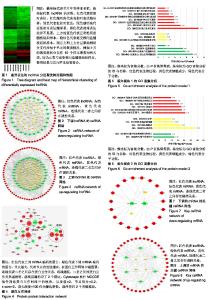
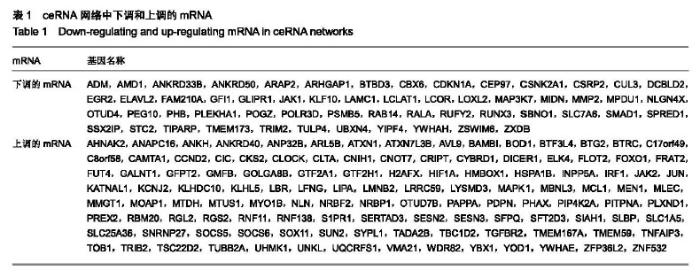
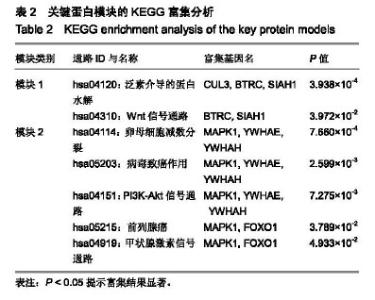
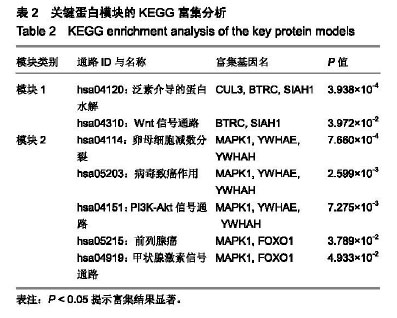
| [1] |
Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang.
Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217.
|
| [2] |
Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan.
Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236.
|
| [3] |
Liu Cong, Liu Su.
Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074.
|
| [4] |
Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang.
Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013.
|
| [5] |
Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng.
Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771.
|
| [6] |
Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng.
An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790.
|
| [7] |
Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan.
Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094.
|
| [8] |
Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu.
Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710.
|
| [9] |
Yuan Changshen, Rong Weiming, Lu Zhixian, Duan Kan, Guo Jinrong, Mei Qijie.
Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2740-2746.
|
| [10] |
Shen Fu, Kuang Gaoyan, Yang Zhuo, Wen Meng, Zhu Kaimin, Yu Guizhi, Xu Wuji, Deng Bo .
Immune infiltration mechanism of differential expression genes in rheumatoid arthritis and potential therapeutic prediction of Chinese herbs
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2183-2191.
|
| [11] |
Li Shengqiang, Xie Bingying, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong.
Interaction proteomics of long noncoding RNA uc431+ gene in postmenopausal osteoporosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1641-1646.
|
| [12] |
Liu Peidong, Feng Jiangfeng, Xu Wenjie, Xu Xiaodong, Yang Ziquan .
Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile and key pathways related to fatty infiltration after rotator cuff injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1773-1778.
|
| [13] |
Ren Chunmei, Liu Yufang, Xu Nuo, Shao Miaomiao, He Jianya, Li Xiaojie.
Non-coding
RNAs in human dental pulp stem cells: regulations and mechanisms
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1130-1137.
|
| [14] |
Xun Chong, Wang Qiang, Li Changzhou, Liu Xiaofeng.
Potential molecular targets and therapeutic mechanisms underlying transplantation of autologous bone marrow stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury based on bioinformatics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4927-4933.
|
| [15] |
Yuan Yiming, Wang Yan, Chen Chengcheng, Zhao Mingyue, Pei Fei.
Efficacy of exosomes in peripheral nerve injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5079-5084.
|