Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3716-3722.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2728
Previous Articles Next Articles
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and bone destruction: problems and mechanisms
Shi Dongmei, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong
- Department of Endodontics, Dalian Medical University School of Stomatology, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-23Revised:2019-10-10Accepted:2019-11-29Online:2020-08-18Published:2020-07-30 -
Contact:Niu Weidong, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Endodontics, Dalian Medical University School of Stomatology, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Shi Dongmei, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Endodontics, Dalian Medical University School of Stomatology, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81700962
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Dongmei, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and bone destruction: problems and mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3716-3722.
share this article
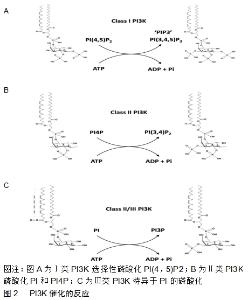
2.1 PI3K/Akt信号通路的组成及活化 2.1.1 酰肌醇3激酶(phosphoinositide 3-kinase,PI3K) 是肌醇与磷脂酰肌醇(phosphatidylinositol,PI)的重要激酶,位于细胞内,由p110和p85组成的异源二聚体,分别起着催化亚单位和调节亚单位的作用[16]。PI3K分为Ⅰ(研究最广泛)、Ⅱ、Ⅲ型3种类型,其中Ⅰ型p110亚基具有双重活性即丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性和PI3K的活性。PI3K是在肌醇环的3-位催化一种或多种肌醇磷脂的磷酸化的酶,其催化的反应见图2。Ⅰ型PI3K选择性磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇(4,5)P2,Ⅱ型PI3K磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇和PI4P,Ⅲ型PI3K特异于磷脂酰肌醇的磷酸化。Ⅰ型合成磷脂“PIP3”。PIP3是许多不同细胞表面受体用来控制细胞运动、生长、存活和分化的“第二信使”。适于接受特定受体亚型的有效刺激。关于Ⅱ型PI3K的功能知之甚少,但最新研究表明它们可以合成PI3P和磷脂酰肌醇(3,4)P2,并参与内吞作用的调节。Ⅲ型PI3K合成了磷脂PIP3,它调节体内溶酶体运输和自噬的诱导、病原体杀伤、抗原加工和免疫细胞存活所涉及的途径[17]。 "
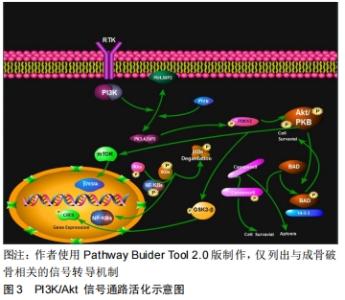
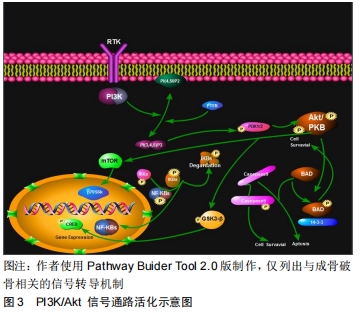
2.1.2 丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(serine/threonine kinase,Akt)又称蛋白激酶B,是一种蛋白激酶,主要表达在细胞质内。目前已知,丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶有3种亚型,分别为丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶1,2,3。其结构由PH结构域、中间催化域和调节域3部分组成,其中Akt的活化与PH结构域密切相关。它是PI3K信号传导途径中一个重要的下游靶激酶。PI3K可被G蛋白偶联受体或蛋白酪氨酸激酶受体激活,也可被Ras蛋白激活。PI3K的功能是将磷酸化脂质底物磷脂酰肌醇2磷酸(phosphatidylinositol 4,5 biphosphate,PIP2)转变成磷脂酰肌醇3磷酸(phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5biphosphate,PIP3)。活化的PIP3募集胞质内的Akt,通过与Akt N端的PH结构域结合使其转移到细胞膜上并在3-磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶1(Phosphoinositide- dependent Kinase-1,PDKI)和3-磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶2((Phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-2,PDK2)的辅助下,分别使Akt蛋白上的苏氨酸磷酸化位点(Thr308)和丝氨酸磷酸化位点(Ser473)磷酸化进而使其激活,进而影响下游如核因子κB、糖原合成激酶 3β(Glycogen synthesis kinase3β,GSK3β)、促凋亡蛋白Bad(Bxl-xl/bcl-2-associated death promoter)、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白 (mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR)、叉头框转录因子O亚家族环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白等多种蛋白,参与调节细胞存活、增殖、凋亡以及血管生成等[18-22](见图3)。 "

2.2 PI3K/Akt信号通路对破骨细胞的影响 2.2.1 破骨细胞 破骨细胞来源于骨髓造血干细胞,是一个高度分化的多核巨细胞,主要功能是直接参与骨吸收[23]。破骨细胞的形成和活化需要两个因素:RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子[24]。破骨细胞的数量与功能方面受到外界因素的影响,则会导致以骨破坏为主要特征的疾病[25-27]。RANKL与核因子κB 受体活化因子结合在破骨细胞存活、分化和活化方面是扮演着重要角色[28]。调控破骨细胞分化的信号通路主要集中在RANKL相关信号通路上。RANKL联合RANKL和激活肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子。只有肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6在破骨过程中起着重要作用[29]。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6激活多条下游信号通路,主要是核因子κB、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和Akt,激活了抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和组织蛋白酶K等与破骨细胞有关基因的表达。 2.2.2 破骨细胞与PI3K/Akt信号通路 有许多研究表明,破骨细胞分化、存活与多种细胞因子的之间相互作用以及PI3K/Akt信号通路有着重要关系[30-31],但是具体作用机制仍不明确。有研究发现,PI3K参与多种细胞功能,包括有丝分裂、存活、运动和分化。这种脂质激酶产生D3-磷酸肌醇,吸收含有PH结构域的蛋白质,包括PDK-1和Akt,这种募集允许Akt的磷酸化和后续激活下游的相关靶蛋 白[32]。在破骨细胞中,PI3K可刺激肌动蛋白丝的形成,调节细胞骨架功能,如趋化、附着和扩散[33-36]。此外,PI3K的抑制已被证明可以阻止成熟的破骨细胞的骨吸收[37-38]。LEE等[39]发现PI3K的特异性抑制剂LY294002能显著减少RANKL/M-CSF诱导的破骨细胞的产生。提示PI3K可能参与破骨细胞的功能及产生。肌醇-5-磷酸酶(SH2 domain containing inositol 5’-phosphatase,SHIP)被称为PI3K/Akt通路的负调节因子,能特异性水解磷PIP3中的5’-磷酸基团,PIP3是PI3K的主要产物,负调节PI3K活性[40]。尽管PI3K启动并调节促进破骨细胞前体存活和分化的信号,但SHIP -/-小鼠显示出破骨细胞前体数量增加和破骨细胞生成增强,导致严重的骨质疏松症[41],表明SHIP可能不是PI3K的唯一负调节剂,另一种解释是可能与其他信号通路共同调节破骨细胞分化。RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子在一定程度上通过激活Akt通路来进破骨细胞的存活[42-43]。虽然以前的研究已显示PI3K /Akt途径对破骨细胞的生成、分化、存活很重要,但尚未揭示涉及破骨细胞分化的具体作用机制。MOON等[13]研究发现Akt通过调节GSK3β/ NFATc1信号级联诱导破骨细胞分化。KIM等[44]研究发现马齿苋通过在体外抑制Akt/GSK3-c-Fos-NFATc1信号传导来抑制破骨细胞分化和骨吸收活性,并在体内预防脂多糖诱导的骨丢失。表明PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/NFATc1信号轴在破骨细胞形成中起重要作用。 SUGATANI等[45]在破骨前体细胞中敲除Akt1和Akt2,发现由于IkB激酶α/β活性的下调,IkB激酶α的磷酸化,核因子κB p50的核转位和DNA的下调,导致Akt1和Akt2蛋白的缺失从而抑制破骨细胞分化,然而,Akt1和Akt2蛋白的缺失不刺激切割的胱天蛋白酶3 (Caspases-3)活性并且不能促进细胞凋亡,表明Akt1和 Akt2对于破骨细胞增殖和分化是必需的,但是对于破骨细胞的存活是不必要的。 此外,Akt在骨形成的发展过程中扮演着重要角色。KAWAMURA等[46]发现缺乏Akt1的小鼠的骨质减少,并且破骨细胞中Akt1缺乏导致细胞自主功能障碍从而引起骨吸收受损。Akt1敲除小鼠表现为体型减少、骨长度变短及延迟继发性骨化[47],而Akt1/Akt2双敲除的小鼠在出生后不久死亡,表现出侏儒症和骨骼骨化的发育迟缓[48]。 许多研究表明,PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号传导在破骨细胞存活过程中发挥重要作用。mTOR是分离的破骨细胞前体细胞存活所必需的[45]。mTOR是造血细胞存活的关键下游介质[49]。mTOR对分离的破骨细胞前体的存活至关重要,使用雷帕霉素(mTOR抑制剂)完全阻断了破骨细胞的形成[50]。此外,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子,肿瘤坏死因子α和RANKL也通过mTOR信号传导促进破骨细胞存活[51]。 microRNA是内源的非编码小RNA,在调节各种生物学和病理过程中起着至关重要的作用。ZHAO等[52]研究表明,miR-214通过靶向Pten/PI3k/Akt途径促进破骨细胞生成。表明microRNA对于破骨细胞的分化、功能和存活是必需的。此外,先前已证明microRNA通过调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞分化来调节骨代谢。因此,LI等[53]研究表明,MYB诱导的miR-363-3p上调通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路调节骨质疏松症的发病机制。SHAO等[54]研究表明microRNA-497的下调通过骨肉瘤中的PI3K/Akt途径促进细胞生长和顺铂耐药性。这提示可以通过靶向microRNA来研究相关疾病的治疗药物,从而减少患者的痛苦,提高患者的生存质量。 2.3 PI3K/Akt信号通路对成骨细胞的影响 2.3.1 成骨细胞 成骨细胞的主要功能是参与骨形成。成骨细胞起源于间充质干细胞,间充质干细胞可以分化成许多谱系,包括骨、脂肪、肌肉和软骨。这种分化依赖于细胞外信号传导和影响常见细胞内信号传导网络的转录因子的激活或抑制[55]。骨形成是由成骨细胞、间充质干细胞参与调节的,其寿命和活性通过生长因子信号网络调节进行的。几种生长因子家族,如骨形态发生蛋白和转化生长因子β已被证明通过调节其他生长因子的作用直接或间接调节成骨细胞分化[56]。此外,Wnt、骨形态发生蛋白、Notch等信号通路均在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化过程成扮演重要角色[56]。 2.3.2 成骨细胞与PI3K/Akt信号通路 PI3K/Akt途径可被生长因子和其他细胞外信号激活,以调节包括细胞生长、增殖、分化及存活、凋亡在内的许多基本细胞过程。MUKHERJEE等[57]研究发现IGF激活的PI3K/Akt信号通路调节骨形态发生蛋白2介导的成骨细胞分化。ZHANG等[58]研究表明转化生长因子β1通过PI3K/AKT/ mTOR/S6K1(S6激酶1)信号传导途径促进成骨细胞的存活、成骨分化和迁移。SUZUKI等[59]研究发现重复的转化生长因子β1处理降低了MC3T3-E1细胞中的碱性磷酸酶活性。然而,组成型活性(CA)-Akt的强制表达在重复转化生长因子β1给药的条件下改善了这种碱性磷酸酶活性的抑制。虽然转化生长因子β1处理后碱性磷酸酶活性增加,但骨钙素的mRNA水平降低。因此结果表明,Akt活化是转化生长因子β1诱导的小鼠前成骨细胞成骨细胞分化中的关键步骤,但其功能作用根据成骨阶段而不同。然而,MUKHERJEE等[57]研究发现,在成骨细胞分化和功能的所有阶段都需要Akt活性。这有可能是在成骨分化细胞的过程中存在几个不同的Akt靶标,这些靶标控制着成骨细胞发育和功能的不同方面。另外,GHOSH-CHOUDHURY等[60]研究发现用LY294002和显性失活的PI3K均阻止了骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的碱性磷酸酶,证实了该脂质激酶参与了成骨分化的过程。骨形态发生蛋白2在成骨细胞前体细胞中以PI3K依赖性方式刺激Akt的活性。Akt的显性失活突变体对Akt活性的抑制阻断了骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶活性。以上结果表明PI3K/ Akt信号通路参与成骨细胞的分化。 细胞增殖和分化之间的关系是相辅相成的,增殖为了使行使功能的细胞提供足够的数量,而分化则为了使增殖的细胞能够行使功能。PI3K/Akt信号通路除了参与成骨细胞的分化外,还能够增加成骨细胞增殖活性。GU等[12]在3种不同Ti表面(分别为SLActive、SLA、PT)上,培养MC3T3-E1细胞,分别加入LY294002后,与Ti表面相关的成骨细胞增殖活性的减少(SLActive>SLA>PT),与成骨分化有关的碱性磷酸酶活性的增加。表明PI3K/ Akt信号通路在促进成骨细胞分化的同时抑制其增殖,这可能与细胞在分化增加的同时减少了细胞增殖有关系。 BURGERS等[61]研究发现PTEN基因(在人类10号染色体上缺失的磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物)编码的PIP磷酸酶使PIP3脱磷酸并负调控PI3K诱导的激活。PTEN阻断Akt的激活,影响细胞周期、翻译和凋亡。当Pten功能被阻断时,PIP3会累积并且Akt不断被激活,导致细胞增殖、存活和迁移增加。携带Cre介导的成骨细胞特异性Pten基因缺失的小鼠具有正常的体型,但在整个生命过程中骨量和密度显着增加。来自这些突变小鼠的成骨细胞对细胞凋亡的敏感性较低,并且加速了分化能力。这些发现提供了体内证据,即通过PI3K/Pten途径的信号传导促进成骨细胞存活和功能。 DUFOUR等[62]研究表明,转化生长因子β2通过PI3K/Akt靶向Bcl-2以防止在卸载骨骼中成骨细胞凋亡。XI等[63]在大鼠骨质疏松模型中,阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路促进大鼠成骨细胞的凋亡。DENG等[64]研究发现,地塞米松通过ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β信号通路诱导成骨细胞凋亡。这些发现表明PI3K/Akt信号通路促进了成骨细胞的凋亡。 PI3K/Akt信号通路除了参与在成骨细胞的增殖、分化及存活、凋亡的基本细胞过程外,也参与了骨质疏松、骨关节炎等以骨破坏为主要特征的相关疾病中。XI等[63]在大鼠骨质疏松模型中,体内和体外研究表明,PI3K/Akt细胞信号通路通过促进成骨细胞增殖、分化和骨形成而参与骨质疏松的抑制。LIN等[10]研究发现抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB轴能够预防骨关节炎小鼠的异常骨形成并减轻软骨变性。LIAN等[65]首先证实了PI3K/Akt/ mTOR信号通路相关基因在骨肉瘤患者中的高表达。这提示在临床治疗中可以通过靶向信号通路中关键因子,从而研制出新的药物,造福更多的患者。 2.4 抑制剂与PI3K/Akt信号通路 PI3K抑制剂有2种类型,即pan-PI3K和同种型特异性抑制剂。泛抑制剂也称为PI3K的第一代抑制剂,包括可以结合所有Ⅰ类PI3K的化合物Wortmannin(一种真菌代谢产物)和LY294002。为了改善药代动力学性质,已经出现了能够选择性抑制PI3Kp110α,β,δ或γ催化亚基的同工型特异性抑制剂。这种更大的特异性提供了减少副作用的可能性,从而允许更高的耐受剂量。此外,双重PI3K/ mTOR抑制剂也被研究中,其可靶向PI3K的所有p110亚型以及两个mTOR复合体的ATP位点,从而更完全地抑制了整个PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号轴。最近研究的抑制剂除了在浆细胞恶性多发性骨髓瘤、人B细胞恶性肿瘤、骨肉瘤等肿瘤方面取得进展外,对破骨细胞、成骨细胞的分化、增殖也有一定的影响,这为以后研制治疗骨破坏相关疾病的抑制剂提供了新思路。 MARTIN等[66]发现PI3K/Akt途径介导浆细胞恶性多发性骨髓瘤(MM)浆细胞中的增殖、存活和药物抗性,并且还参与调节骨形成成骨细胞和骨再吸收破骨细胞的形成和活性。NVP-BKM120(Buparlisib,Novartis)是一种PI3K抑制剂,目前正在几种肿瘤环境中进行临床评估。在这项研究中,检查了BKM120在免疫活性小鼠多发性骨髓瘤模型中的抗肿瘤发生作用及其对成骨细胞和破骨细胞形成和功能的影响。BKM120治疗(40 mg/kg)导致血清副蛋白和肿瘤负荷显著降低,并且胫骨近端的μCT分析显示BKM120治疗的动物中溶骨性骨病变的数量显著减少。BKM120还介导血清水平的成骨细胞标记物P1NP显著增加,并且血清水平的破骨细胞标记物TRAcP5显著降低。在体外,BKM120降低了多发性骨髓瘤浆细胞增殖、破骨细胞的形成和功能,促进了成骨细胞的形成和功能。这些研究结果表明,除了其抗肿瘤特性外,BKM120还可用于治疗多发性骨髓瘤患者的溶骨性骨病。 YEON等[67]在此研究了破坏细胞分化如何受到idelalisib(也称为CAL-101)的影响,idelalisib是p110δ选择性抑制剂,被批准用于治疗特定的人B细胞恶性肿瘤。研究发现RANKL的受体激活剂诱导PI3Kδ蛋白表达,而idelalisib抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化。接下来,通过蛋白质印迹分析和实时PCR证实了idelalisib对RANKL诱导的Akt-c-Fos/NFATc1信号级联激活的抑制作用。最后,idelalisib通过下调Akt-c-Fos/NFATc1信号级联反应在破骨细胞分化的最后阶段抑制破骨细胞前迁移,有可能扩展idelalisib的临床用途以控制破骨细胞分化。总之,目前的结果有助于理解PI3Kδ作为可药物靶标的临床价值以及相关治疗剂(包括破骨细胞生成)的功效。 PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路是一种有吸引力的抗癌靶标,因为它在细胞生长、分裂和分化的调节中起关键作用。LIAN等[65]首先证实了PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路相关基因在骨肉瘤患者中的高表达。因此,进一步研究了A005(一种新合成的双PI3K Akt/mTOR抑制剂)对骨肉瘤细胞和小鼠异种移植肿瘤模型的影响。结果证实A005抑制人骨肉瘤细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭。此外,A005还抑制RANKL诱导的破骨细胞受体激活剂体外分化和骨吸收。因此,A005进一步应用于SaOS-2骨肉瘤诱导的小鼠骨溶解模型。A005通过调节PI3K/Akt/ mTOR途径抑制肿瘤生长并预防骨肉瘤相关的骨溶解。总之,结果显示A005抑制破骨细胞生成并通过抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号传导来预防骨肉瘤诱导的骨溶解。这些发现表明A005可能是治疗人骨肉瘤的有希望的候选药物。 这提示可以研究PI3K/Akt信号通路在骨破坏相关疾病中的抑制剂,从而为临床药物治疗提供新思路。 "

| [1]JIAO H, XIAO E, GRAVES DT. Diabetes and its effect on bone and fracture healing.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13:327-335. [2]SCHETT G, TEITELBAUM SL. Osteoclasts and arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 2009,24:1142-1146. [3]EDWARDS JR, WEIVODA MM. Osteoclasts: malefactors of disease and targets for treatment.Discov Med. 2012;13(70): 201-210. [4]XIAOW, WANGY, GRAVESDT, et al. Cellular and Molecular Aspects of Bone Remodeling. Frontiers of Oral Biology. 2016; 18:9-16. [5]王莲莲,郭晓英.破骨细胞分化过程中的信号通路及信号因子的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):742-748. [6]CHEN Y, ALMAN BA. Wnt pathway, an essential role in bone regeneration. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106:353-362. [7]AI-AQL ZS, ALAGL AS, EINHORN TA, et al. Molecular mechanisms controlling bone formation during fracture healing and distraction osteogenesis.J Dent Res.2008;87:107-118. [8]CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci.2012; 8:272-288. [9]XI JC, ZANG HY, MA YZ, et al. The PI3K/AKT cell signaling pathway is involved in regulation of osteoporosis.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):640-645. [10]LIN C, SHAO Y, CAI D, et al. Blocking PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis.J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):6135-6147. [11]HUANG S, JIN A. ZIC2 promotes viability and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells by suppressing SHIP2 expression and activating PI3K/AKT pathways.J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(2): 2248-2257. [12]GU YX,DU J,SI MS,et al. The roles of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in regulating MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation on SLA and SLActive titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A.2013; 101: 748-754. [13]MOON JB, KIM JH, KIM K, et al. Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3beta/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol. 2012;188: 163-169. [14]ZOU W, YANG S, ZHOU D, et al. Hypoxia enhances glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in osteoblastic cells.J Bone Miner Metab. 2015; 33(6):615-624. [15]FUKUDA A, HIKITA A, WAKEYAMA H, et al. Regulation of osteoclast apoptosis and motility by small GTPase binding protein Rac1. J Bone Miner Res.2005;20: 2245 -2253. [16]ITO Y, HART JR. Isoform-specific activities of the regulatory subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases-potentially novel therapeutic targets.Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2018;22(10): 869-877. [17]HAWKINS PT, STEPHENS LR. PI3K signalling in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(6):882-897. [18]MAYER IA, ARTEAGA CL. The PI3K/AKT pathway as a target for cancer treatment. Annu Rev Med.2016; 67: 11-28. [19]TIAN L, ZHAO Z, XIE L, et al. MiR-361-5p suppresses chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells by targeting FOXM1 via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncotarge.2017; 9(4): 4886-4896. [20]TANG H, RONGPING LI, LIANG P, et al. miR-125a inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells via suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(2): 681-686. [21]南振华,潘灵辉.布洛芬通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路调控肝癌QGY- 7703细胞迁移和侵袭的机制[J].肿瘤防治研究,2016,43(12):1035-1038. [22]ZHANG Y, ZHENG L, DING Y, et al. MiR-20a induces cell radioresistance by activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92(5): 1132-1140. [23]于世凤.破骨细胞及其骨吸收调控研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2000, 6(1):78-83. [24]MIRON R J, BOSSHARDT DD. OsteoMacs: Keyplayers around bone biomaterials. Biomaterials.2016;82(3):1-19. [25]FUJII T, KITAURA H, KIMURA K, et al. IL-4 inhibits TNF-α-mediated osteoclast formation by inhibition of RANKL expression in TNF-α-activated stromal cells and direct inhibition of TNF-α-activated osteoclast precursors via a T-cell-independent mechanism in vivo. Bone.2012,51(4): 771-780. [26]NEALE SD,SMITH R,WASS JA, et al.Osteoclast differentiation from circulating mononuclear precursors in Paget’s disease is hypersensitive to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 and RANKL. Bone. 2000;27(3): 409-416. [27]HWANG YS, MA GT, PARK KK, et al.Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates osteoclast fusion through OC-STAMP and P2X7 receptor signaling. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(2):110-122. [28]WANG HUA-BEI.The present research situation of OPG / RANKL / RANK signaling pathway in the bone related diseases.Chinese Journal of Clinical Research.2012;25 (1):80-81. [29]BALASUBRAMANYAM K, ALTAF M, VARIER RA, et al. Polyisoprenylated benzophenone, garcinol, a natural histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, represses chromatin transcription and alters global gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2004;279(32): 33716-33726. [30]LEE SE, CHUNG WJ, KWAK HB, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha supports the survival of osteoclasts through the activation of Akt and ERK. J Biol Chem.2001;276(52): 49343- 49349. [31]LEE ZH, LEE SE, KIM CW, et al. IL-1alpha stimulation of osteoclast survival through the PI3-kinase /Akt and ERK pathways. J Biochem. 2002;131(1): 161-166. [32]TOKER A, NEWTON AC. Cellular signaling: pivoting around PDK-1.Cell.2000;103(2):185-188. [33]CHELLAIAH M,FITZGERALD C,ALVAREZ U,et al.c-Srcis required for stimulation of gelsolin-associatedphosphatidylinositol3-kinase.J Biol Chem. 1998;273(19):11908-11916. [34]CHELLAIAH M, HRUSKA K. Osteopontin stimulates gelsolin-associated levels and phosphoinositide phosphatidylinositol triphosphate-hydroxyl kinase.Mol Biol Cell. 1996;7(5) :743-753. [35]LAKKAKORPI PT, WESOLOWSKI G, ZIMOLO Z, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase association with the osteoclast cytoskeleton,and its involvement in osteoclast attachment and spreading.Exp Cell Res.1997;237 (2):296-306. [36]PILKINGTON MF, SIMS SM, DIXON SJ. Dixon.Wortmannin inhibits spreading and chemotaxis of rat osteoclasts in vitro.J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(4):688-694. [37]NAKAMURA I, TAKAHASHI N, SASAKI T, et al.Wortmannin,a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, blocks osteoclastic bone resorption.FEBS Lett.1995;361(1):79-84. [38]HALL TJ, JEKER H, SCHAUEBLIN M. Schaueblin. Wortmannin, apotentinhibitorofphosphatidylinositol3-kinase, inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro.Calcif Tissue Int.1995;56(4):336-338. [39]LEE SE, WOO KM, KIM SY, et al. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,p38,and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in osteoclast differentiation. Bone.2002;30(1):71 -77. [40]LIU Q, SASAKI T, KOZIERADZKI I, et al. SHIP is a negative regulator of growth factor receptormediated PKB/Akt activation and myeloid cell survival. Genes Dev.1999;13:786-791. [41]TAKESHITA S, NAMBA N, ZHAO JJ, et al. SHIP-deficient mice are severely osteoporotic due to increased numbers of hyper-resorptive osteoclasts.Nat. Med.2002;8: 943-949. [42]WONG BR, BESSER D, KIM N, et al. TRANCE, a TNF family member, activates Akt/PKB through a signaling complex involving TRAF6 and c-Src. Mol Cell.1999;4:1041-1049. [43]LEE ZH, KIM HH. Signal transduction by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 305:211-214. [44]KIM JY, OH HM, KWAK SC, et al. Purslane suppresses osteoclast differentiation and bone resorbing activity via inhibition of Akt / GSK3β-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling in vitro and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss in vivo.Biol Pharm Bull. 2015; 38(1):66-74. [45]SUGATANI T, HRUSKA KA. Akt1 /Akt2 and mammalian target of rapamy- cin /Bim play critical roles in osteoclast differentiation and survival,respectively,whereas Akt is dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J Biol Chem.2005;280(5): 3583-3589. [46]KAWAMURA N, KUGIMIYA F, OSHIMA Y, et al.Akt1 in osteoblasts and osteoclasts controls bone remodeling. Plos One.2007;2(10): 1058. [47]ULICI V, HOENSELAAR KD, AGOSTON H, et al. The role of Akt1 in terminal stages of endochondral bone formation: angiogenesis and ossification.Bone.2009;45: 1133-1145. [48]PENG XD, XU PZ, CHEN ML, et al.D warfism,impaired skin development, skeletal muscle atrophy,delayed bone development, and impeded adipogenesis in mice lacking Akt1 and Akt2. Genes Dev.2003; 17: 1352-1365. [49]HOSOI H, DILLING MB, HOUGHTON PJ, et al. Rapamycin causes poorly reversible inhibition of mTOR and induces p53-independent apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells.Cancer Res.1999;59(4): 886-894. [50]SUGATANI T, ALVAREZ UM, HRUSKA KA. Activin A stimulates IkappaB-alpha/NFka-ppaB and RANK expressio-n for osteoclastdifferentiation,but not AKT survival pathway in osteoclast precursors.J Cell Biochem. 2003;90(1):59-67. [51]GLANTSCHNIG H, FISHER JE, RESZKA AA, et al. M-CSF,TNFalpha and RANK ligand promote osteoclast survival by signaling through mTOR/S6 kinase.Cell Death Differ. 2003; 10(10):1165-1177. [52]ZHAO C, SUN W, ZHANG P, et al. miR-214 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting Pten/PI3k/Akt pathway. RNA Biol. 2015;12(3):343-353. [53]LI M, LUO R, YANG W, et al .miR-363-3p is activated by MYB and regulates osteoporosis pathogenesis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(5):376-386. [54]SHAO X, MIAO M, XUE J, et al. The Down-Regulation of MicroRNA -497 Contributes to Cell Growth and Cisplatin Resistance Through PI3K/Akt Pathway in Osteosarcoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.2015; 5(36):2051-2062. [55]GUNTUR AR, ROSEN CJ. The skeleton: a multi-functional complex organ: new insights into osteoblasts and their role in bone formation: the central role of PI3Kinase.J Endocrinol. 2011;211(2):123-130. [56]HONG D, CHEN HX, YU HQ, et al.Morphological and proteomic analysis of early stage of osteoblast differentiation in osteoblastic progenitor cells.Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(14):2291-2300. [57]MUKHERJEE A, ROTWEIN P. Akt promotes BMP2-mediated osteoblast differentiation and bone development. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 5):716-726. [58]ZHANG Z,ZHANG X,ZHAO D,et al.TGF β1 promotes the osteoinduction of human osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 signalling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):3505-3518. [59]SUZUKI E, OCHIAI-SHINO H, AOKI H, et al.Akt Activation is Required for TGF-β1-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Pre-Osteoblasts.PLoS One. 2014; 9(12): e112566. [60]GHOSH-CHOUDHURY N, ABBOUD SL, NISHIMURA R, et al. Requirement of BMP-2-induced Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase and Akt Serine/Threonine Kinasein Osteoblast Differentiation and Smad-dependent BMP-2Gene Transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(36):33361-33368. [61]BURGERS TA, HOFFMANN MF, COLLINS CJ, et al .Mice Lacking Pten in Osteoblasts Have Improved Intramembranous and Late Endochondral Fracture Healing.PLoS One. 2013;8(5): e63857. [62]DUFOUR C, HOLY X, MARIE PJ. Transforming growth factor-beta prevents osteoblast apoptosis induced by skeletal unloading via PI3K/Akt, Bcl-2, and phospho-Bad signaling.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;294(4):E794-801. [63]XI JC, ZANG HY, GUO LX, et al . The PI3K/AKT cell signaling pathway is involved in regulation of osteoporosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015;35(6):640-645. [64]DENG S, DAI G, CHEN S, et al . Dexamethasoneinduces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:602-608. [65]LIAN Z, HAN J, HUANG L, et al. Retraction of: A005, a novel inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin, prevents osteosarcoma-induced osteolysis.Carcinogenesis. 2019; 40(2):e1-e13. [66]MARTIN SK, GAN ZY, FITTER S, et al .The effect of the PI3K inhibitor BKM120 on tumour growth and osteolytic bone disease in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2015;39(3):380-387. [67]YEON JT, KIM KJ, SON YJ, et al .Idelalisib inhibits osteoclast differentiation and pre-osteoclast migration by blocking the PI3Kδ-Akt-c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling cascade.Arch Pharm Res. 2019; 42(8):712-721. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Chen Qiaoling, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Lin Tao, Luo Xuwei. Osteoblast differentiation after conditional knockout of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3785-3789. |
| [4] | You Wulin, Huang Guicheng, Wang Jianwei. Osteogenic differentiation potential of microencapsulated transgenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3852-3857. |
| [5] | Li Fangyu, Xia Wenfang, Cui Shun. Abnormally expressed beta-amyloid affects bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3152-3157. |
| [6] | Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Regulatory role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in bone homeostasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 271-275. |
| [7] | Wang Weiwei, Ou Zhixue, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Zhou Yi, Li Tong. Regulatory mechanism of exosomes in signal communication network of steroid induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3056-3064. |
| [8] | Wang Jing, Wang Wanyuji, Zhang Yi, Ma Yaping, Wang Xin. Interleukin 6 involved in a series of reaction processes of osteogenesis and bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2945-2951. |
| [9] | Huang Fayi, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi, Huang Haoran, Chen Weijian, He Wei, Wang Haibin. Belamcandin inhibits osteoclast differentiation: its role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(17): 2636-2641. |
| [10] | Zhang Hongmei, Sun Xirao, Wang Chengyue. Effect of polymethyl methacrylate/mineralized collagen/Mg-Ca composite material on osteogenic differentiation of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2498-2503. |
| [11] | Yang Bingxuan, Jiang Tao, Jia Min, Li Peng, Liao Rongzhen, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Icariin promotes differentiation of mouse preosteoblasts via activating autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 64-69. |
| [12] | Huang Tao, Cheng Zhijian, Jia Zhiqiang, Zhao Xiaoguang, Wang Lei, Zhai Wenjing, Zhou Yongxin. Mechanism by which miR-146a regulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 70-75. |
| [13] | Feng Zhiguo, Sun Haibiao, Han Xiaoqiang. Regulation of proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of bone-related cells by long-stranded non-coding RNA [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 112-118. |
| [14] | Wang Jing, Lang Xuemei, Wang Weiqun, Zhang Hanxiang, Zhang Yi, Wang Xin. Participation and regulatory mechanism of interleukin-1 during bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5851-5858. |
| [15] | Zhou Quan, Zhang Yanan, Bai Yiguang, Zhang Qiong, Nong Haibin, Liu Mingfu, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Effect of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 regulating osteoclasts on bone mineral density in osteoporotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4680-4684. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||