透明质酸支架加入富血小板血浆构建的组织工程结构注射到大鼠皮下,可以维持注射部位的外形,注射的细胞产生Ⅰ型胶原并从注射细胞中衍生出新的胶原纤维束,且所有注射大鼠均无严重的不良反应如感染、溃疡或红斑等。YAMADA等[56]将骨髓间充质干细胞应用于3例龈乳头增量的患者中(其中包括一名外伤后种植的患者),用于改善牙龈“黑三角”问题,发现黑三角均得到明显改善,且2-5年的随访发现龈乳头增量体积稳定,无萎缩。 在根面覆盖术方面,ZANWAR等[57-58]通过两项随机对照试验研究了脐带间充质干细胞负载于聚乳酸/聚羟基乙酸支架用于牙龈退缩的治疗,在与自体结缔组织移植瓣对照研究当中[57],6个月随访时,虽然实验组的平均根面覆盖率(72.4±13.6)%低于对照组的(82.1±11.0)%,但是角化龈获得量上两组未见明显差异;另一项与单独聚乳酸/聚羟基乙酸支架比较的研究中[58],实验组的平均根面覆盖率(66.3±27.0)%优于单纯支架组(57.4±15.6)%,表明脐带间充质干细胞在根面覆盖术中的积极作用。 间充质干细胞在干细胞移植疗法中的应用,操作方便、疼痛少、增量龈乳头的保持效果良好。在根面覆盖术中的应用表明了间充质干细胞在牙周软组织增量中的效果,然而,有必要进行大样本、多中心的临床研究,从统计学上证实该方法实用性与疗效。 各细胞支架复合体在角化龈增量、根面覆盖术和龈乳头增量术中的效果及临床特点,见表1。 "
| [1] CHAMBRONE L, SALINAS ORTEGA MA, SUKEKAVA F, et al. Root coverage procedures for treating localised and multiple recession-type defects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;10:CD007161. [2] WU Q, QU Y, GONG P, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of keratinized mucosa augmentation techniques around dental implants: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2015;113(5):383-390. [3] ZUCCHELLI G, MAZZOTTI C, MOUNSSIF I, et al. Esthetic treatment of peri-implant soft tissue defects: a case report of a modified surgical-prosthetic approach. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2013;33(3):327-335. [4] 毛尔加.牙周膜龈手术的临床应用Ⅱ:异体材料的应用[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(2):117-122. [5] CAIRO F, NIERI M, PAGLIARO U. Efficacy of periodontal plastic surgery procedures in the treatment of localized facial gingival recessions. A systematic review. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41 Suppl 15:S44-S62. [6] LANGER R, VACANTI J. Advances in tissue engineering. J Pediatr Surg. 2016;51(1):8-12. [7] 钟泉,李艳芬,闫福华,等.基因修饰牙龈成纤维细胞及脱细胞真皮基质制备牙周组织工程复合物[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(43):6906-6912. [8] NAAHIDI S, JAFARI M, LOGAN M, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(5):530-544. [9] SCULEAN A, GRUBER R, BOSSHARDT DD. Soft tissue wound healing around teeth and dental implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41 suppl 15:s6-22. [10] Häkkinen L, Larjava H, Fournier BP. Distinct phenotype and therapeutic potential of gingival fibroblasts. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(9): 1171-1186. [11] UM MIN ALLAH N, BERAHIM Z, AHMAD A, et al. Biological Interaction Between Human Gingival Fibroblasts and Vascular Endothelial Cells for Angiogenesis: A Co-culture Perspective. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;14(5):495-505. [12] KALTSCHMIDT B, KALTSCHMIDT C, WIDERA D. Adult craniofacial stem cells: sources and relation to the neural crest.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012;8(3):658-671. [13] CHIQUET M, KATSAROS C, KLETSAS D. Multiple functions of gingival and mucoperiosteal fibroblasts in oral wound healing and repair. Periodontol 2000. 2015;68(1):21-40. [14] PINI PRATO GP, ROTUNDO R, MAGNANI C, et al. Tissue engineering technology for gingival augmentation procedures: a case report. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2000;20(6):552-559. [15] PPINI RATO GP, ROTUNDO R, MAGNANI C, et al. An autologous cell hyaluronic acid graft technique for gingival augmentation: a case series.J Periodontol. 2003;74(2):262-267. [16] BACAKOVA M, PAJOROVA J, BROZ A, et al. A two-layer skin construct consisting of a collagen hydrogel reinforced by a fibrin-coated polylactide nanofibrous membrane. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:5033-5050. [17] WILLERSHAUSEN I, BARBECK M, BOEHM N, et al. Non-cross-linked collagen type I/III materials enhance cell proliferation: in vitro and in vivo evidence.J Appl Oral Sci. 2014;22(1):29-37. [18] HE Y, LIU W, GUAN L, et al. A 3D-Printed PLCL Scaffold Coated with Collagen Type I and Its Biocompatibility. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018: 5147156. [19] MOHAMMADI M, SHOKRGOZAR MA, MOFID R. Culture of human gingival fibroblasts on a biodegradable scaffold and evaluation of its effect on attached gingiva: a randomized, controlled pilot study. J Periodontol. 2007;78(10):1897-1903. [20] KÖSEOĞLU S, DURAN İ, SAĞLAM M, et al. Efficacy of collagen membrane seeded with autologous gingival fibroblasts in gingival recession treatment: a randomized, controlled pilot study. J Periodontol. 2013;84(10):1416-1424. [21] MILINKOVIC I, ALEKSIC Z, JANKOVIC S, et al. Clinical application of autologous fibroblast cell culture in gingival recession treatment. J Periodontal Res. 2015;50(3):363-370. [22] ABBASALIZADEH S, PAKZAD M, CABRAL JMS, et al. Allogeneic cell therapy manufacturing: process development technologies and facility design options. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2017;17(10):1201-1219. [23] MCGUIRE MK, NUNN ME. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of periodontal applications of a living tissue-engineered human fibroblast-derived dermal substitute. I. Comparison to the gingival autograft: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Periodontol. 2005; 76(6):867-880. [24] WILSON TG JR, MCGUIRE MK, NUNN ME. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of periodontal applications of a living tissue-engineered human fibroblast-derived dermal substitute. II. Comparison to the subepithelial connective tissue graft: a randomized controlled feasibility study. J Periodontol. 2005;76(6):881-889. [25] INTINI C, ELVIRI L, CABRAL J, et al. 3D-printed chitosan-based scaffolds: An in vitro study of human skin cell growth and an in-vivo wound healing evaluation in experimental diabetes in rats. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;199:593-602. [26] WIECKIEWICZ M, BOENING KW, GRYCHOWSKA N, et al. Clinical Application of Chitosan in Dental Specialities. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(5):401-409. [27] AMIR LR, SOEROSO Y, FATMA D, et al. Periodontal Ligament Cell Sheets and RGD-Modified Chitosan Improved Regeneration in the Horizontal Periodontal Defect Model. Eur J Dent. 2020;14(2):306-314. [28] LOTFI G, SHOKRGOZAR MA, MOFID R, et al. A clinical and histologic evaluation of gingival fibroblasts seeding on a chitosan-based scaffold and its effect on the width of keratinized gingiva in dogs. J Periodontol. 2011;82(9):1367-1375. [29] NOVAES AB JR, MARCHESAN JT, MACEDO GO, et al. Effect of in vitro gingival fibroblast seeding on the in vivo incorporation of acellular dermal matrix allografts in dogs. J Periodontol. 2007; 78(2):296-303. [30] 陈欣戬,钟泉,赵欣,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因修饰的组织工程化复合物促进牙龈组织再生实验研究[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志,2011,4(10):602-605. [31] CAIRO F, PAGLIARO U, BUTI J, et al. Root coverage procedures improve patient aesthetics. A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2016; 43(11):965-975. [32] HANIFFA MA, COLLIN MP, BUCKLEY CD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: the fibroblasts’ new clothes Haematologica. 2009;94(2):258-263. [33] KINIKOGLU B, DAMOUR O, HASIRCI V. Tissue engineering of oral mucosa: a shared concept with skin. J Artif Organs. 2015;18(1):8-19. [34] VRANCKX JJ, HONDT MD. Tissue engineering and surgery: from translational studies to human trials. Innov Surg Sci. 2017;2(4): 189-202. [35] UEDA M, HATA KI, SUMI Y, et al. Peri-implant soft tissue management through use of cultured mucosal epithelium. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86(4):393-400. [36] IZUMI K, NEIVA RF, FEINBERG SE. Intraoral grafting of tissue-engineered human oral mucosa. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(5): e295-303. [37] NAKANISHI Y, IZUMI K, YOSHIZAWA M, et al. The expression and production of vascular endothelial growth factor in oral mucosa equivalents. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36(10):928-933. [38] XU Q, IZUMI K, TOBITA T, et al. Constitutive release of cytokines by human oral keratinocytes in an organotypic culture. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(6):1256-1264. [39] KENJI I. Tissue engineered oral mucosa. Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering in Dental Sciences, 2015:721-731. [40] KHMALADZE A, KUO S, KIM RY, et al. Human oral mucosa tissue-engineered constructs monitored by Raman fiber-optic probe. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(1):46-51. [41] KUO S, ZHOU Y, KIM HM, et al. Biochemical indicators of implantation success of tissue-engineered oral mucosa. J Dent Res. 2015;94(1): 78-84. [42] SCHULTZ GS, DAVIDSON JM, KIRSNER RS, et al. Dynamic reciprocity in the wound microenvironment. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(2): 134-148. [43] GOODARZI P, FALAHZADEH K, NEMATIZADEH M, et al. Tissue Engineered Skin Substitutes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1107:143-188. [44] MCGUIRE MK, SCHEYER ET, NUNN ME, et al. A pilot study to evaluate a tissue-engineered bilayered cell therapy as an alternative to tissue from the palate. J Periodontol. 2008;79(10):1847-1856. [45] MCGUIRE MK, SCHEYER ET, NEVINS ML, et al. Living cellular construct for increasing the width of keratinized gingiva: results from a randomized, within-patient, controlled trial. J Periodontol. 2011;82(10): 1414-1423. [46] SCHEYER ET, NEVINS ML, NEIVA R, et al. Generation of site-appropriate tissue by a living cellular sheet in the treatment of mucogingival defects.J Periodontol. 2014;85(4):e57-e64. [47] NEVINS ML. Tissue-engineered bilayered cell therapy for the treatment of oral mucosal defects: a case series. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2010;30(1):31-39. [48] MCGUIRE MK, SCHEYER ET, GWALTNEY C. Commentary: Incorporating Patient-Reported Outcomes in Periodontal Clinical Trials. J Periodontol. 2014;85(10):1313-1319. [49] SCHMIDT C. Gintuit cell therapy approval signals shift at US regulator. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(6):479-479. [50] WOJTOWICZ AM, OLIVEIRA S, CARLSON MW, et al. The importance of both fibroblasts and keratinocytes in a bilayered living cellular construct used in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(2):246-255. [51] 康嘉宇,吕建伟,赵志虎,等.骨软骨组织工程分层支架的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(22):1413-1420. [52] SHI Y, ZHANG H, ZHANG X, et al. A comparative study of two porous sponge scaffolds prepared by collagen derived from porcine skin and fish scales as burn wound dressings in a rabbit model. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(1):63-70. [53] MASHIMO T, SATO Y, AKITA D, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance bone marrow regeneration in dental extraction sockets. J Oral Sci. 2019;61(2):284-293. [54] MCGUIRE MK, TAVELLI L, FEINBERG SE, et al. Living cell-based regenerative medicine technologies for periodontal soft tissue augmentation. J Periodontol. 2020;91(2):155-164. [55] OKABE K, YAMADA Y, ITO K, et al. Injectable soft-tissue augmentation by tissue engineering and regenerative medicine with human mesenchymal stromal cells, platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid scaffolds.Cytotherapy. 2009;11(3):307-316. [56] YAMADA Y, NAKAMURA S, UEDA M, et al. Papilla regeneration by injectable stem cell therapy with regenerative medicine: long-term clinical prognosis.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(3):305-309. [57] ZANWAR K, LAXMANRAO BHONGADE M, KUMAR GANJI K, et al. Comparative evaluation of efficacy of stem cells in combination with PLA/PGA membrane versus sub-epithelial connective tissue for the treatment of multiple gingival recession defects: a clinical study. J Stem Cells. 2014;9(4):253-267. [58] ZANWAR K, KUMAR GANJI K, BHONGADE ML. Efficacy of Human Umbilical Stem Cells Cultured on Polylactic/ Polyglycolic Acid Membrane in the Treatment of Multiple Gingival Recession Defects: a Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. J Dent (Shiraz). 2017;18(2): 95-103. [59] HEß V, KASIM M, MATHIA S, et al. Episodic Hypoxia Promotes Defence Against Cellular Stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(5):1075-1091. [60] 陈发明.牙周组织工程与再生[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017,52(10): 610-614. [61] CHOI EJ, KIL IS, CHO EG. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Senescent Fibroblasts Attenuate the Dermal Effect on Keratinocyte Differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1022. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [9] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [10] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [11] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [12] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [13] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||