Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3723-3729.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2694
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role of OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of giant-cell tumor of bone
Liang Chenliang1, Zhao Zhenqun2, Liu Wanlin2
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-07-18Revised:2019-12-06Accepted:2020-01-08Online:2020-08-18Published:2020-07-30 -
Contact:Zhao Zhenqun, Chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Liu Wanlin, Professor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liang Chenliang, Master candidate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8166110173
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Chenliang, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. The role of OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of giant-cell tumor of bone[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3723-3729.
share this article
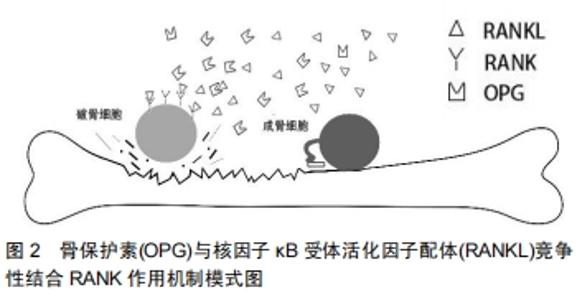
2.1 OPG/RANKL/RANK系统的生物学作用及信号通路 在20世纪90年代研究人员指出,破骨细胞起源于造血细胞系髓系中的单核前体细胞,这种前体细胞能产生巨噬细胞。破骨细胞祖细胞经成骨细胞/基质细胞表面所表达的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子作用后,可分化为成熟的破骨细胞。研究结果表明,敲除巨噬细胞集落刺激因子基因的转基因小鼠由于缺乏破骨细胞从而出现骨坏死现象,这表明巨噬细胞集落刺激因子对破骨细胞的形成至关重要。然而,由于成骨细胞和基质细胞所表达的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子并不能单独使破骨细胞祖细胞分化成成熟的破骨细胞,这就表明在这一过程中还需要额外的刺激因素进行调控才能完成破骨细胞的分化和成熟,研究发现,OPG/RANK/RANKL系统参与了这一过程。 2.1.1 骨保护素 1997年,美国的Simonet等在分析小鼠肠道中的互补DNA时发现了这一分子,进一步研究发现过量表达骨保护素基因的转基因小鼠由于破骨细胞数量的减少而发生骨软骨病,从而证实骨保护素在成骨过程中起着重要的作用[2]。几乎同时,Rodan和Martin等在日本通过另一种方法鉴定并报道了这一分子。20世纪80年代初,Rodan和Martin提出假设,认为成骨细胞可以调节破骨细胞的形成,并且成骨细胞可能表达与骨破坏相关的刺激因子。随后的研究证实了这一假设,然而调控破骨细胞形成的具体因素仍然未从知晓,直到他们成功分离出一个抑制破骨细胞生成的分子,经检测该分子与Simonet等所鉴定的分子相同。 骨保护素的发现促进了对破骨细胞发生机制的进一步研究。骨保护素是肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族(TNFRS)的一员,又称肿瘤坏死因子11B(TNFRS11B)或破骨形成抑制因子(OCIF),与CD40具有相似的结构域,因此能够与CD40配体结合。最初的骨保护素包括401个氨基酸的多肽和一个21个氨基酸的前肽经修饰后得到一个380个氨基酸的成熟蛋白。与TNFRS其他成员不同的是,骨保护素缺乏跨膜和细胞质结构域,并且以可溶性形式高表达[3],从而作为RANKL的诱骗受体发挥作用。骨保护素可在多个组织和器官中表达,包括肺、心、肾、肝、骨髓、成骨细胞等。然而,骨保护素在其中一些组织中的具体功能尚不清楚。有研究指出高表达骨保护素的转基因小鼠会出现骨硬化症,而骨保护素表达过低或是缺陷的小鼠则出现骨质疏松[2,4]。 2.1.2 RANKL RANKL是由美国的Simonet等、日本的Rodan和Martin等首次报道,用RANKL作为探针来鉴定骨保护素的配体。随后他们将RANKL命名为骨保护素配体(OPGL)和破骨细胞分化因子(ODF)。随着研究的深入学者们将OPGL/ODF重新命名为RANKL。RANKL作为肿瘤坏死因子家族的一员,在物种间高度保守。RANKL与肿瘤坏死因子相关的凋亡诱导配体和Fas配体相关,其序列同源性分别为34%和28%。RANKL基因位于人类染色体13q14,全长约36 kb的基因组DNA上,由6个外显子组成。RANKL是一种含317个氨基酸的多肽,可形成45 000的膜相关蛋白。RANKL可在多个组织和器官中表达,包括骨和骨髓,以及淋巴组织(淋巴结、胸腺、脾脏)等。RANKL是破骨细胞发生的关键调节因子,缺乏RANKL的转基因小鼠由于破骨细胞缺乏而出现骨坏死。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL的存在是破骨细胞前体细胞完全分化为成熟破骨细胞的必要条件和充分条件,在一定浓度的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子下,RANKL与破骨细胞前体细胞表面的RANK结合,促进破骨细胞前体细胞分化和增殖,从而导致骨破坏[5-6]。 2.1.3 RANK 随着骨保护素和RANKL的发现, 1997年Anderson首次将发现的RANKL受体检测并定义为RANK[7]。RANK是一种由616个氨基酸组成的多肽[8],包括一个N端胞外区和一个C端胞质结构域,以及一个28个氨基酸的信号肽和一个21个氨基酸的短跨膜区。RANK主要表达于破骨细胞前细胞、T细胞和B细胞、树突状细胞和成纤维细胞等巨噬细胞/单核细胞系的细胞,并且高表达于破骨细胞祖细胞和成熟破骨细胞表面,通过与RANKL结合来翻译破骨细胞生成信号。随着RANKL配体及其受体RANK的发现,以及对RANKL/ RANK信号通路的进一步研究,在破骨细胞发生过程中有多种途径参与RANKL/RANK信号转导,包括核因子κB (NF-κB)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶/激活蛋白1(AP-1)、 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAKP)3种途径参与破骨细胞的激活和存活,与此同时肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子(TRAF1、2,3,5,6)也参与介导RANKL/RANK信号转导[9]。 2.1.4 OPG/RANKL/RANK系统的生物学作用 骨形态的维持主要由两个系统控制,即骨基质的合成过程和吸收过程。OPG/RANK/RANKL 通路在破骨细胞行使其功能以及在破骨细胞分化和成熟的过程中起到了较为重要的作用[10]。骨保护素与RANKL之间的竞争性结合是调控破骨细胞成熟和分化生理过程中较为重要的一环。作为一种肿瘤坏死配体蛋白,RANKL可以识别破骨细胞前体细胞表面所表达的RANK,当RANKL配体与RANK受体结合后,即可引导破骨细胞的分化并激活破骨破骨活性,促进骨吸收。同时成骨细胞可表达骨保护素,骨保护素与RANKL相互竞争,竞争性抑制破骨细胞的分化和激活,从而减少过度的骨吸收,骨保护素与RANKL竞争性结合RANK作用机制模式图见图2。骨保护素甚至还可以与RANKL-RANK结合体再次结合进一步起到抑制RANKL-RANK的作用[11]。研究结果表明,骨的形成和吸收,与RANKL/OPG比值相关[12-13]。骨保护素高表达,则倾向于新骨形成;反之RANKL高表达,则倾向于旧骨吸收。因此可将RANKL/OPG比率作为判断骨代谢状态的可靠指标,同时还可以作为评估新药或治疗方法的疗效[14]。 "
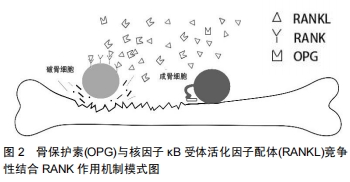
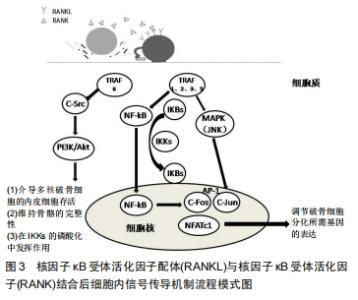
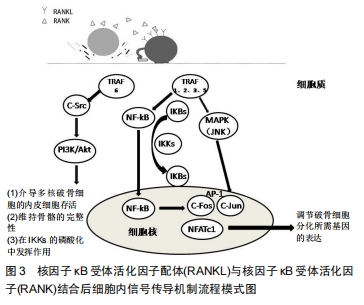
2.1.5 OPG/RANKL/RANK系统的信号通路 在OPG/ RANKL/RANK系统中,骨保护素是一种抑制破骨细胞分化的分泌型糖蛋白;RANK为Ⅰ型跨膜蛋白,是RANKL的受体;RANKL是一种由成骨细胞所产生的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,三者均属于肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族[14]。 RANKL同时也是肿瘤性梭形基质细胞中最重要的表面标记物,与骨巨细胞瘤的肿瘤生物学密切相关。RANKL由TNFSF11基因(13q14.11)编码,在正常单核细胞、巨噬细胞和骨髓基质细胞以及多种良恶性病变(包括原发性多发性骨髓瘤、慢性淋巴细胞性白血病、乳腺癌、前列腺癌和骨巨细胞瘤)中表达。 CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β(CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β C/EBPβ)、甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白、CD40、骨保护素、钙敏感受体(CaSR)、基质金属蛋白酶1、肿瘤坏死因子α转化酶等多种因子调控着骨巨细胞瘤中RANKL的表达。C/EBPβ通过直接结合增强RANKL启动子活性[15]。甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白可诱导T淋巴细胞的CD40配体,并通过自分泌方式增强梭形基质细胞RANKL的表达[16]。骨保护素和Ca2+结合的CaSR具有降低RANKL表达的趋势。来源于单核细胞的基质金属蛋白酶1和肿瘤坏死因子α转化酶所释放的可溶性RANKLs也是生成破骨细胞的来源之一。 当RANKL与RANK配体受体结合后激活RANK受体,将细胞内TRAF(肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子- TRAF1、TRAF2、TRAF3、TRAF5和TRAF6)募集到RANK细胞质区进行信号转导。RANK与TRAF (TRAF-1,2,3,5)结合可诱导丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)、核因子κB和JNK(c-jun氨基末端激酶)的激活,并进一步激活蛋白1家族成员(AP-1)即c-jun和c-Fos的表达与活化。核因子κB诱导活化I-κB,而I-κB激酶(IKKS)又抑制I-ΚB上的丝氨酸残基磷酸化,并以此为靶点进行蛋白酶体降解。I-κB激酶的降解暴露了核因子κB的核定位序列,进而使其进入细胞核。在细胞核内,核因子κB增加c-Fos的表达,c-Fos与活化T细胞的核因子1 (NFATc1破骨细胞发生的主要调节因子)相互作用,以调节破骨细胞分化所需基因的表达[17]。RANK细胞质尾部的接头分子与TRAF6适配分子相结合,TRAF6与c-Src相互作用,刺激PI-3K/Akt信号转导通路(介导多核破骨细胞的内皮细胞存活和维持骨骼的完整性,并在IKKS的磷酸化中发挥作用)。TRAF6增强了c-Src的激酶活性,导致下游信号分子NF-κB和AP-1的磷酸化,这些信号分子是破骨细胞形成和功能的关键激活剂,RANKL与RANK结合后细胞内信号传导机制流程模式图如图3。骨保护素通过与RANKL结合,抑制RANKL与RANK的相互作用,竞争性地结合RANKL,从而起到保护骨骼免受过度的骨吸收。RANKL/OPG比值在活化和分化为破骨细胞时升高,在未分化的前成骨细胞分化为成熟成骨细胞时下降。因此,RANKL和骨保护素的平衡相互作用是破骨细胞生成、骨重塑以及骨量和骨骼完整性的重要决定因素。骨保护素、RANKL、RANK 的相互作用和竞争性结合,共同维持着调节骨代谢平衡的OPG/RANKL/ RANK通路。 "
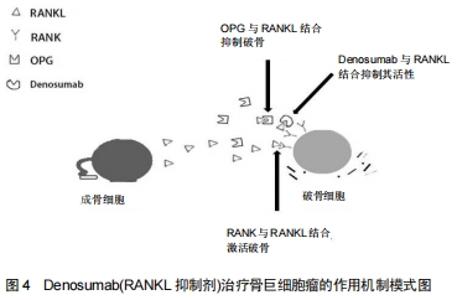
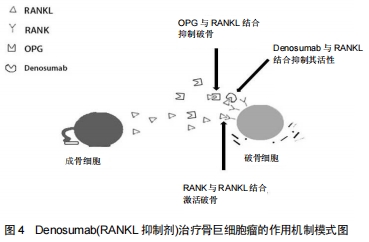
2.2 OPG/RANKL/RANK通路对骨巨细胞瘤发病机制的调控 骨巨细胞瘤占全身原发性骨肿瘤的4%-10%[18],患者多为20-30岁左右青壮年,女性发病率略高。骨巨细胞瘤通常单发并且有局部侵袭性,其侵袭程度表现不一,有时甚至可发生播散转移。1980年美国骨骼肌肉肿瘤学会将正式其列为低度恶性肿瘤[19]。骨巨细胞瘤好发于四肢长骨的骨骺区域,如股骨远端、胫骨近段和桡骨远端,也有少数一部分发生于骨盆、脊柱和颅骨。骨巨细胞瘤的主要临床表现为疼痛、肿胀、畸形和受累肢体区域的关节功能受限。骨的坚固性和完整性需要骨重建过程的维持动态平衡,即成骨细胞介导的骨形成与破骨细胞介导的骨吸收之间的平衡。而肿瘤细胞则破坏了骨代谢的动态平衡过程,导致溶骨性或成骨性病变。 骨巨细胞瘤由3部分组成,包括“肿瘤性”梭形基质细胞、“反应性”多核巨细胞和巨噬细胞样圆形细胞。梭形基质细胞是主要的肿瘤成分[20],证实梭形基质细胞是真正的肿瘤成分的线索如下:①梭形基质细胞是骨巨细胞瘤的主要成分;②具有较高的增殖潜能;③有较多的遗传变异;④表达较多核巨细胞更为重要的细胞因子和分化标志。梭形基质细胞可被分泌Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原并具有甲状旁腺激素受体的成纤维细胞激活。它们通过表达和分泌多种趋化因子(如白细胞介素6,8,11,17,34、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、肿瘤坏死因子α、血管内皮生长因子、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等)促进巨细胞形成。组织蛋白酶K;白细胞介素8、转化生长因子β1、基质衍生因子1等趋化因子,基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13等酶,所有这些因素都有助于激活和分化循环中的单核细胞为巨噬细胞。在这些因子中,基质衍生因子1似乎是一种趋化因子,参与了单核细胞的募集。此外,一些研究表明血管内皮生长因子和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达与骨破坏的程度和复发的可能性有关[17]。相关研究指出,OPG/RANKL/RANK通路与骨巨细胞瘤的发病机理密切相关。骨巨细胞瘤基质细胞表达高水平的RANKL,这被认为是该疾病发展的关键环节,但根本原因尚不清楚。 与肿瘤性梭形基质细胞相比,有许多证据表明,破骨细胞样多核巨细胞是反应性成分,它起源于破骨细胞前体细胞(骨髓源性单核细胞),其分化标志与破骨细胞是具有相似性的。巨细胞是直接导致病变内骨吸收增加的原因,由于受到梭形基质细胞的刺激而获得破骨细胞活性,从而改变了它们在骨环境中的基因表达模式[19,21-22]。大量研究结果表示,巨细胞还是推动破骨细胞发生过程中一种关键介质,其可使RANK受体的表达增加。由梭形基质细胞分泌的RANKL激活该受体,促进破骨细胞的形成、激活和存活。与此同时,肿瘤细胞还可通过OPG/RANKL/ RANK信号通路,分泌大量细胞因子和生长因子,这些因子可增加RANKL的表达或降低骨保护素的表达,从而影响RANKL/OPG比例,导致骨重塑平衡被破坏,造成骨质破坏。由于破骨活跃,因此骨微环境发生改变,如钙离子水平升高,活化生长因子从骨基质释放,以及骨衍生生长因子如转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白的产生增加,进一步活化破骨细胞,加重破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和骨破坏,并促进肿瘤细胞增殖。因此,导致骨巨细胞瘤病变内骨破坏增加。此外,被激活的破骨细胞,便可进一步释放肿瘤生长因子到骨微环境,启动恶性循环。 2.3 OPG/RANKL/RANK通路在骨巨细胞瘤中治疗中的应用 骨巨细胞瘤的治疗以手术为主,辅以放化疗。但是其较高的复发率(18%-50%[23])仍然是困扰大部分临床医师的难题。随着对OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路的深入研究,可能会为治疗提供了新的靶点。双膦酸盐(如唑来膦酸盐,帕米膦酸盐和阿仑膦酸盐)可以诱导多核破骨细胞样巨细胞和基质细胞凋亡,预防肿瘤细胞诱导的骨溶解,降低复发率,减少骨吸收,并纠正OPG/RANKL比例。CHENG等[24]用双膦酸盐治疗12例骨巨细胞瘤患者,发现这些药物可显著诱导破骨细胞样巨细胞和肿瘤基质细胞凋亡。CHANG等[25]研究发现,使用双膦酸盐类药物可以诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,进而降低骨巨细胞瘤的复发率。有学者通过RANKL研究了双膦酸盐对破骨细胞分化的影响,并以双膦酸盐浓度依赖性和时间依赖性方式诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡进而直接抑制RANKL刺激的破骨细胞分化。目前,尚未有研究指出双膦酸盐治疗后会出现的严重并发症,但仍应严格控制双膦酸盐类药物的用量,明确量效关系。REID等[26],BALKE等[27]的研究指出,长期大量静脉注射双膦酸盐可直接导致药物毒性颌骨坏死。UDAY等[28]使用Denosumab治疗青年骨巨细胞瘤患者时出现颌骨坏死和反应性高钙血症。近年来,一些靶向RANKL的人单克隆抗体如Denosumab(RANKL抑制剂)已用于治疗骨巨细胞瘤,Denosumab治疗骨巨细胞瘤的作用机制模式图见图4。在BRANSTETTER等[29]的研究中,对骨巨细胞瘤患者进行了Denosumab治疗,成功的减灭了RANK阳性的肿瘤细胞,抑制了与肿瘤相关的骨质破坏,并通过抑制RANKL从而诱导骨形成,并激活RANK阳性的单核细胞和巨噬细胞中的多核破骨细胞,使得骨重塑再次达到动态平衡。Denosumab可与RANKL结合并直接阻断其与RANK的结合,阻止RANK活化,从而抑制破骨细胞生成。此外,Denosumab可以模拟骨保护素的内源性作用并降低RANKL对RANK的影响,进而调节骨吸收。大量研究结果显示,Denosuma治疗可减灭90%的肿瘤细胞,并减弱RANKL的表达,减慢肿瘤基质细胞的增殖,甚至可使无法行手术治疗的患者,经规范化治疗后,显著缩小肿瘤体积并手术切除[30-32]。此外,使用Denosumab长期规范化治疗并未产生严重不良反应,有研究报道1例脊柱骨巨细胞瘤患者,接受了Denosumab的规范化治疗,经过16个月影像学随访结果表明,肿瘤相关性溶骨完全消失,新的皮质骨形成,骨完整性得以恢复[33]。进一步研究结果指出Denosumab的规范化使用以及长期随访有助于确定骨巨细胞瘤治疗的疗效和长期安全性[34-47]。 "
| [1]HOFBAUER LC, HEUFELDER AE. Role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin in bone cell biology. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001;79(5-6): 243-253. [2]DEMPSTER DW, LAMBING CL, KOSTENUIK PJ, et al. Role of RANK ligand and denosumab, a targeted RANK ligand inhibitor, in bone health and osteoporosis: a review of preclinical and clinical data. Clin Ther.2012;34(3):521-536. [3]TYROVOLA JB, SPYROPOULOS MN, MAKOU M,et al. Root resorption and the OPG/RANKL/RANK system: a mini review. J Oral Sci.2008;50(4):367-376. [4]LIU W, XU C, ZHAO HY, et al. Osteoprotegerin Induces Apoptosis of Osteoclasts and Osteoclast Precursor Cells via the Fas/Fas Ligand Pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(11): e0142519. [5]HONMA M, IKEBUCHI Y, KARIYA Y, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of RANKL presentation to osteoclast precursors. Curr Osteoporos Rep.2014;12(1): 115-120. [6]BAUD'HUIN M, LAMOUREUX F, DUPLOMB L, et al. RANKL, RANK, osteoprotegerin: key partners of osteoimmunology and vascular diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci.2007; 64(18): 2334-2350. [7]LESKELA HV, KUORILEHTO T, RISTELI J, et al. Congenital pseudarthrosis of neurofibromatosis type 1: impaired osteoblast differentiation and function and altered NF1 gene expression. Bone.2009; 44(2): 243-250. [8]YAMASHITA T, TAKAHASHI N, UDAGAWA N.New roles of osteoblasts involved in osteoclast differentiation. World J Orthop. 2012;3(11):175-181. [9]谢冰洁,冯捷,韩向龙.破骨细胞生物学特征的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1770-1775. [10]仝晓阳,张玲莉,郭健民,等.运动对骨代谢信号通路影响的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(12):1425-1429. [11]SILVA JA, LOPES FERRUCCI D, PERONI LA, et al. Periodontal disease-associated compensatory expression of osteoprotegerin is lost in type 1 diabetes mellitus and correlates with alveolar bone destruction by regulating osteoclastogenesis. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(2): 137-150. [12]CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connective tissue research. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107. [13]ZHANG S, WANG X, LI G, et al. Osteoclast regulation of osteoblasts via RANKRANKL reverse signal transduction in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):3994-4000. [14]KEARNS AE, KHOSLA S, KOSTENUIK PJ. Receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev.2008;29(2): 155-192. [15]NG PK, TSUI SK, LAU CP, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta is up-regulated in giant cell tumor of bone and regulates RANKL expression. J Cell Biochem.2010;110(2):438-446. [16]MAK IW, TURCOTTE RE, GHERT M. Parathyroid hormone–related protein (PTHrP) modulates adhesion, migration and invasion in bone tumor cells. Bone.2013;55(1):198-207. [17]WU PF, TANG JY, LI KH. RANK pathway in giant cell tumor of bone: pathogenesis and therapeutic aspects. Tumour Biol. 2015; 36(2):495-501. [18]MULPURI K, SONG KM, GOLDBERG MJ, et al. Detection and Nonoperative Management of Pediatric Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip in Infants up to Six Months of Age.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):202-205. [19]XU SF, ADAMS B, YU XC, et al. Denosumab and giant cell tumour of bone—a review and future management considerations. Current Oncology.2013; 20(5): 442-447. [20]NOH BJ, PARK YK. Giant cell tumor of bone: updated molecular pathogenesis and tumor biology. Human pathology. 2018;81:1-8. [21]ROUX S, AMAZIT L, MEDURI G, et al.RANK (receptor activator of nuclear factor κ B) and RANK ligand are expressed in giant cell tumors of bone. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117(2):210-216. [22]ATKINS GJ, BOURALEXIS S, HAYNES DR, et al.Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorbing activity in giant cell tumors of bone. Bone.2001;28(4): 370-377. [23]CLEVEN AH, HÖCKER S, BRIAIRE-DE BRUIJN I, et al. Mutation Analysis of H3F3A and H3F3B as a Diagnostic Tool for Giant Cell Tumor of Bone and Chondroblastoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015; 39(11):1576-1583. [24]CHENG YY, HUANG L, LEE KM, et al. Bisphosphonates Induce Apoptosis of Stromal Tumor Cells in Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2004;75(1):71-77. [25]CHANG SS, SURATWALA SJ, JUNG KM, et al. Bisphosphonates May Reduce Recurrence in Giant Cell Tumor by Inducing Apoptosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(426):103-109. [26]REID IR, CUNDY T. Osteonecrosis of the jaw. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;38(1):5-9. [27]BALKE M, CAMPANACCI L, GEBERT C,et al. Bisphosphonate treatment of aggressive primary, recurrent and metastatic Giant Cell Tumour of Bone.BMC Cancer. 2010;10:462. [28]UDAY S, GASTON CL, ROGERS L, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Rebound Hypercalcemia in Young People Treated With Denosumab for Giant Cell Tumor of Bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(2):596-603. [29]BRANSTETTER DG, NELSON SD, MANIVEL JC, et al. Denosumab Induces Tumor Reduction and Bone Formation in Patients with Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18(16):4415-4424. [30]ABE K,YOSHIMURA Y,DEYAMA Y,et al.Effects of bisphosphonates on osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2012;29(6):1007-1015. [31]DUFRESNE A, DERBEL O, CASSIER P, et al. Giant-cell tumor of bone, anti-RANKL therapy.Bonekey Rep. 2012;1:149. [32]THOMAS D, HENSHAW R, SKUBITZ K,et al.Denosumab in patients with giant-cell tumour of bone: an open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(3):275-280. [33]MAK IW, EVANIEW N, POPOVIC S, et al. A Translational Study of the Neoplastic Cells of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone Following Neoadjuvant Denosumab.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(15): e127. [34]ERRANI C, TSUKAMOTO S, MAVROGENIS AF. How safe and effective is denosumab for bone giant cell tumour? Int Orthop. 2017;41(11):2397-2400. [35]VAN DER HEIJDEN L, DIJKSTRA PDS, BLAY JY, et al. Giant cell tumour of bone in the denosumab era. Eur J Cancer. 2017;77: 75-83. [36]BROEHM CJ, INWARDS CY, AL-IBRAHEEMI A, et al. Giant Cell Tumor of Bone in Patients 55 Years and Older: A Study of 34 Patients.Am J Clin Pathol. 2018;149(3):222-233. [37]ENGELLAU J, SEEGER L, GRIMER R, et al. Assessment of denosumab treatment effects and imaging response in patients with giant cell tumor of bone. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):191. [38]GONG LH, LIU WF, DING Y, et al. Clinical, radiologic and pathologic features of giant cell tumor of bone treated with denosumab. Zhonghua Bing li Xue Zazhi. 2018;47(6):449-454. [39]ITKIN B, STRAMINSKY S, DE RONATO G,et al. Prognosis of metastatic giant cell tumor of bone in the pre-denosumab era. A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2018; 48(7):640-652. [40]KATO I, FURUYA M, MATSUO K, et al. Giant cell tumours of bone treated with denosumab: histological, immunohistochemical and H3F3A mutation analyses. Histopathology. 2018;72(6):914-922. [41]YI J, LEE YH, KIM SK, et al. Response evaluation of giant-cell tumor of bone treated by denosumab: Histogram and texture analysis of CT images.J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(3):570-577. [42]PURI A, GULIA A, HEGDE P, et al. Neoadjuvant denosumab: its role and results in operable cases of giant cell tumour of bone. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(2):170-177. [43]RUTKOWSKI P, GASTON L, BORKOWSKA A, et al. Denosumab treatment of inoperable or locally advanced giant cell tumor of bone - Multicenter analysis outside clinical trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(9):1384-1390. [44]URAKAWA H, YONEMOTO T, MATSUMOTO S, et al. Clinical outcome of primary giant cell tumor of bone after curettage with or without perioperative denosumab in Japan: from a questionnaire for JCOG 1610 study. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):160. [45]WENDLING D, GUILLOT X, SONDAG M, et al. Giant cell tumor of bone under Denosumab treatment. Joint Bone Spine. 2018; 85(4): 491. [46]SHIBUYA I, TAKAMI M, MIYAMOTO A, et al. In Vitro Study of the Effects of Denosumab on Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: Comparison with Zoledronic Acid.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019;25(1):409-419. [47]AGARWAL A, LARSEN BT, BUADU LD, et al. Denosumab chemotherapy for recurrent giant-cell tumor of bone: a case report of neoadjuvant use enabling complete surgical resection. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:496351. [48]LOPEZ-POUSA A, MARTIN BROTO J, GARRIDO T, et al. Giant cell tumour of bone: new treatments in development.Clin Transl Oncol. 2015;17(6):419-430. [49]HAQUE AU, MOATASIM A. Giant cell tumor of bone: a neoplasm or a reactive condition? Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2008;1:489-501. [50]BALKE M, NEUMANN A, SZUHAI K, et al. A short-term in vivo model for giant cell tumor of bone. BMC cancer. 2011;11:241. [51]LI GN, WANG SP, XUE X, et al. Monoclonal antibody-related drugs for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Ther. 2013;7(5):178-184. [52]SIEVERS EL, SENTER PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy.Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:15-29. [53]PEREZ HL, CARDARELLI PM, DESHPANDE S, et al. Antibody-drug conjugates: current status and future directions. Drug discovery today. 2014;19(7):869-881. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [3] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [4] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [5] | Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping. Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 456-460. |
| [6] | Tan Xu, Liang Yu, Liang Yan, Liao Jian. Hypoxia-treated dental pulp stem cell exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3961-3967. |
| [7] | Chen Jiawen, Sun Tianyu, Liu Peng, Wu Buling, Wu Jingyi. Proteoglycans in tooth development and its role in regulating stem cell homeostasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4064-4069. |
| [8] | Chen Qiaoling, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Lin Tao, Luo Xuwei. Osteoblast differentiation after conditional knockout of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [9] | Zhou Fanqi, Li Baoying, Wang Kaitao, Tan Quanquan, Yun Chenxia, Leng Jing. Isolation and identification of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from tree shrews and establishment of TLR8 pathway related molecular detection methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3721-3727. |
| [10] | Cai Zhiguo, Du Shasha, Yang Kun, Zhao Na, Liu Qi. Lipopolysaccharides mediate autophagy of mouse insulinoma βtc6 cells in high glucose state [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3127-3132. |
| [11] | Yang Lin, Wu Yao, Zhou Binbin. Interaction of Nogo-A/NgR signaling pathway and NGF/TrkA signaling pathway during the regeneration of injured spinal cord nerve axons [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3220-3224. |
| [12] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [13] | Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Regulatory role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in bone homeostasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 271-275. |
| [14] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [15] | Lai Han, Wang Jiao, Dong Miaomiao, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Electroacupuncture intervenes with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion due to middle cerebral artery occlusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 225-231. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||